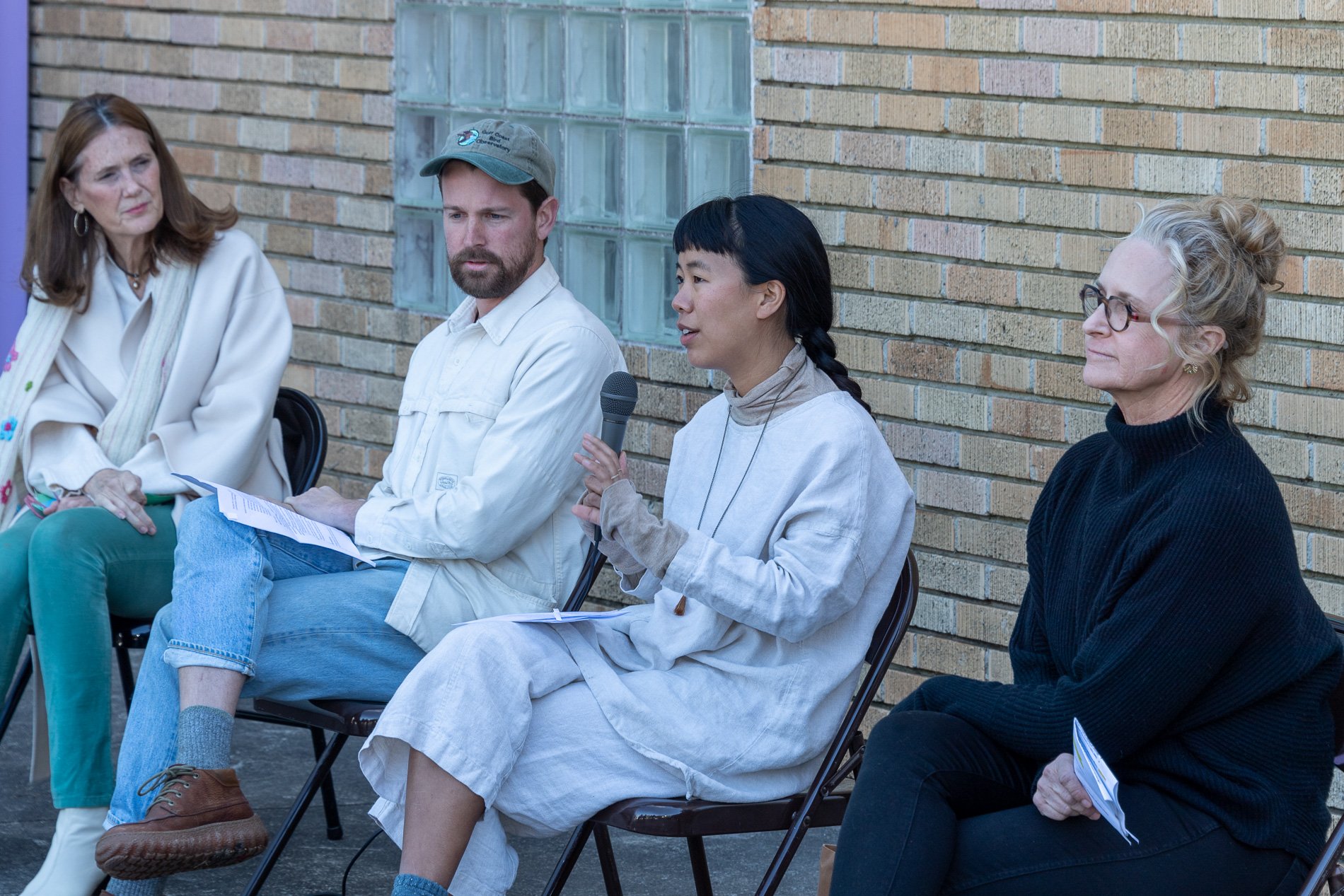
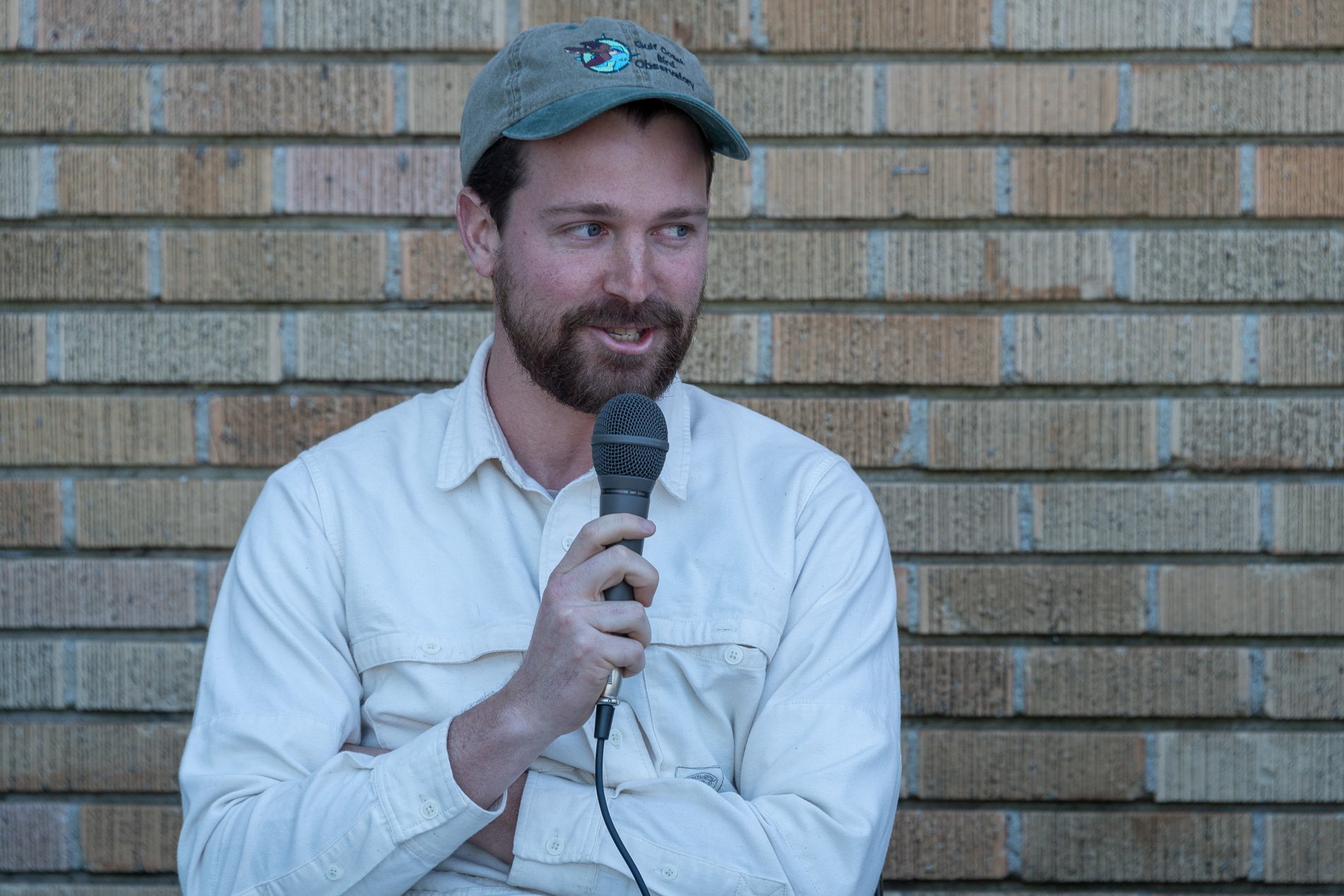
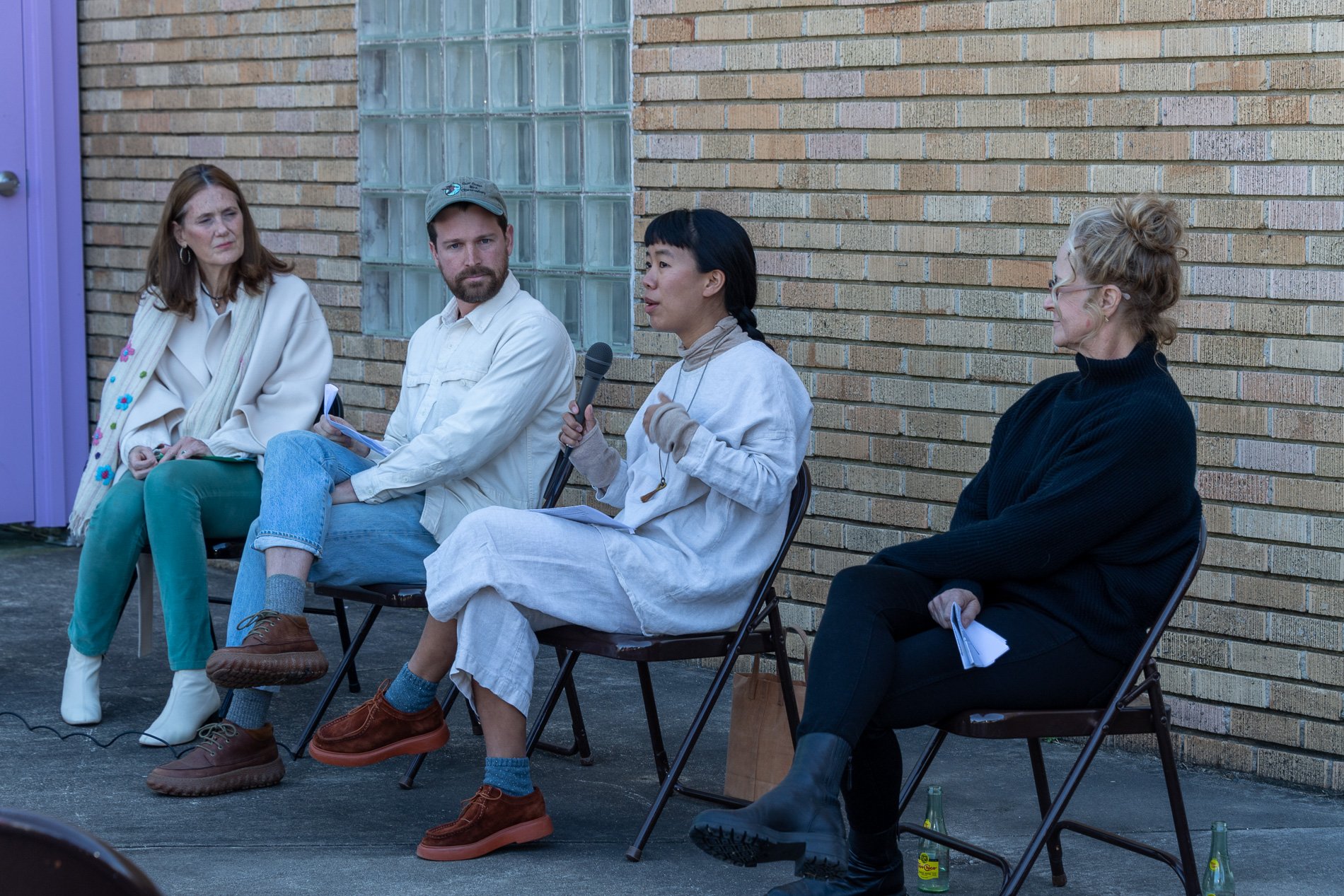
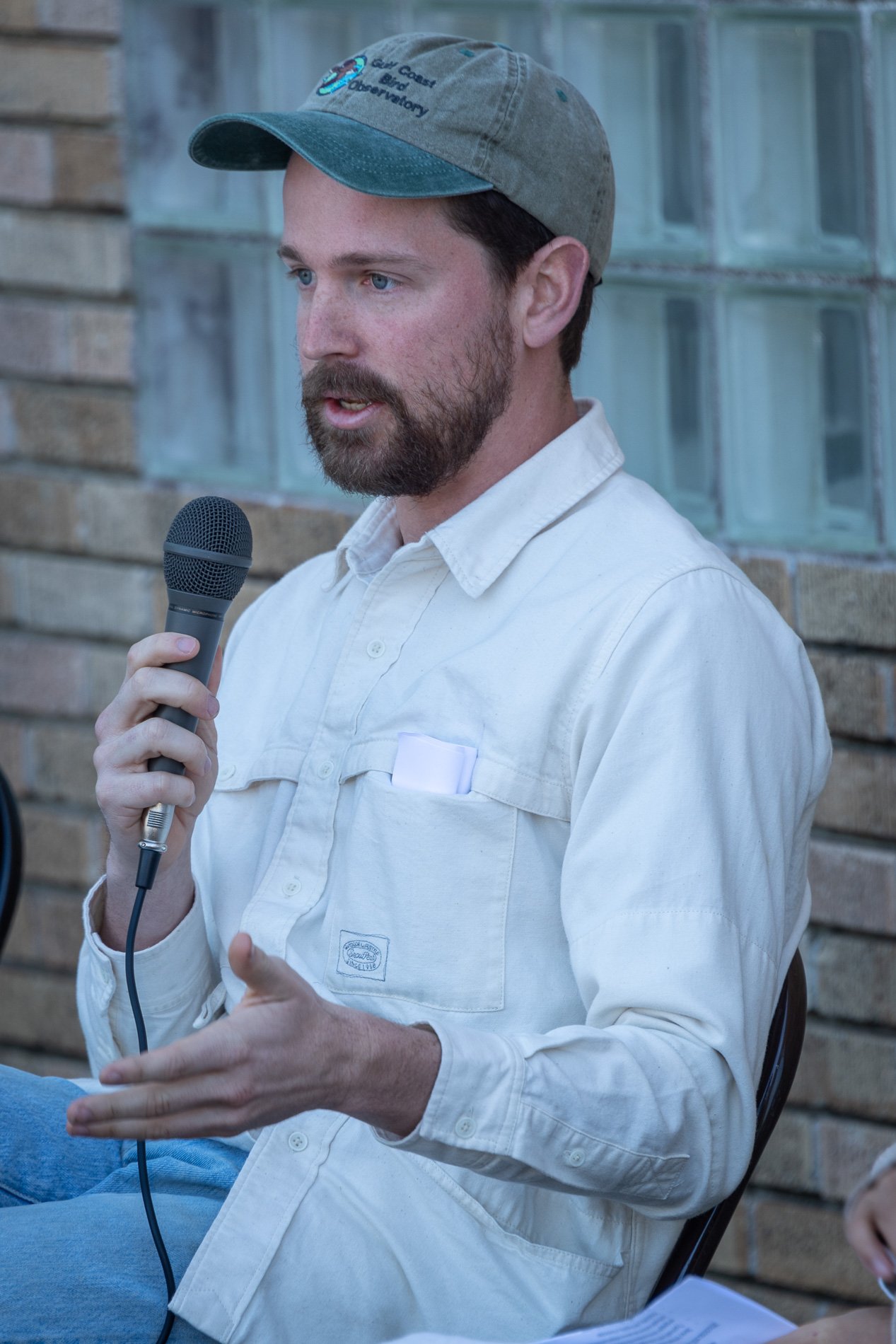
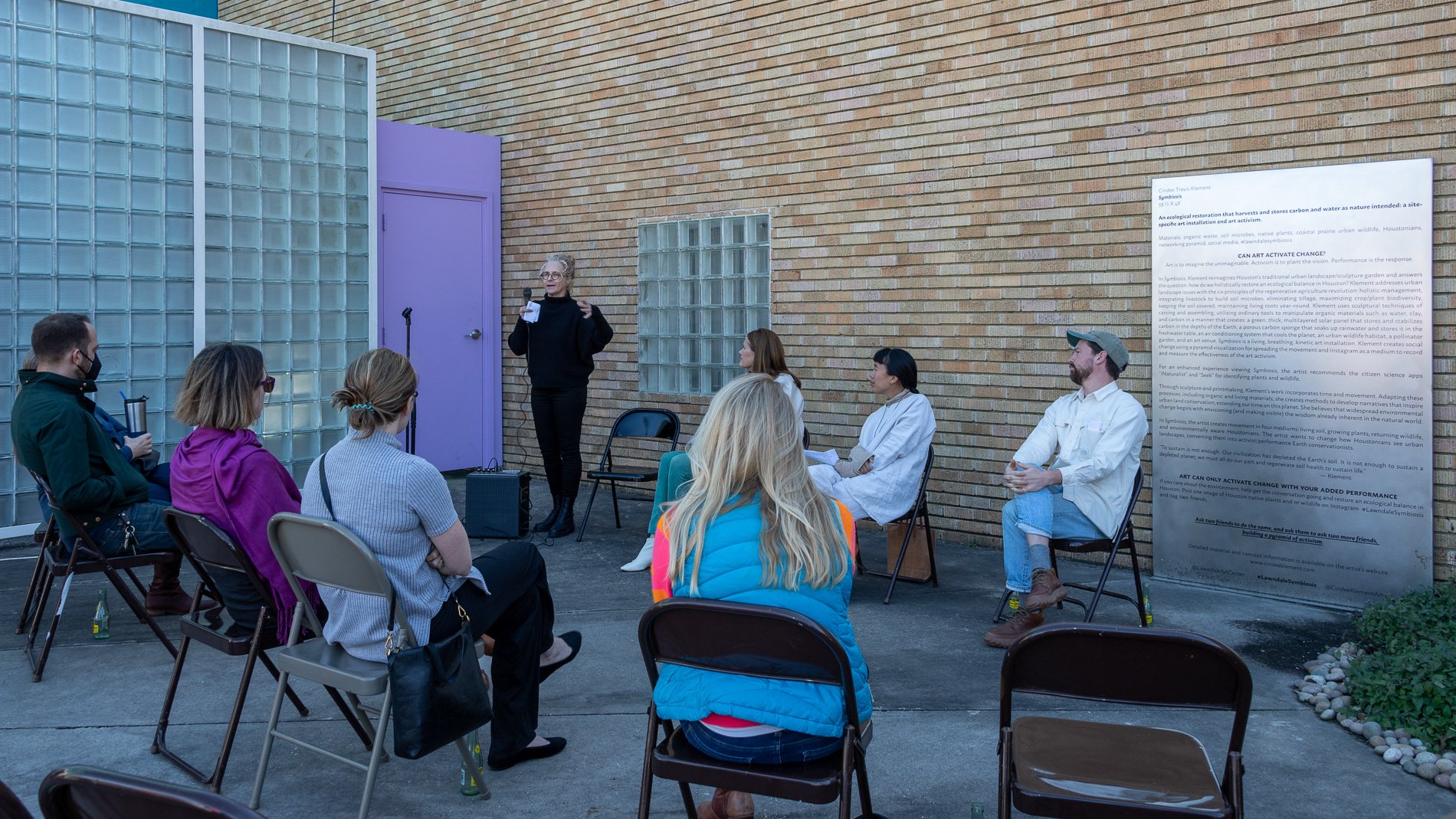
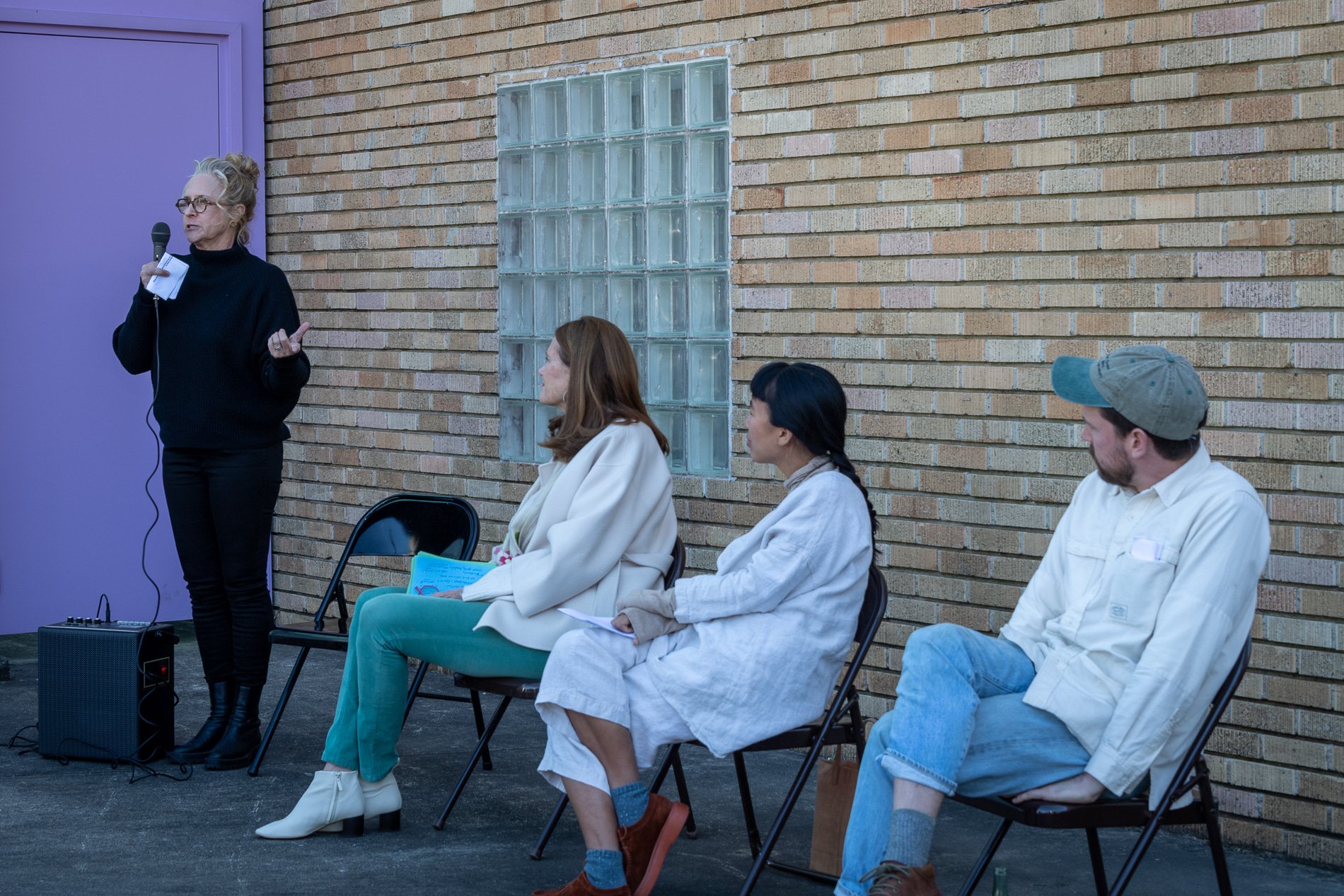
Symbiosis Relationships 10/2022
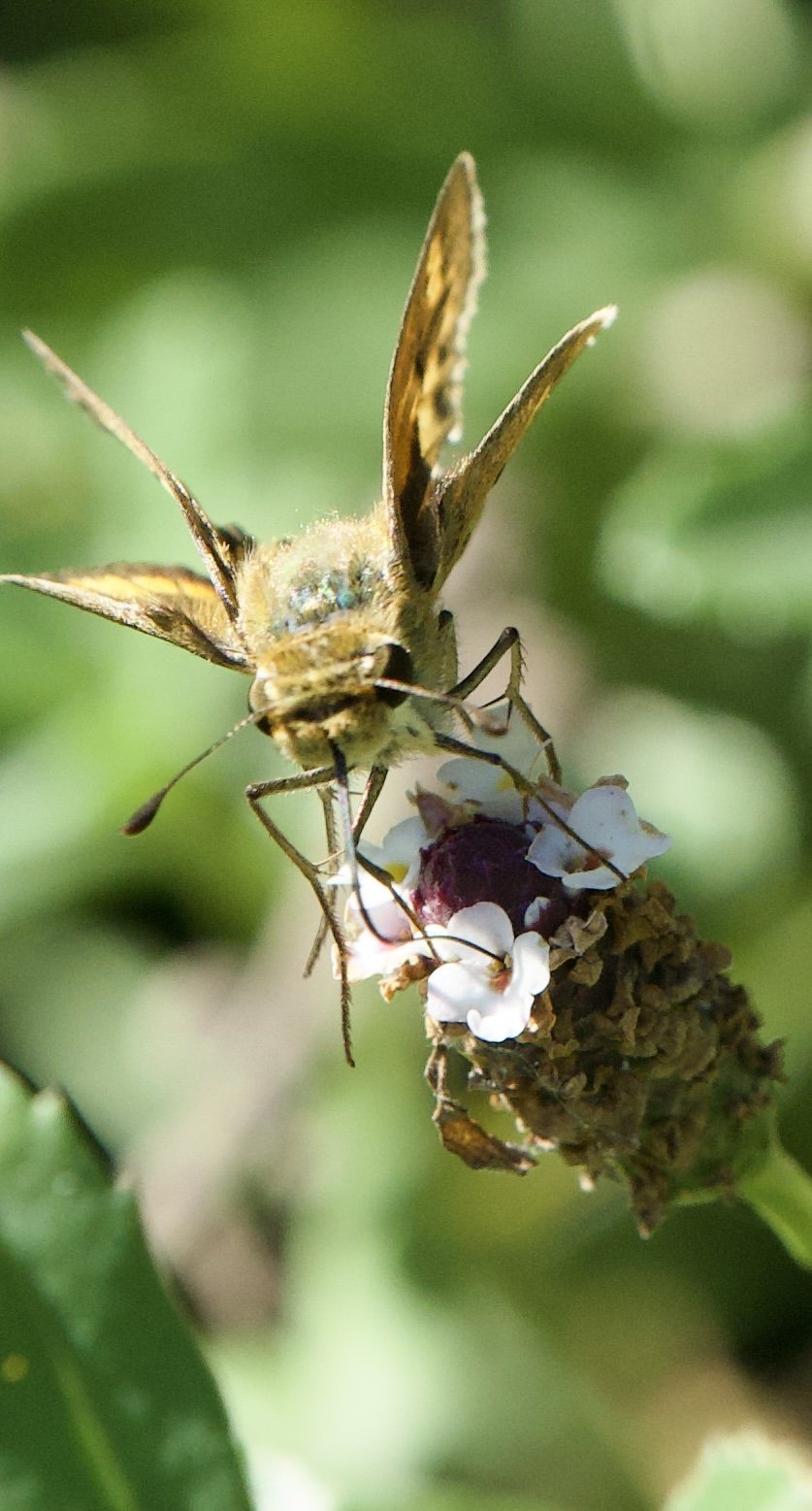
New World Giant Swallowtail and Milkweed and the health of Monarchs. This tropical mikweed HAS to be cut down November 1. The Milkweeds are the host plants for Monarchs. They need to move south by November and won’t head south if Tropical Milkweed is available as a host.
Monarch and Climbing Hempvine. Climbing Hempvine is an aromatic delight. It reminds me if warmed sweet honey. The Monarchs agree.
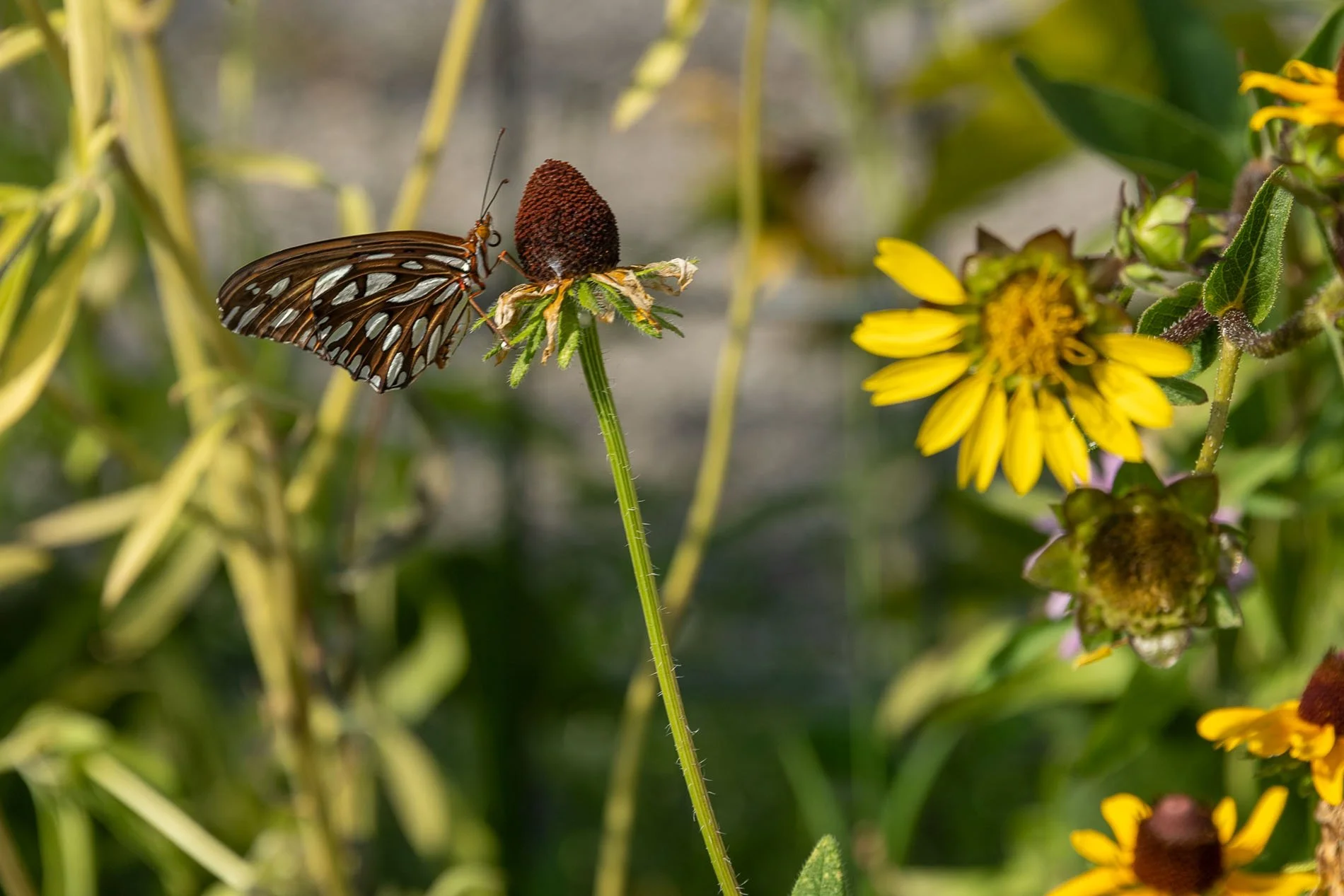
Purple Coneflower and the Gulf Fritillary Butterfly.
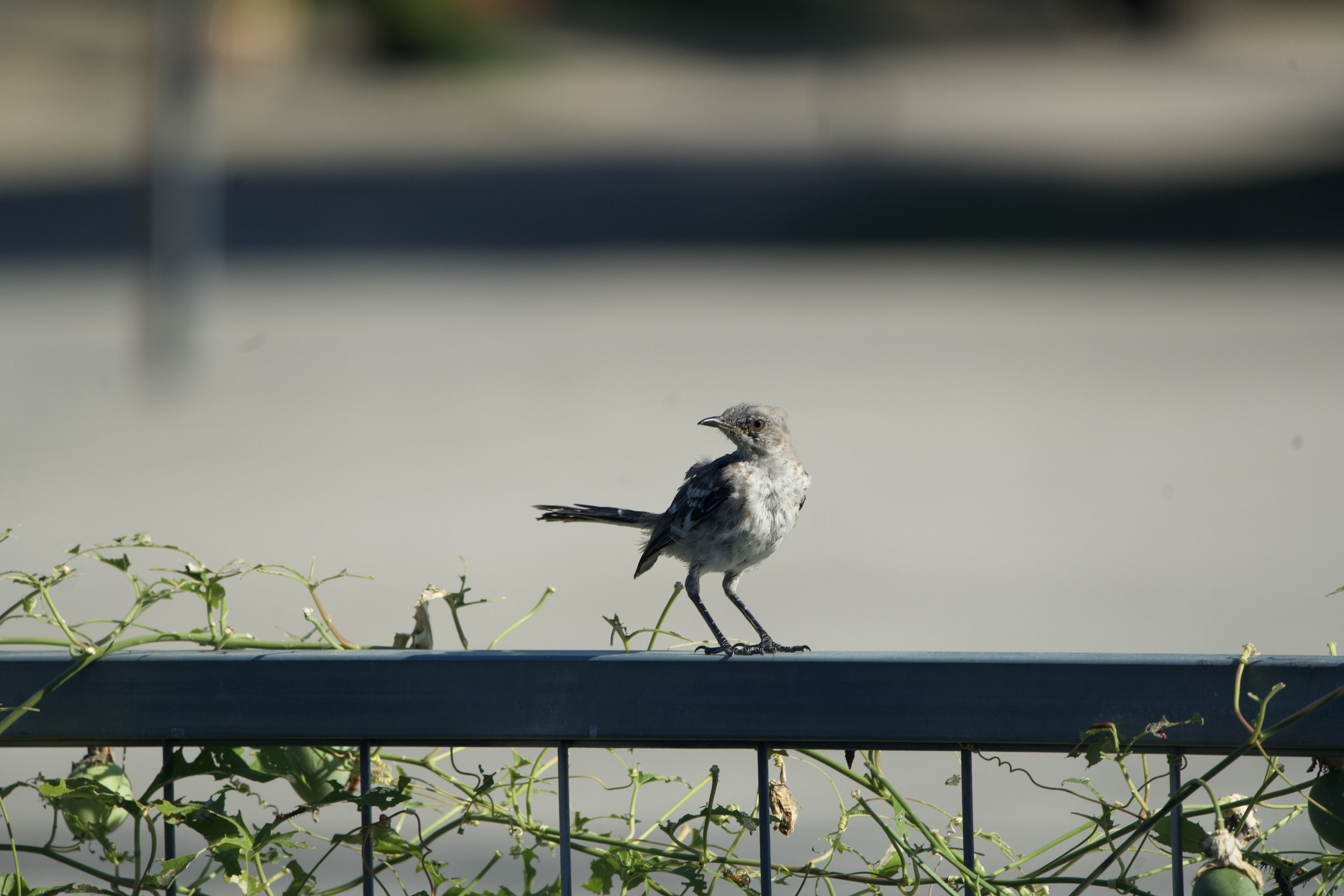
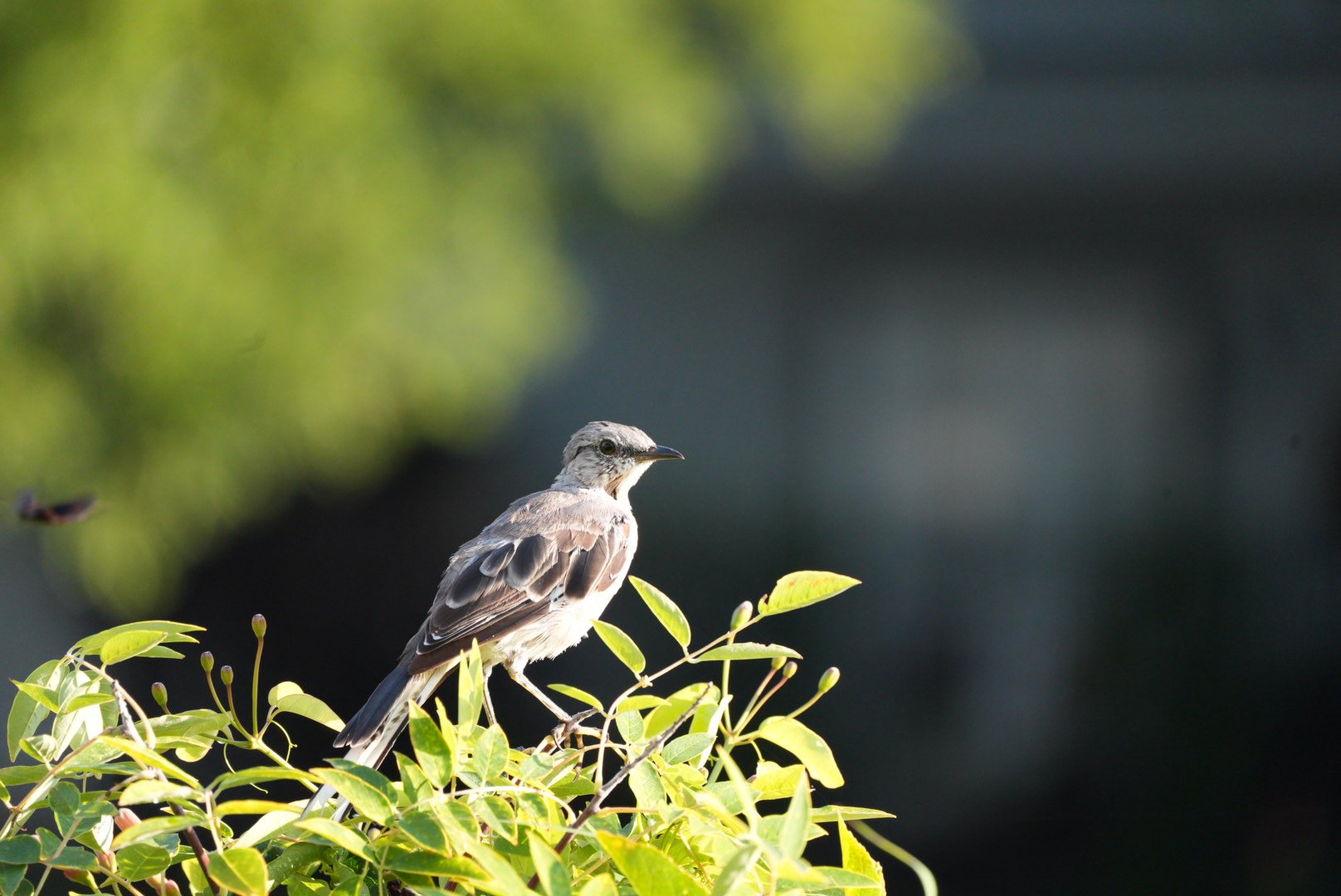
Mockingbirds and the fence. I have learned that birds need habitats with multiple elevations. The fence is a popular place for birds to look for insects and tiny toads to eat while keeping an eye on predators.
Monarch and Climbing Hempvine.
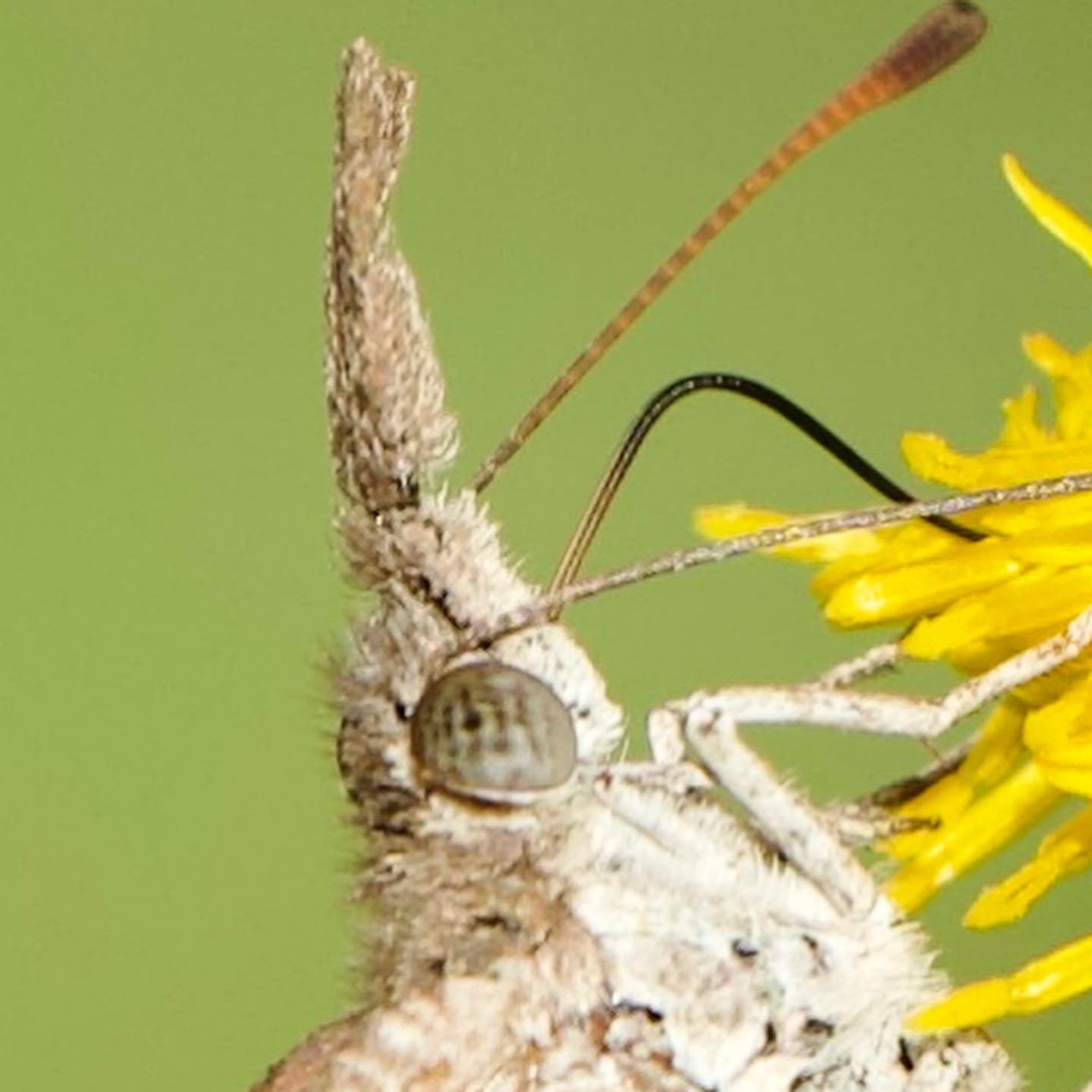
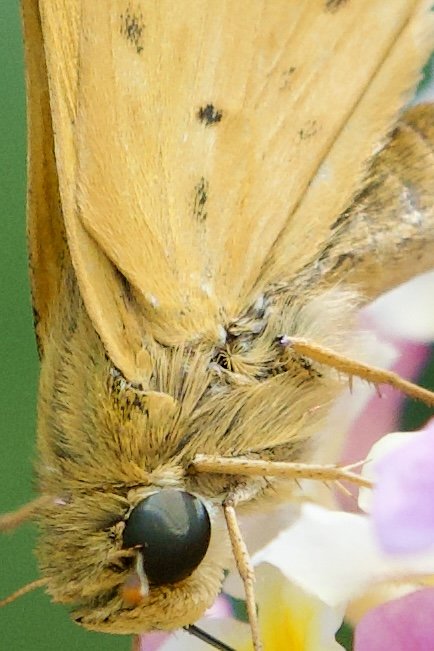
Ask upper of the Hesperiini family
Gulf fritillaryon American beauty berry.
GulfFritillary on Marsh fkeabane pictured below.
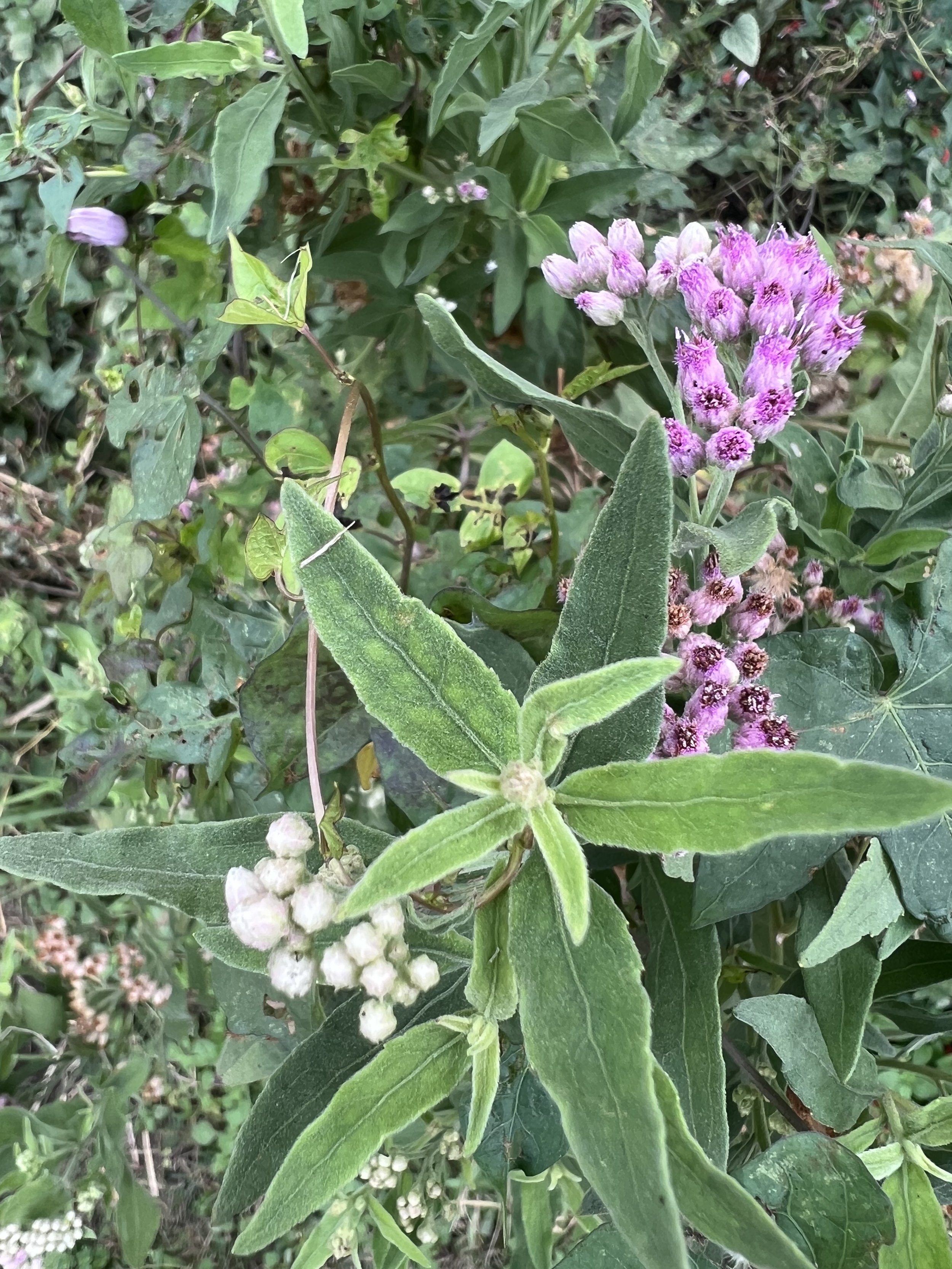
Marsh fleabane
Gulf fritillary and Lawndale’s mailbox. Over a few weeks the count in the doorway climbed to over 200.
In identified mushrooms.
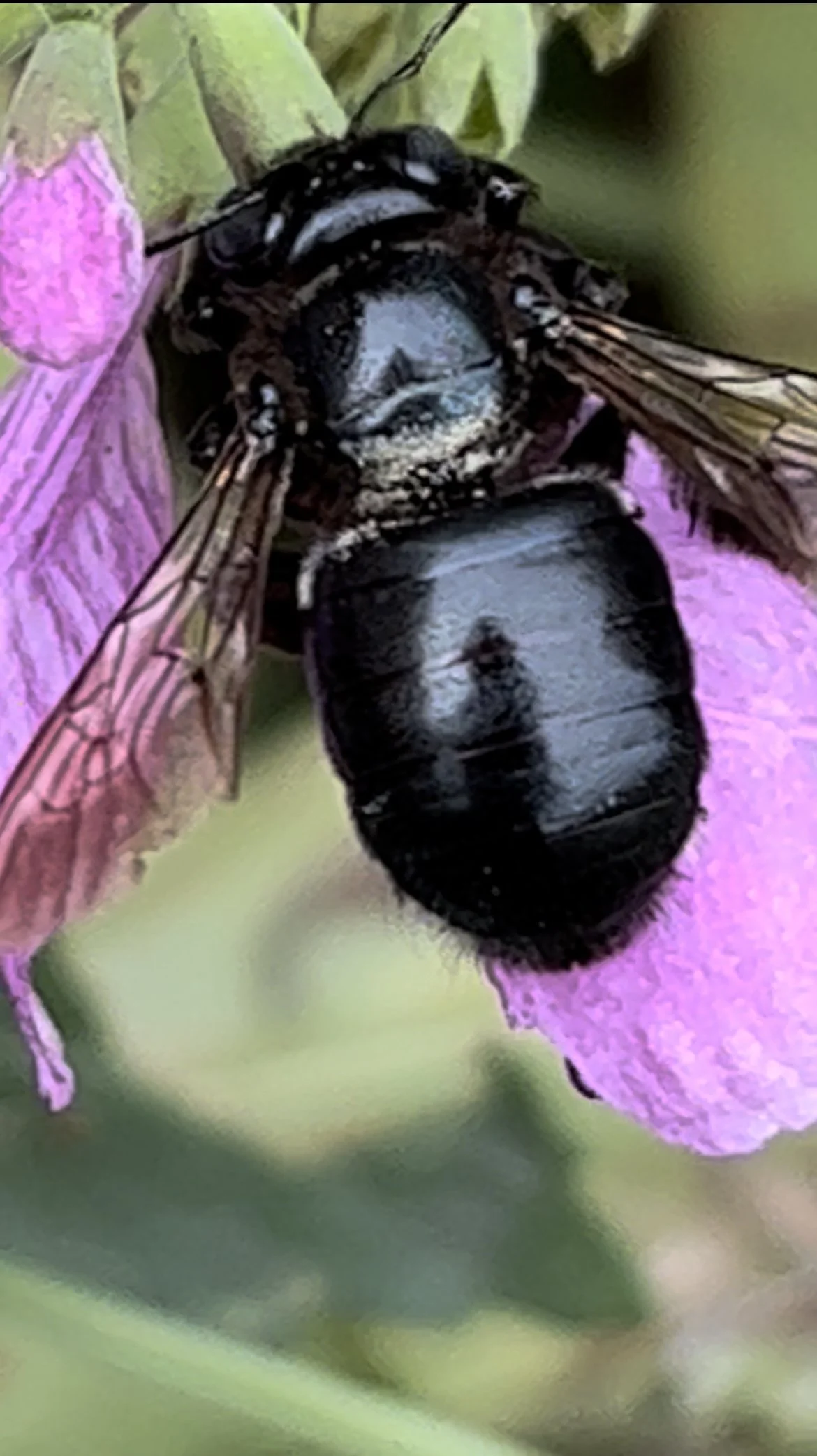
Carpenter bee
Gukf Fritillary are eating everything
How nature arranges itself
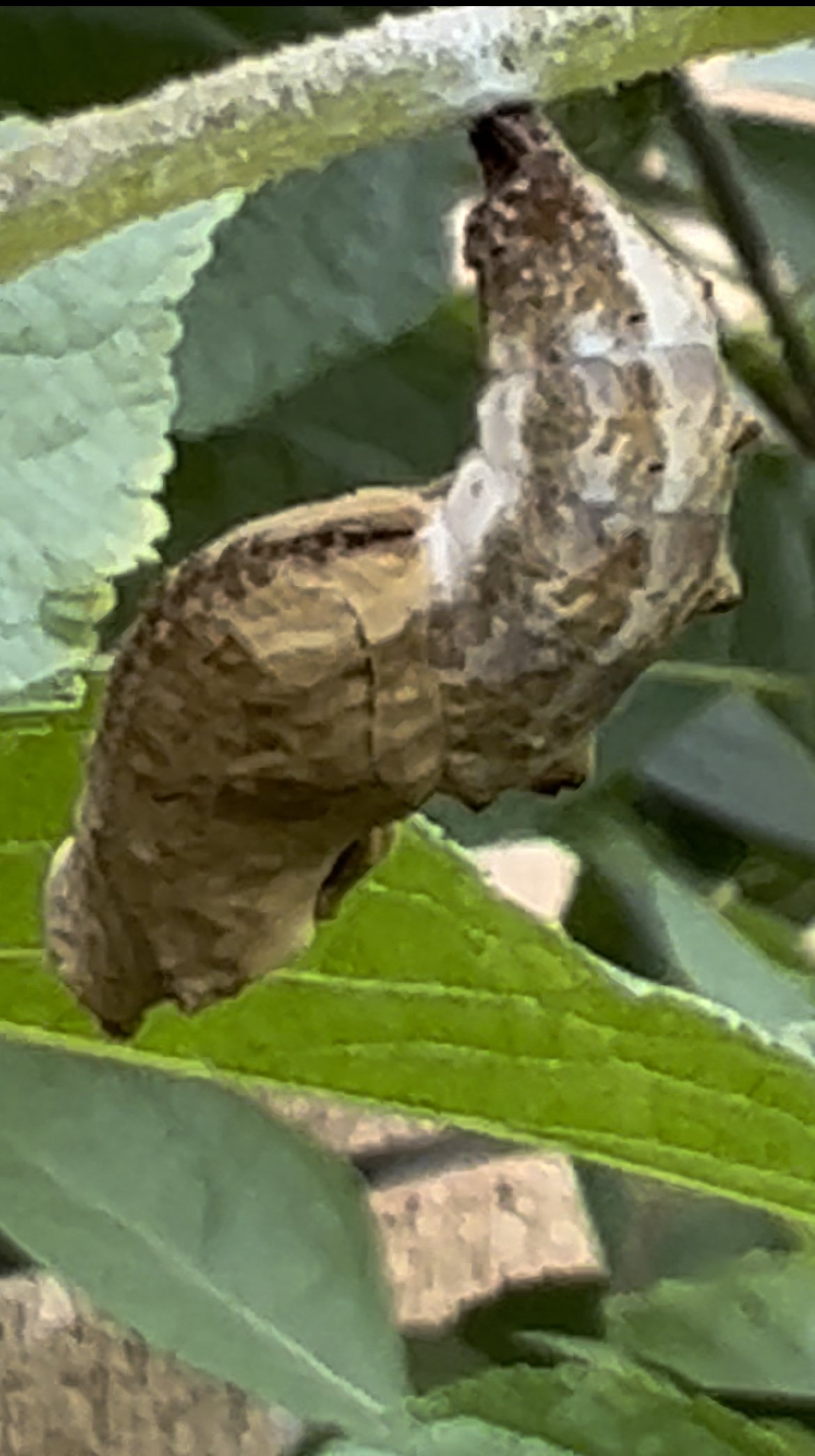
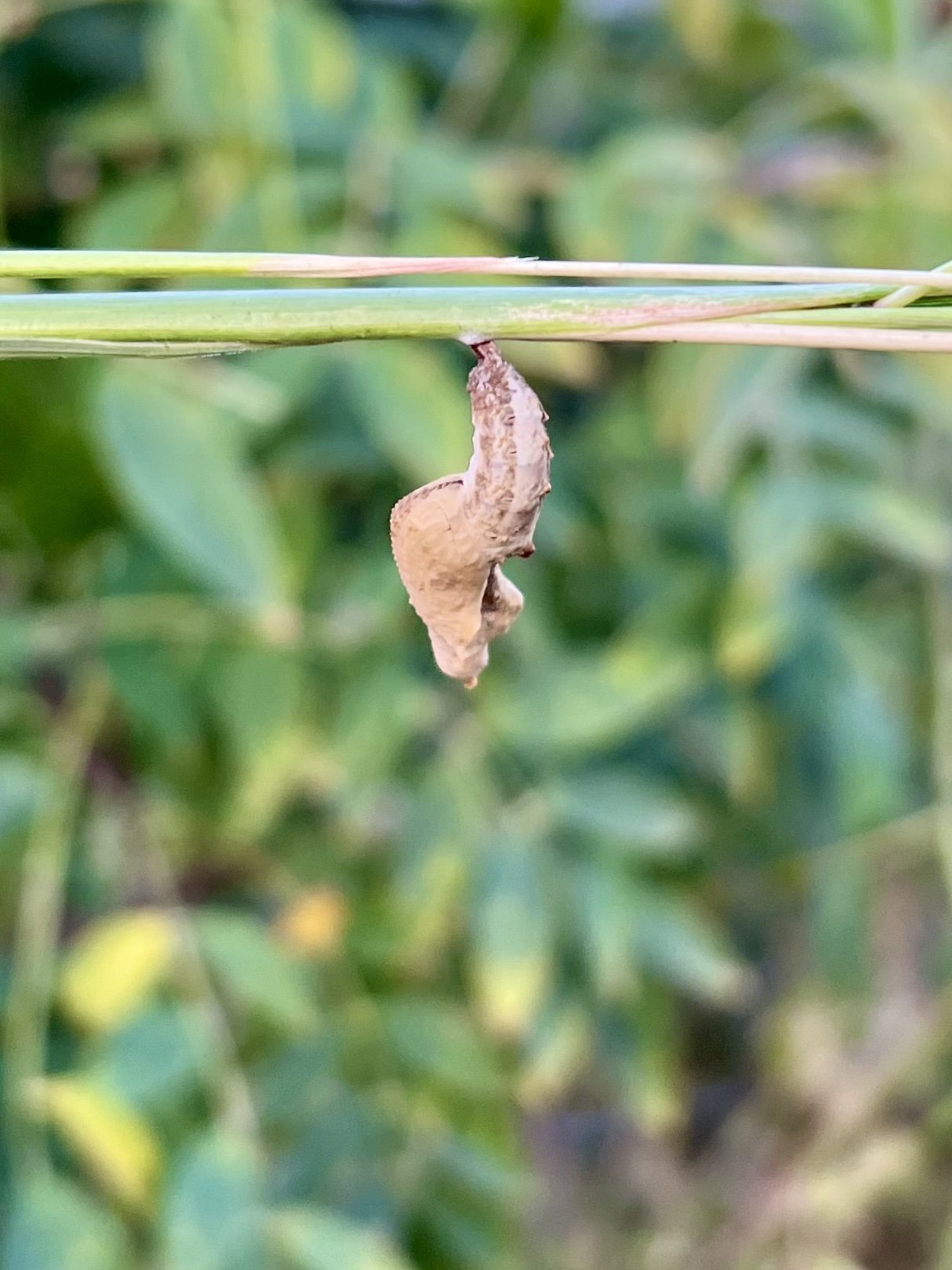
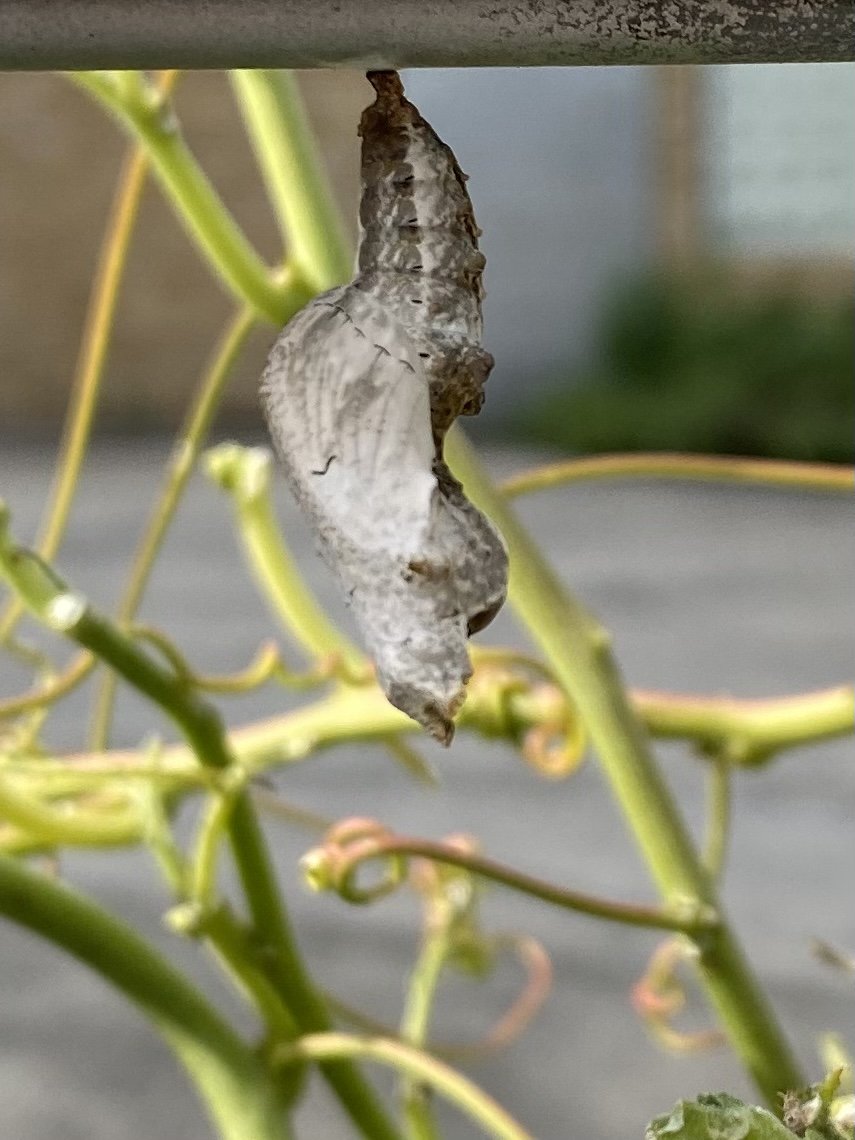
Chrysalis on crabgrass stem
Morning glory, mile a minute vine.
Carpenter bee and Obedient flower
The White viened pipevinesis is the host plant for the Pipelvine swallowtails. I wish I had more. The caterpillars devoures it, and then it comes back.
Cloudless Sulphur and Turkscap
Hemiargus ceraunus, it blue ceraunus,an d pasted native plants.
Monarch and Blue mist flower
Northern Mocking bird perched on the fence.
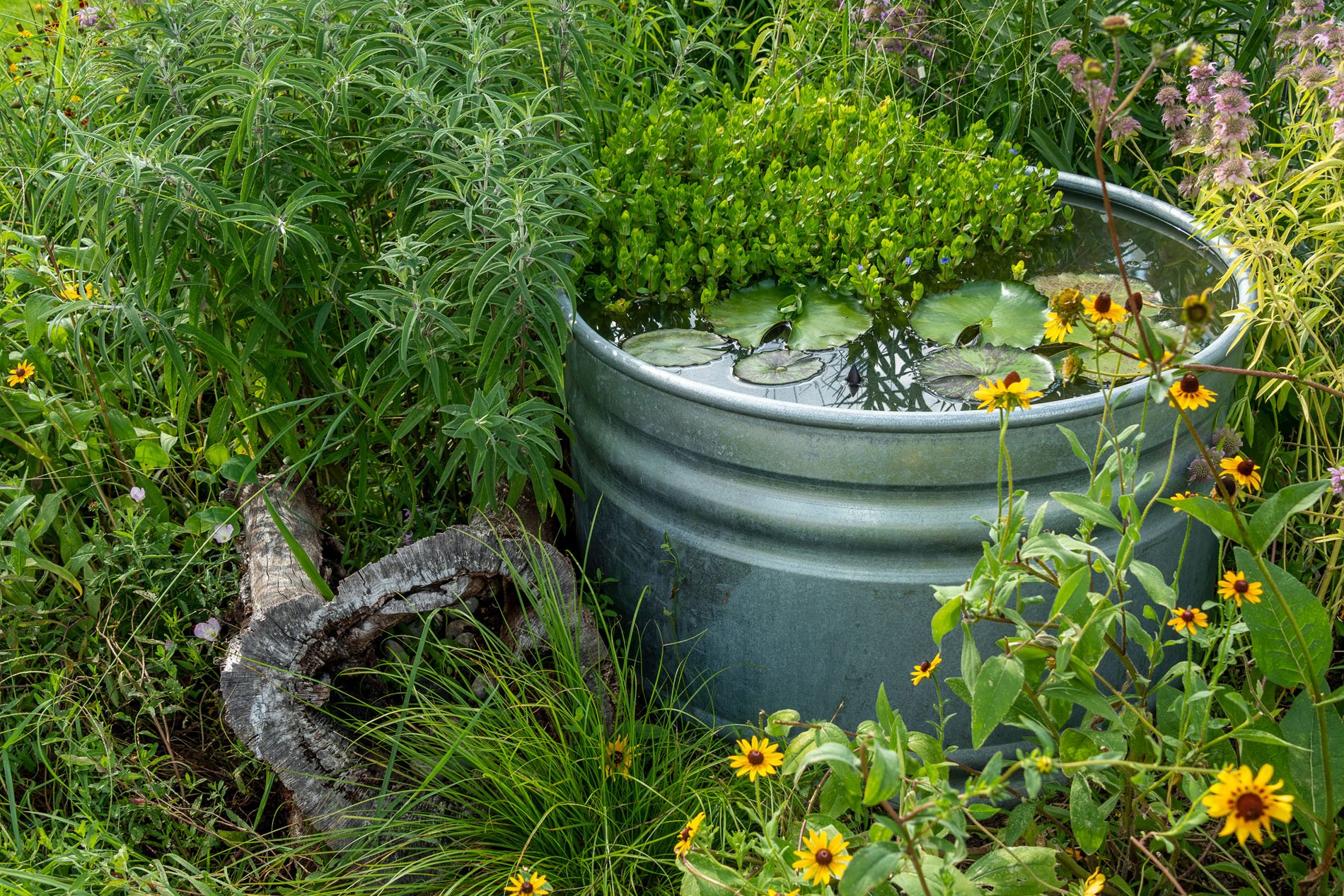
Northern Mockingbird and trough pond
Hesperiina And Frogfruit
Pushfly and Passiflora leaf
True Sparrow stays in messy bush like spaces for safety and for a source of caterpillars
American snout butterfly
Gulf Fritillary with OE
“Ophryocystis elektroscirrha (OE) is a debilitating protozoan parasite that infects monarchs. Infected adult monarchs harbor thousands or millions of microscopic OE spores on the outside of their bodies. When dormant spores are scattered onto eggs or milkweed leaves by infected adults, monarch larvae consume the spores, and these parasites then replicate inside the larvae and pupae. Monarchs with severe OE infections can fail to emerge successfully from their pupal stage, either because they become stuck or they are too weak
to fully expand their wings. Monarchs with mild OE infections can appear normal but live shorter lives and cannot fly was well as healthy monarchs.
Although recent research shows that tropical milkweed can lower OE replication within infected monarchs (due to high levels of cardenolide toxins), this might not benefit the monarch population. In
fact, this could actually promote disease spread by allowing moderately infected
I PROJECT MONARCH
HEALTH
monarchs that otherwise would have died quickly following eclosion to live longer and spread more parasite spores.“- monarch parasites.
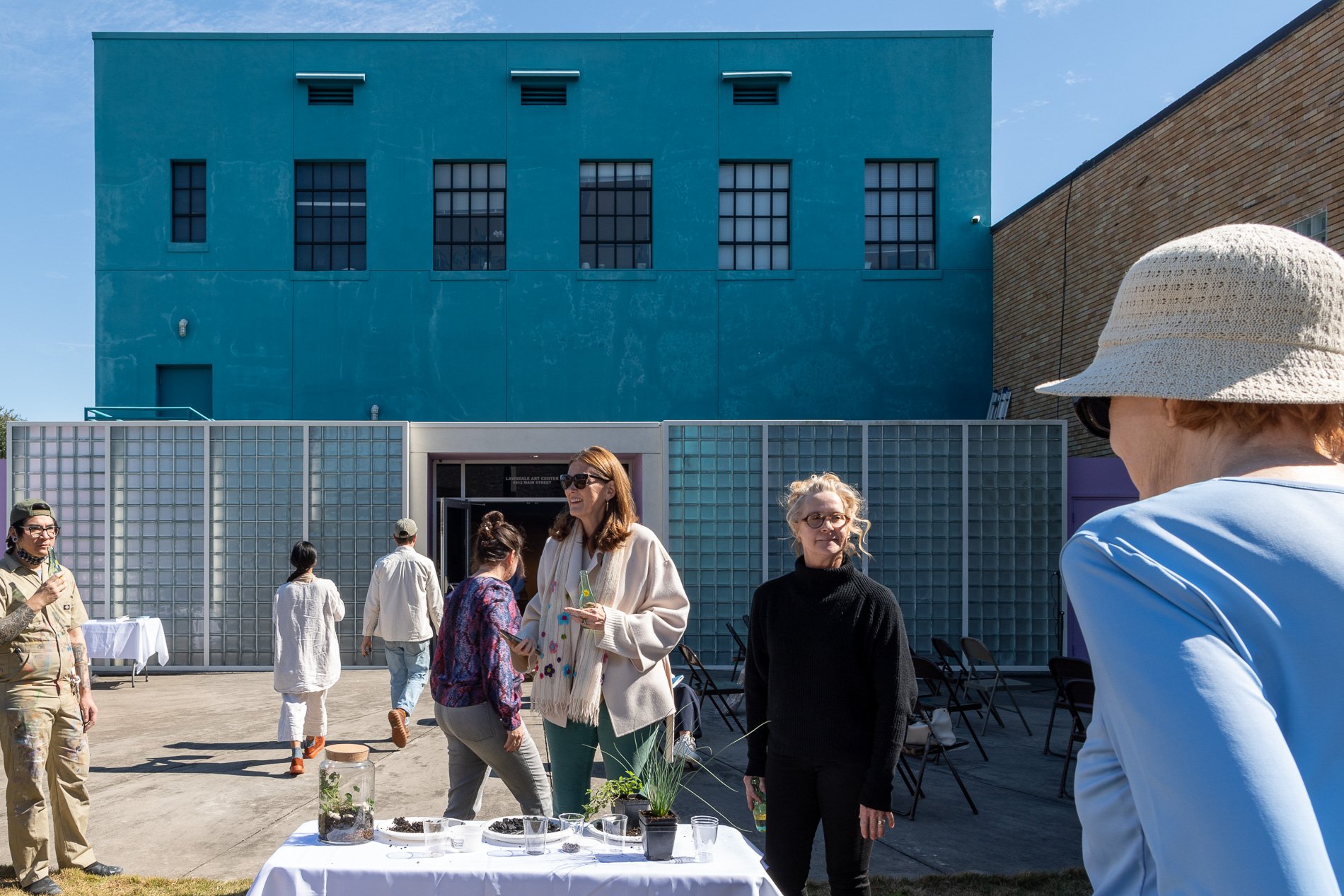
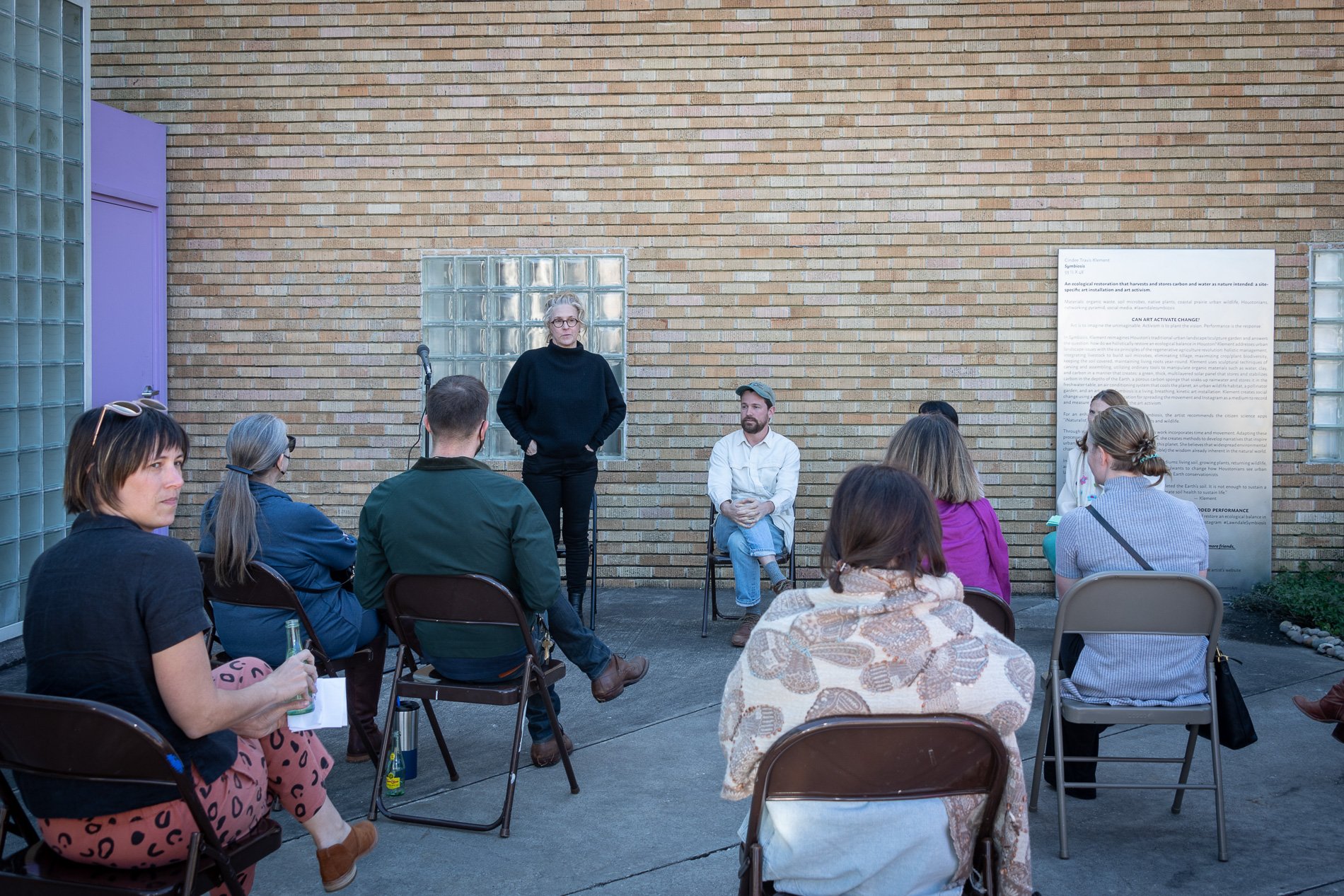
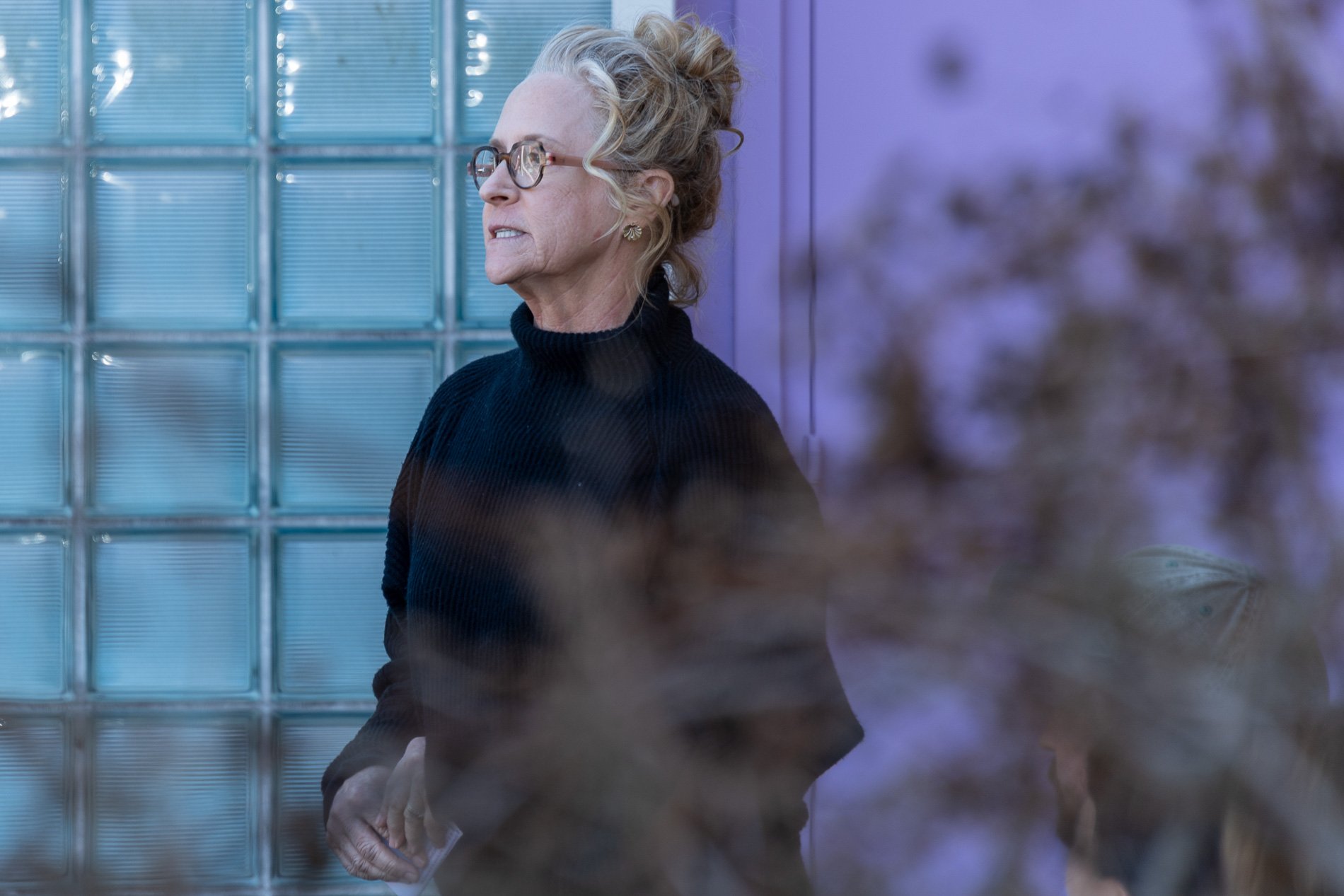
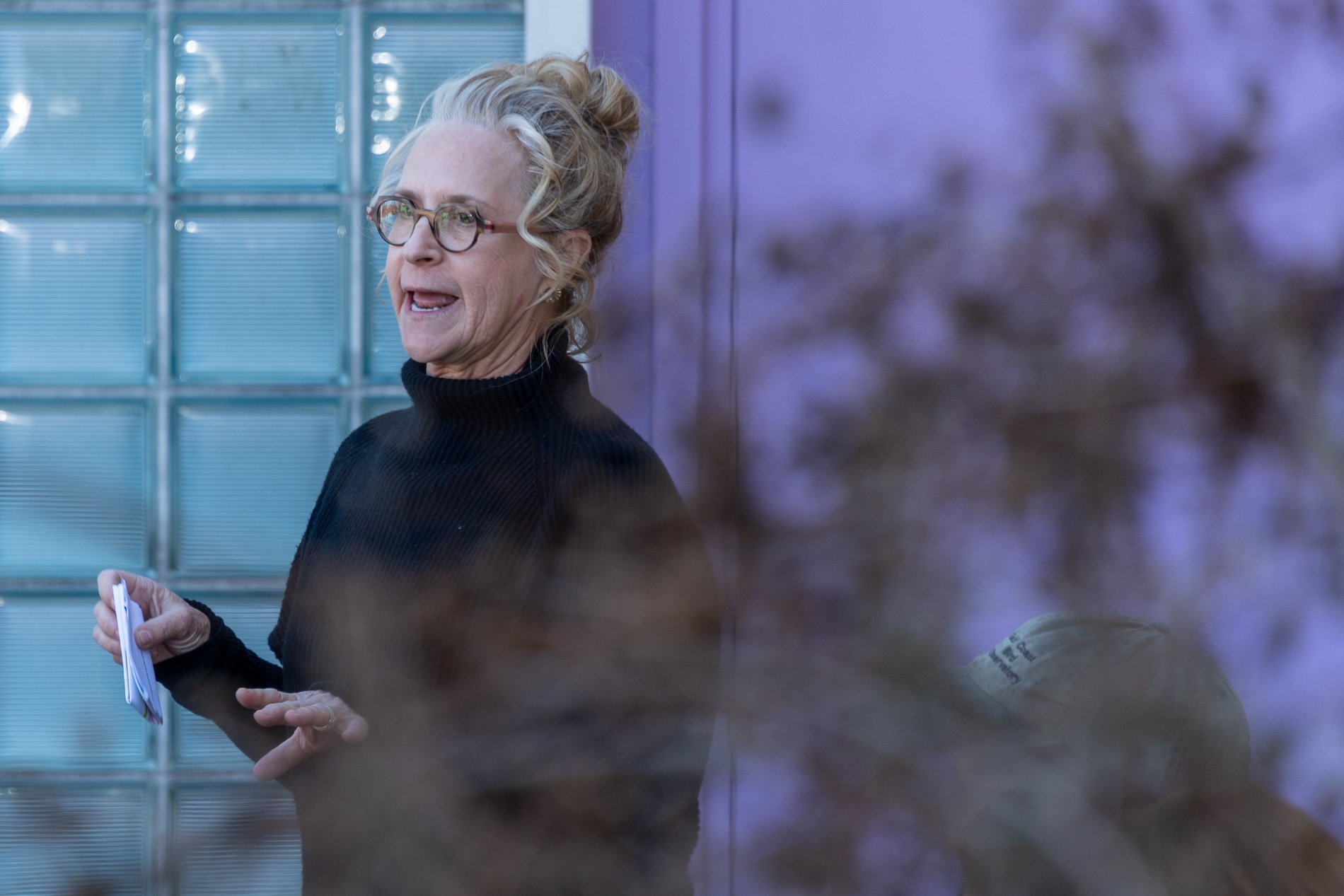
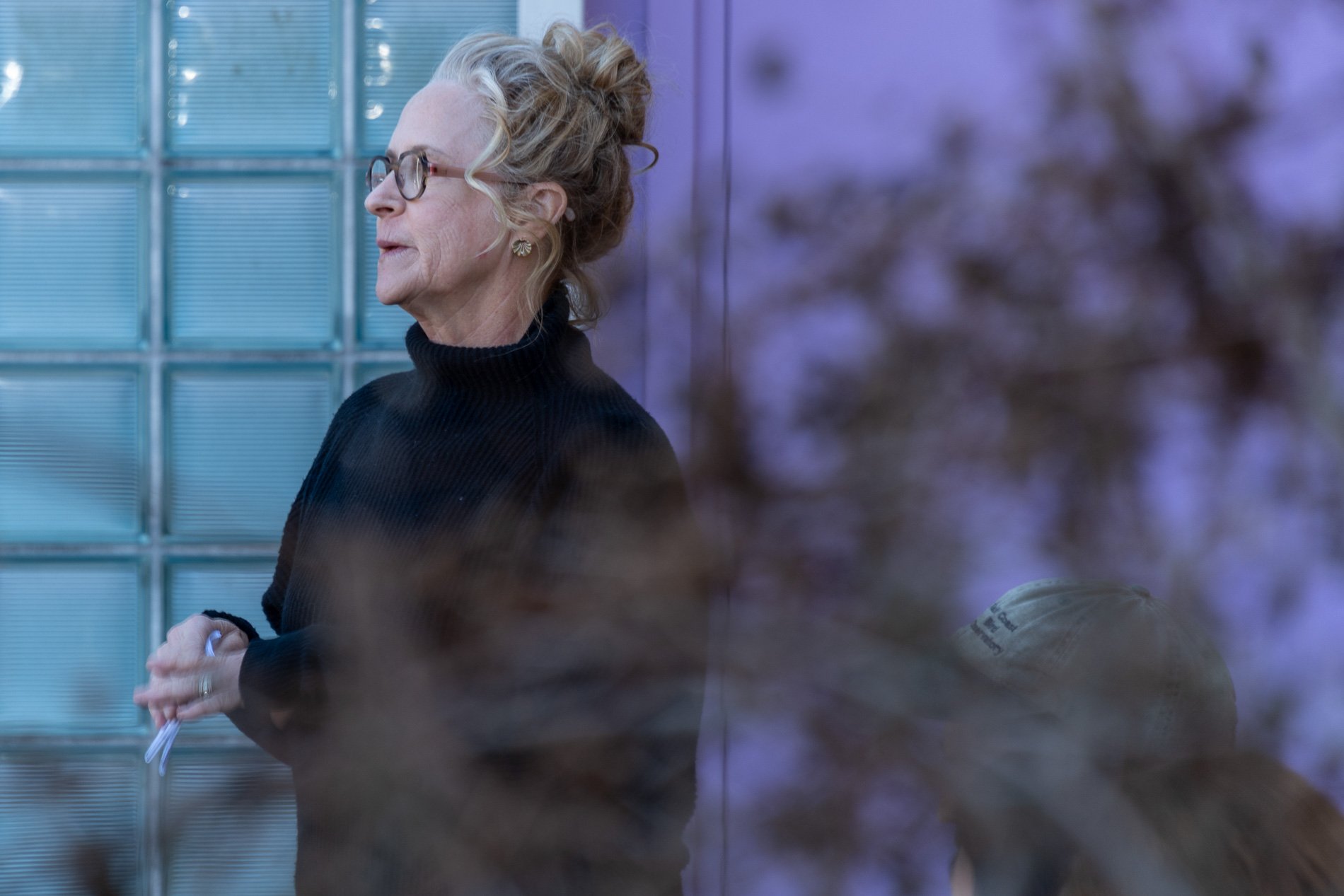
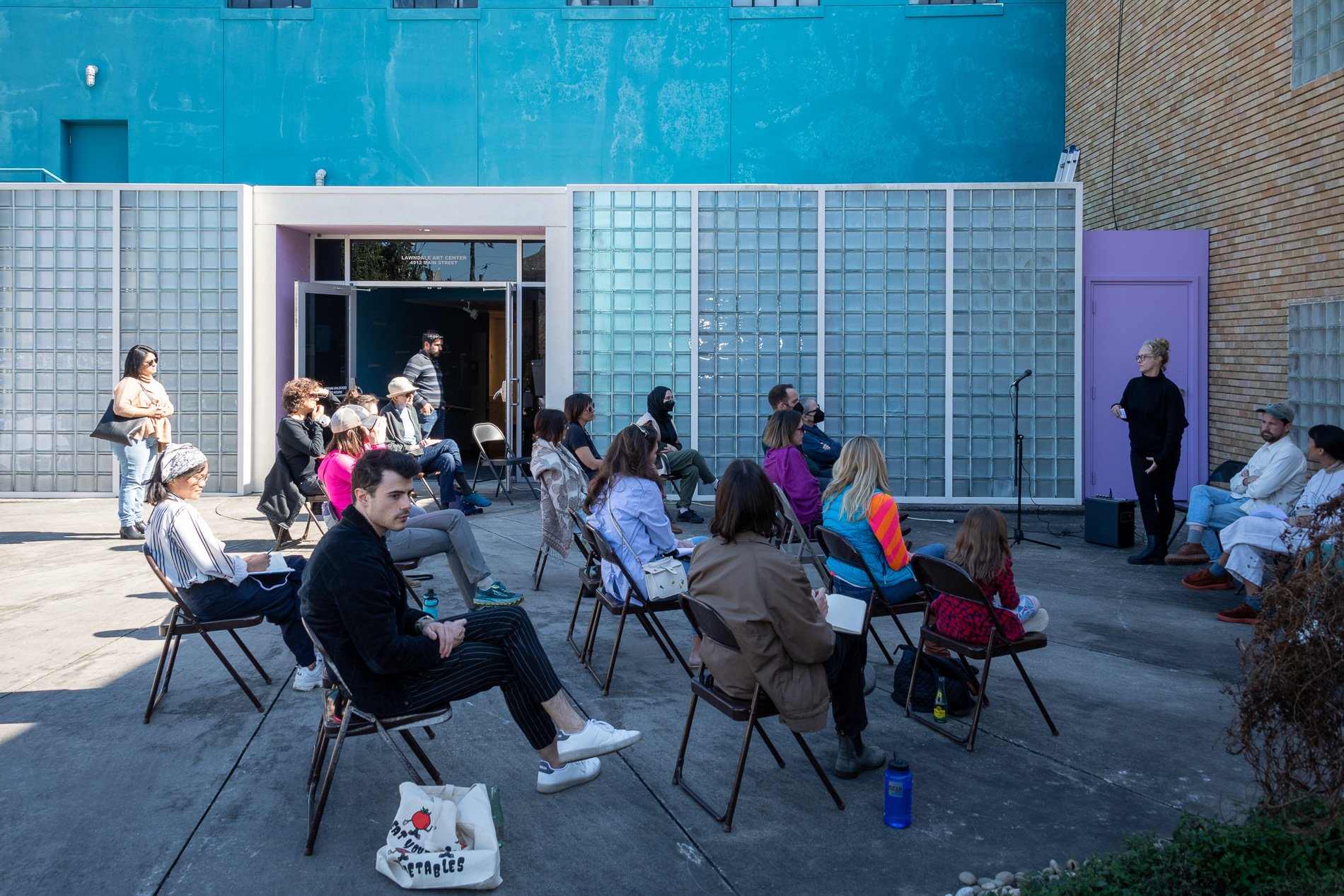
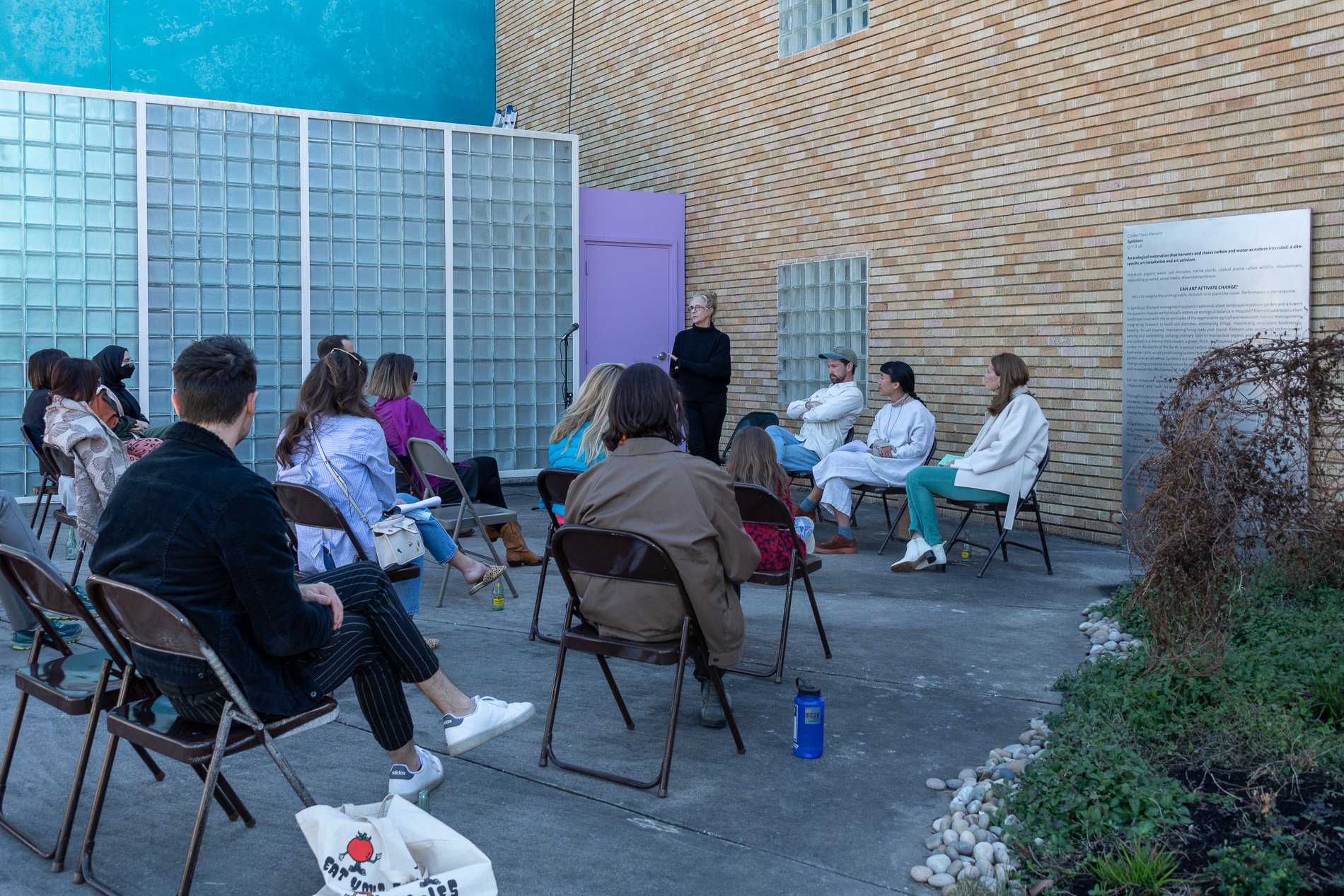
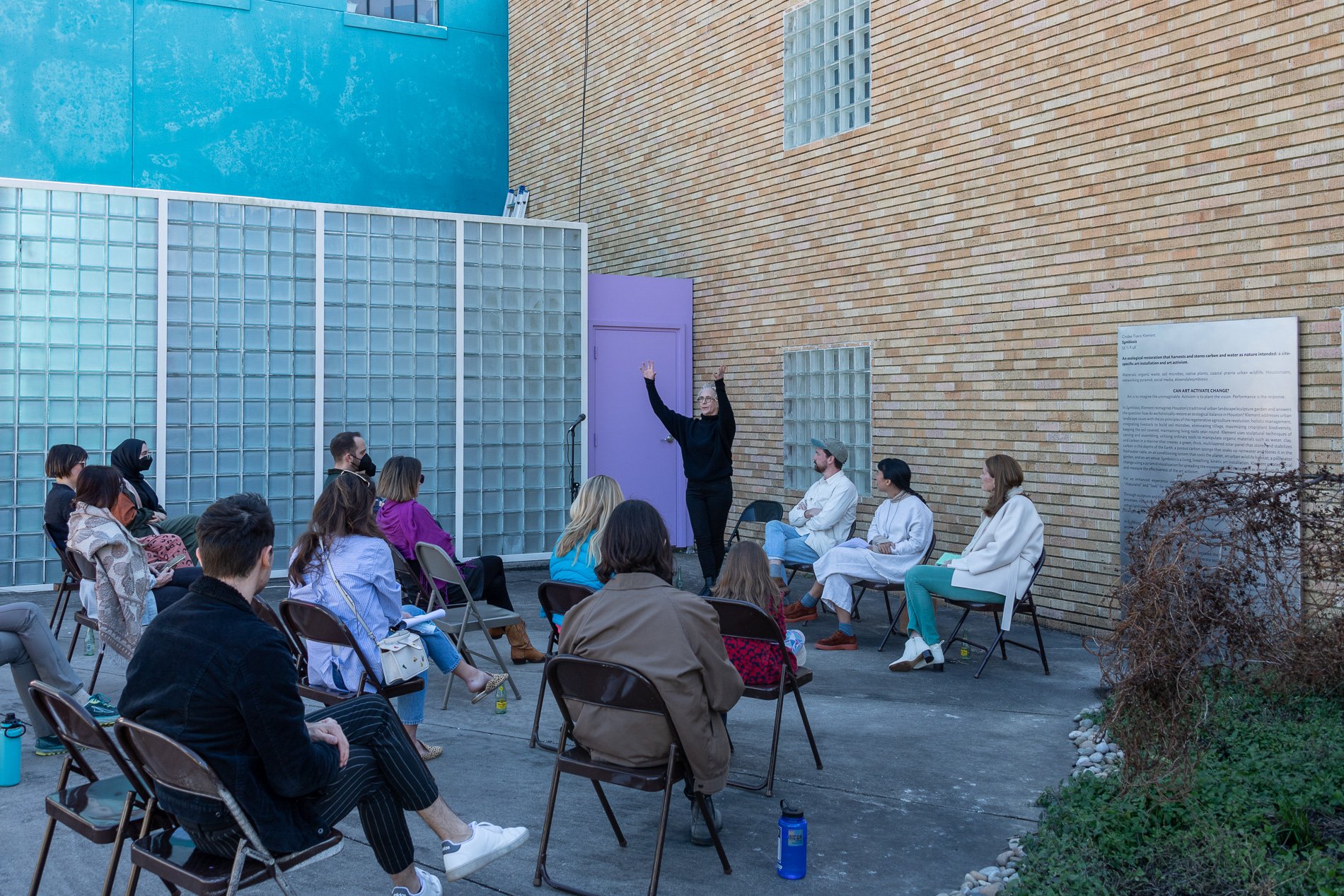
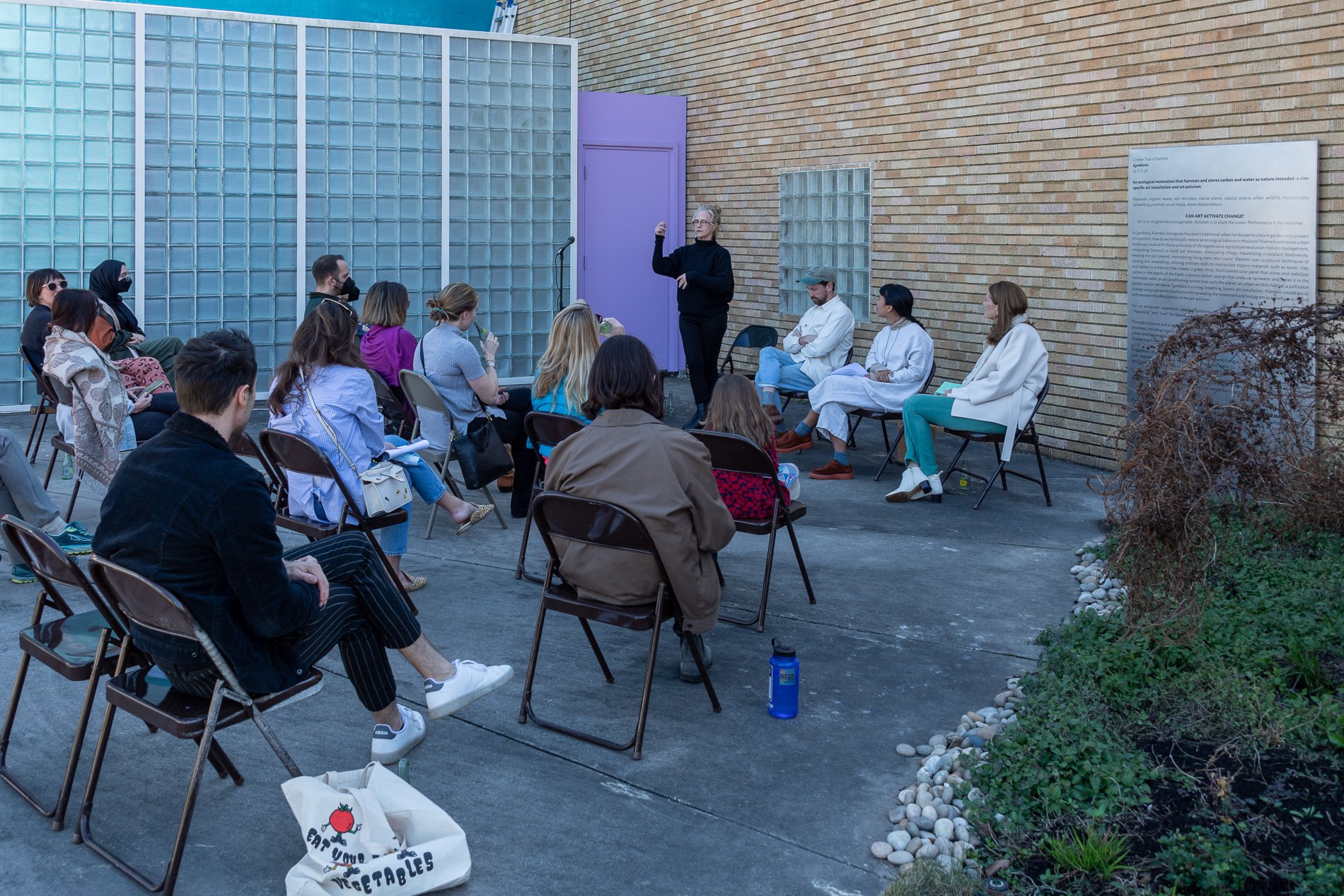
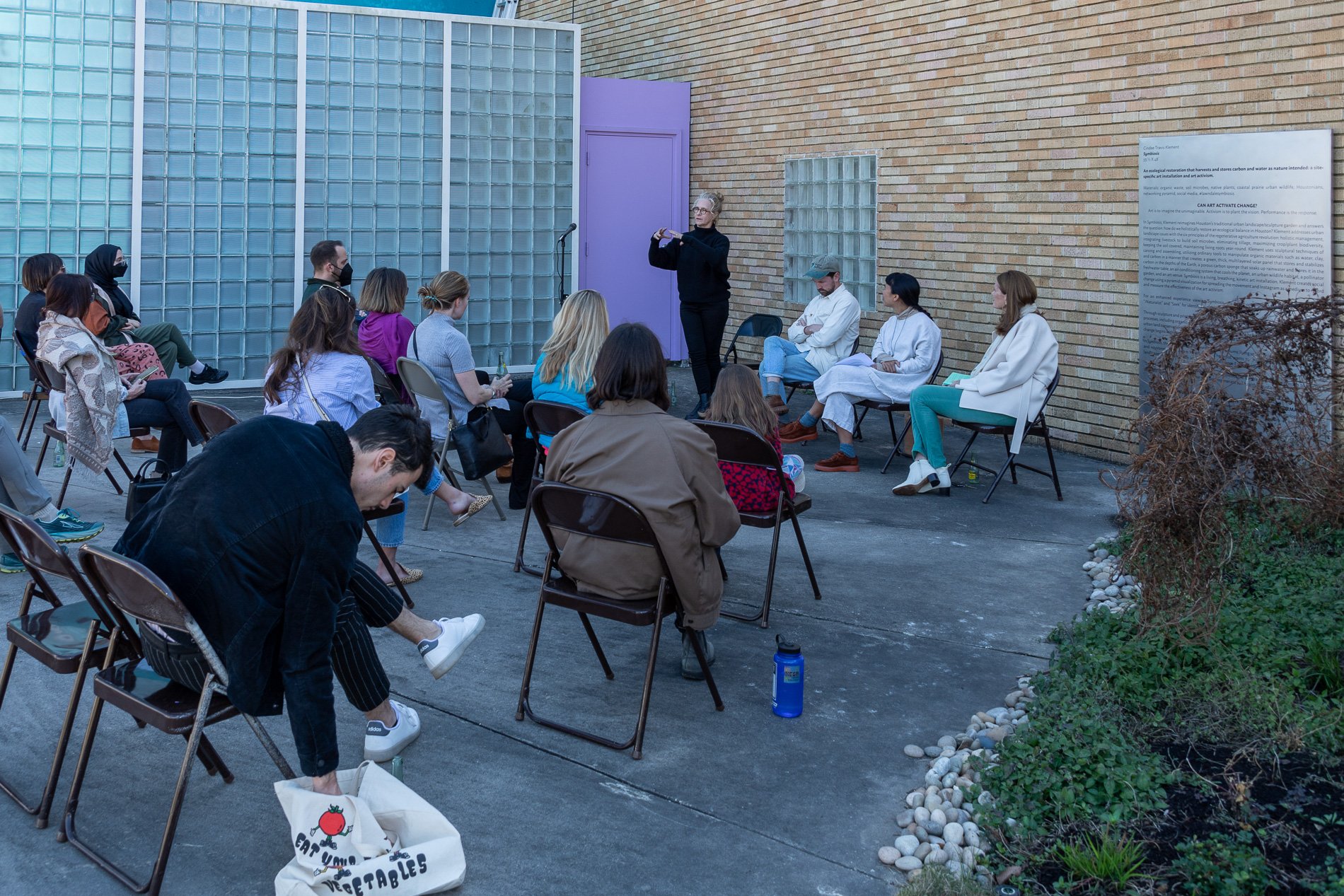
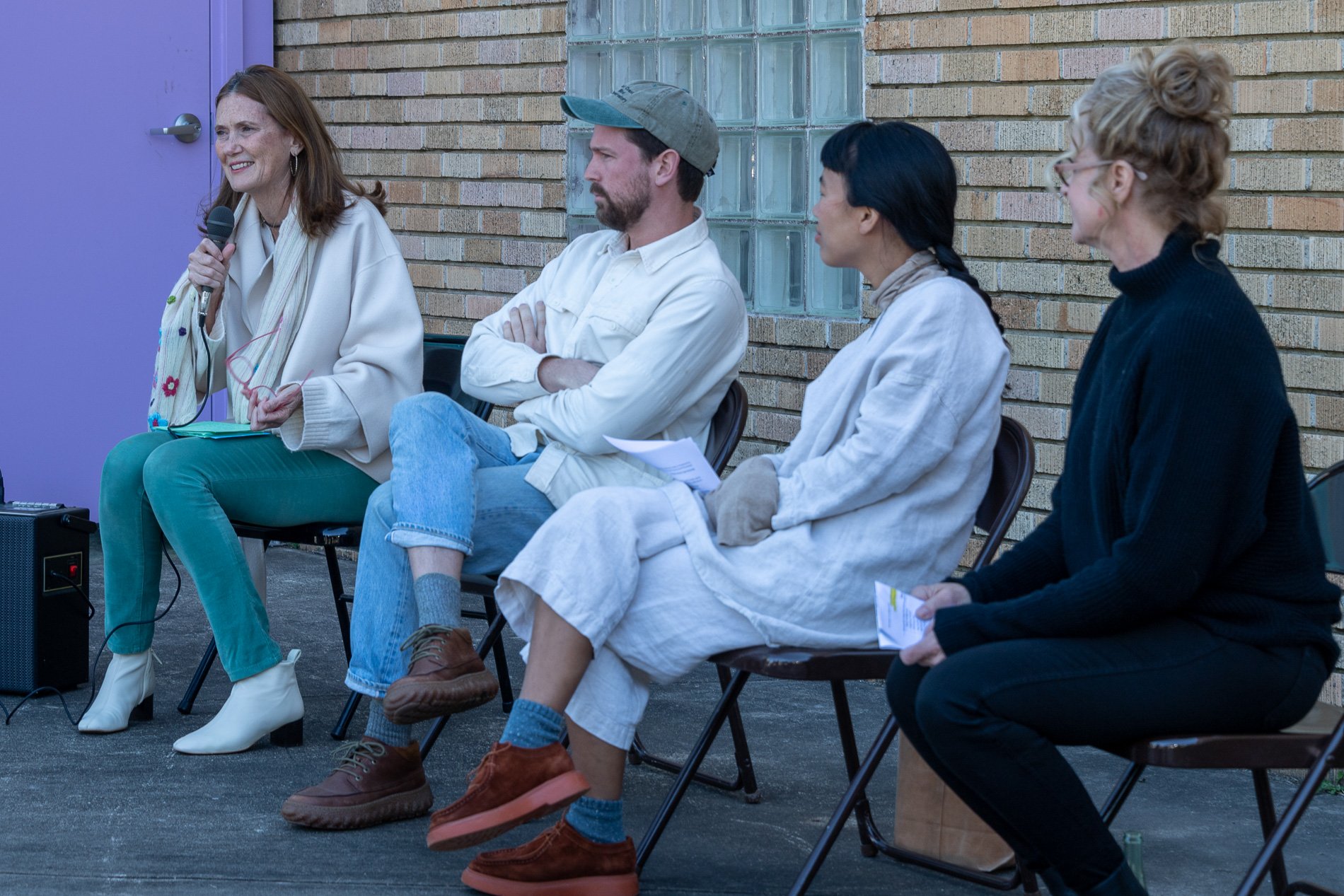
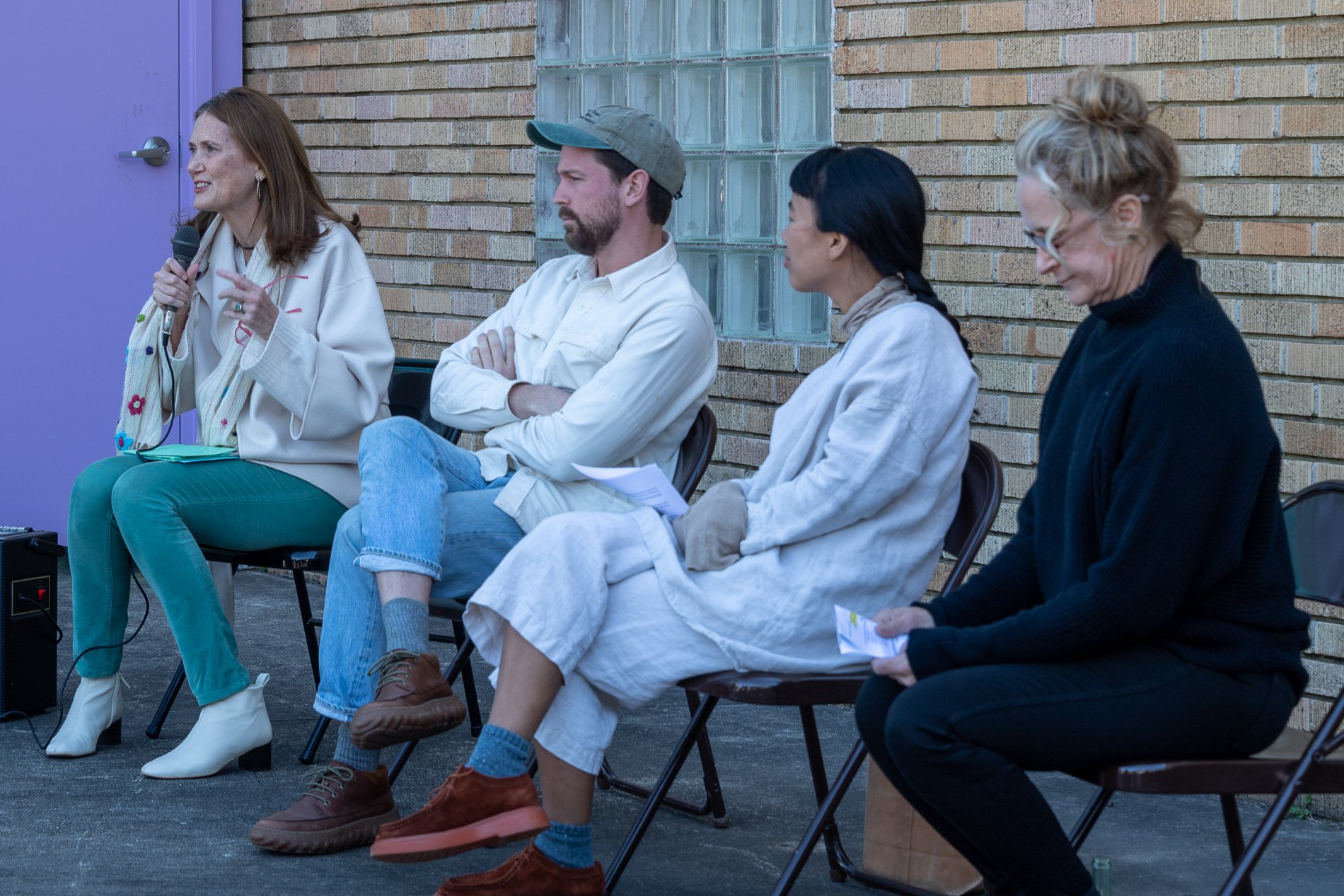
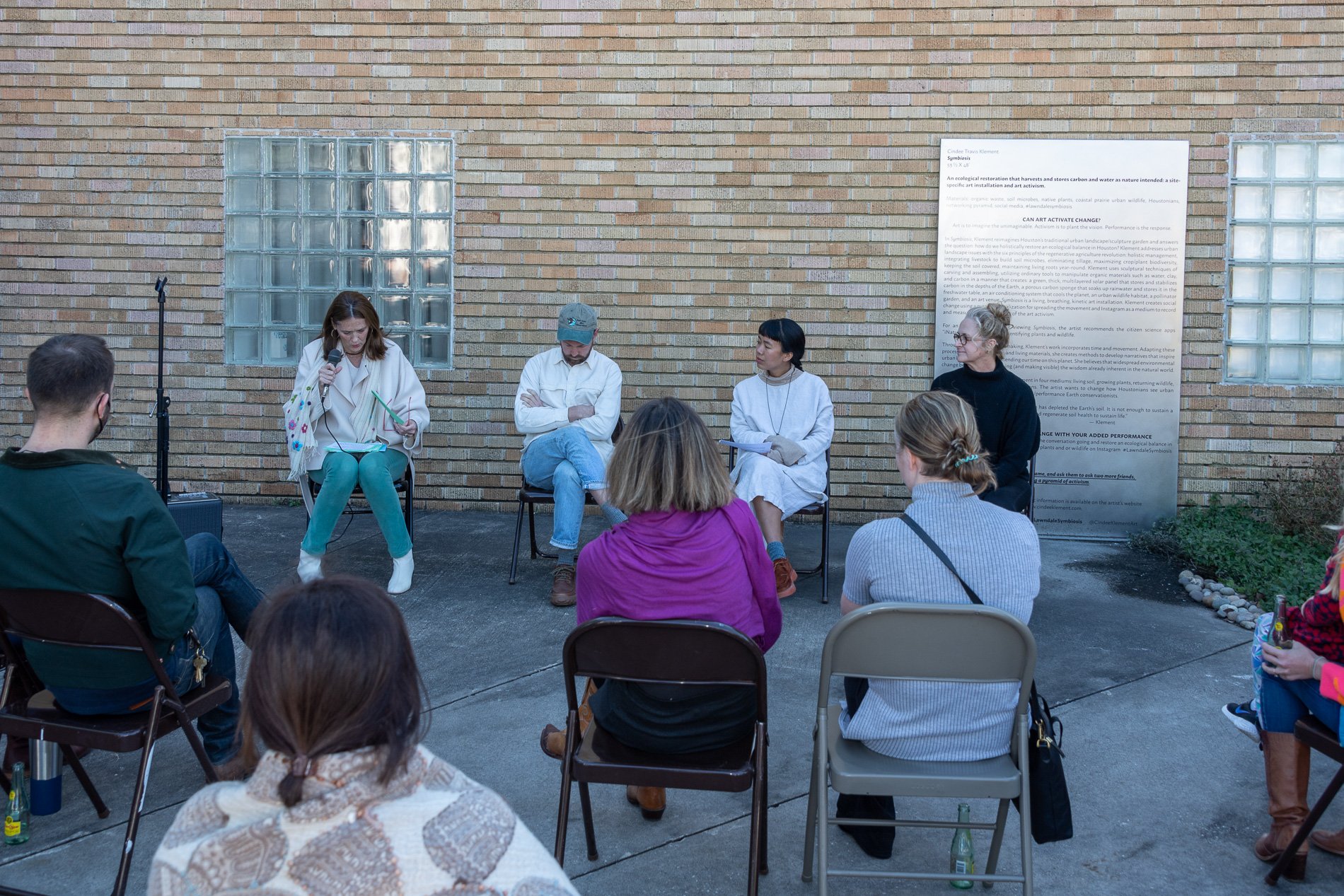
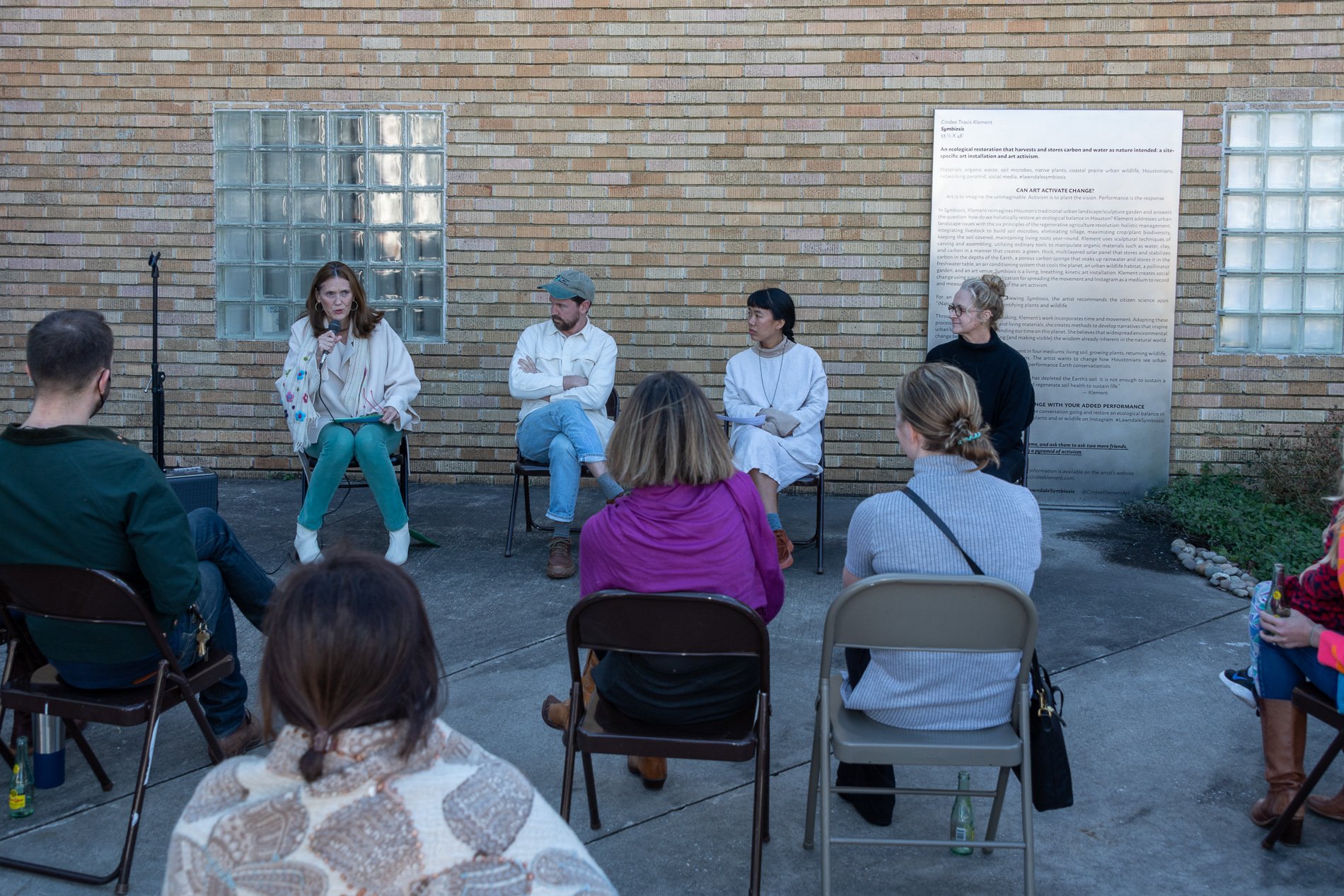
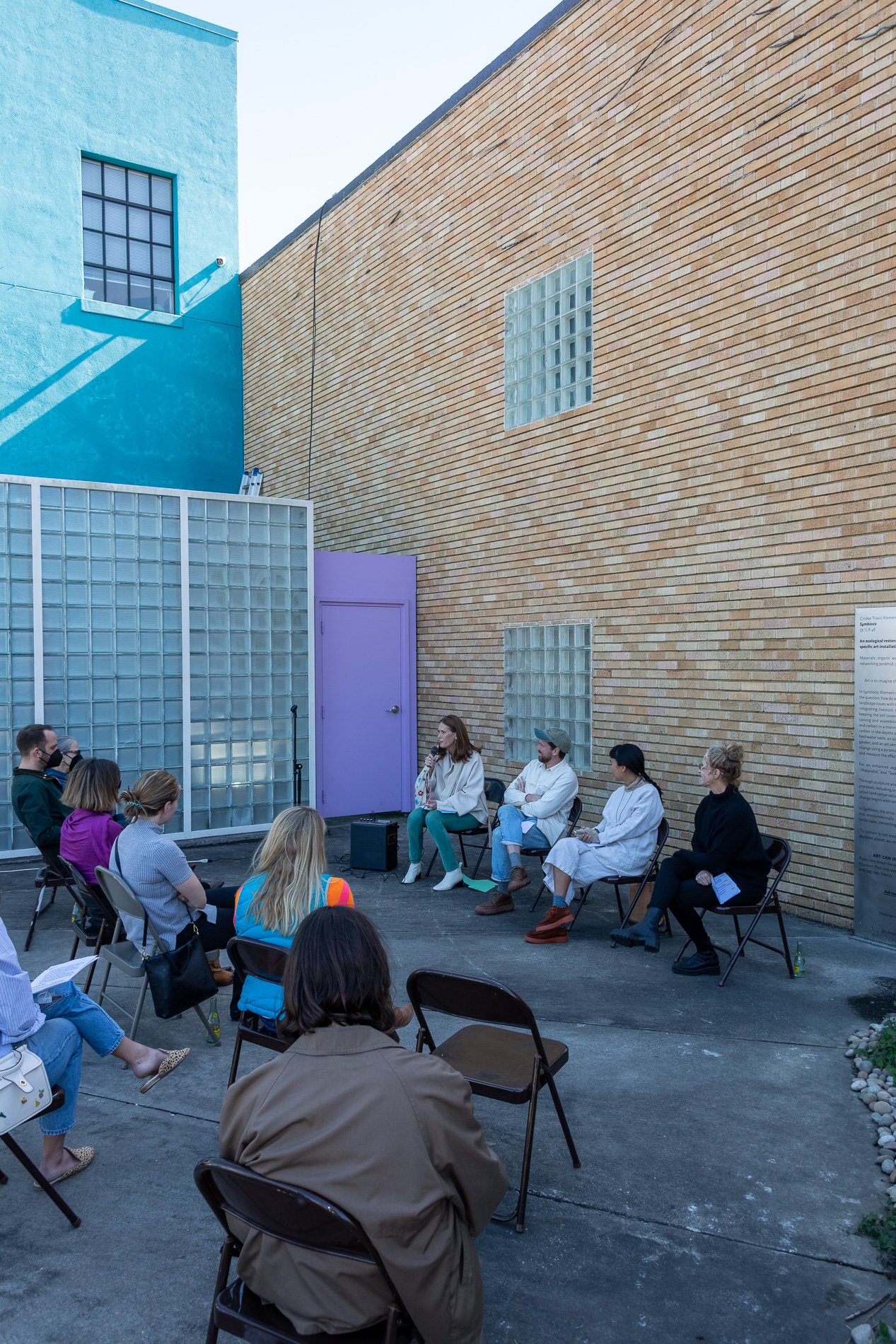
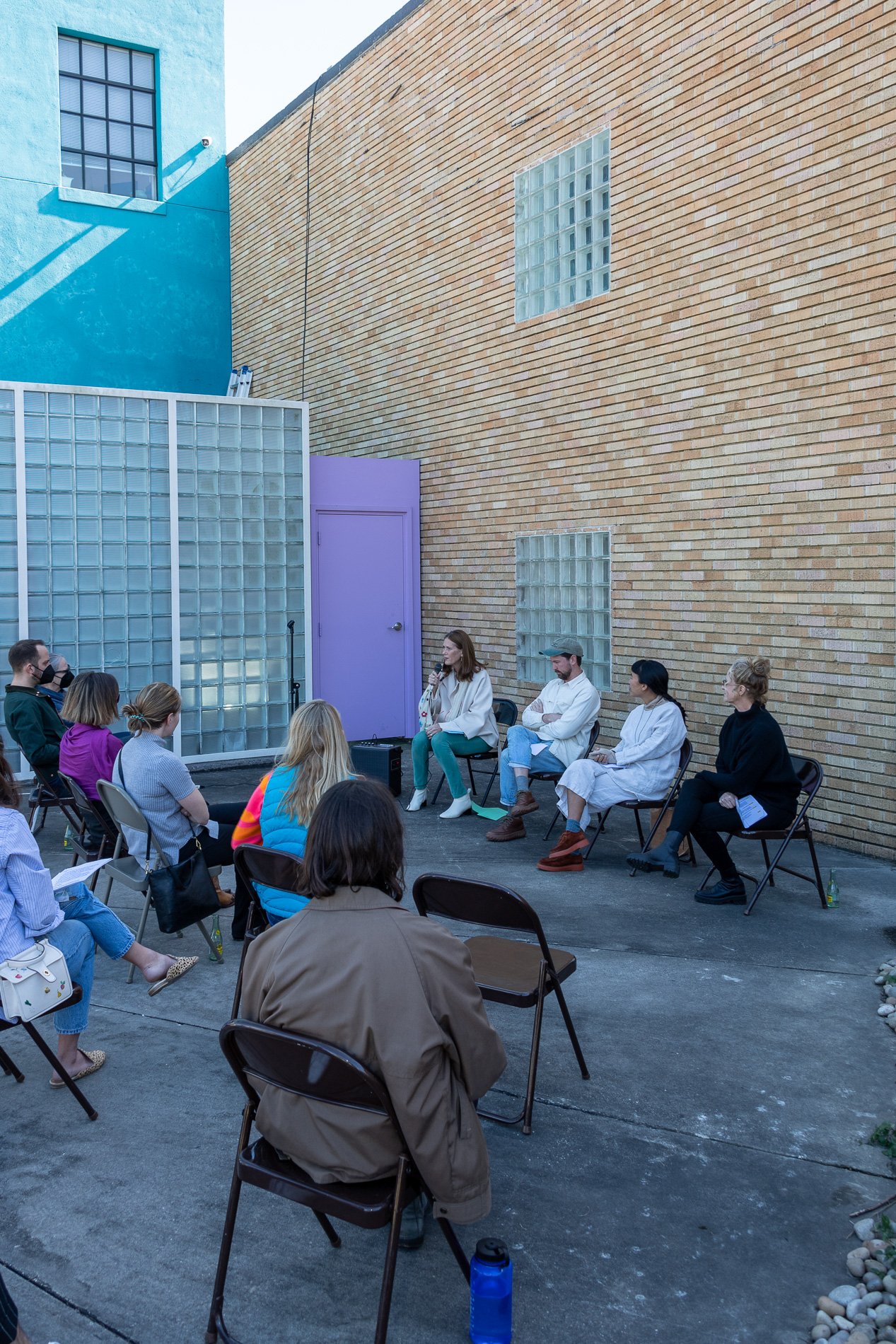
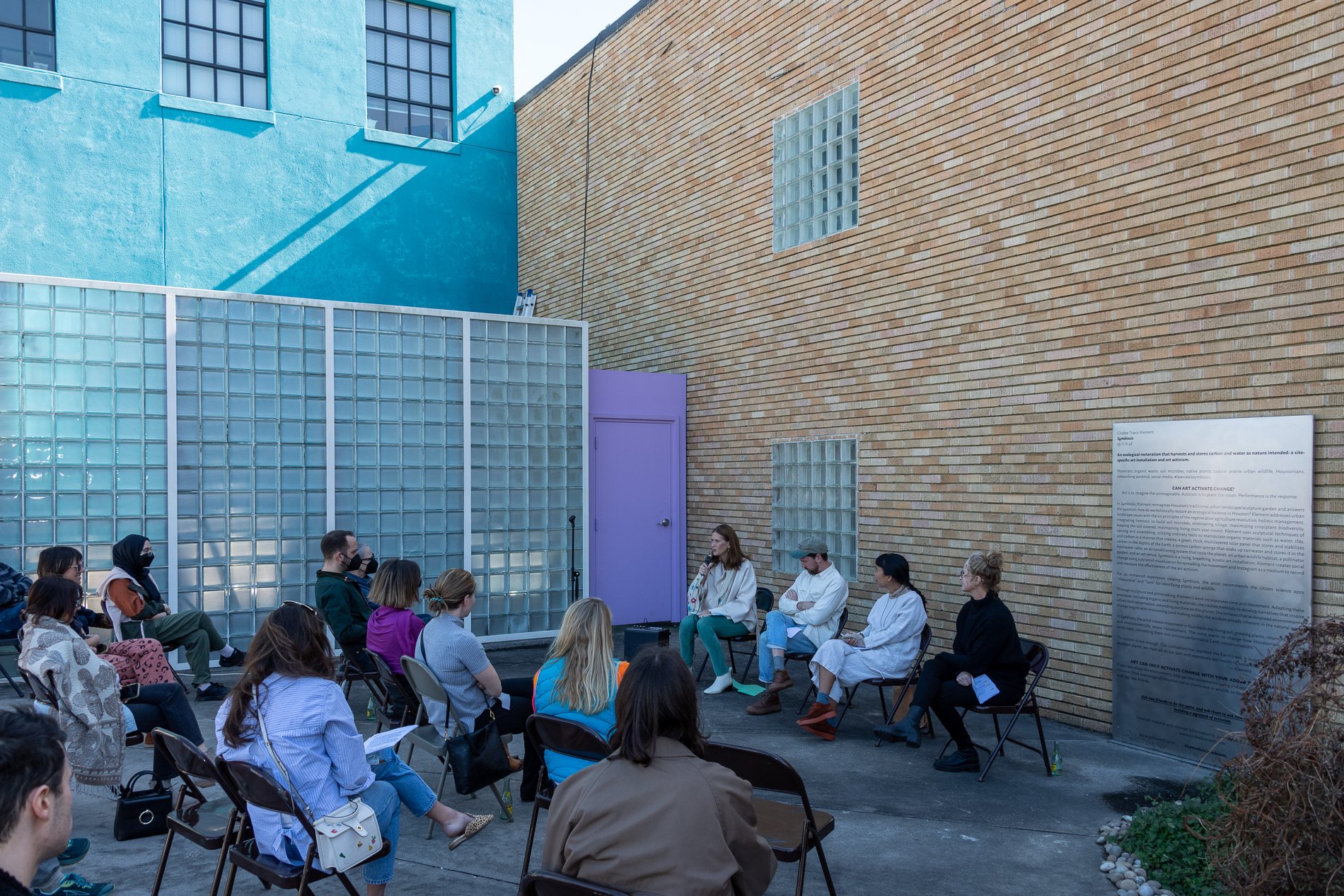
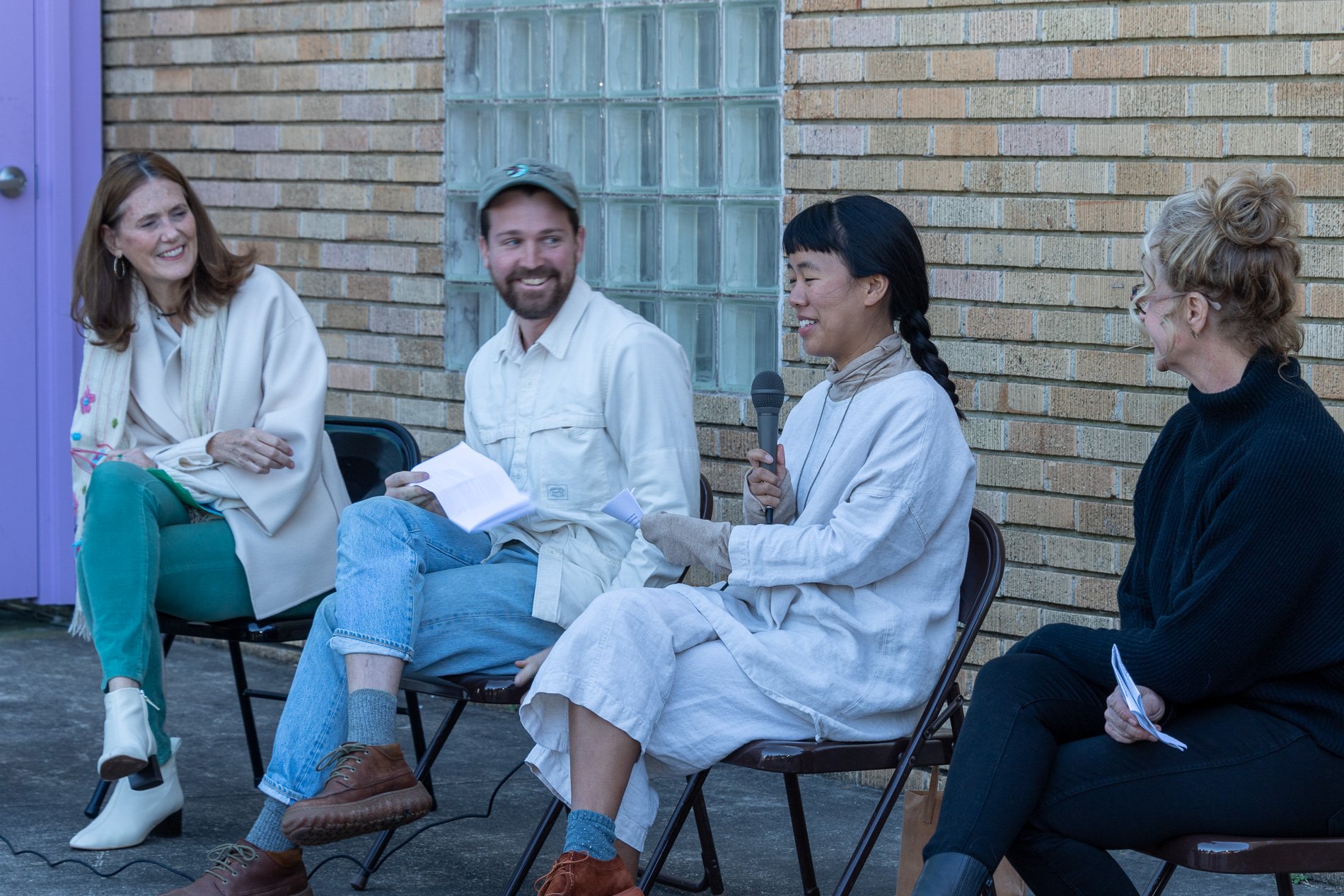
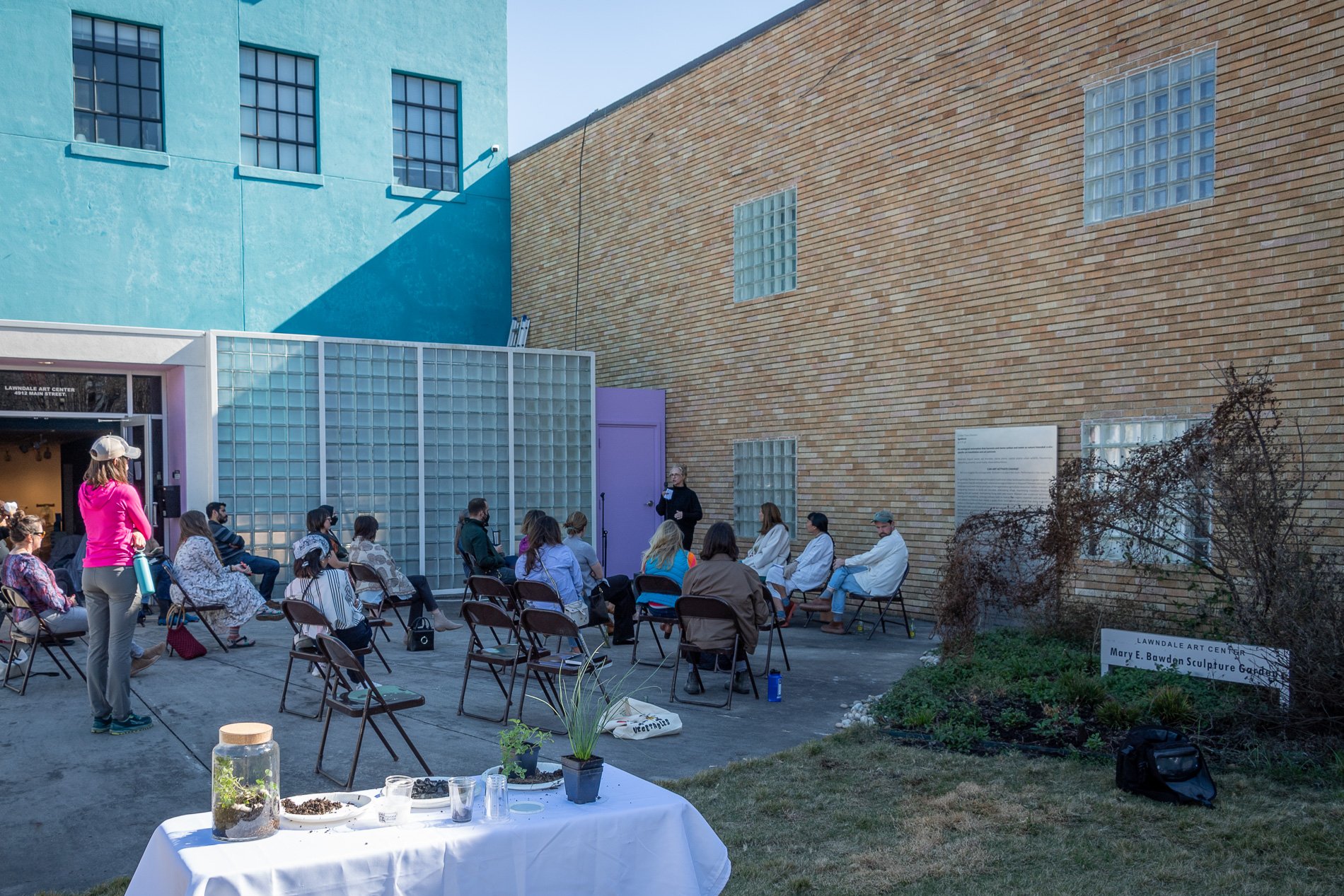
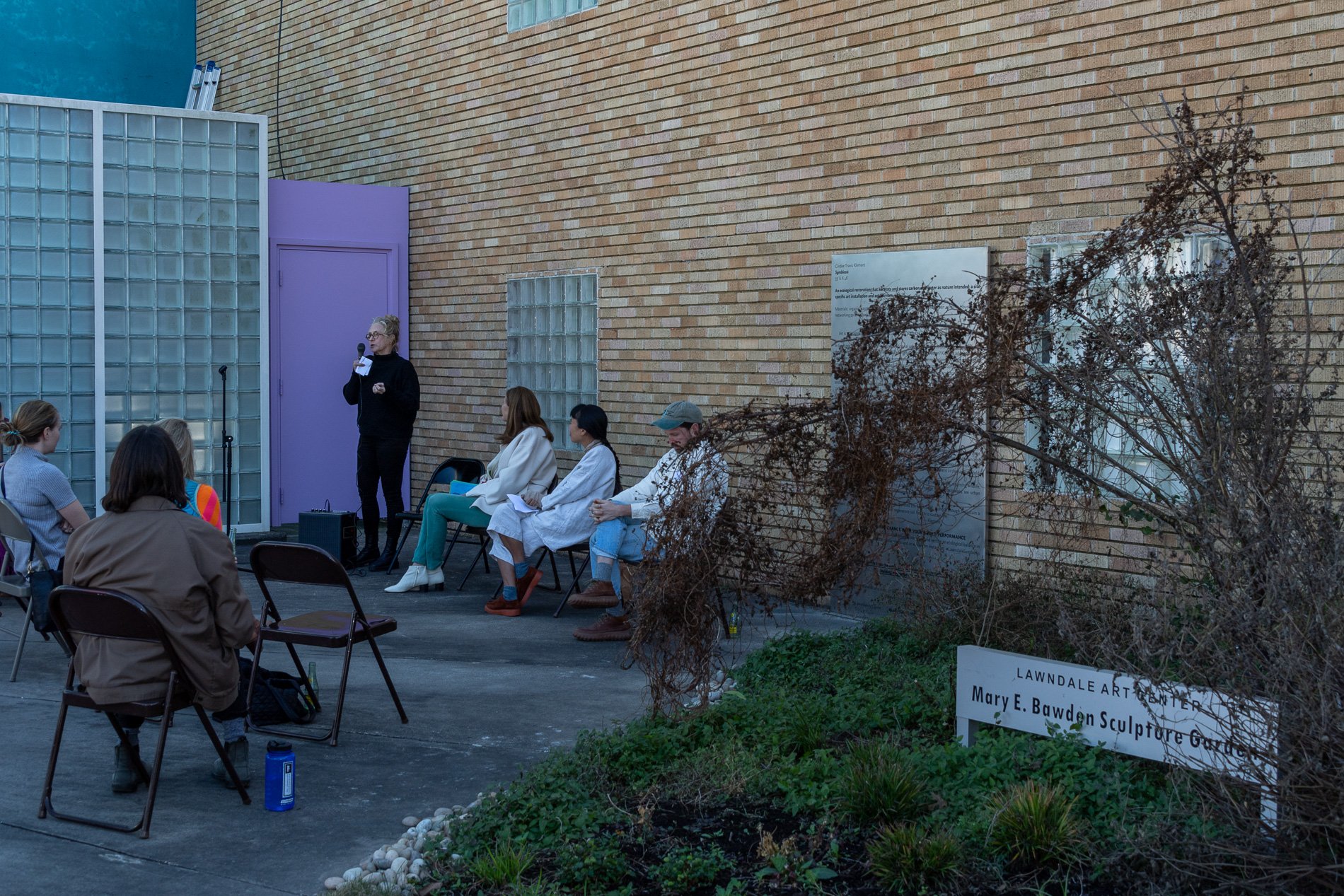
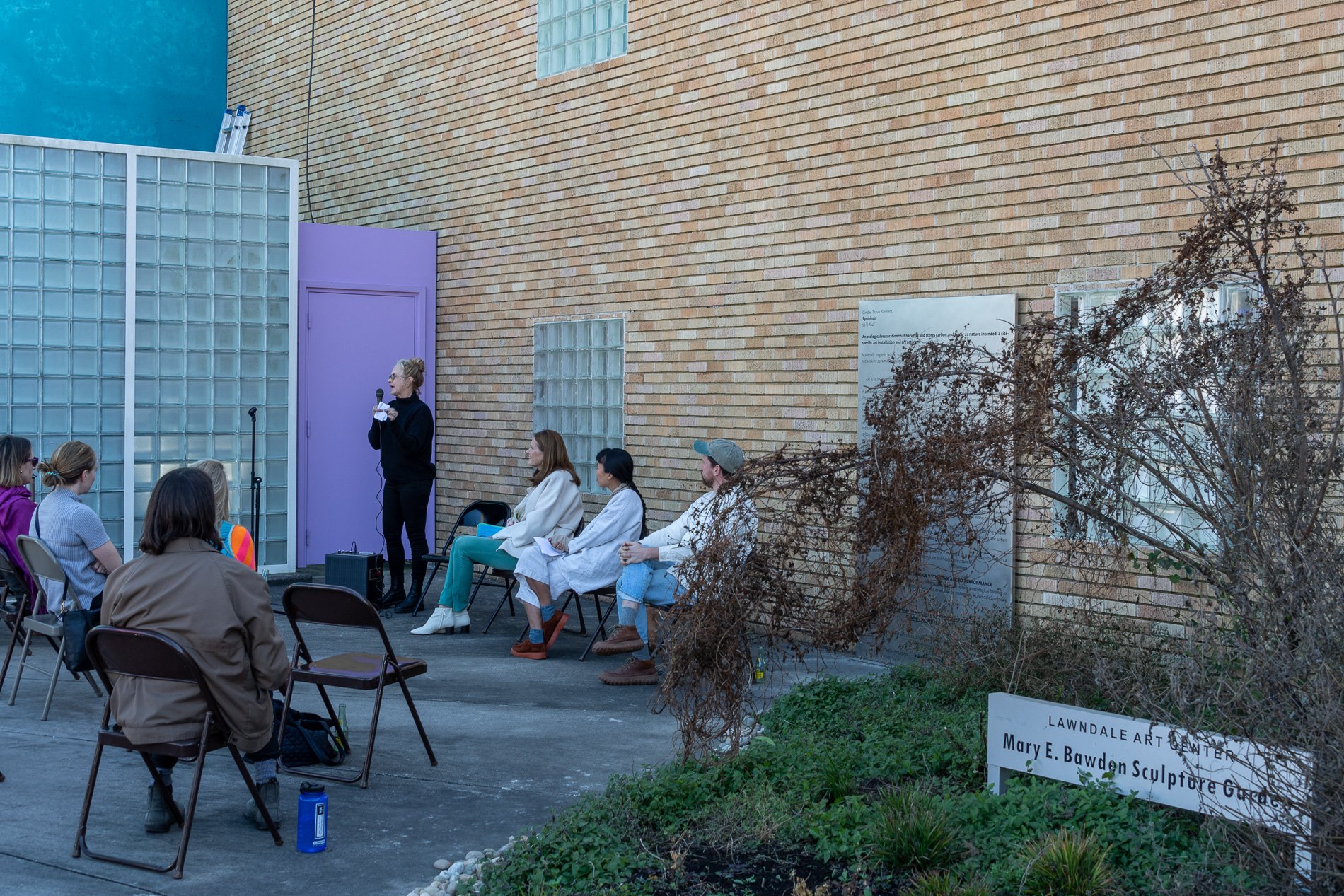
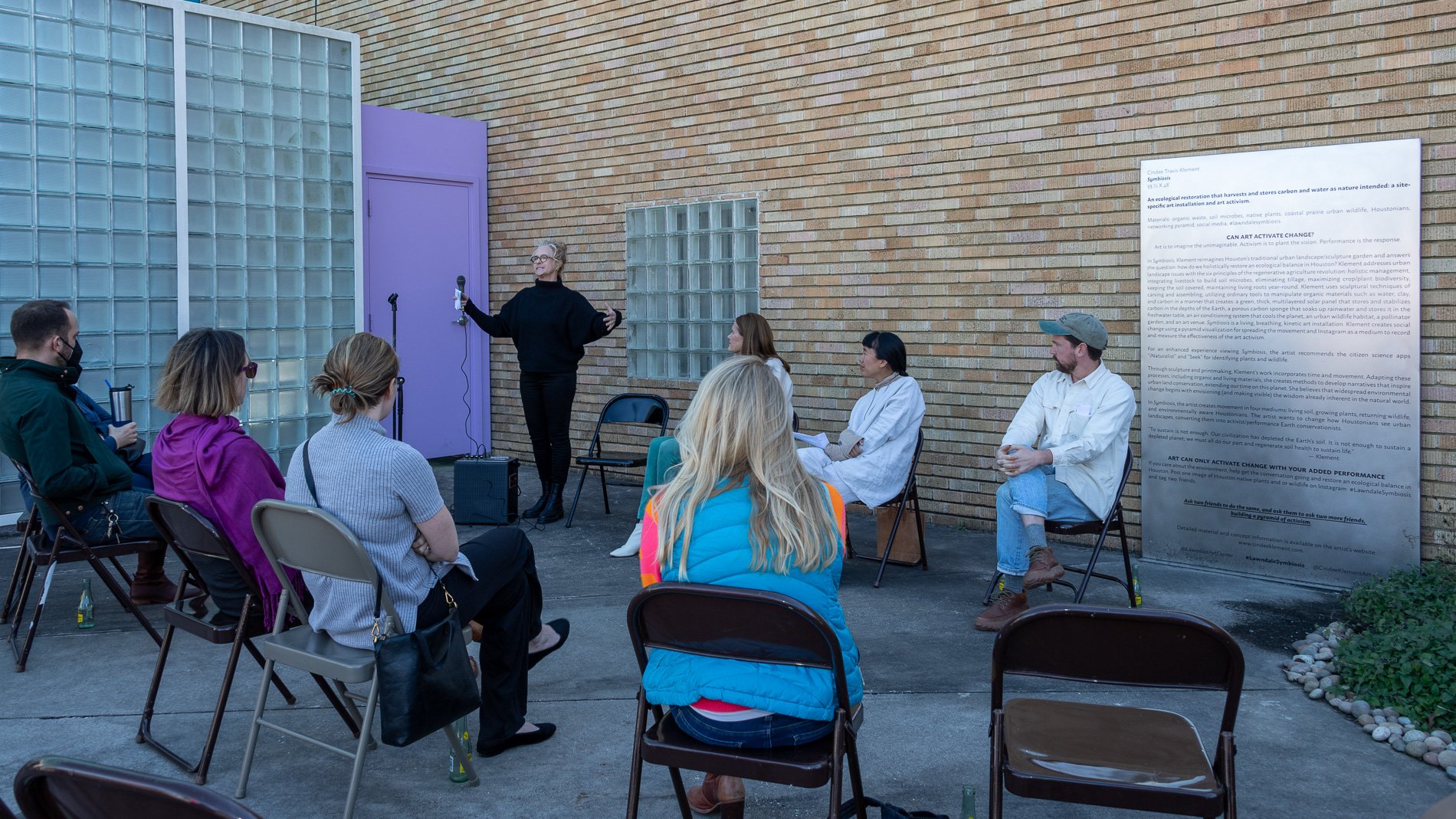
Symbiosis Celebration: Eco—Systems
ECO—SYSTEMS
size varies
financial gain and passed butterflies.
Image by Nash Baker
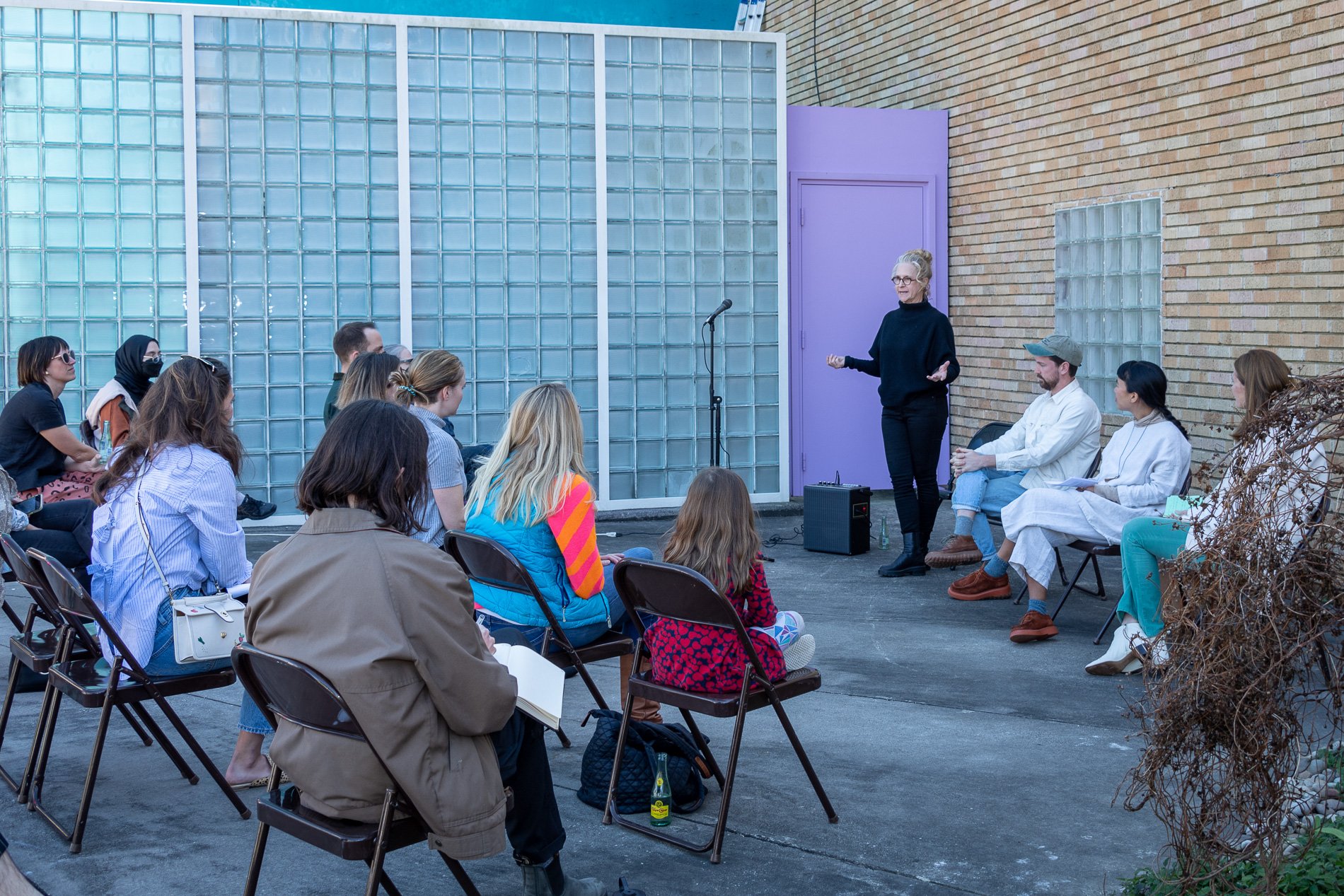
Symbiosis Celebration
social sculpture
—from Chemical Plants to Native Plants—
Native Wildflowers, Food, Art, Music and Migration
Fall color tourism contributes $1 billion per year to North Carolina. Houston has fall and spring color migration; we can cultivate them into tourism and build soil health.
“For profit is the fuel that will change society's landscape practices to embrace the planet's ecological systems in Houston. Applying economics and industrial concepts to my work, I see ecotourism as an untapped resource that can strengthen our environmental and economic health. I propose nurturing and marketing Houston’s ecotourism, through a Symbiosis Celebration of migration, that ultimately encourages and celebrates new mutualistic relationships between Houstonians and the planet. Through fostering relationships that regenerate Houston's micro-ecosystems, we will move our reputation from Chemical Plants to Native Plants — we can prosper as the Green Energy City.” — cindee travis klement
“If you dig deep and keep peeling the onion, artists and freelance writers are the leaders in society - the people who start to get new ideas out.” — Allan Savory
In April 2021, I installed the first native plants in Symbiosis, in Lawndale's Mary E. Bawden Sculpture Garden. Within two months, Symbiosis exploded with bountiful native blooms. Plants expected by the Ladybird Wildflower website to be one to three feet tall in Symbiosis were instead two to four feet tall. In June, the endangered native bees started returning. In the first twelve months, I have witnessed seventy new species in the space: from bird nest fungus to Red Admirals, Monarchs and skippers, skimmers, one of the bumblebees listed as endangered, Bombus pensylvanicus, treefrogs, toads and birds.
Building Mutual Symbiotic Relationships to Power Ecological Recovery
In preparation for the celebration I envision cultivating relationships among the City of Houston, local property owners, Houston's indigenous landscape and its wildlife, soil and climate, food, restaurant, music, visual and performing arts, museums and professional sports team communities.
The following steps will contribute to building these relationships:
· The business and private property owners will need to redirect their existing landscape budgets to native plants that support our wildlife.
· These new landscape practice guidelines will align with the Mayor's Office of Sustainability and Resilience.
· New native wildflower and grass landscapes will slow rainwater, allowing it to soak in and return to the aquifer to cool the planet while sequestering carbon and storing it in the ground where it is stable, providing food and safe habitats for our indigenous wildlife.
· The approximately six hundred species of birds, four hundred and thirty species of butterflies, eight hundred species of Texas native bees, one thousand species of moths, eighteen species of dragonflies, thirty species of turtles, including two box turtles, and seventy-two species of amphibians native to Texas will expand their populations in our city.
· Houston's creatives in the food, restaurant, music, visual and performing arts, museums and professional sports industries will respond to the new mutualistic/symbiotic relationships among Houston's landowners and our unique plant and wildlife in exciting creative ways and performances during the celebratory periods.
· The City of Houston will promote, market, and support the above-described new relationships with its services infrastructure, completing the mutualistic relationship that will support Houston's economy and ecosystems.
Why Houston Can Support Ecotourism
Although Symbiosis taught me the speed with which an urban landscape can transform into a wildlife haven, it was not until I was in Fredericksburg that I realized Houston's ecology is an untapped tourist economy. When you combine Houston's rich soil, high humidity, heat and long growing seasons with the indigenous native plant landscapes supported by Houston's urban irrigated commercial and park landscapes, Houston's native plant wildflower and wildlife tourism can far exceed those of the small towns in Central Texas. Another tremendous asset is Houston's central geographic location in the bird and butterfly migration paths between the North and South American continents and our proximity to the Gulf Coast. Texas has the most butterfly species of any state in the United States. Houston's inner city is 600 square miles; our "sprawl" is an asset to urban ecotourism.
As additional support that Houston can be an ecotourism powerhouse, I have read that one of New York City's most popular tourist attractions is The High Line's native landscaping. In North Texas, Plano also uses wildflowers and music to attract tourism dollars.
Funding
I see businesses and organizations all over the city which are starting to take advantage of the ecological benefits of native landscapes. Unfortunately, many other property owners (business and home) are unaware of the economic and environmental benefits of native plant landscaping. They spend $50-$100 per hour for weekly maintenance and $4—$12 per square foot for seasonal plantings, while also incurring high water usage and bills. Suppose the City appeals to these businesses and individuals to convert their existing non-ecological landscape budgets to native wildflower and grass landscapes. In that case, the City can promote a native plant/wildflower and wildlife, food, arts and music festival that will symbiotically support native ecological systems. The supporting businesses can profit from the tourism they generate.
The Texas Can-Do Spirit
Systems thinking to mitigate climate through industry and the arts is a new territory — will Houstonians embrace this new field of thinking? In Texas, that depends on how you ask and present the need. In our recent history, from Katrina to hurricane Harvey, unsolicited Houstonians volunteered to help their neighbors. In 1901, wildcatters discovered Spindletop, drawing people worldwide to build a better life in unknown territory. “Wildcatter” is used to describe one that drills wells in areas not known to be producing fields. The spirit of the wildcatter is deep in our Texas Can-Do Spirit. It is in our nature to embrace a new field of wild.
Why Big Ideas Are Important.
“The climate needs big, public, audacious goals that everyone can contribute to,” he argues. “Cathedrals were not completed in the lifetime of anyone starting them, but communities bought into these projects.” -The Washington Post. https://www.washingtonpost.com/climate-environment/2023/12/19/climate-change-cathedral-project/
Symbiosis Relationship 9/2022
Skipper and Pokeweed
Endangered bumble bee and Salvia
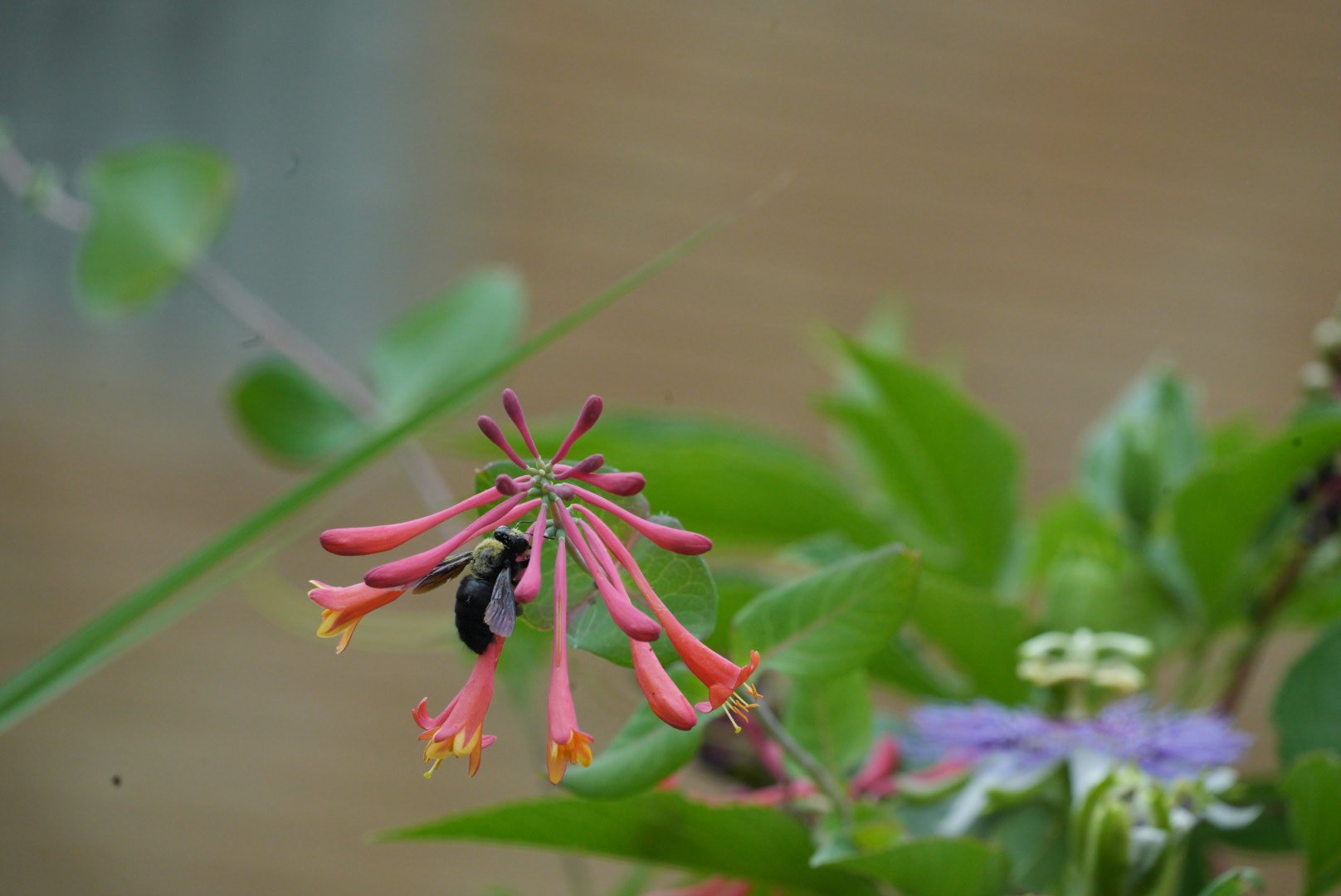
Coral honeysuckle and a native bee.
Mocking bird using an American Westeria vine as a lookout for insects to eatt.
Passiflora incarnate and carpenter bee.
Turkey tail mushrooms breakdown rotting trees recycling the nutrients.
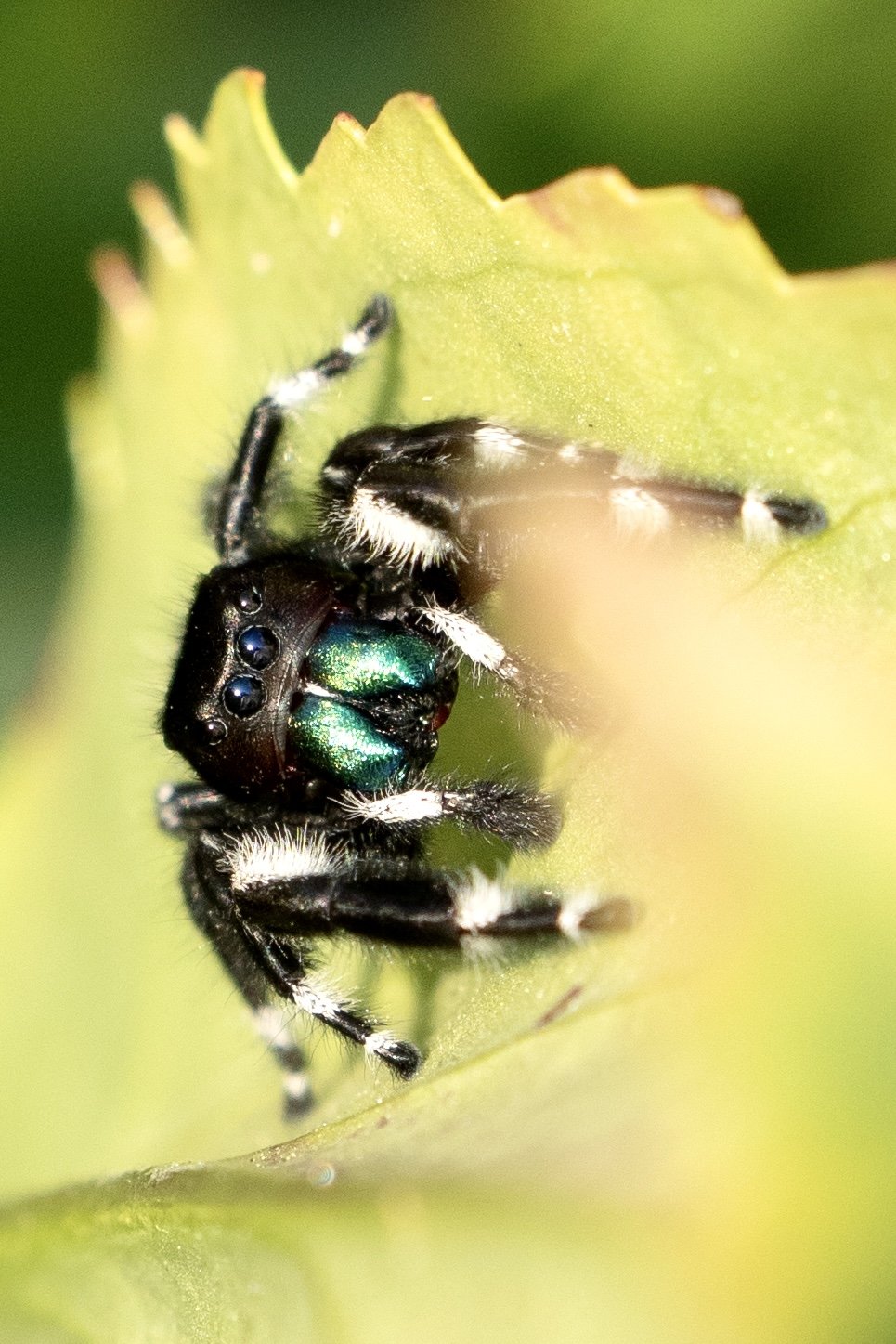
Jumping spider
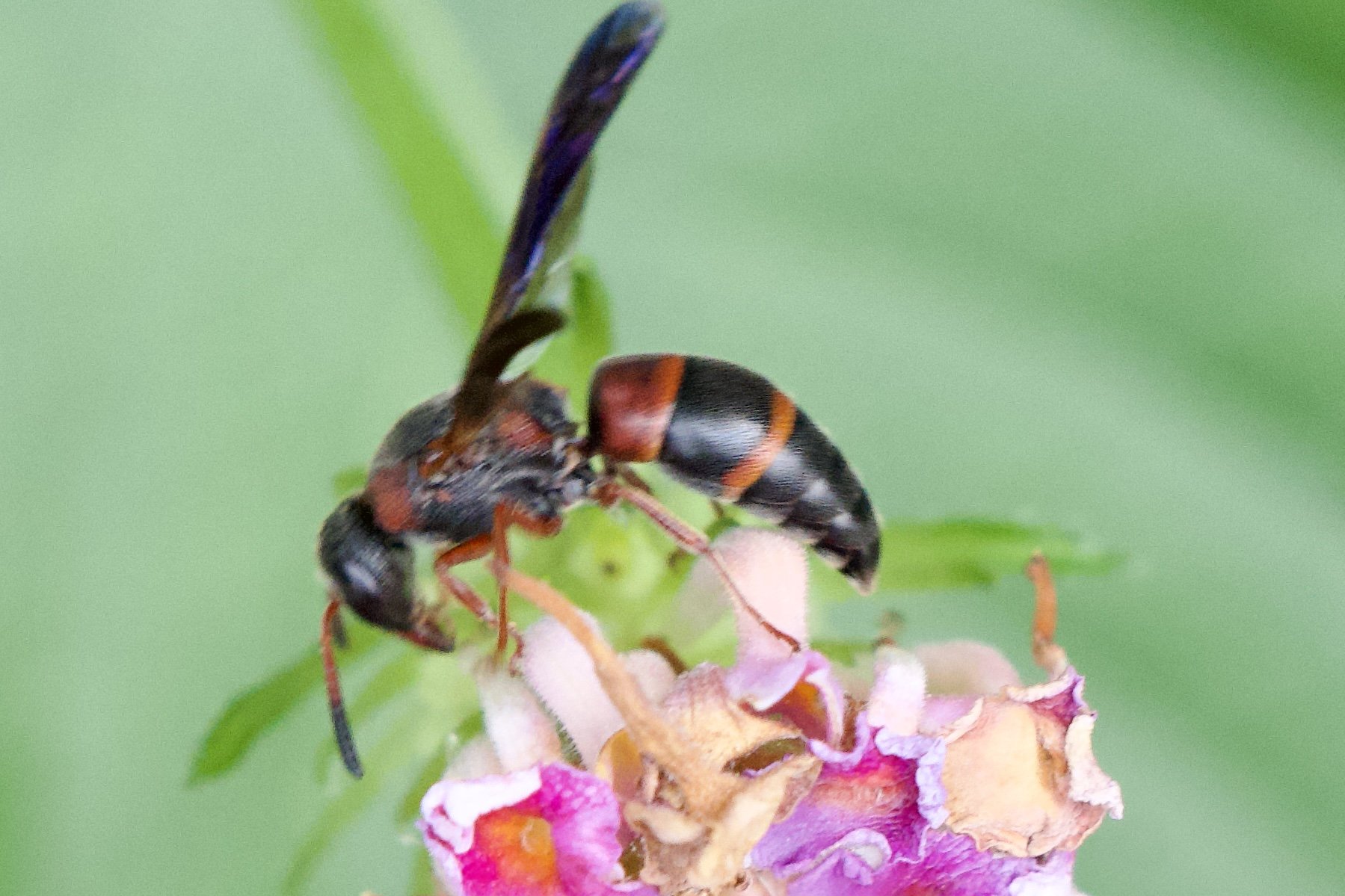
Pachodynerus erynnis, known generally as the red-marked pachodynerus or red and black mason wasp and Lantana camera. Lantanas are complex, I am not certain if this is a native to tropical US or an import. I think it is camara since I see beetles and wasps on it.
Clouded skipper on Lantana camara.
Common green June beetle and lantana camara.
Genus Pyrisitia minisa Yellow butterfly
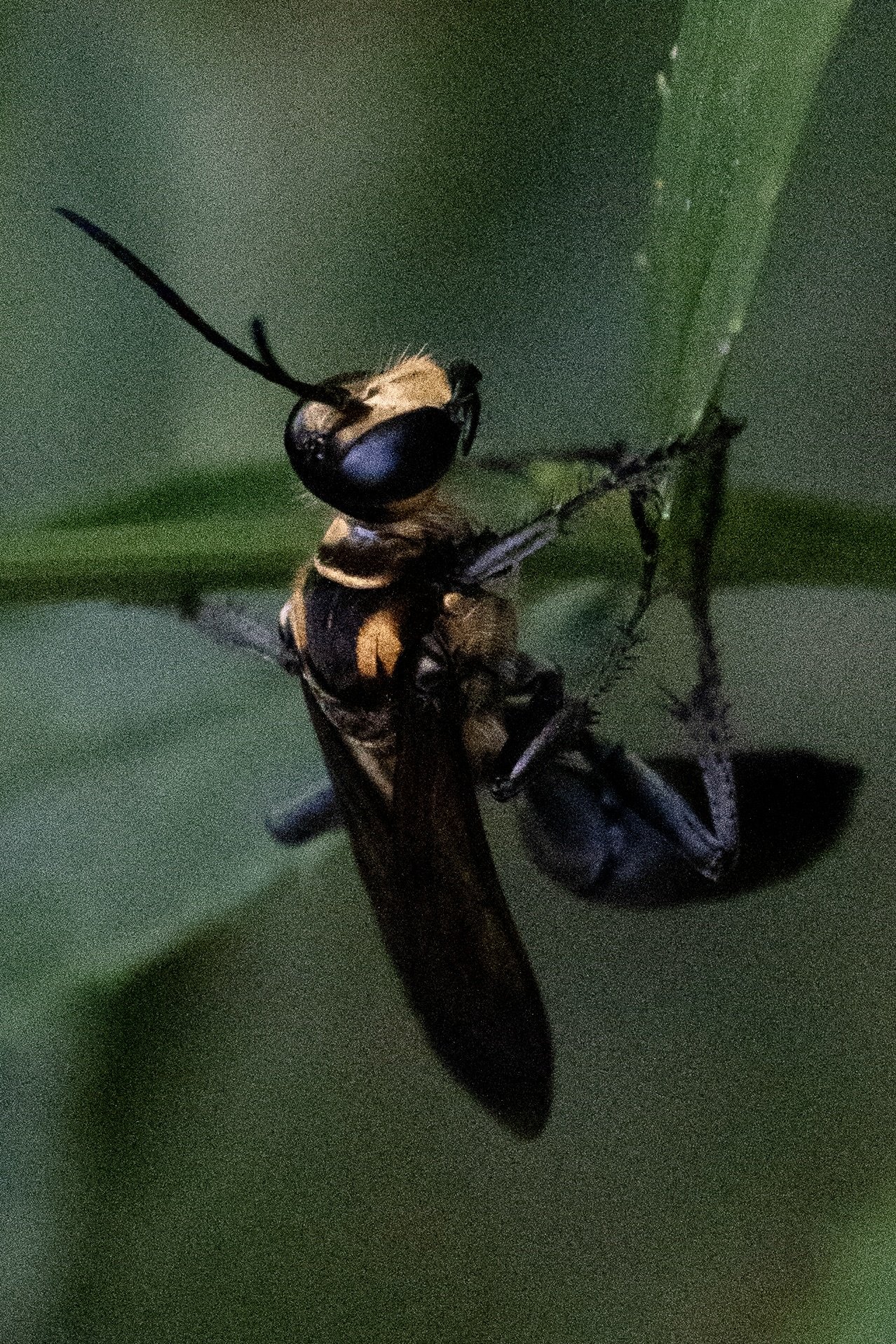
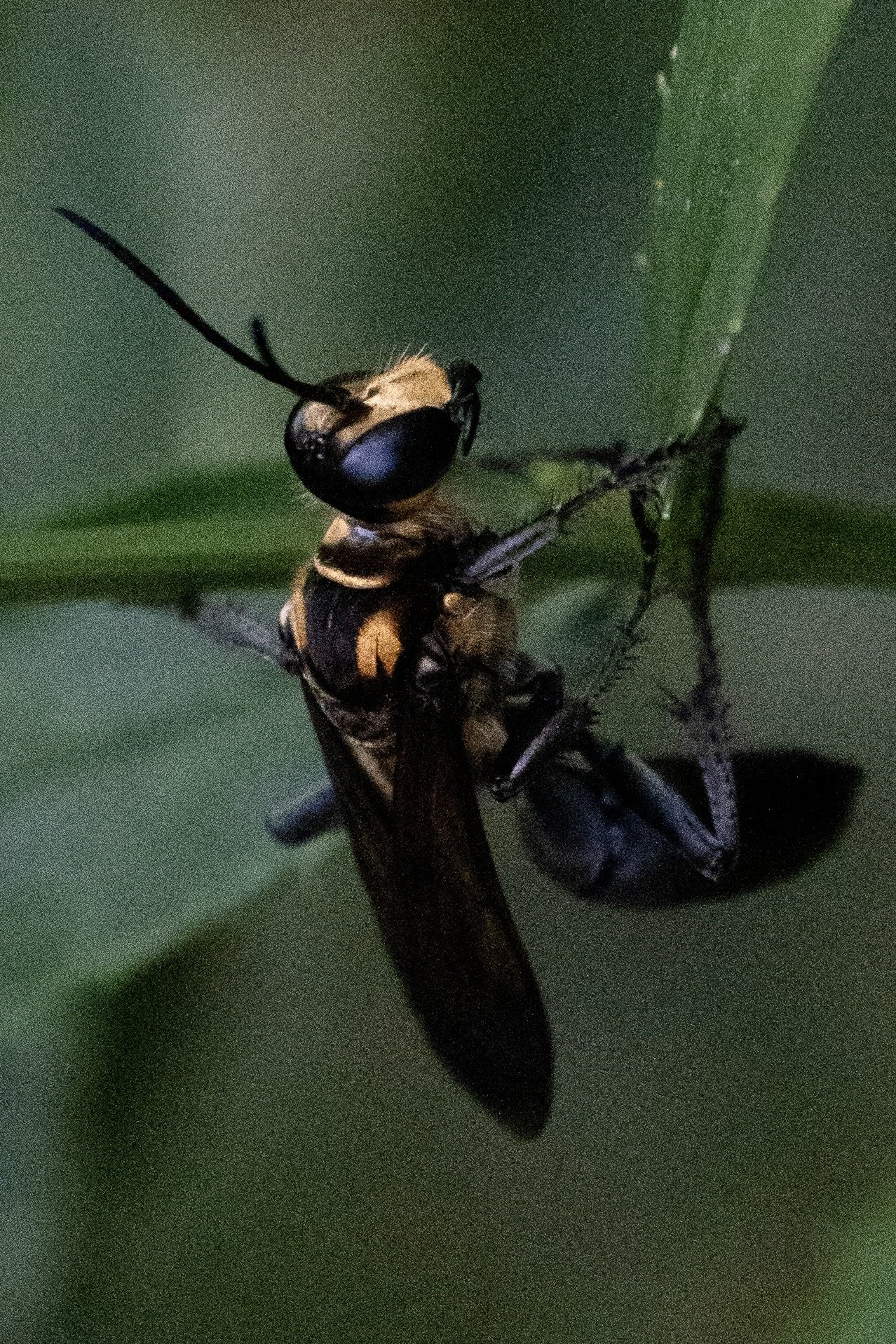
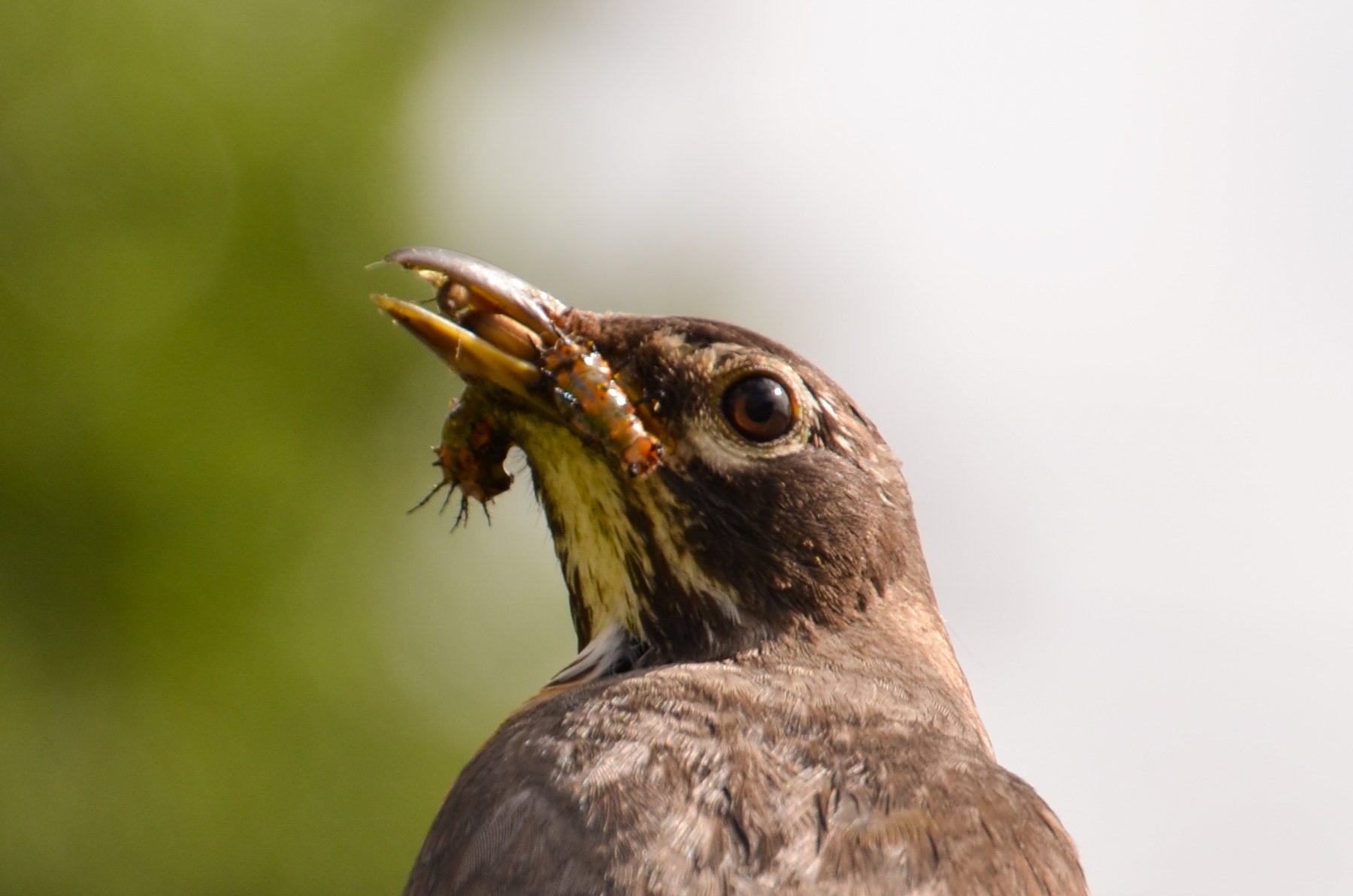
Golden-reined Digger Wasp
Despite its vivid alarm coloration, the Great Golden Digger Wasp is not an aggressive species of wasp. They tend to mind their own business and can be found sipping on flower nectar during the summer, but in the early spring, females prepare to lay eggs.
Females will dig into loose soil and create many deep tunnels. When established, she then covers them to hide their existence. A female will track a small insect and sting them to paralyze them, but not to kill them. Once the prey is immobile, she will clutch it using her antennae and mandible (mouth parts) in order to fly it back to the tunnels. While in flight with her prey, it is not uncommon to see birds like robins or tanagers attempt to steal her meal from her by chasing her until she drops it. No other known species of Digger Wasp is known to be harassed by birds in this way. If the female is successful in returning to her tunnels with her catch, she will place the paralyzed prey aside to quickly inspect a tunnel. If it looks like it's still intact, she will pull the paralyzed insect, head first, down into it. She then lays an egg on the insect, exits the tunnel, and covers it over again. She repeats this process for each tunnel. Unlike other wasps, she does not actively defend her nest. Once hatched, the wasp larvae will feed on the living, yet immobile, insect until they are developed enough to leave the tunnel lair in the summer. Eventually, the parasitism of the paralyzed insect kills it.
Scientists are studying the behavior of this unique species. Great Golden Digger Wasps seem to display a type of internal programming. If their insect prey is moved away from the tunnel while the female inspects it, she will emerge, relocate it, bring it back to the tunnel entrance and start the inspection all over again. Every female exhibited the same repetitive 'start inspection again' behavior when tested in that way.
Females have also shown that they do not keep a tally of how many insects they catch versus how many tunnels they create. If some meals are stolen by birds, they do not realize that they are short on insects compared to tunnels.
With such gorgeous orange and black coloration, mild demeanor, and interesting behaviors, the Great Golden Digger Wasp is one to admire, not destroy. Perhaps a careful observer will discover even more fascinating things about this species.
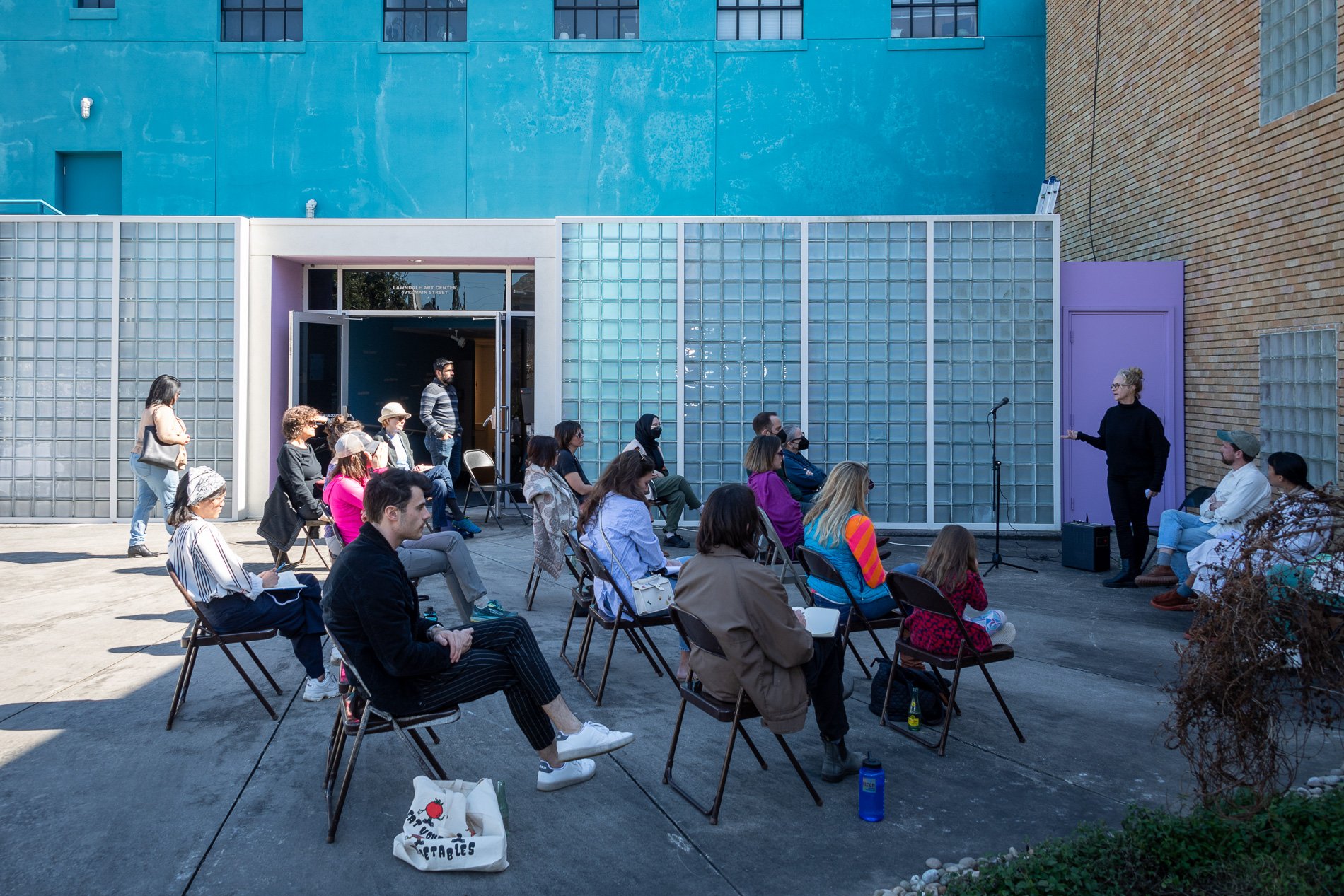
Symbiosis Celebration — Social Sculpture
Symbiosis Celebration
Social Sculpture
Proposal
By
Cindee Travis Klement
Proposed to Mayor’s Office of Cultural Affairs June 8, 2022
Fall color tourism contributes $1 billion per year to North Carolina. Houston has Fall color migration,
we can cultivate it into tourism and build soil health.
—from Chemical Plants to Native Plants—
Native Wildflowers, Food, Art and Music Festival
“If you dig deep and keep peeling the onion, artists and freelance writers are the leaders in society - the people who start to get new ideas out.” — Allan Savory
In April 2021, I installed the first native plants into Lawndale's sculpture garden. Within two months, Symbiosis exploded with bountiful native blooms. Plants expected by the Ladybird Wildflower website to be one to three feet tall in Symbiosis were instead two to four feet tall. In June, the endangered native bees started returning. In the first twelve months, I have witnessed seventy new species in the space: from bird nest fungus to Red Admirals, Monarchs and skippers, skimmers, one of the bumblebees listed as endangered, Bombus pensylvanicus, treefrogs, toads and birds.
Since Hurricane Harvey, harnessing the power of public opinion to mutualistically build Houston's landscapes into healthy ecosystems has been the focus of my art practice.
In our web meeting, I explained that in my artwork, Symbiosis, sponsored by the City's Initiative Grant at the Lawndale Art Center, I integrate holistic, regenerative biological systems into an urban landscape. I was inspired to create Symbiosis because I have read that our cities are fast-forwarding evolution. If this is true, integrating holistic, regenerative biological systems into urban landscapes will fast-forward ecological recovery. In Symbiosis, I use systems thinking to find a balance between humanity and Houston's wildlife; already, since the installation began in 2021, we are seeing a return of the lower food chain, which is critical for supporting birds and other wildlife that control the insects harmful to humans.
In the systems thinking state of mind, I also realize that profit is the fuel that will change society's landscape practices to embrace the planet's ecological systems in Houston. Applying economics and industrial concepts to the work, I propose that ecotourism is an untapped resource that can strengthen our environmental and economic health. I am writing to you with a proposal to start a wildflower festival, a Symbiosis Celebration, that ultimately encourages and celebrates new mutualistic relationships between Houstonians and the planet. Through fostering symbiotic relationships that regenerate Houston's micro-ecosystems, we will move our reputation from Chemical Plants to Native Plants — we can prosper as the Green Energy City.
STIMULUS
18” X 4.5” X 10”
$1500 in large bills and passed butterflies.
Building Mutual Symbiotic Relationships to Power Ecological Recovery
I envision this festival cultivating relationships among the City of Houston, local property owners, Houston's indigenous landscape and its wildlife, soil and climate, food, restaurant, music, visual and performing arts, museums and professional sports team communities.
The following steps will contribute to building these relationships:
· The business and private property owners will need to redirect their existing landscape budgets to native plants that support our wildlife.
· These new landscape practice guidelines will align with the Mayor's Office of Sustainability and Resilience.
· New native wildflower and grass landscapes will slow rainwater, allowing it to soak in and return to the aquifer to cool the planet while sequestering carbon and storing it in the ground where it is stable, providing food and safe habitats for our indigenous wildlife.
· The approximately six hundred species of birds, four hundred and thirty species of butterflies, eight hundred species of Texas native bees, one thousand species of moths, eighteen species of dragonflies, thirty species of turtles, including two box turtles, and seventy-two species of amphibians native to Texas will expand their populations in our city.
· Houston's creatives in the food, restaurant, music, visual and performing arts, museums and professional sports industries will respond to the new mutualistic/symbiotic relationships among Houston's landowners and our unique plant and wildlife in exciting creative ways and performances during the festival.
· The City of Houston will promote, market, and support the above-described new relationships with its services infrastructure, completing the mutualistic relationship that will support Houston's economy and ecosystems.
Why Houston Can Support Ecotourism
Although Symbiosis taught me the speed with which an urban landscape can transform into a wildlife haven, it was not until I was in Fredericksburg that I realized Houston's ecology is an untapped tourist economy. When you combine Houston's rich soil, high humidity, heat and long growing seasons with the indigenous native plant landscapes supported by Houston's urban irrigated commercial and park landscapes, Houston's native plant wildflower and wildlife tourism can far exceed those of the small towns in Central Texas. Another tremendous asset is Houston's central geographic location in the bird and butterfly migration paths between the North and South American continents and our proximity to the Gulf Coast. Texas has the most butterfly species of any state in the U.S. Houston's inner city is 600 square miles; our "sprawl" is an asset to urban ecotourism.
As additional support that Houston can be an ecotourism powerhouse, I have read that one of New York City's most popular tourist attractions is The High Line's native landscaping. In North Texas, Plano also uses wildflowers and music to attract tourism dollars.
Funding
I see businesses and organizations all over the city which are starting to take advantage of the ecological benefits of native landscapes. Unfortunately, many other property (business and home) owners are unaware of the economic and environmental benefits of native plant landscaping. They spend $50-$100 per hour for weekly maintenance and $4—$12 per square foot for seasonal plantings, while also incurring high water usage and bills. Suppose the City appeals to these businesses and individuals to convert their existing non-ecological landscape budgets to native wildflower and grass landscapes. In that case, the City can promote a native plant/wildflower and wildlife, food, arts and music festival that will symbiotically support native ecological systems. The supporting businesses can profit from the tourism they generate.
When
With Houston projected to double in size by 2050, if we start now, benefits will compound. The timing of the festival should fall during one of the migration periods.
The Texas Can-Do Spirit
Systems thinking to mitigate climate through industry and the arts is a new territory — will Houstonians embrace this new field of thinking? In Texas, that depends on how you ask and present the need. In our recent history, from Katrina to hurricane Harvey, unsolicited Houstonians volunteered to help their neighbors. In 1901, wildcatters discovered Spindletop, drawing people worldwide to build a better life in unknown territory. “Wildcatter” is used to describe one that drills wells in areas not known to be producing fields. The spirit of the wildcatter is deep in our Texas Can-Do Spirit. It is in our nature to embrace a new field of wild.
The Next Step
Recently I went to a free event at the Ion; the people giving the talk are in the business of researching the economics to support new business ideas. They also create "stacks" or PowerPoint presentations to gain financial support for new ideas. Their fee is $6,000. Unfortunately, it is beyond my budget.
Is this sort of analysis provided by the Mayor’s Office of Cultural Affairs or another City of Houston office to determine the new cultural or social events that would benefit our city?
The support of the Mayor’s Office of Cultural Affairs is critical for social sculpture to transform the city from Chemical Plants to Native plants and earn the title of The Green Energy City.
The white pedestal?
When I started in the MFAH Glassell School block program, I needed pedestals for my smaller sculptures. I made stark white cubes as I saw in museums and galleries.
Over the years, my work has transitioned to tell a specific story. I make work to reveal the beauty in diversity, the messiness in the natural world and the connections between all living things on the planet. And most importantly, I work to inspire society to step into a rhythm that will flow with the natural world and celebrate the beauty in its messiness. My work conflicts with borders that separate, clean lines that divide and sterile objects.
The white cube pedestals are a symptom of sameness, monocultures and sterile environments, a symptom of me wanting to ” look “ like I belong and fit in. A change is an imminent.
I am leting my eyes and mind play with how objects that physically support my work should look. Work that reimagines urban landscapes to balance humanity and natural systems should not be sterile cubes. What should, - what could they be?
The images below are some thoughts I am considering. .
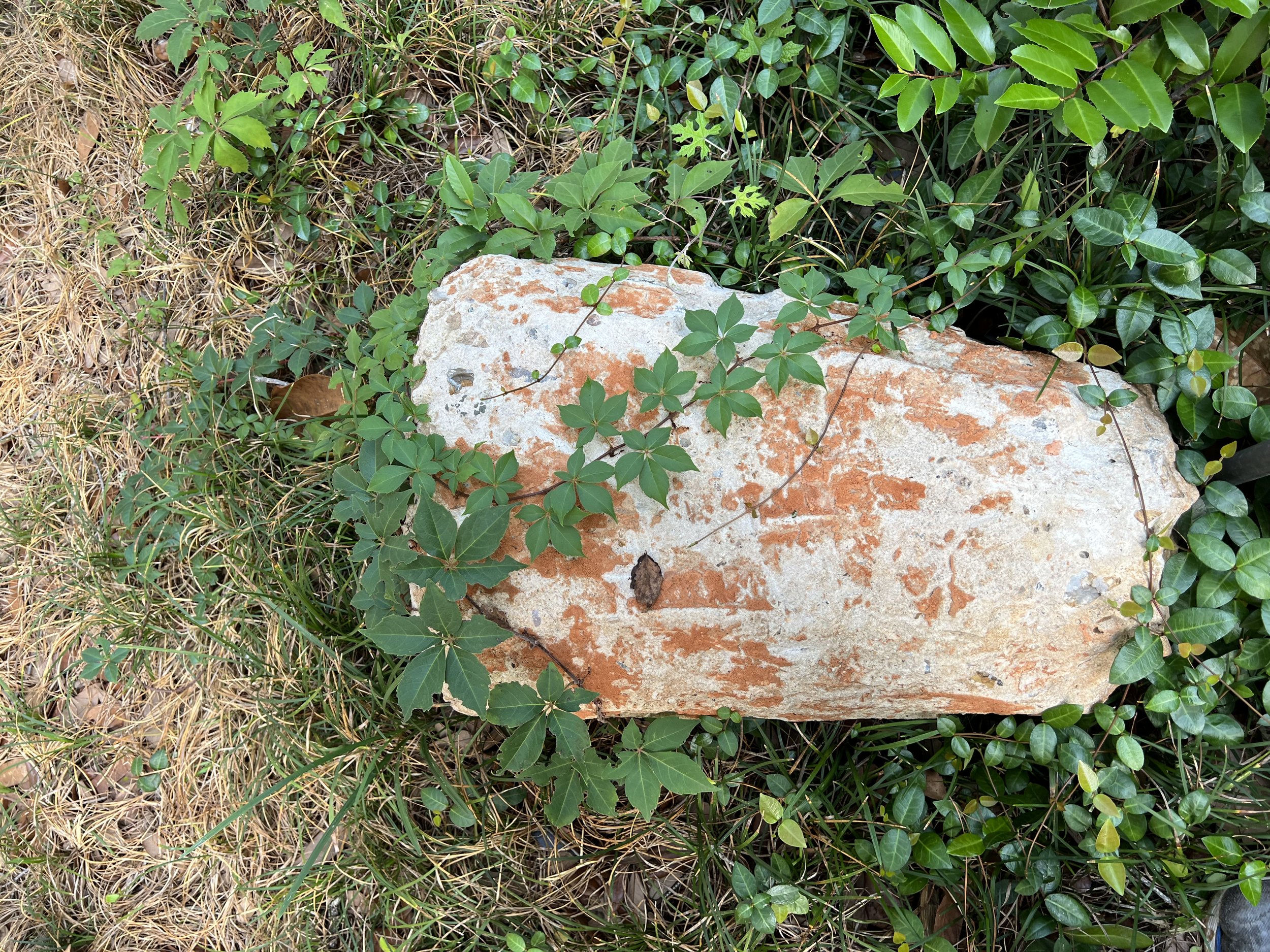
Rocks
Bricks
Stones or concrete.
Cracks
Dried plant material
Electrical wire
Upcycled lawn furniture.
Palm tree trunk skin
Salvaged construction site rotting root with interesting chain link necklace imbedded across her shoulders.
Ragweed
Why we shouldn’t rag on ragweed? The seeds of ragweed are rich in fatty oils. Fats are not only Ebut also is for fattening up birds and small mammals such as Eastern Cottontail, Meadow Vole, grasshoppers which eat the leaves, Dark-eyed Junco, Brown-headed Cowbird, Northern Bobwhite, Purple Finch, Mourning Dove, American Goldfinch, and the Red-bellied Woodpeckers to get them through the lean winter months.
It is an ancient grain for humans and ragweed is a valuable food source for the caterpillars of many butterflies and moths including the striking wavy-lined emerald and the uniquely adapted bird dropping moths. The seeds of ragweed are rich in fatty oils. Birds and small mammals readily consume ragweed seeds to help fatten up for the lean months to come.
Endangered Knowledge: The Soul of Humus — The Bison in the Texaco Star
The Bison in the Texaco Star
The third pasture/exhibition
As in agriculture that rejuvenates the soil, the bison has rotated to its third pasture/exhibition. It began in a historic grain silo/art venue in Sculpture Month Houston's Altamira, which considered modern caveman's materials and message to the future, followed by the Blue Norther exhibit, where the bison addressed extreme weather's connection to soil. Now it brings its message to the Houston Forever exhibition in the former Texaco Building in downtown Houston.
The Star building, former home of Texaco, the company that developed the Spindletop gusher in 1901 and took the US into the oil age, is a key location in the sculpture's rotation. The bison in the Star embodies our civilization's conflict "between" ecology and commerce. Before Spindletop, oil was primarily used for lighting and as a lubricant. With Spindletop's abundance, Texaco began marketing petroleum for mass consumption. What can we learn about natural carbon cycling through the soil from the herd's eating and waste habits — also called consumption and regeneration — contrasted with the development of the energy industry and our society's mass consumption without individual responsibility for regeneration? Comparing and contrasting these two energy sources, both receive energy from the earth: one where each consumer returns carbon to the soil and the other supplying a chain of energy but still trying to figure out how to repay its debt of carbon for future generations. Integrating natural systems of regeneration can steer our innovation and creative minds to a future in which consumption, conservation and regeneration of earth's resources are in balance.
Rosinweed sunflower bloom and spider.
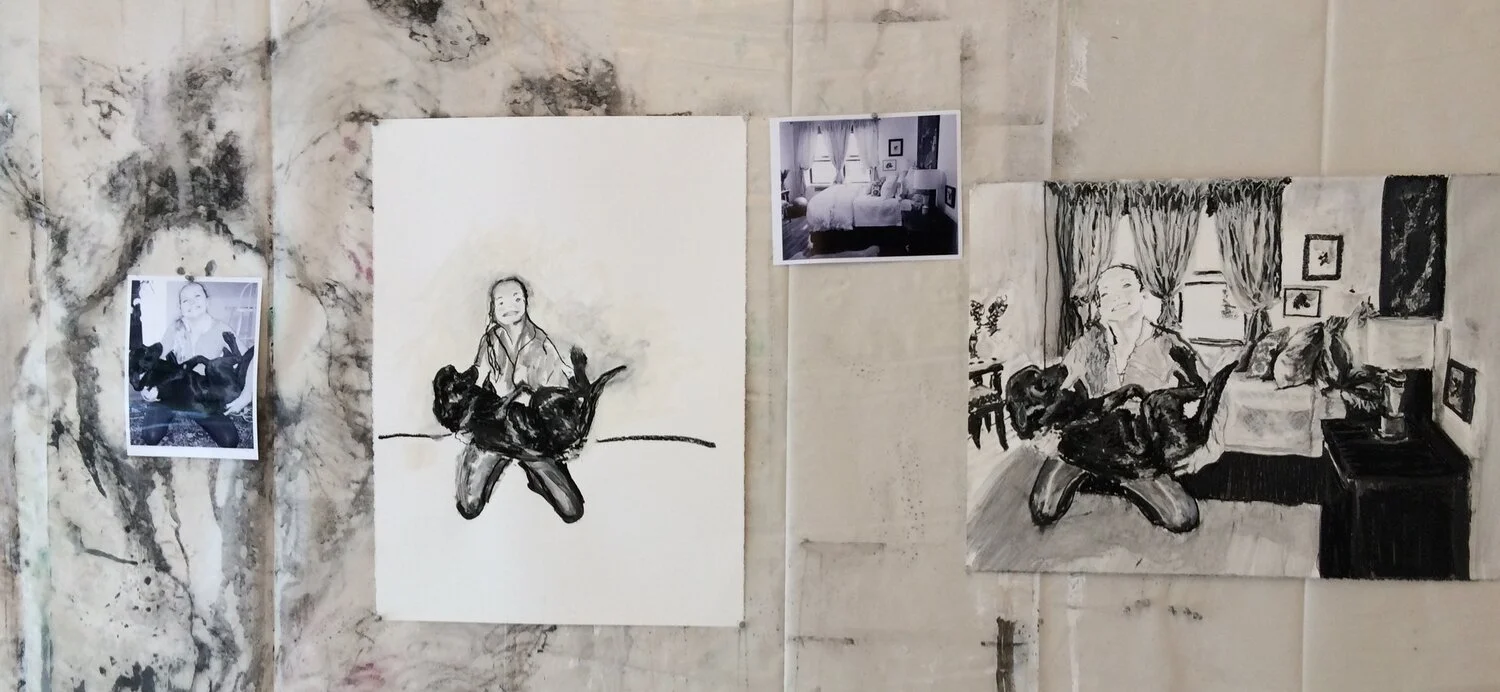
Tiny spent sunflower bloom/seed head-the colors - suttle and faded, still rich and deep. The shapes of the seeds as they dried ❤️ The beauty of the natural world when you stop and look. I studied this dried object probably 4 minutes turning it in my fingers watching the white blooms from the crepe myrtle attached by the thread of a spider and then turning it over hiding underneath- a creature. As we enter the Anthropocene, saving insects is a priority in “Symbiosis.” When I edit out any materials such as this elegant, delicate, dried Rosinweed sunflower head from the garden, I do not bag them and put them in a trash can. I chop and drop. This tiny spider is evidence that chopping and dropping not only builds soil and saves money it also saves insects.
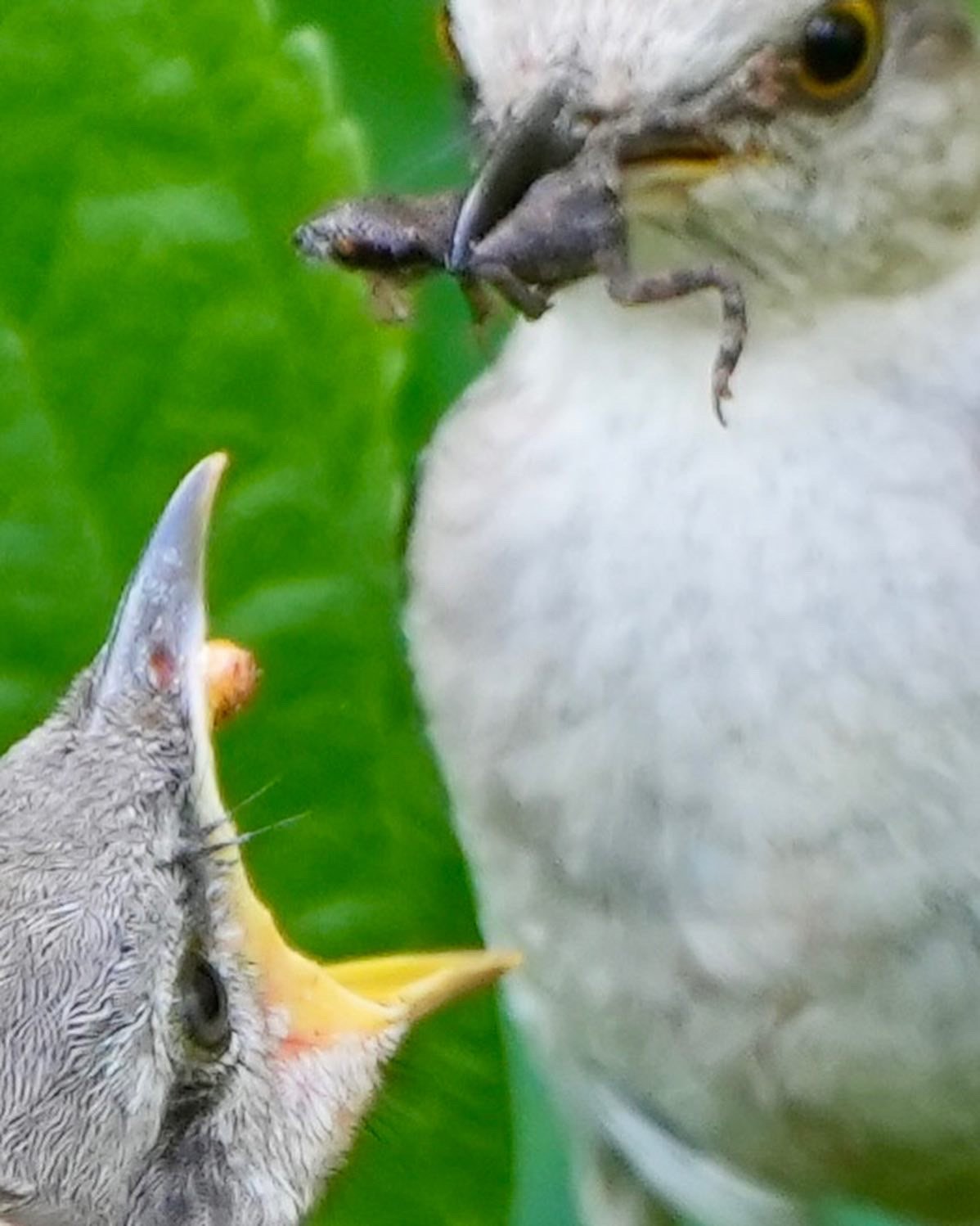
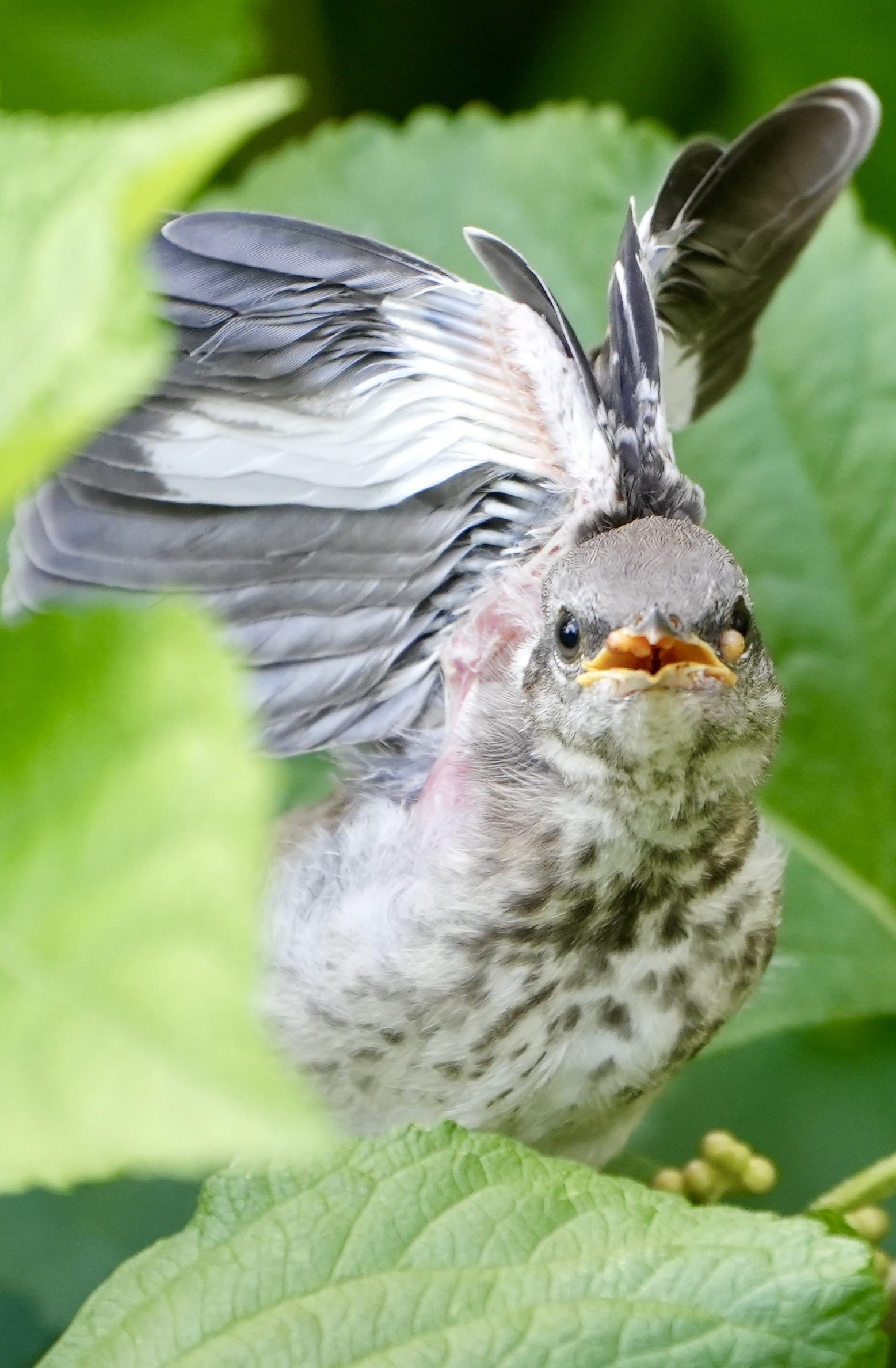
Symbiosis- Food chain - Mockingbirds and Toads
On an early July morning, with a new camera in my hands, I was hopeful the zoom lens would document unseen details in Symbiosis. I focused the lens on the “feed me” gesture of the juvenile bird. Later zooming in on the image on my computer revealed the middle of the food chain — A Mockingbird feeding a juvenile, not a caterpillar, wasp, or an insect but a slight blurry silhouette of a toad. On my laptop, I witnessed the middle of the food chain, a moment in a living sculpture, evidence of a healthy ecosystem and hope in a sea of asphalt on the Gulf Coast.
In Symbiosis building, a food chain that has not been exposed to chemicals or pesticides is crucial to building a base and armature that supports the more visible kinetic elements — wildlife and humans, the upper food chain. Its strength is critical to the success of the whole.
I use systems thinking to plan and organize my sculptural additions and extractions to the piece. In this case, not using pesticides to control insect pests or unruly vegetation is a priority. The water feature in the garden invites mosquitos, dragonflies, frogs, toads, and aquatic insects to lay their eggs in the still water. The tadpoles, nymphs, and Texas mosquito fish eat the mosquito larvae.
In the work, all of the individual species are linked by the health and abundance of the lower species. “Symbiosis” is an element of the “living” Earth, a community of organisms existing within the Art center's sculpture garden and social sculpture.
That Was Then This is Now.
July 2020 - the sculpture garden as it was when Stephanie and I first discussed the project.
February 2021. After the Texas freeze
May 2022 - 12 months from installation.
I ❤️Aphids and what insects tell us.
I Leave aphids be. It may look alarming but It is a necessary step in regaining a balance of good bugs and bad in "Symbiosis". I am looking forward to see which beneficial insects show up to help the planet manage the aphids. Aphids feed through a needle-like mouthpart. After they insert their mouthpart into a plant's tissue, they then use it like a straw to suck out plant juices. The do not kill the host plant. Aphids aid benefical bugs they are food for thousands of different species of predatory insects. As protein Aphids help build a broad diversity of beneficial bugs in nature.
After writing this post I came across one of the most interesting insect control articles.
We have so much to unlearn.
Land Art vs Living Sculpture
Land art or earth art has paved the way for what I hope will become a new art movement.
The Tate defines Land art or earth art as the art made directly in the landscape, sculpting the land itself into earthworks or making structures in the landscape using natural materials such as rocks or twigs. With the Tate's definitions, Symbiosis is land art, a part of the conceptual art movement, and environmental art.
What separates Symbiosis from these traditional classifications of art are the concepts I apply to my creative decision-making process and the materials I use support and regenerate life. It values all living creatures as participants in the creative process.
My process for creating a living sculpture involves holistic decision-making. First, I incorporate a systems thinking approach to create a functional balance between the healthy ecosystem, human economics and societal landscape norms. For example, contemporary landscape designs are structured in monocrop rows or groupings separated with bare earth. To maintain the manicured design, weed-killing chemicals and gas-operated mowers and edgers are the most economical. This lack of plant diversity, geometric-in-shape groomed plantings, and chemical inputs make these landscapes uninhabitable for a diversity of wildlife other than a few lizards. For many valuable insects and microorganisms, the inputs are deadly. These designs do not consider supporting the food chain necessary in a healthy ecosystem. In Symbiosis, I keep the ground covered with a diversity of plantings that drift in and out of each other and with the seasons; this provides camouflage from predators, nesting materials, and a variety of nourishment all year. Weeds fit into this landscape and help build the microorganisms and structure or armature in the soil. This less structured planting design is balanced with a classical symmetrical layout. Symbiosis is designed to build the food chain. The maintenance required is easily accomplished with handheld clippers. The clippings are put back into the garden to decompose by insects and natural systems that build the soil health and retain water and carbon, or into a vase to be enjoyed. Ultimately Lawndale benefits economically through lower maintenance, chemical inputs, and utility costs, while enjoying a toxin-free environment—living sculpture.
I use materials that support plants and wildlife specific to the site's ecological history. I begin with a water source, animal waste and decaying plant materials native to the area. These materials build habitat and nourishment for microorganisms in the soil, in the water feature and up the food chain to sustain each other in extreme Texas weather. When combined with our clay soil they: store carbon, cool and return water to the aquifer, support life beneficial to humans and keep harmful pests at bay. In addition, they assist in cleaning the air, slowing rainwater, and reducing land erosion.
For example, I have created symbiotic relationships between humans, mosquitos, dragonflies, fish, and chemical-free water. In a hot environment, animals need a freshwater source to drink and reproduce. I installed a small pond without a filter or pump. Using plants to filter the water, I utilize the eating and waste habits of the Texas Mosquitofish to control the algae and build the water's biology. Mosquitos and dragonflies are attracted to still water with a balance of healthy bacteria and algae to deposit their larvae. The larvae become protein for the fish. Attracted by the water source, the dragonflies hover above the garden and on dried plant materials hunting mosquitos, supporting human health. Lawndale benefits economically by not utilizing an electric pump, needing a mosquito misting machine or pesticides and enjoys the beauty of the water feature and a kinetic, ephemeral rainbow of dragonflies hovering and darting over the living sculpture.
In Symbiosis, as the lower food chains develop, it begins to regenerate life and recover what is lost. Perpetual, it is art for now and future generations. In a living sculpture, the ways to evaluate it are space, shape, line, color, texture and regeneration.
I submit below images and descriptions of symbiotic relationships, ephemeral parts of the installation from April 2021-April 2022.
Dung loving birds nest fungus
Gulf Fritillary butterfly on rosin weed sunflower. It roots can extend 16’.
image by Nash Baker courtesy of Lawndale Art Center
Black Swallowtail (Papilio polyxenes) on Monarda citriodora lemon beebalm image by Nash Baker courtesy of Lawndale Art Center.
Gulf fritillary butterfly on Gulf verain Verbena xutha image by Nash Baker courtesy of Lawndale Art Center
Battus philenor a pipevine swallowtail
Gulf fritillary on Rudkeckia hirta
Long-tailed skipper Urbanus proteus on Salvia azure
Junonia coenia the common buckeye butterfly on a blanket flower Gaillardia puchella with dew drops.
Black Swallowtail (Papilio polyxenes) on scarlet sage Salvia coccinea.
Gulf Fritillary butterfly on purple cone flower
Red arrow Rhodothemis lieftincki on dead olive tree limb.
Mosquito control and water source for winged species.
Past bushy blue stem and Seaside Golden rod. I leave them through March so the winds can spread their seeds to other gardens, and to provide shelter for birds, tree frogs, toads, and field mice.
Plathemis Whitetail Skimmer
Mosquito control and water source for winged species.
Past bushy blue stem and Seaside Golden rod. I leave them through March so the winds can spread their seeds to other gardens, and to provide shelter for birds, tree frogs, toads, and field mice.
Brown skipper and Rudbeckia hirta
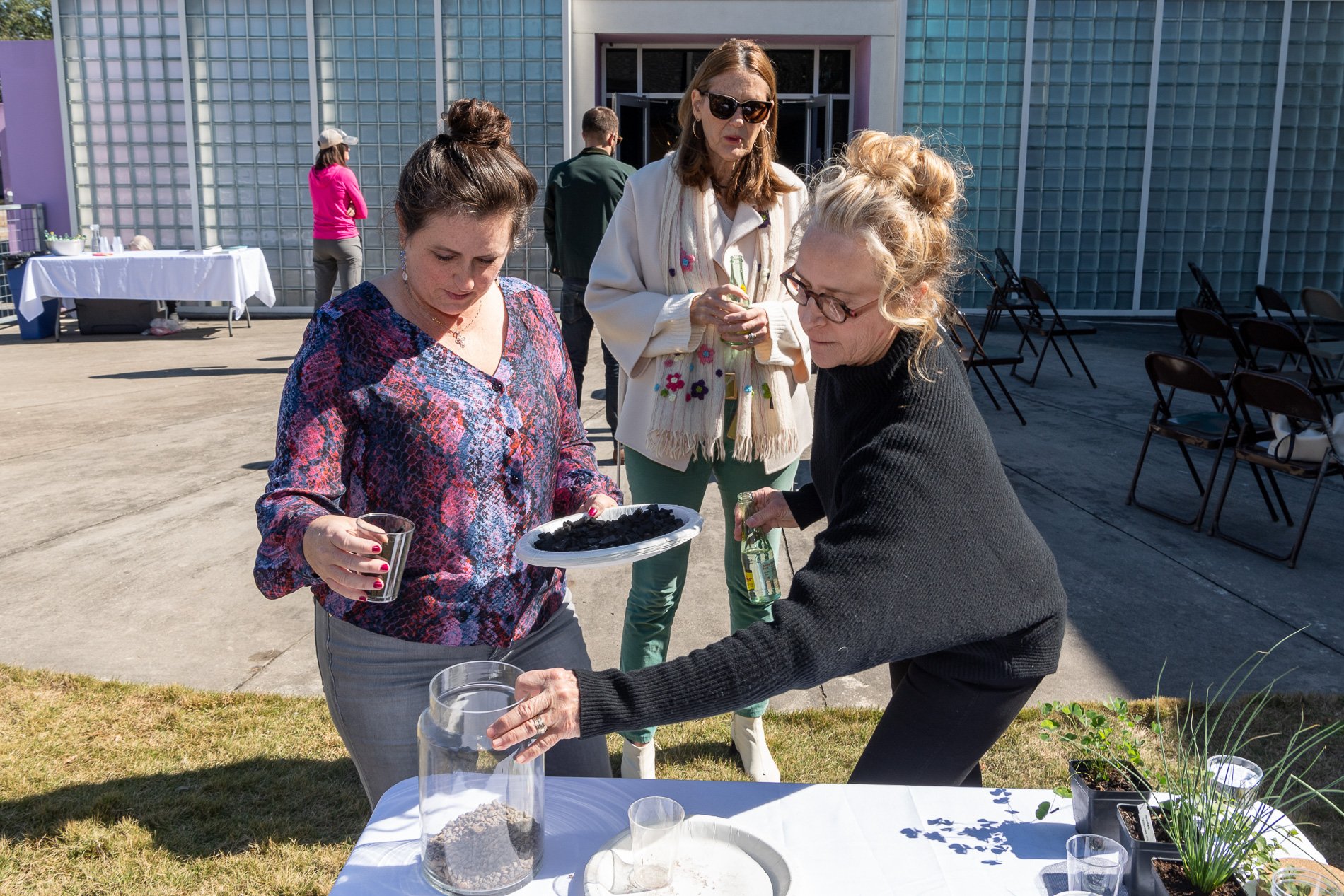
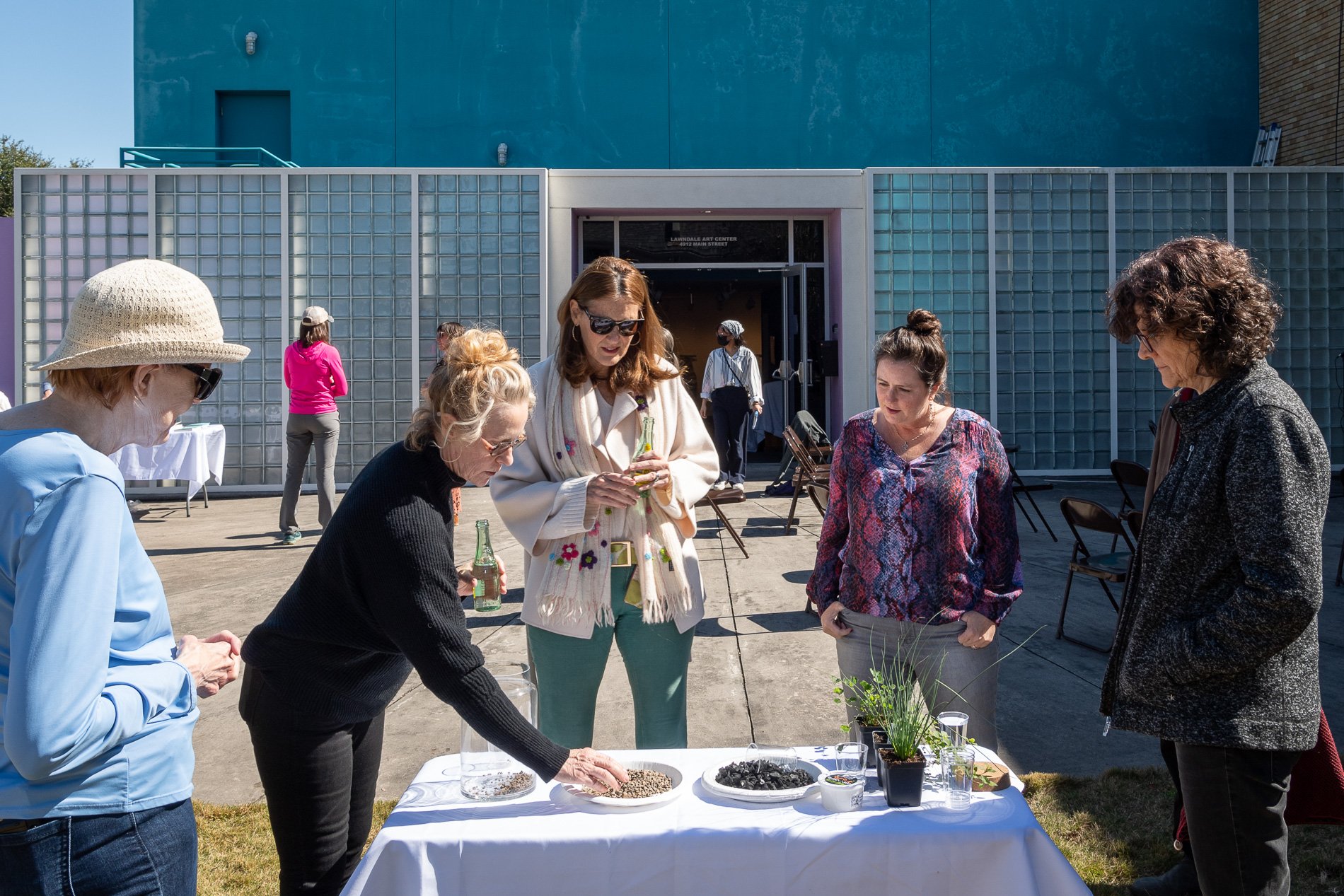
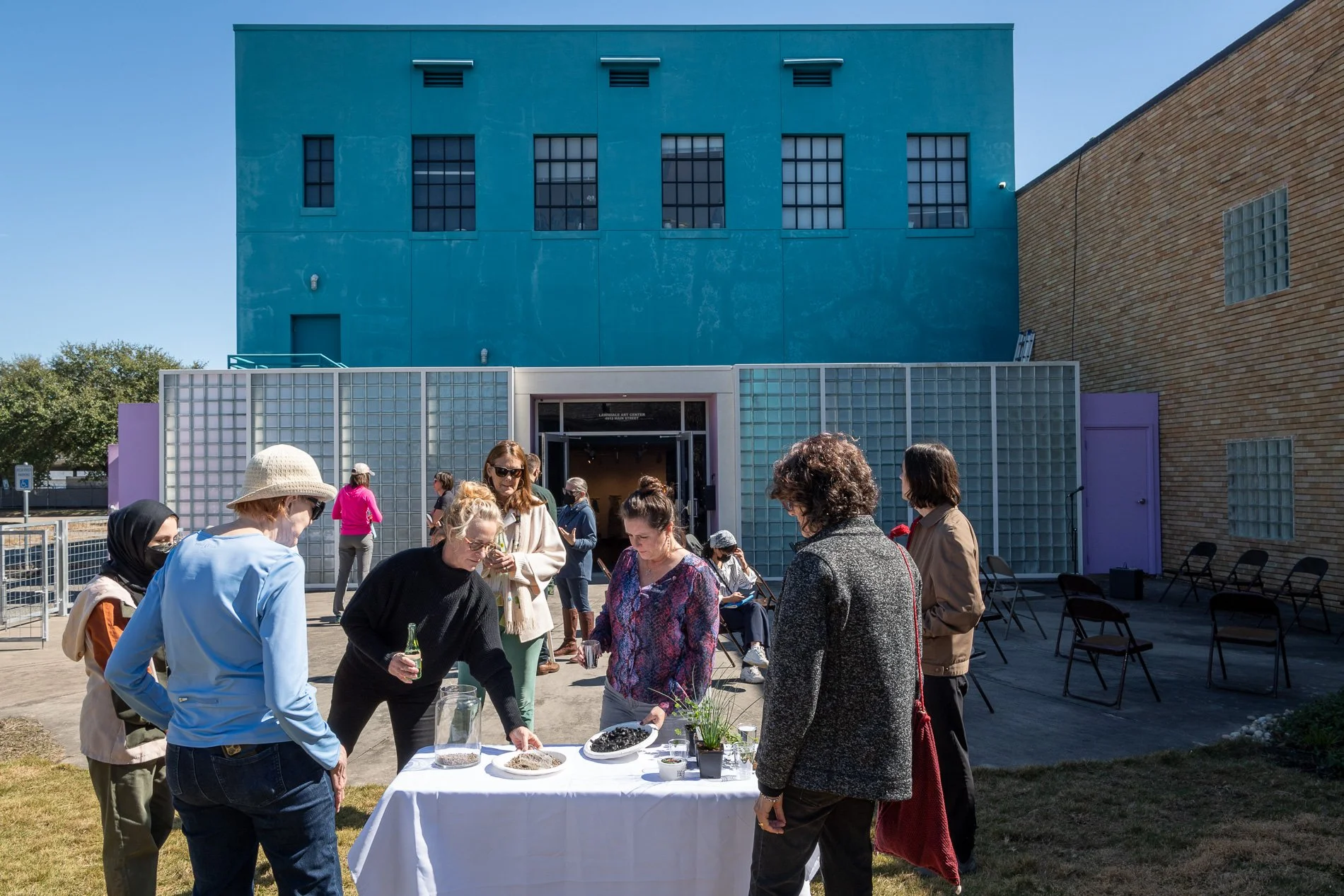
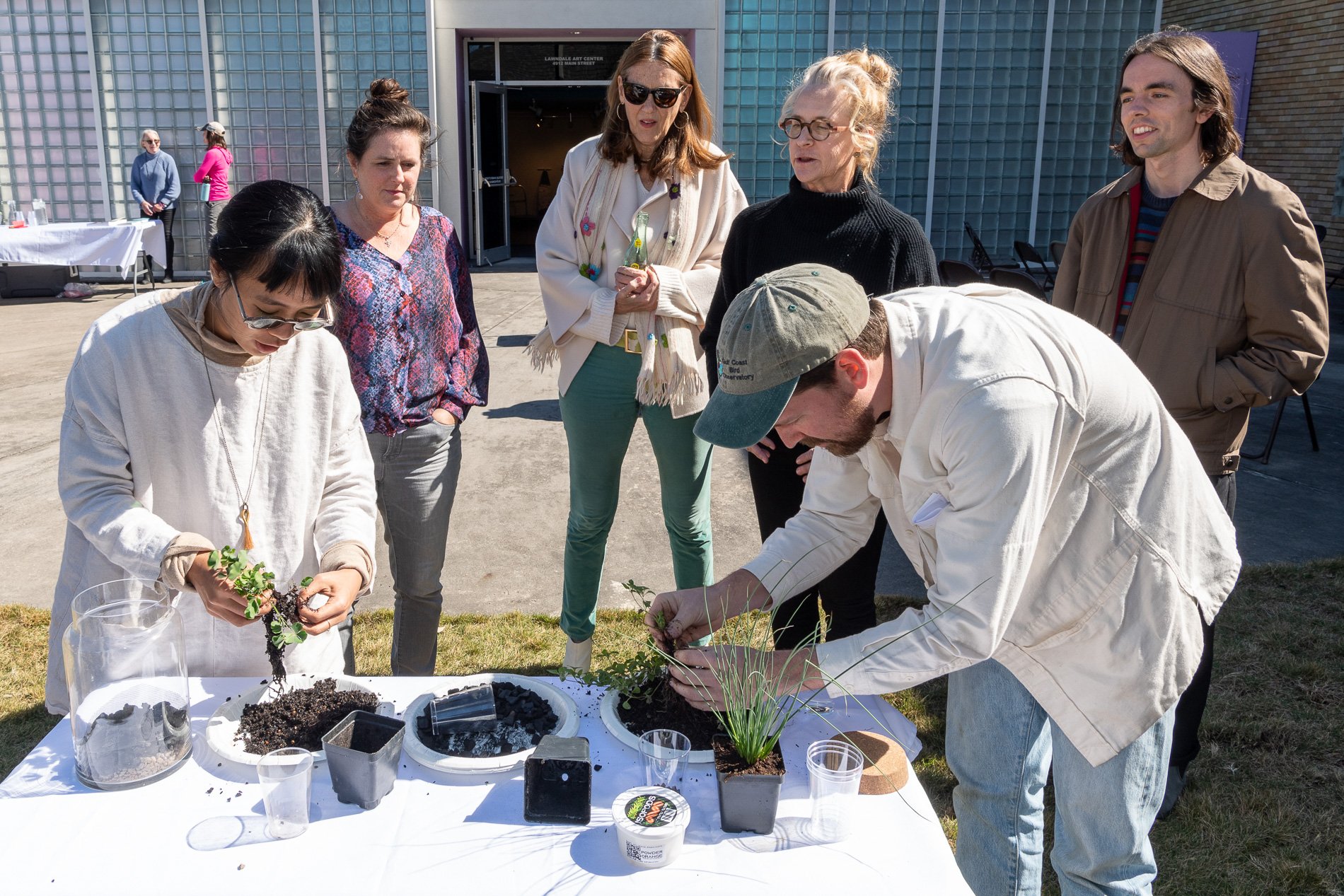
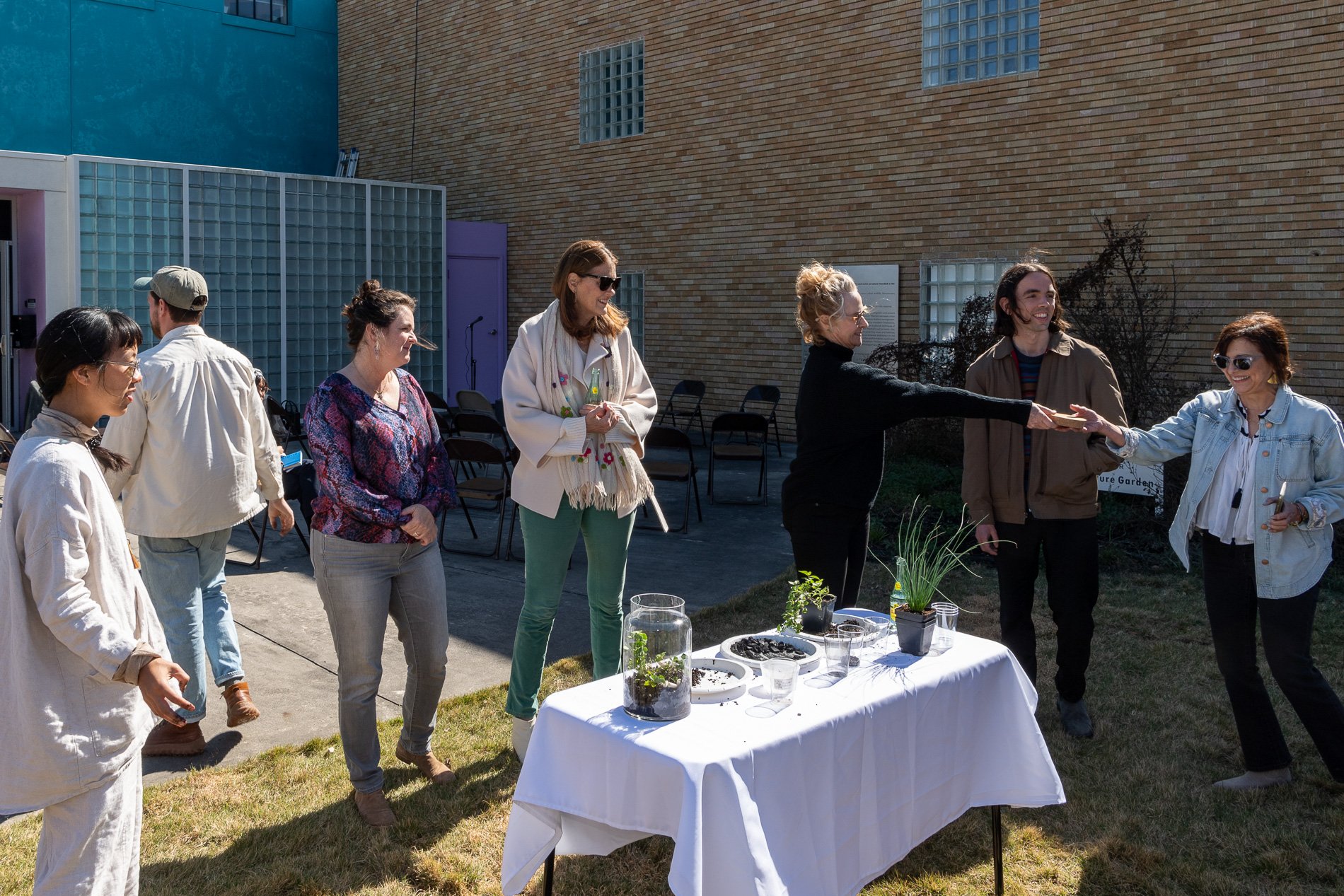
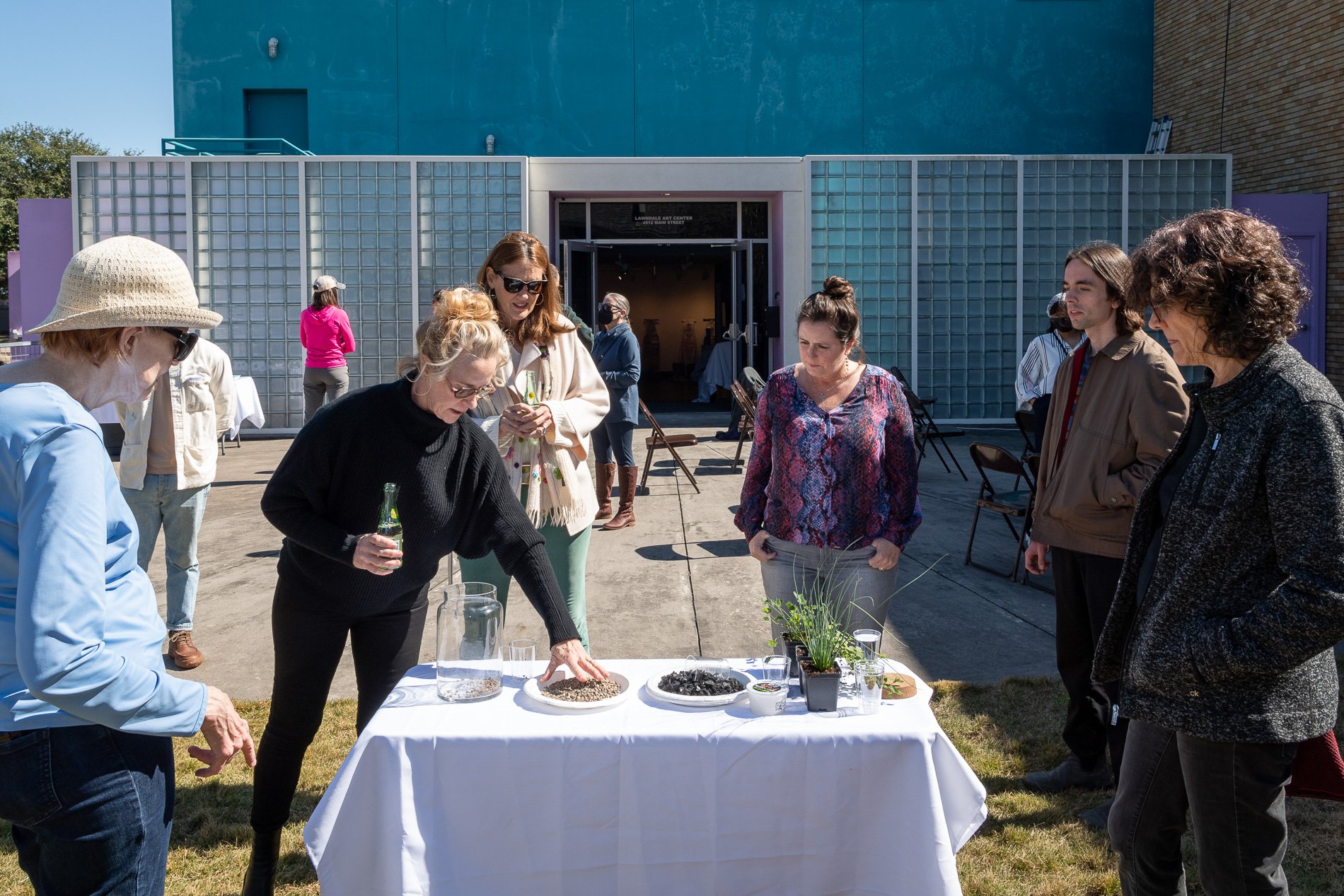
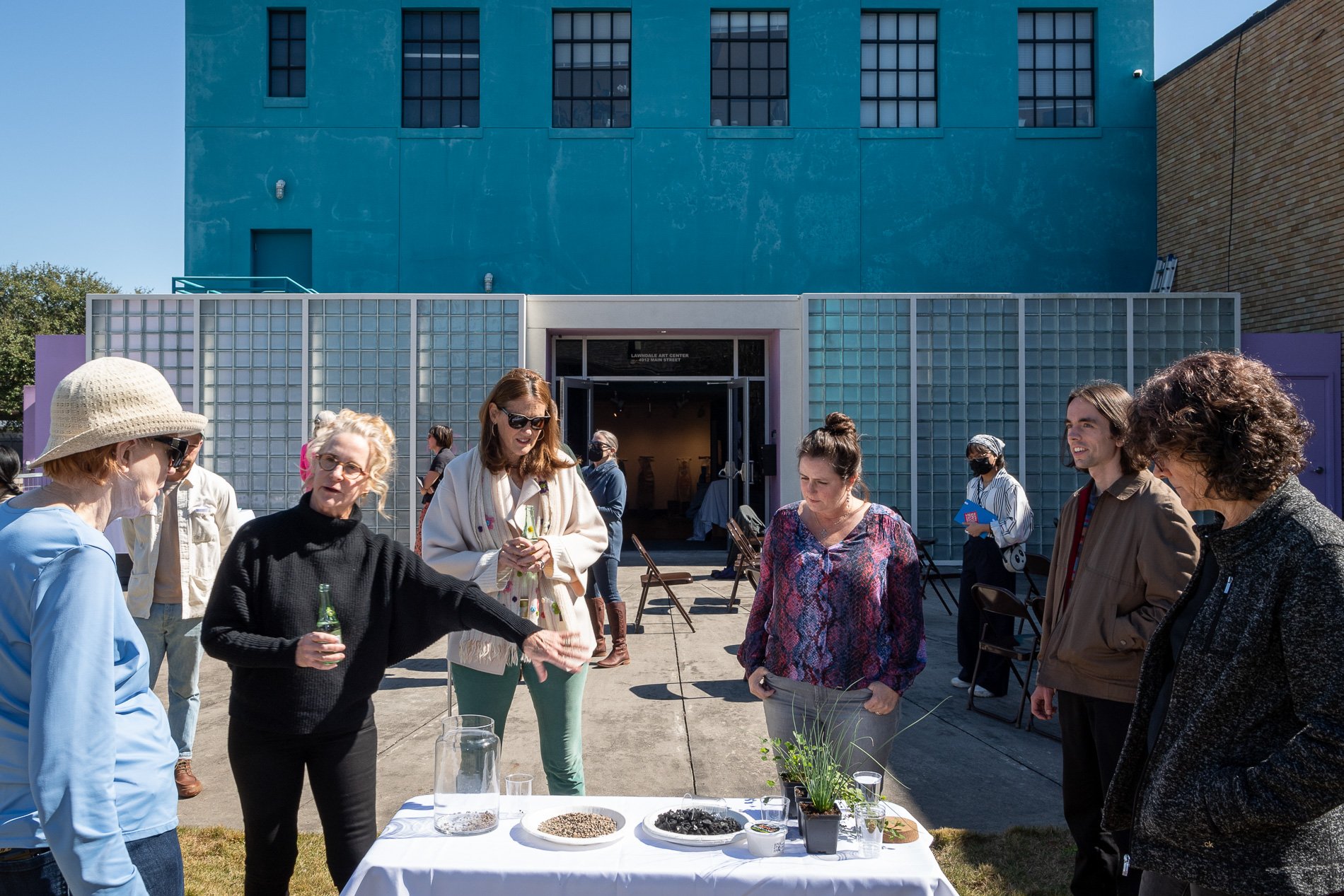
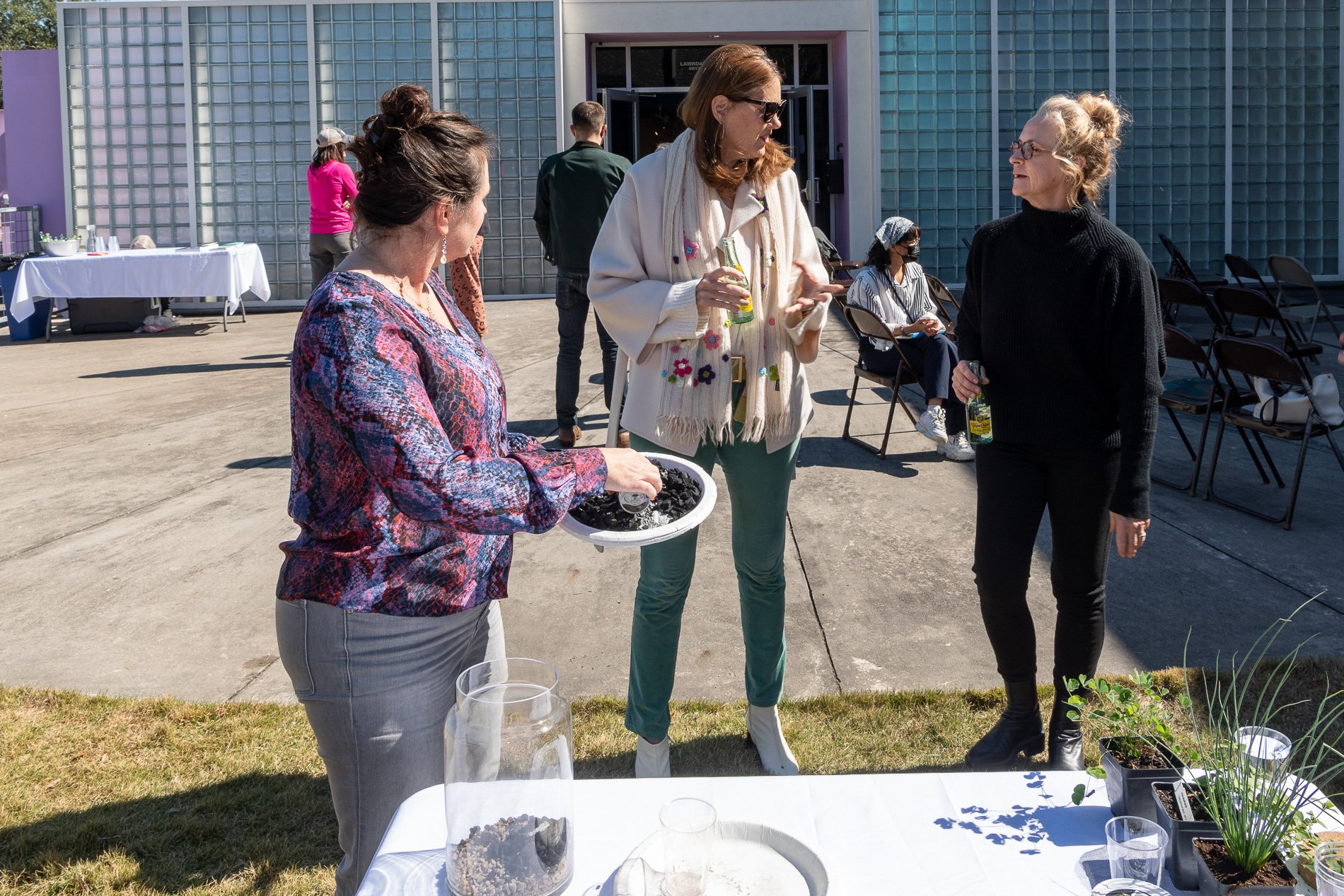
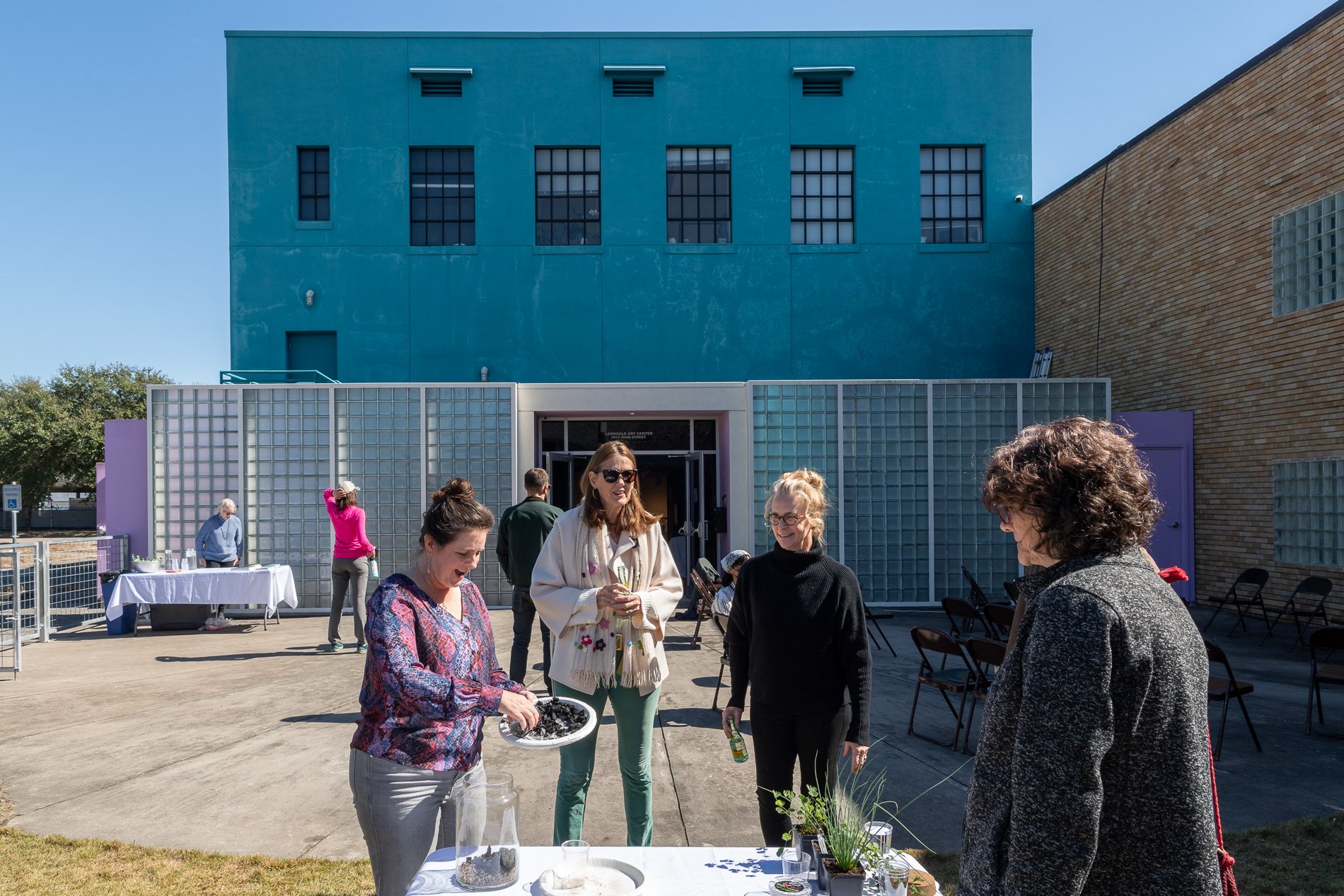
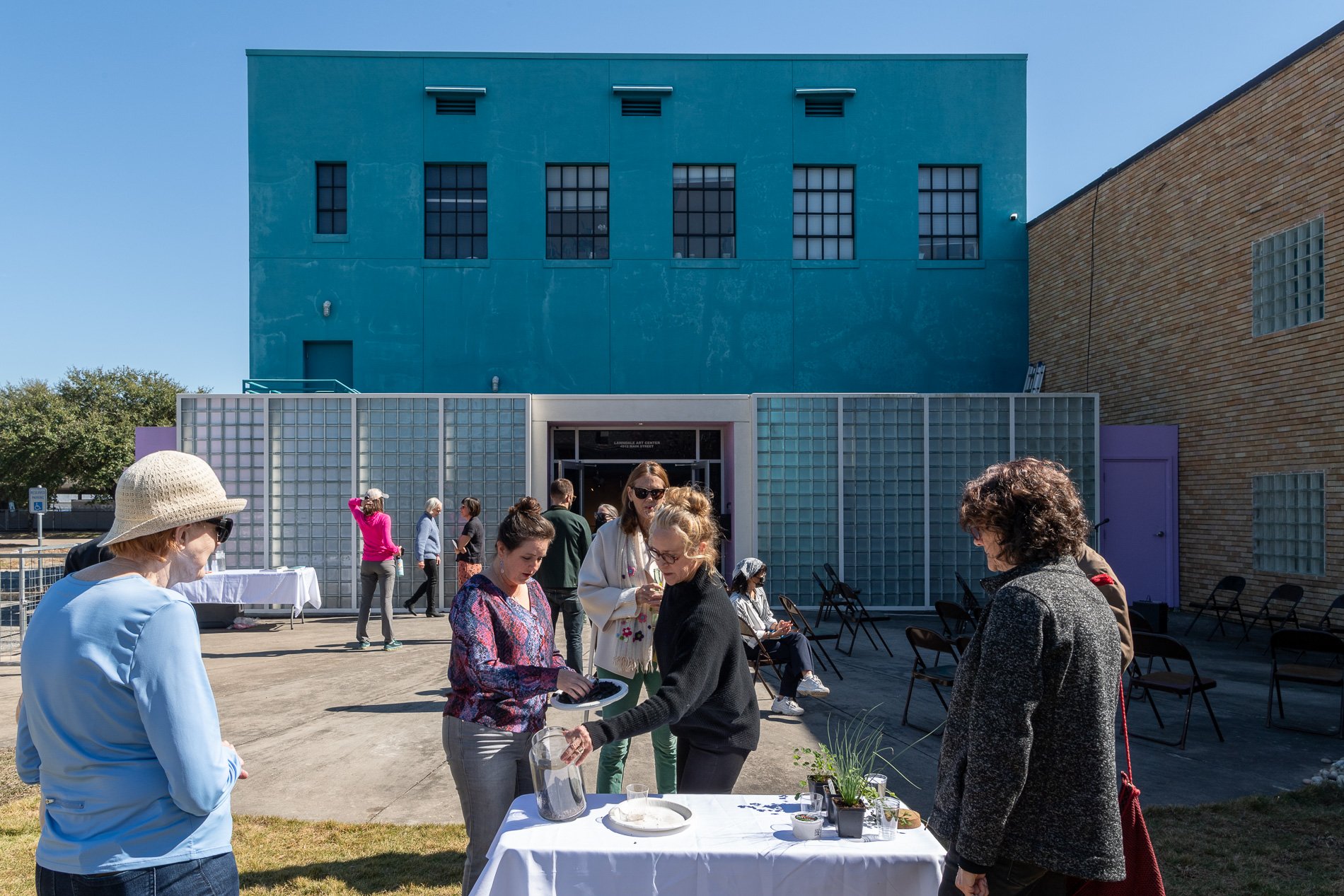
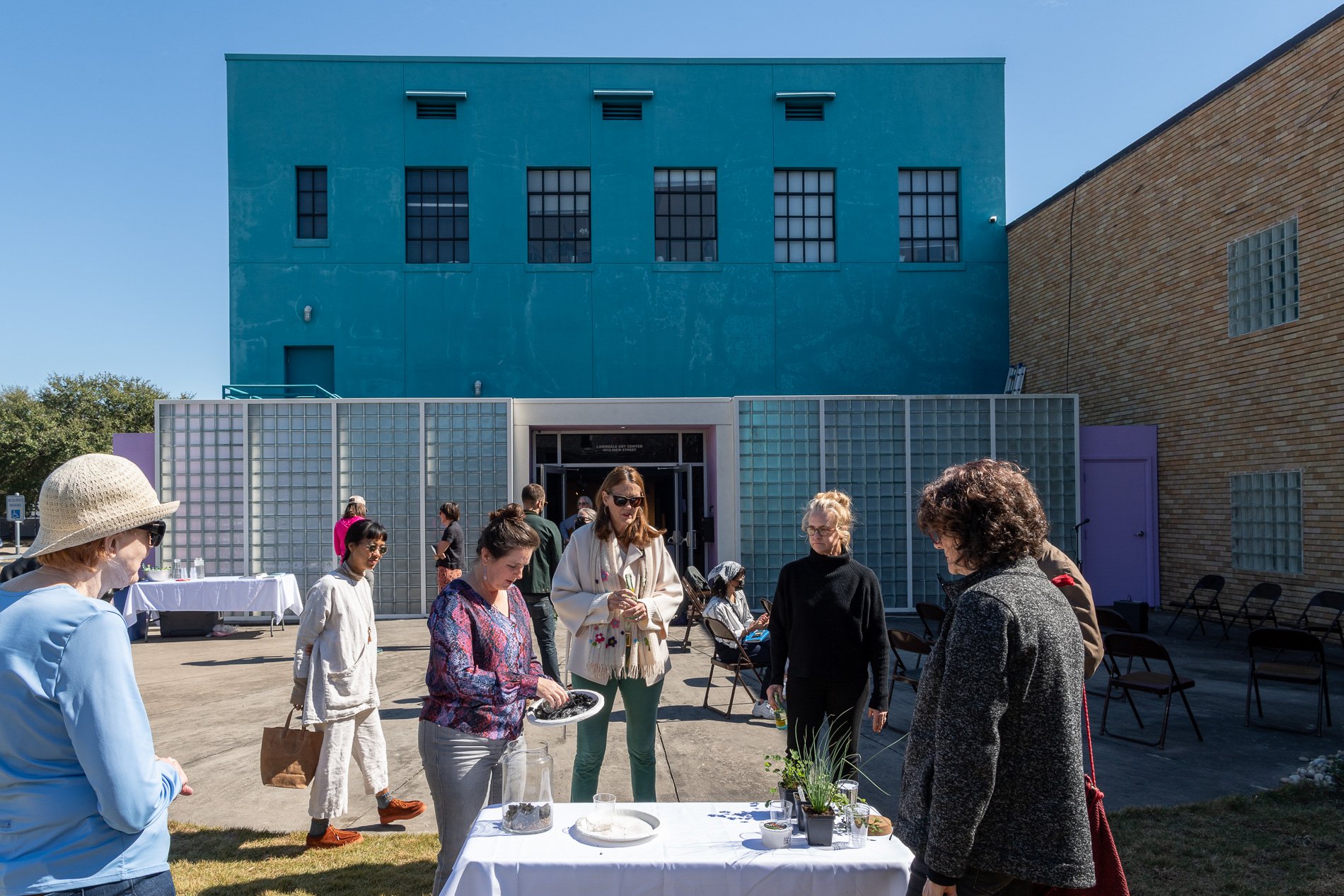
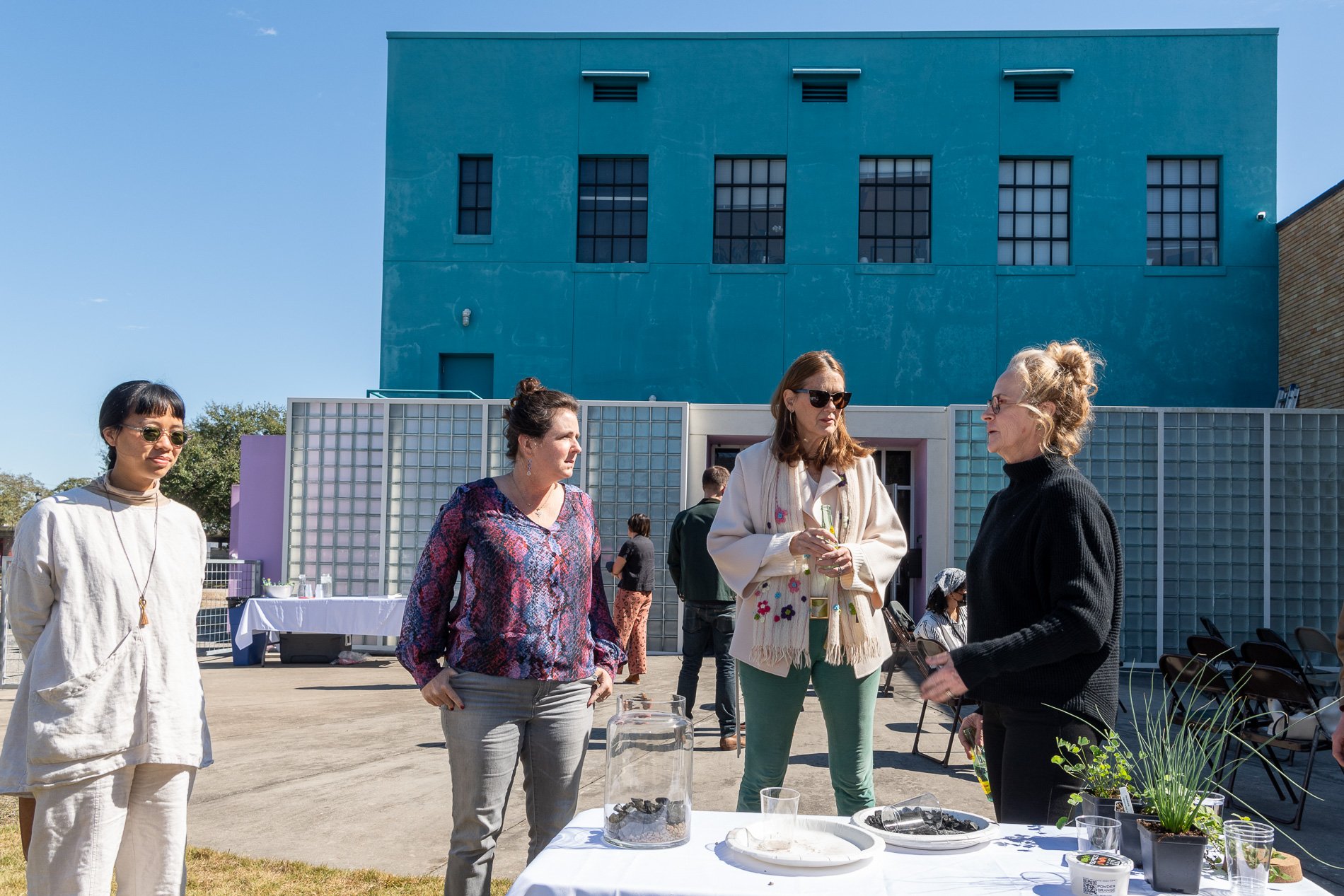
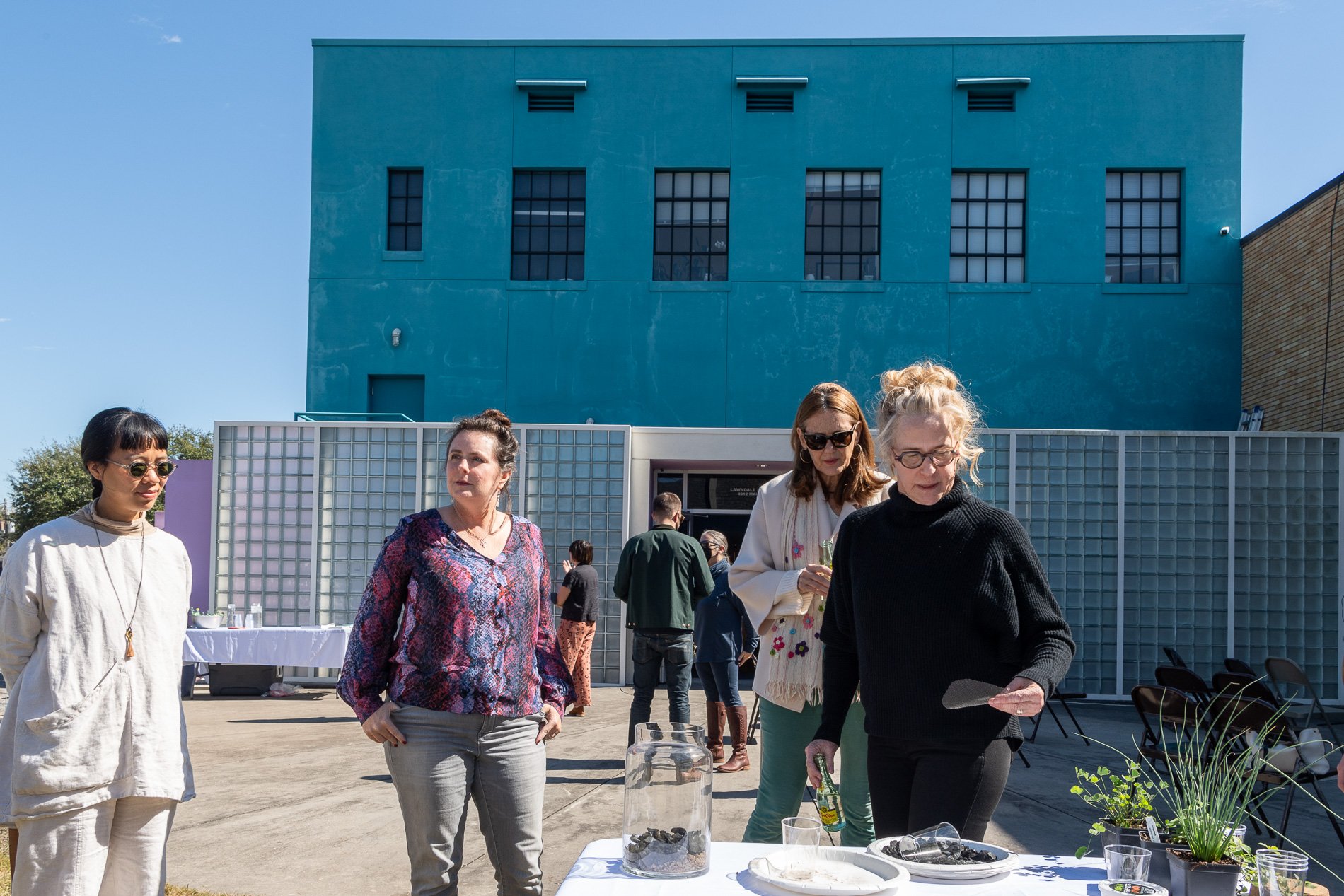
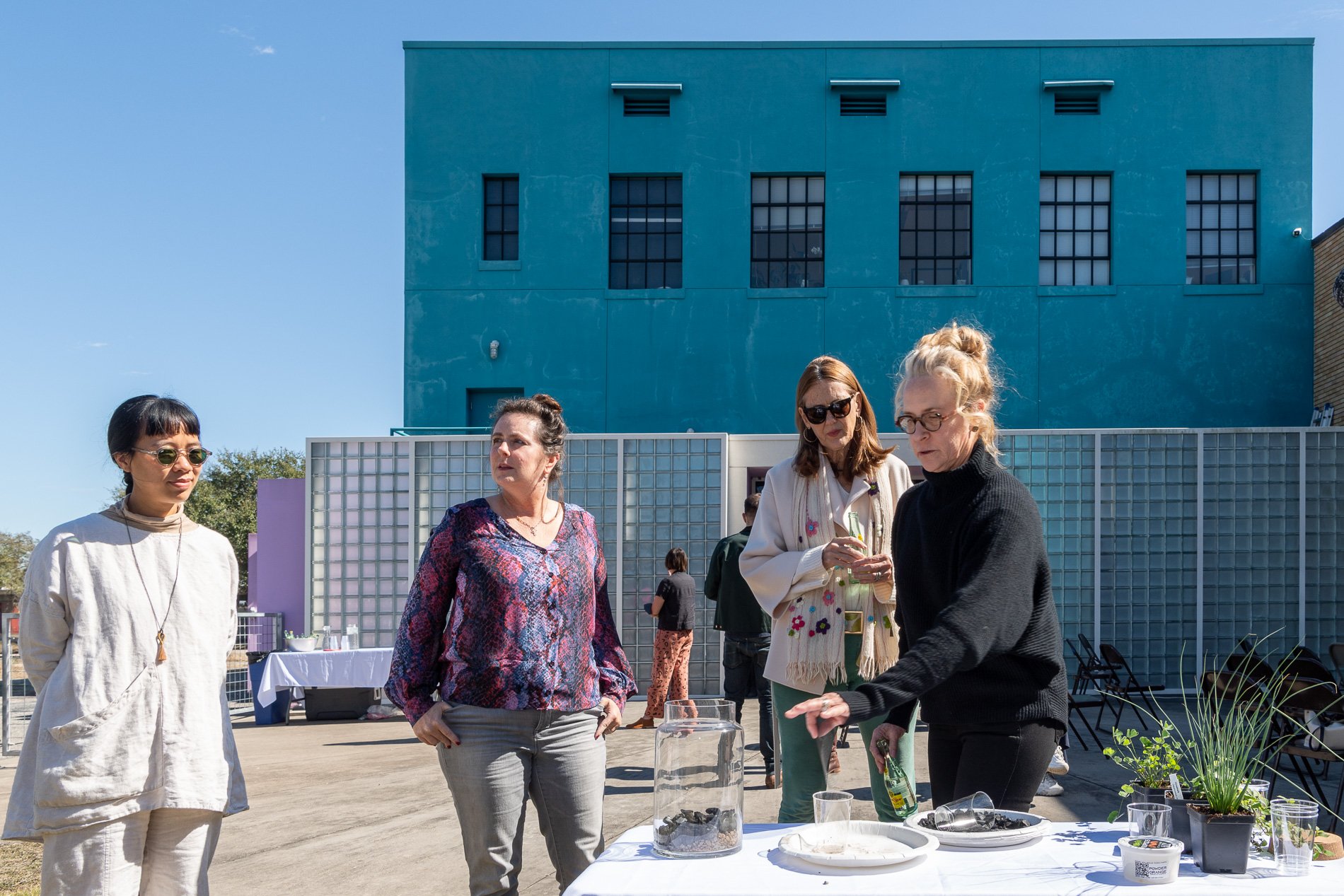
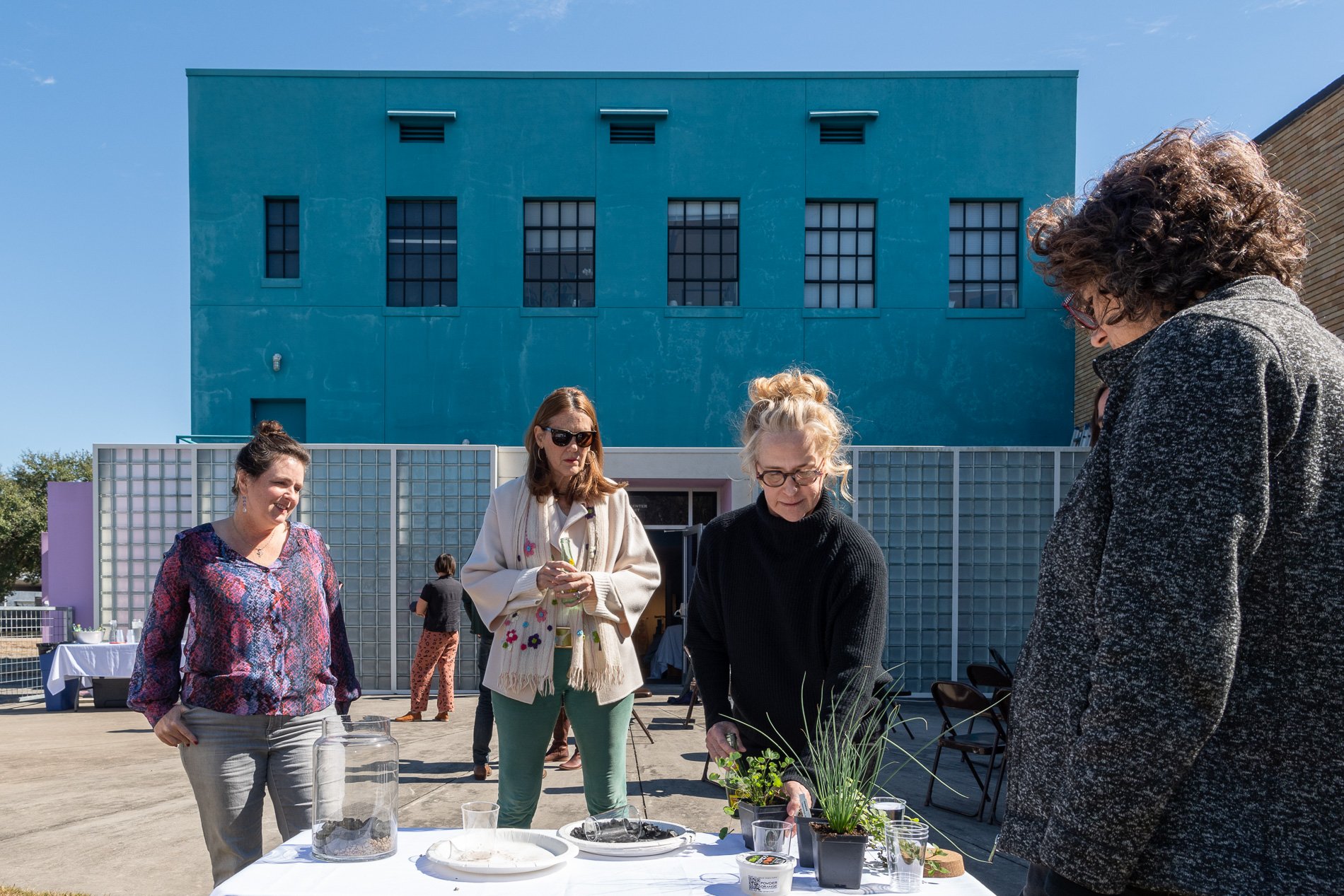
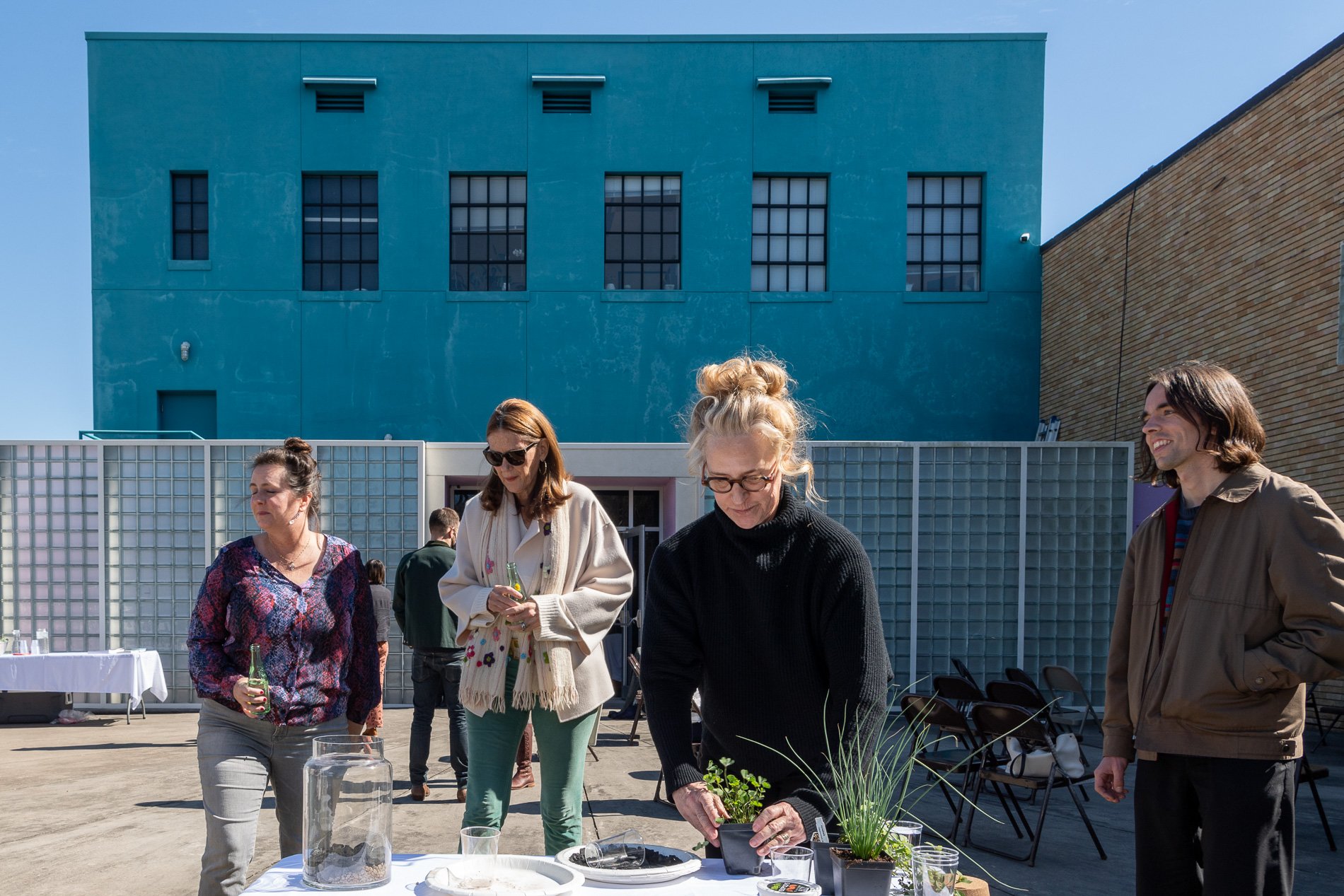
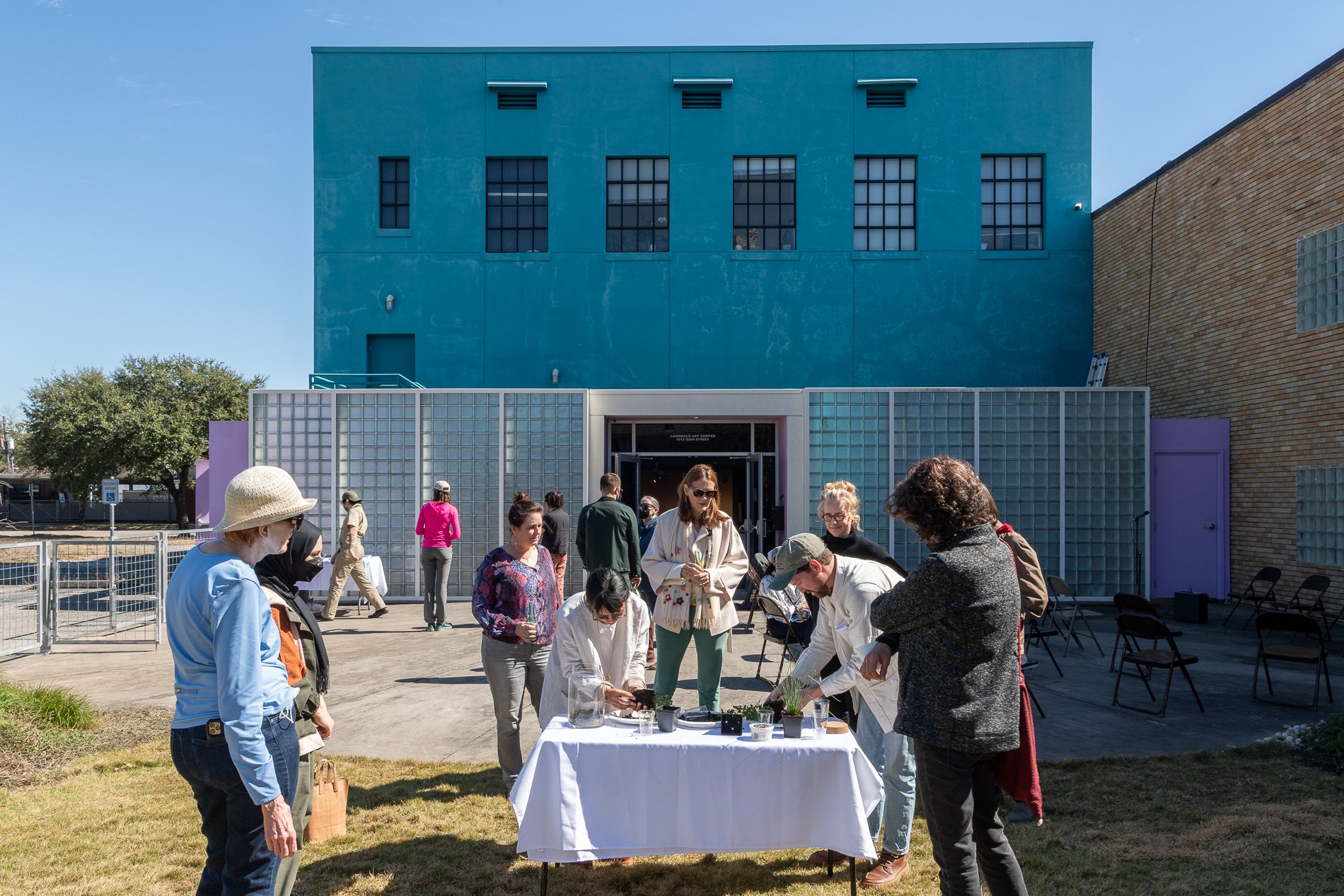
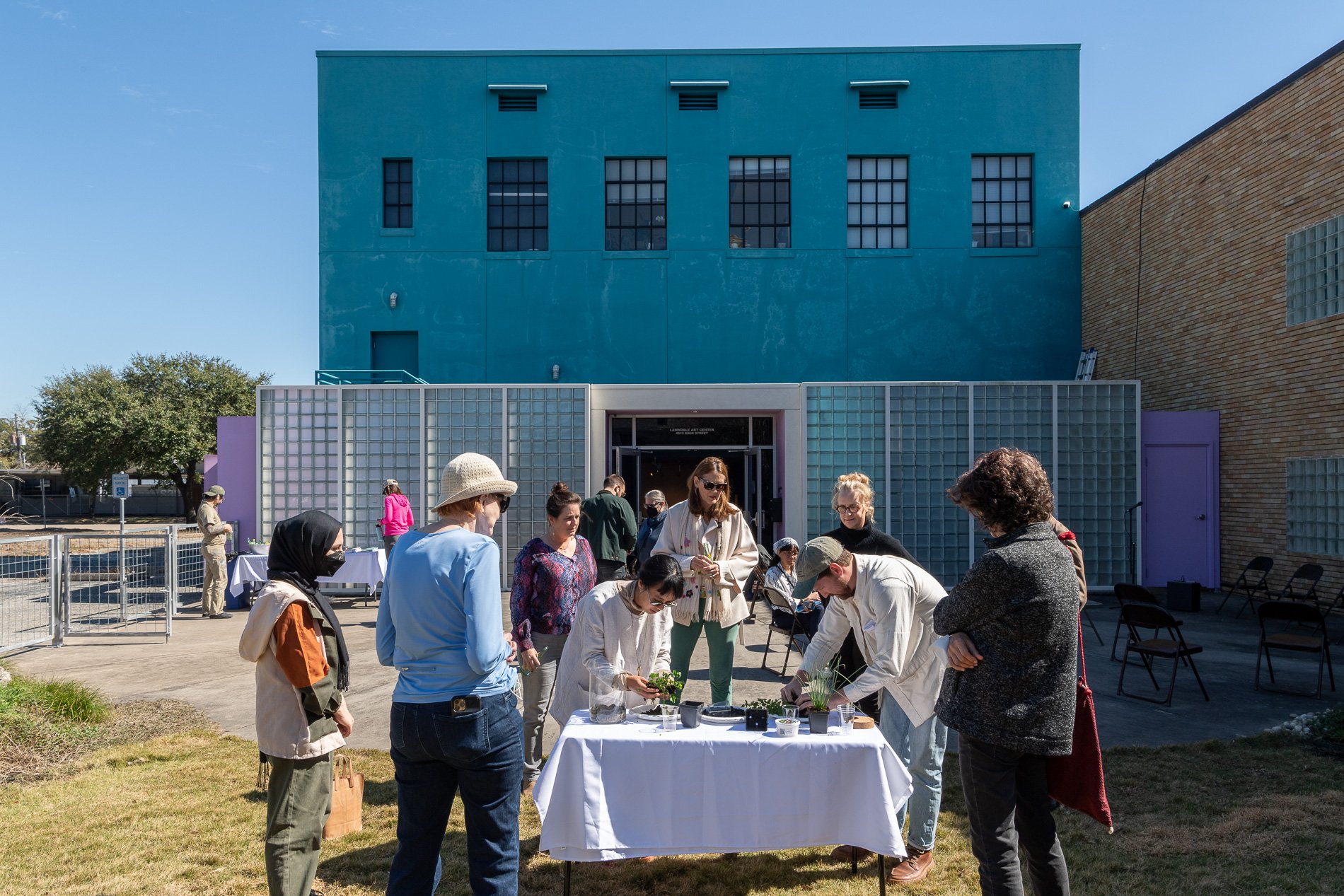
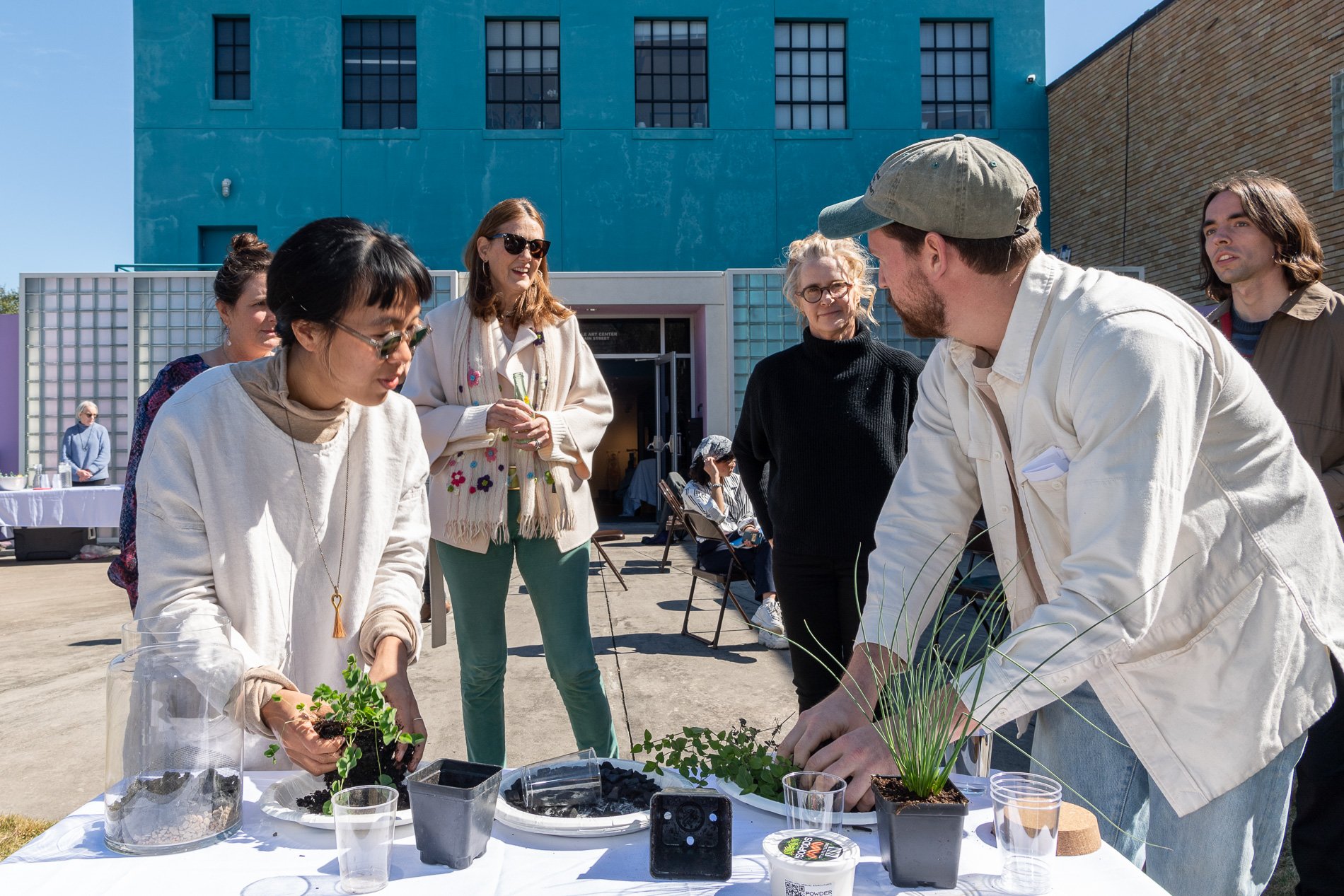
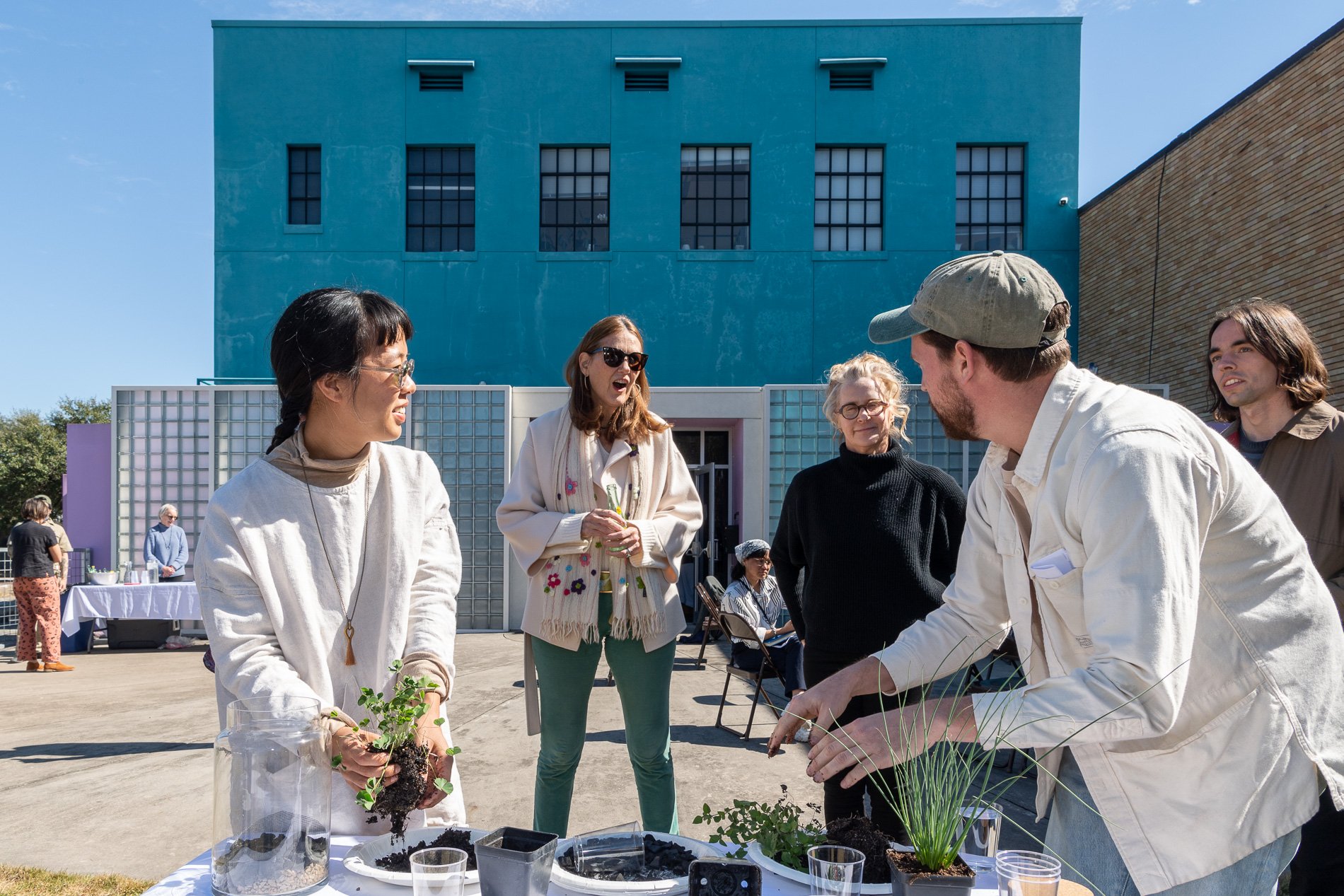
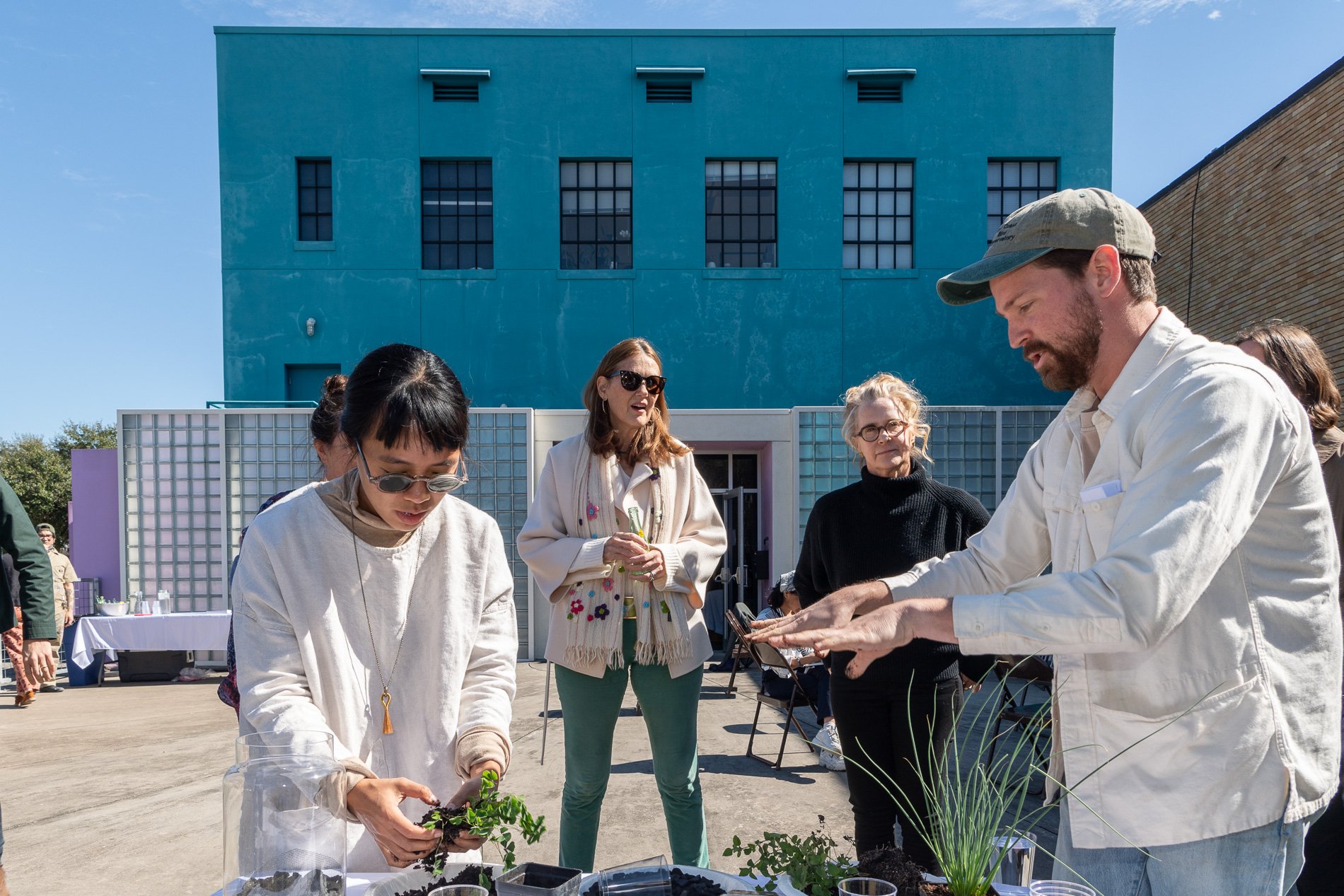
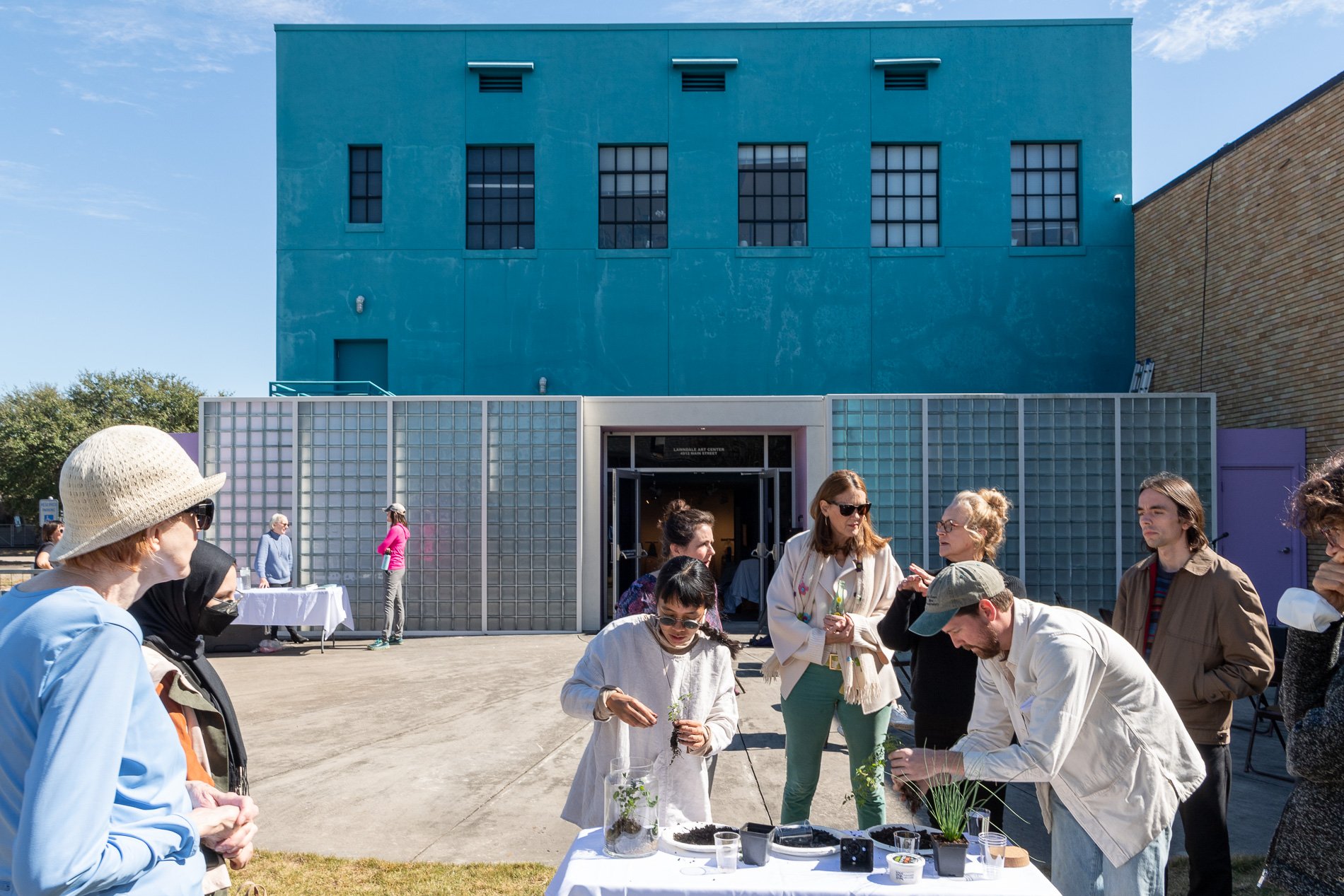
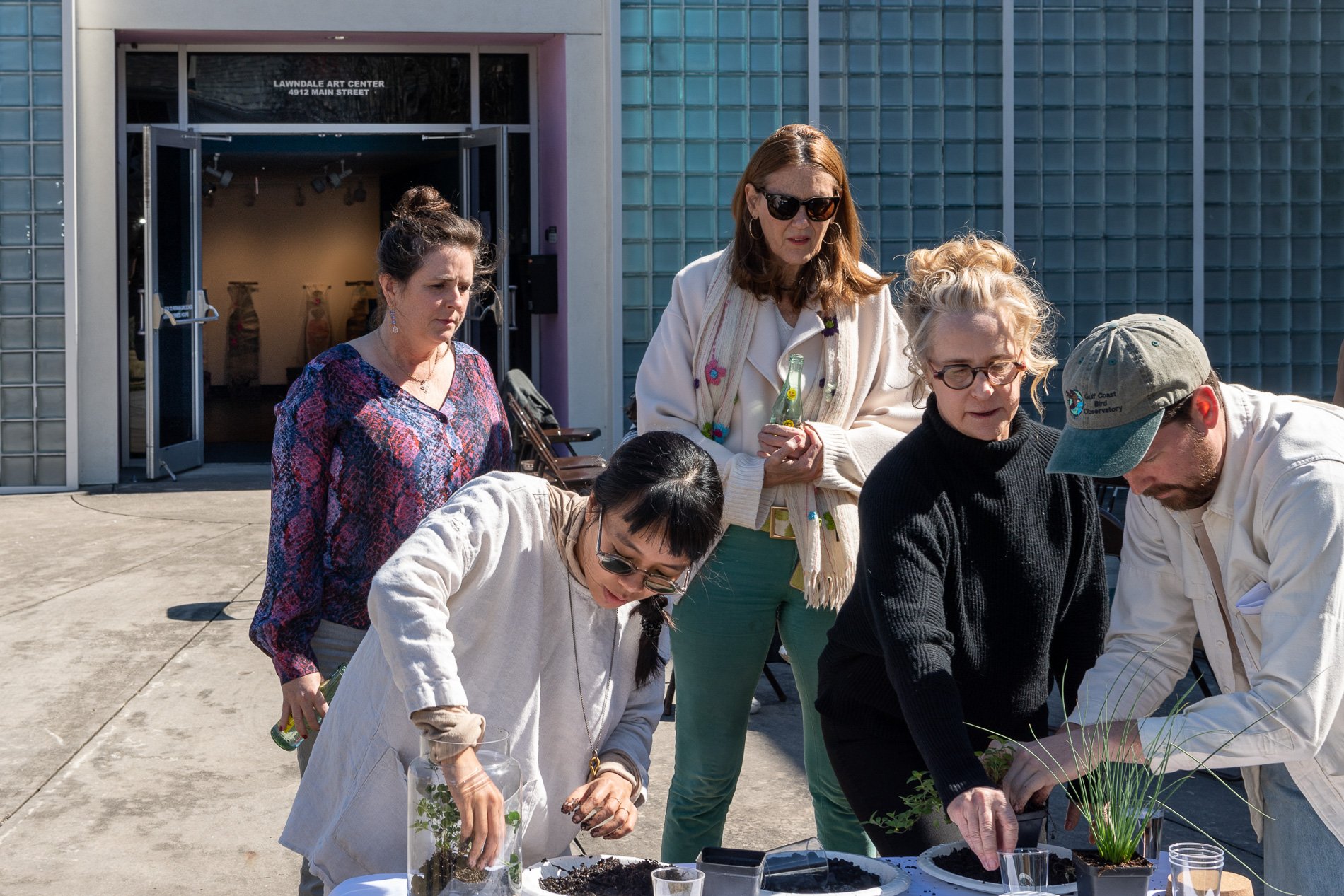
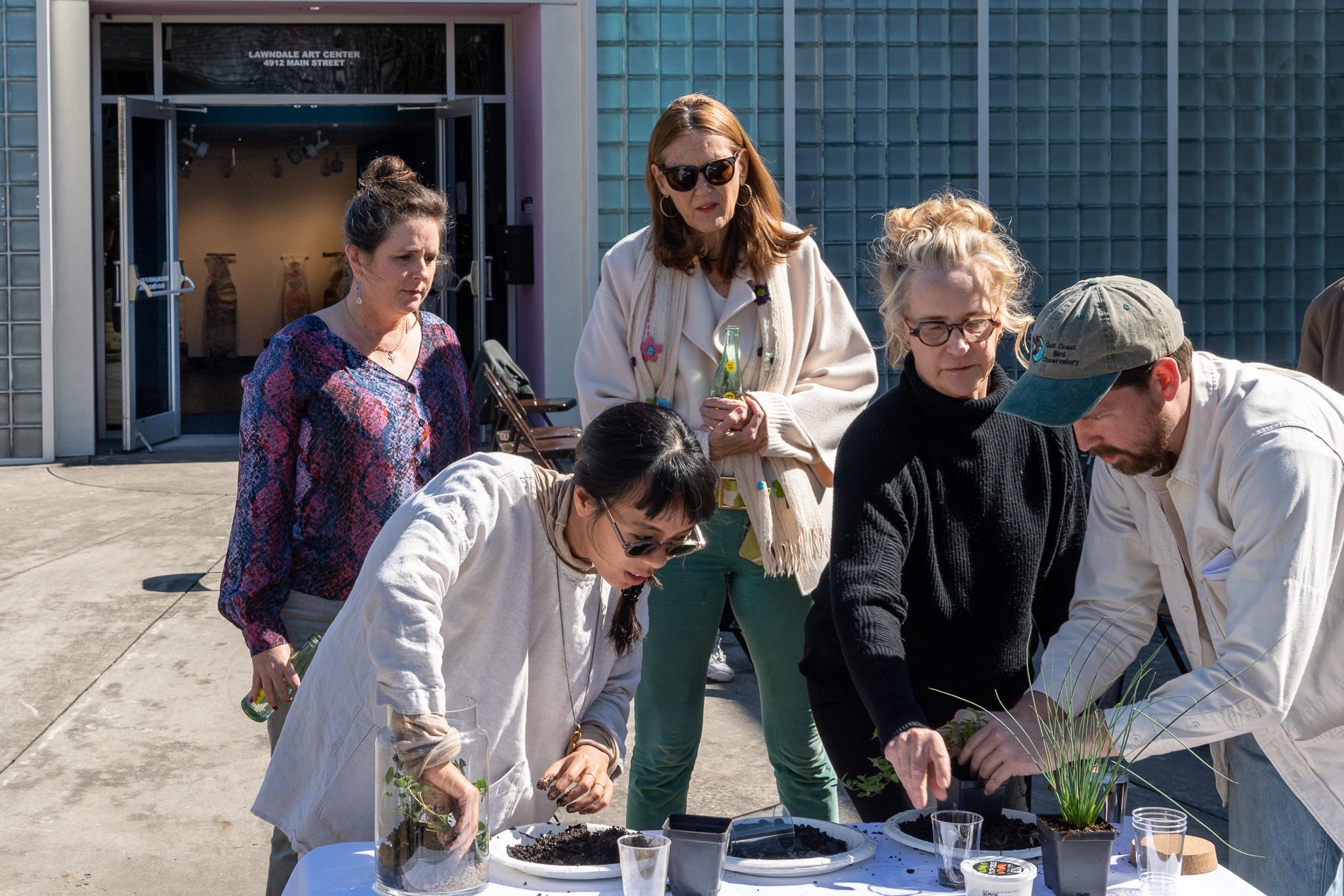
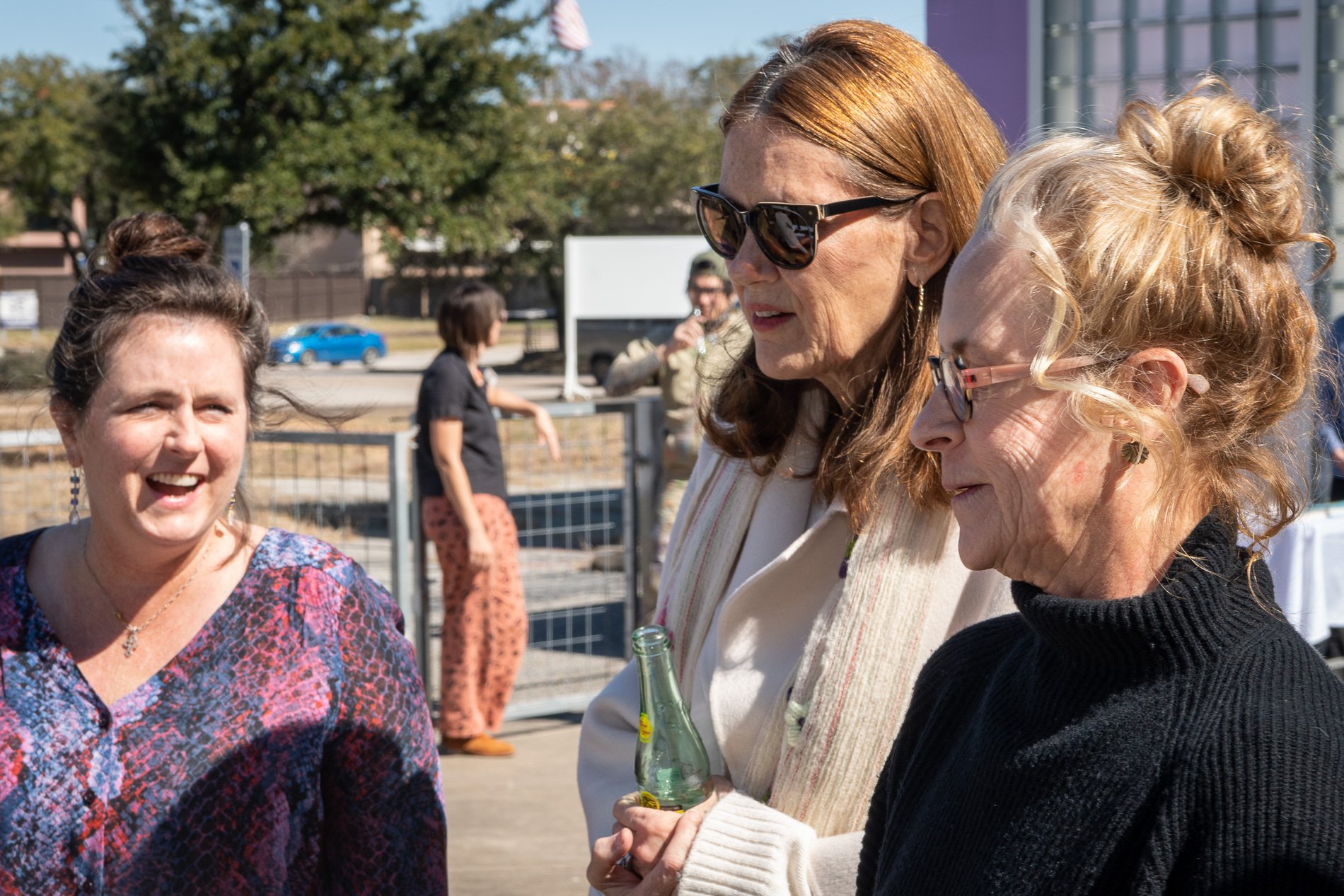
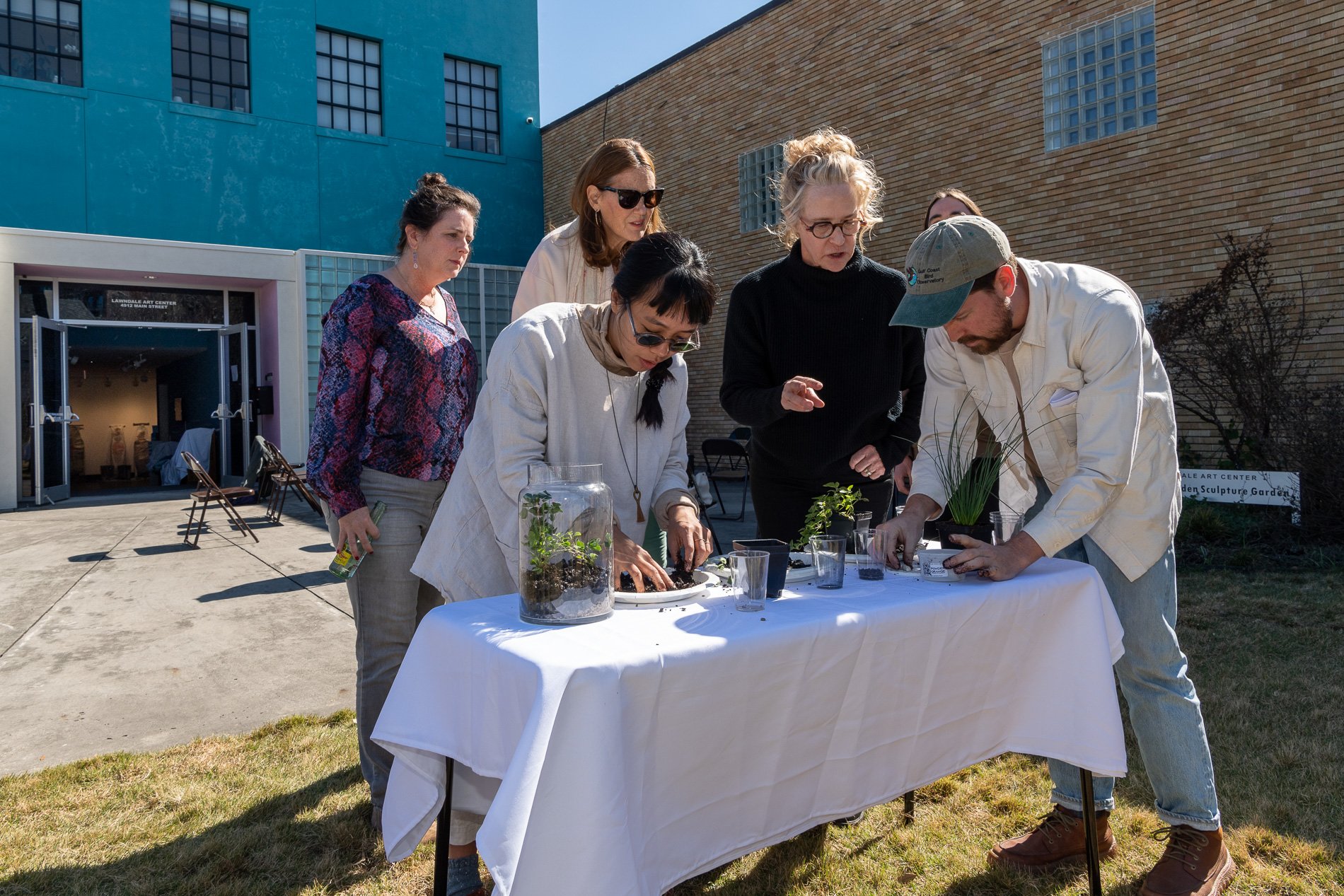
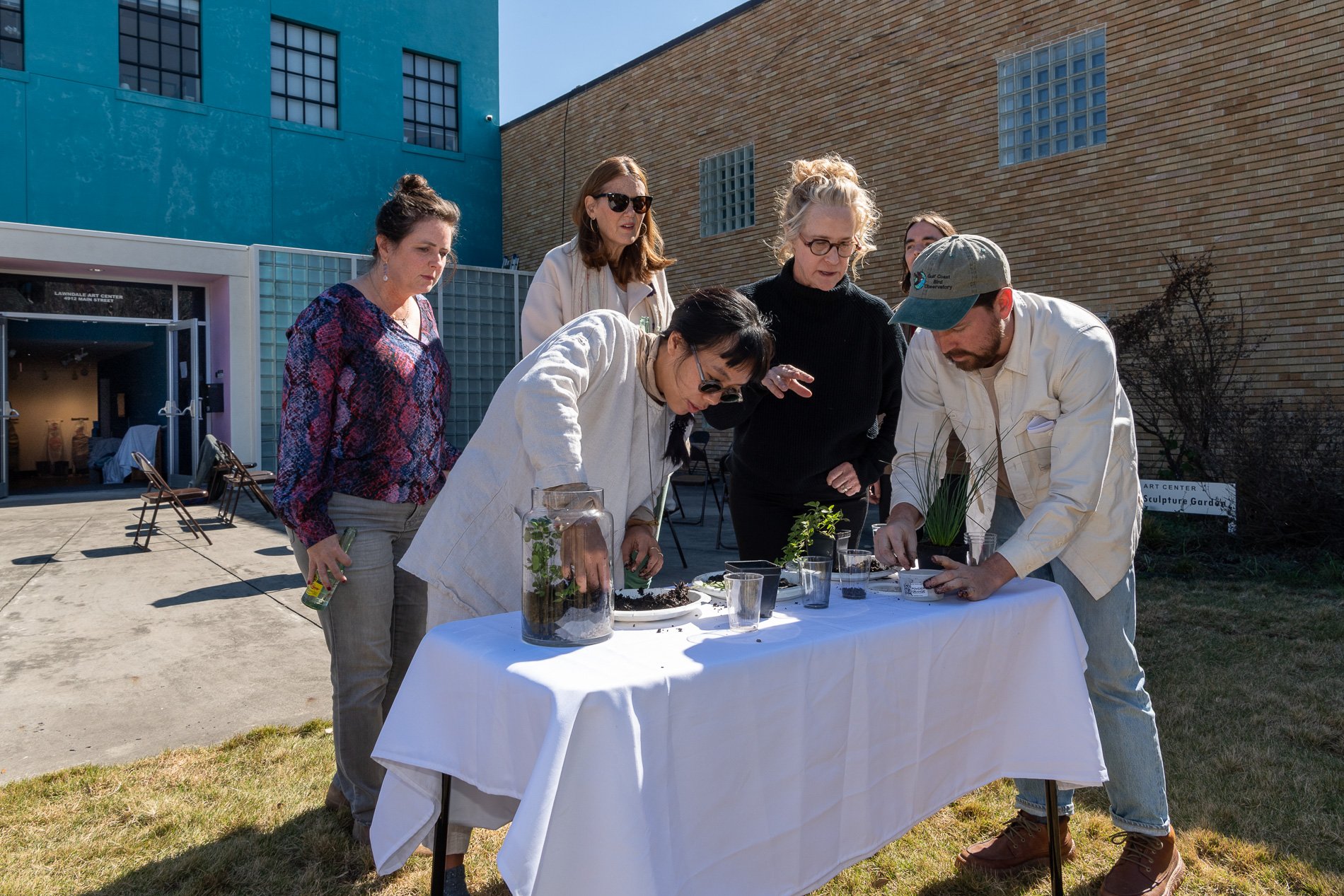
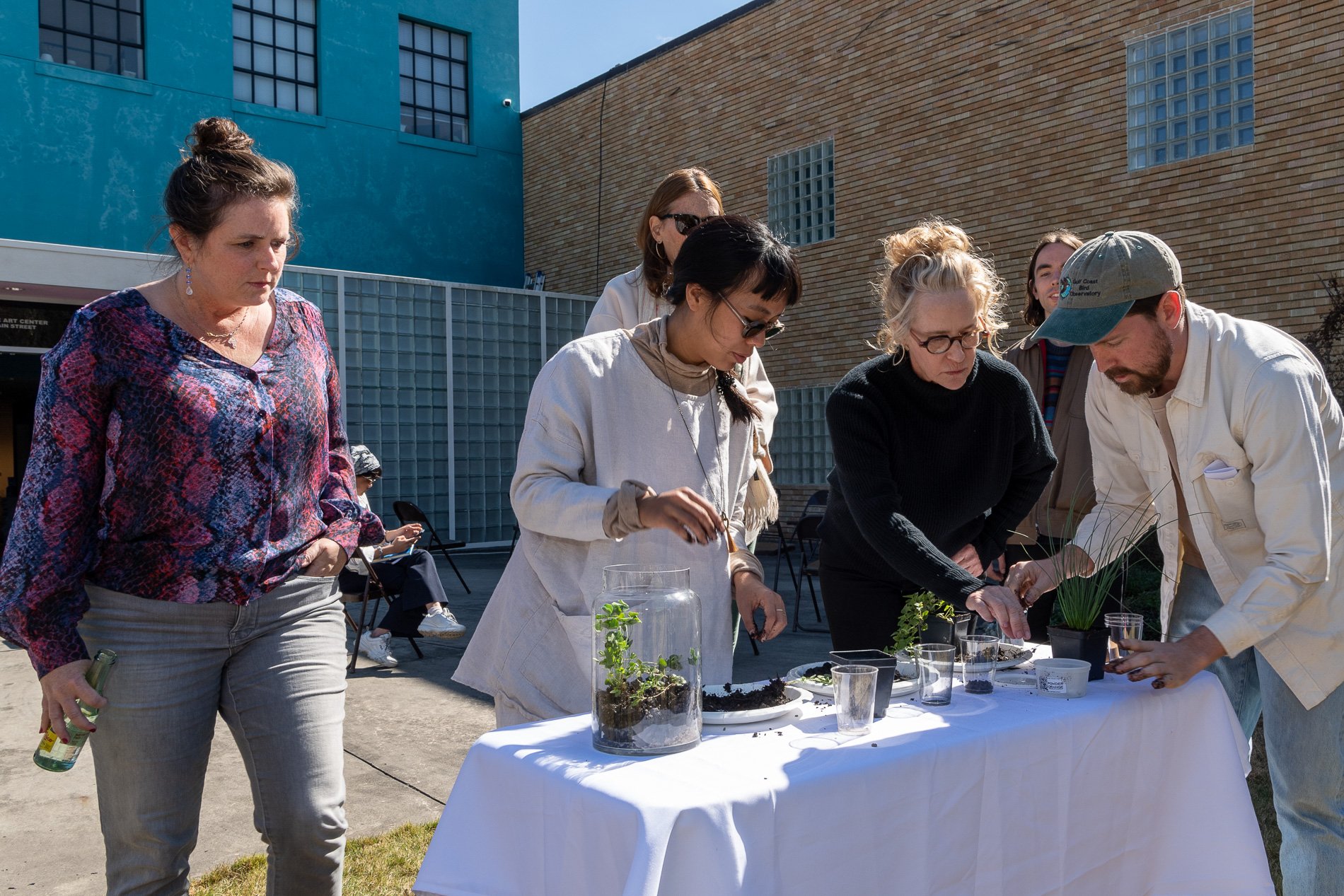
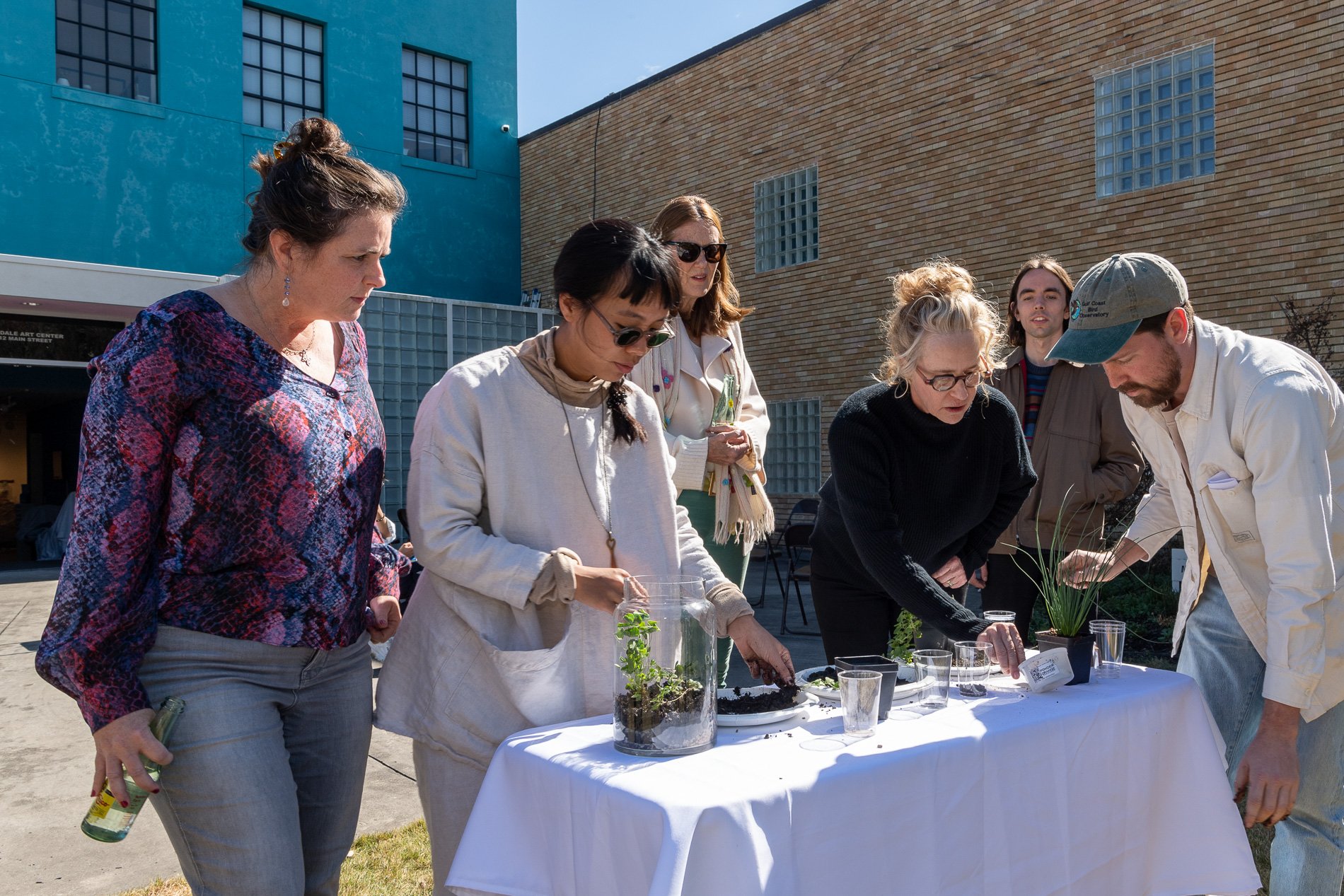
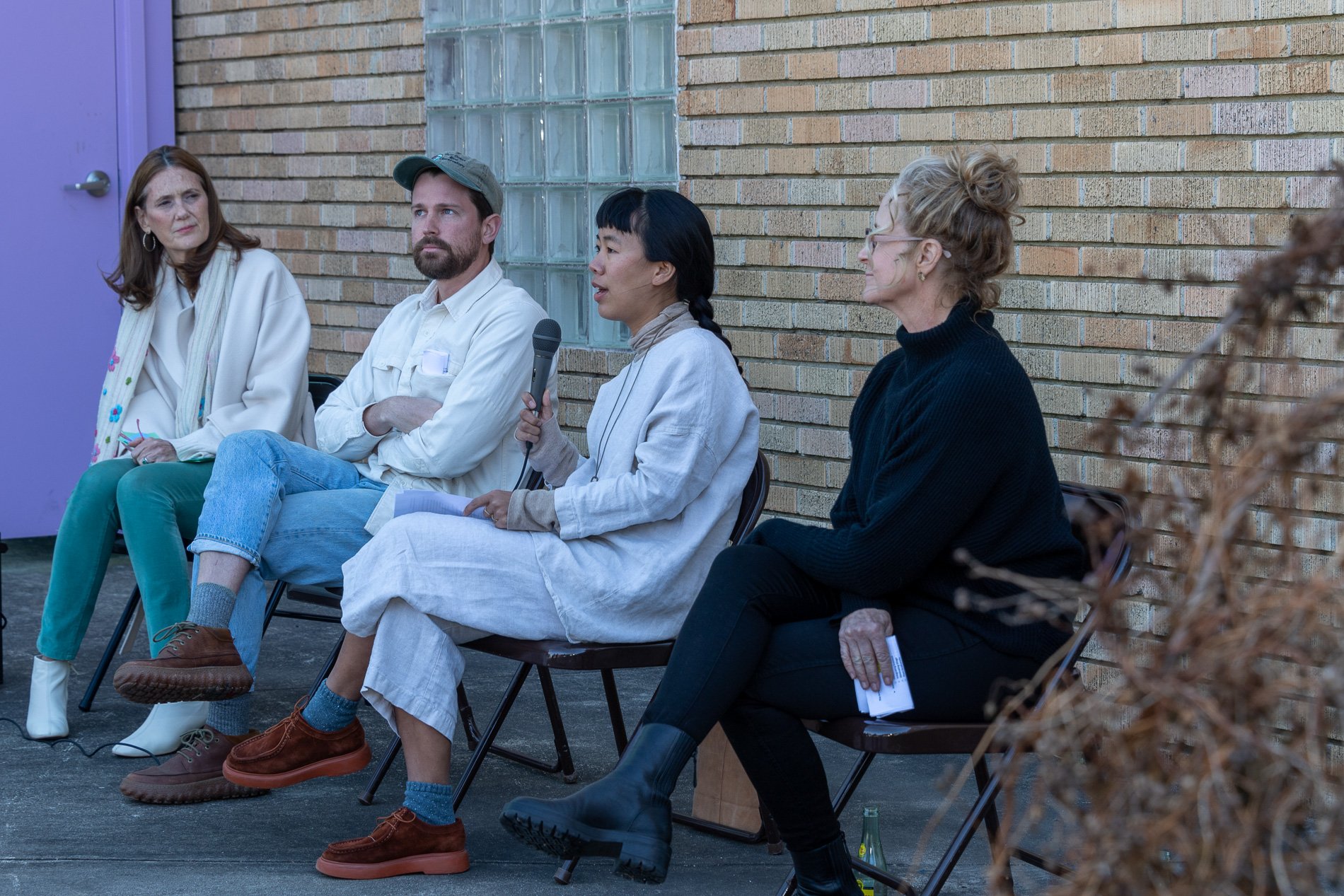
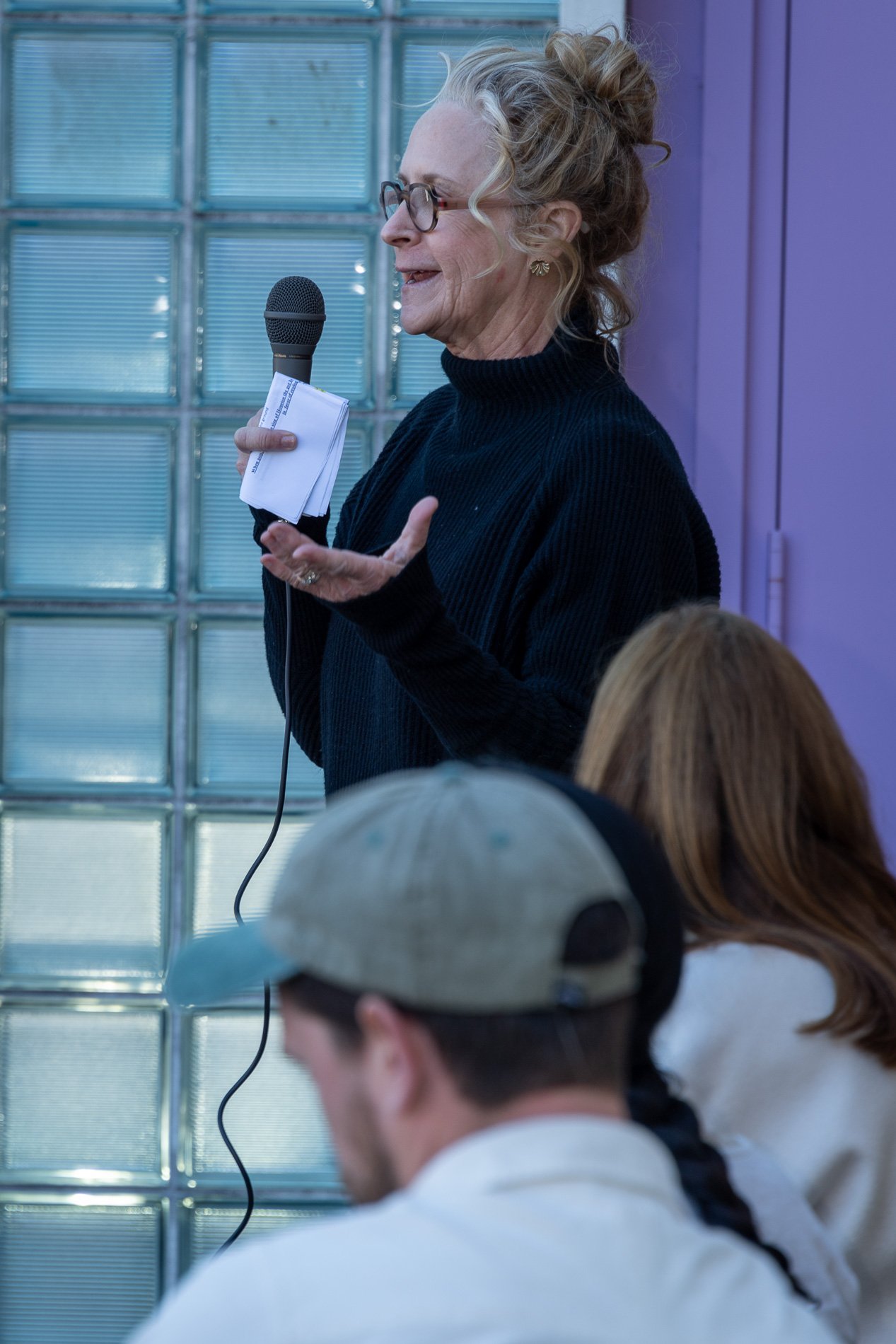
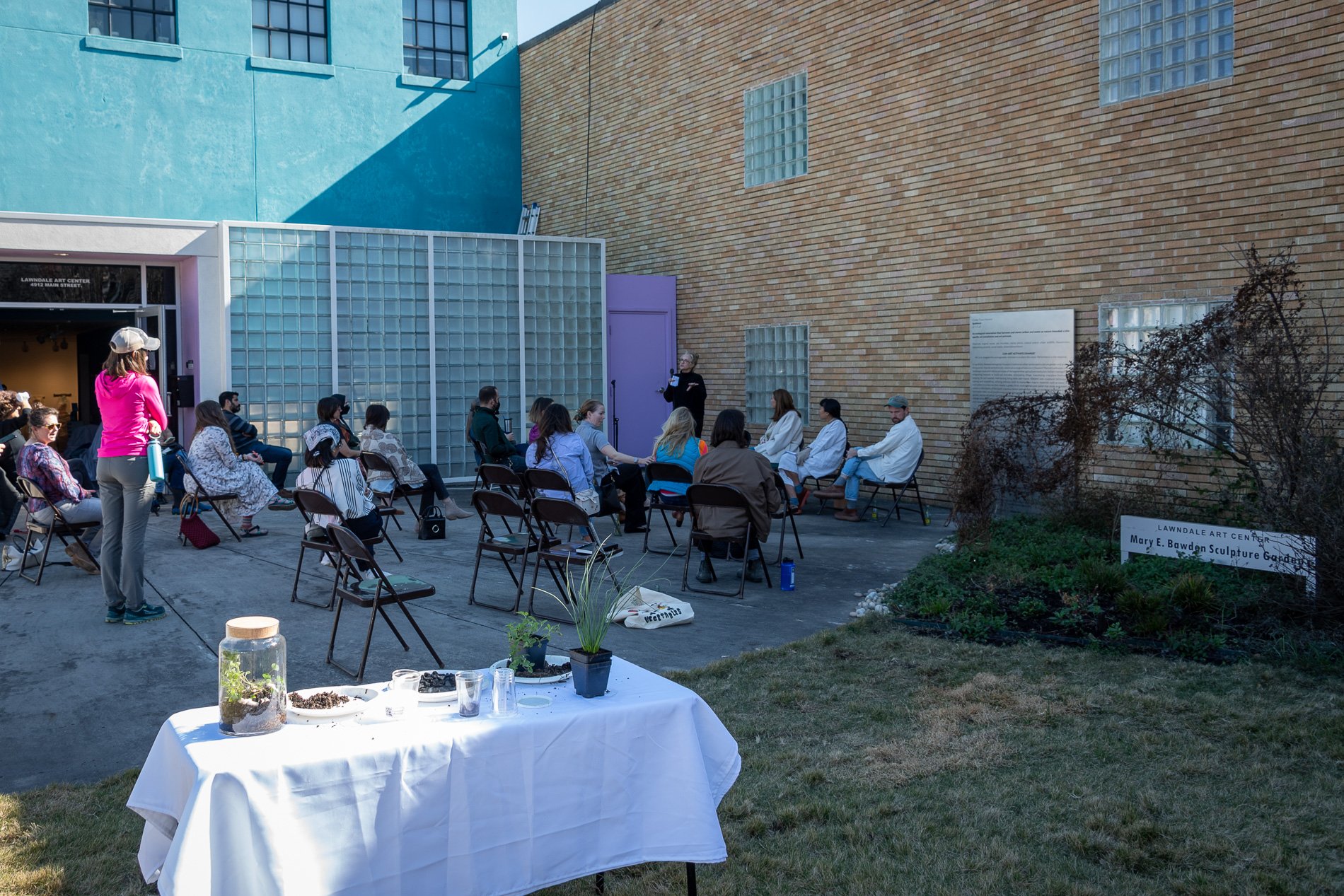
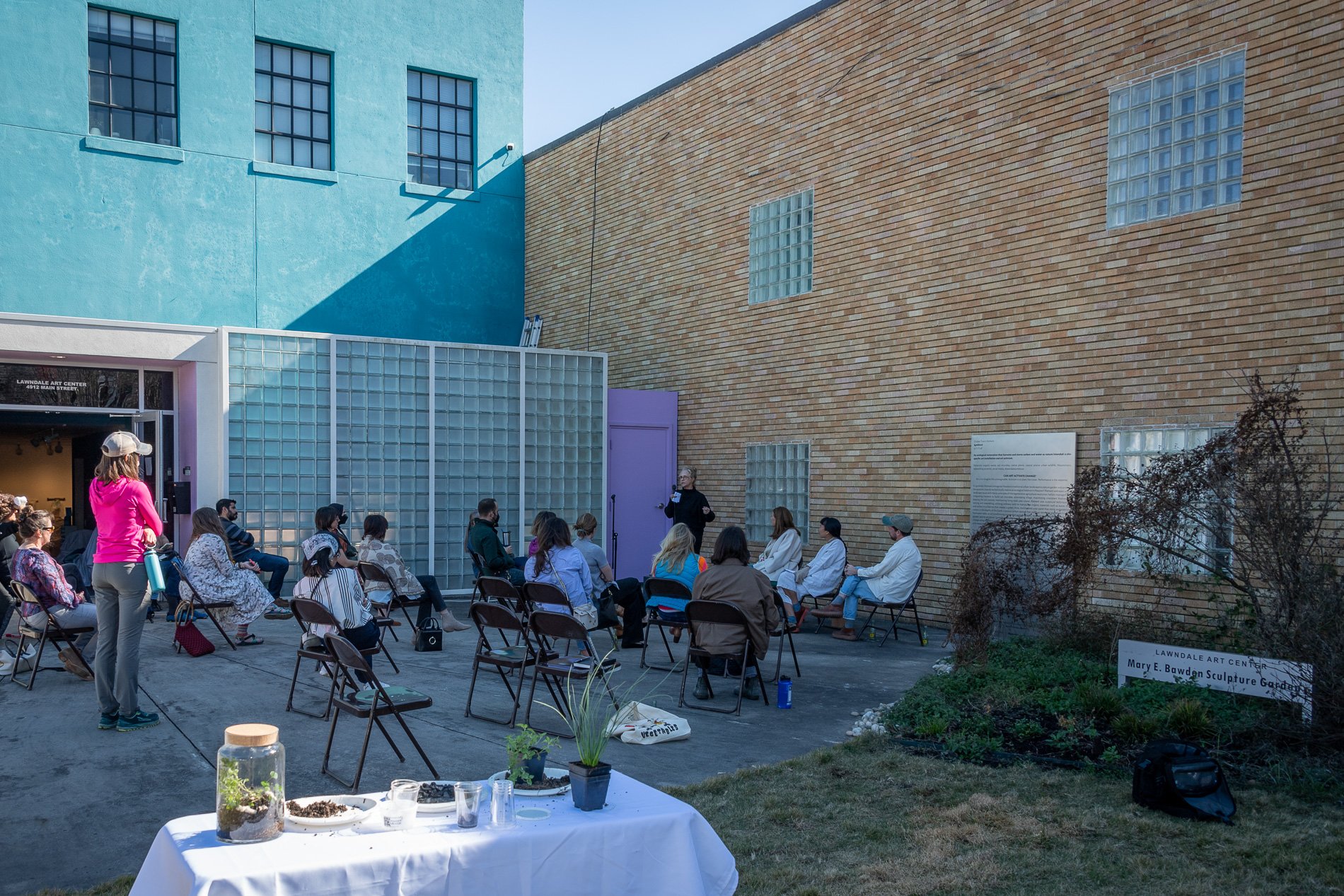
water + air + citizens - the actual event
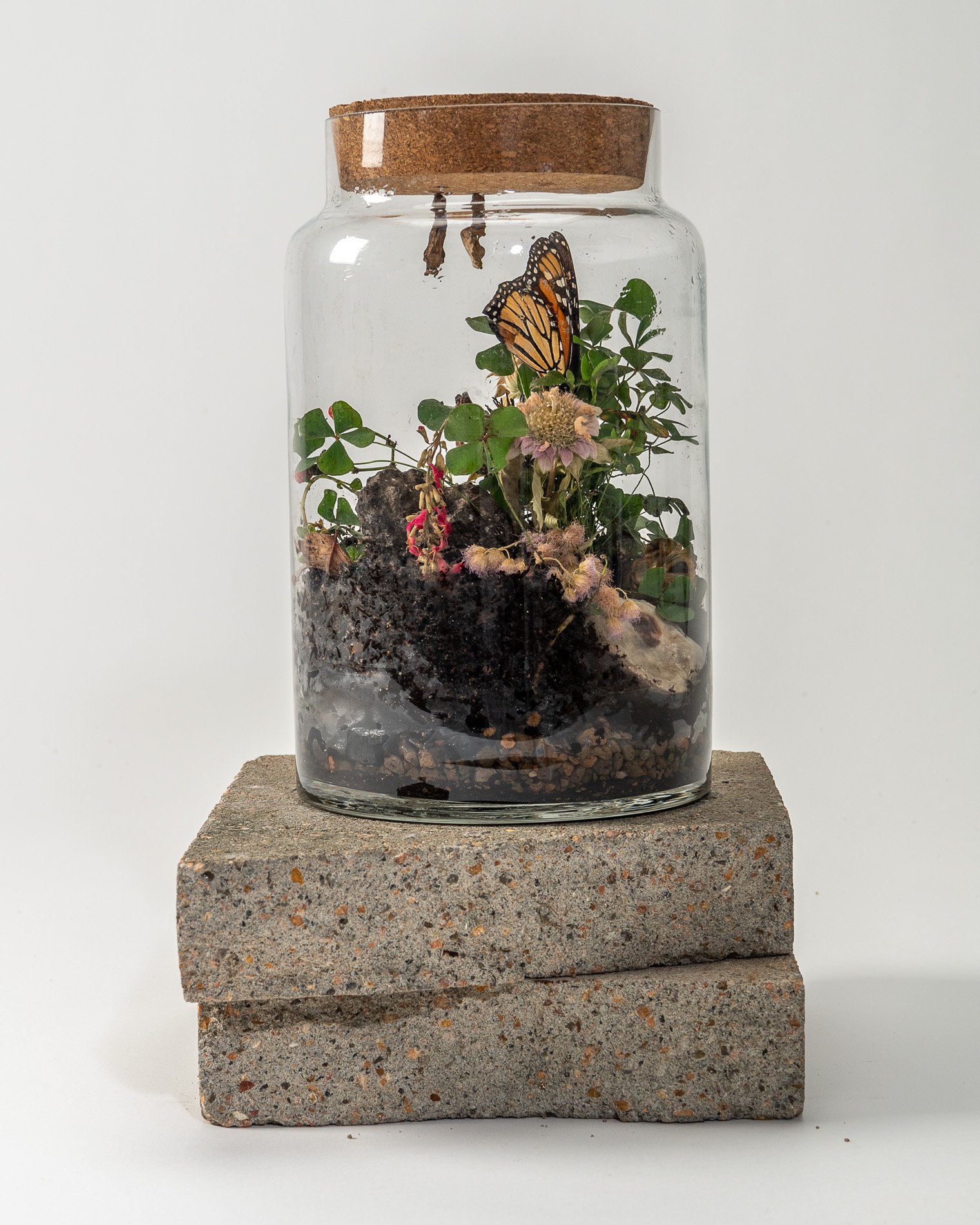
14” X 6” X 6”
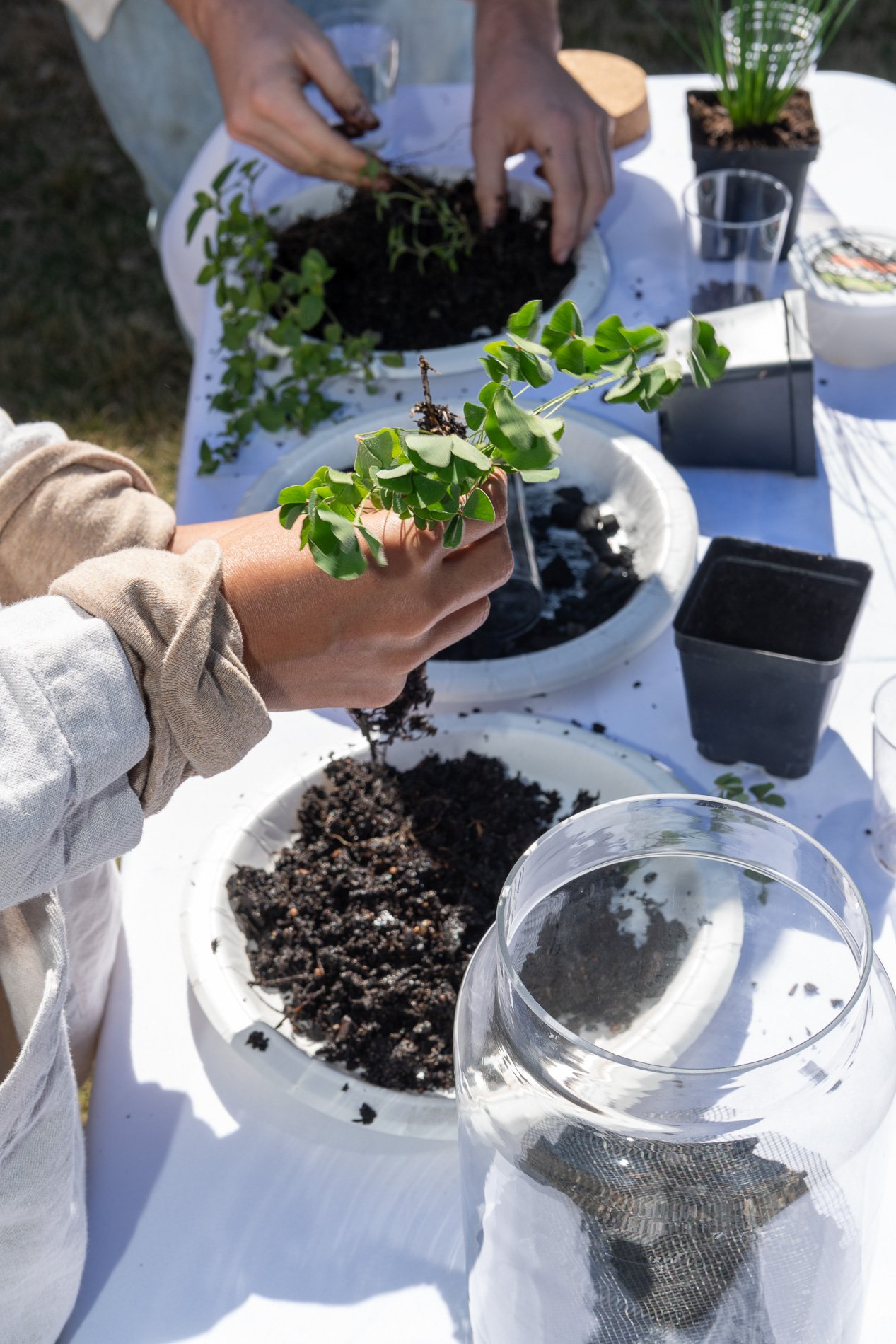
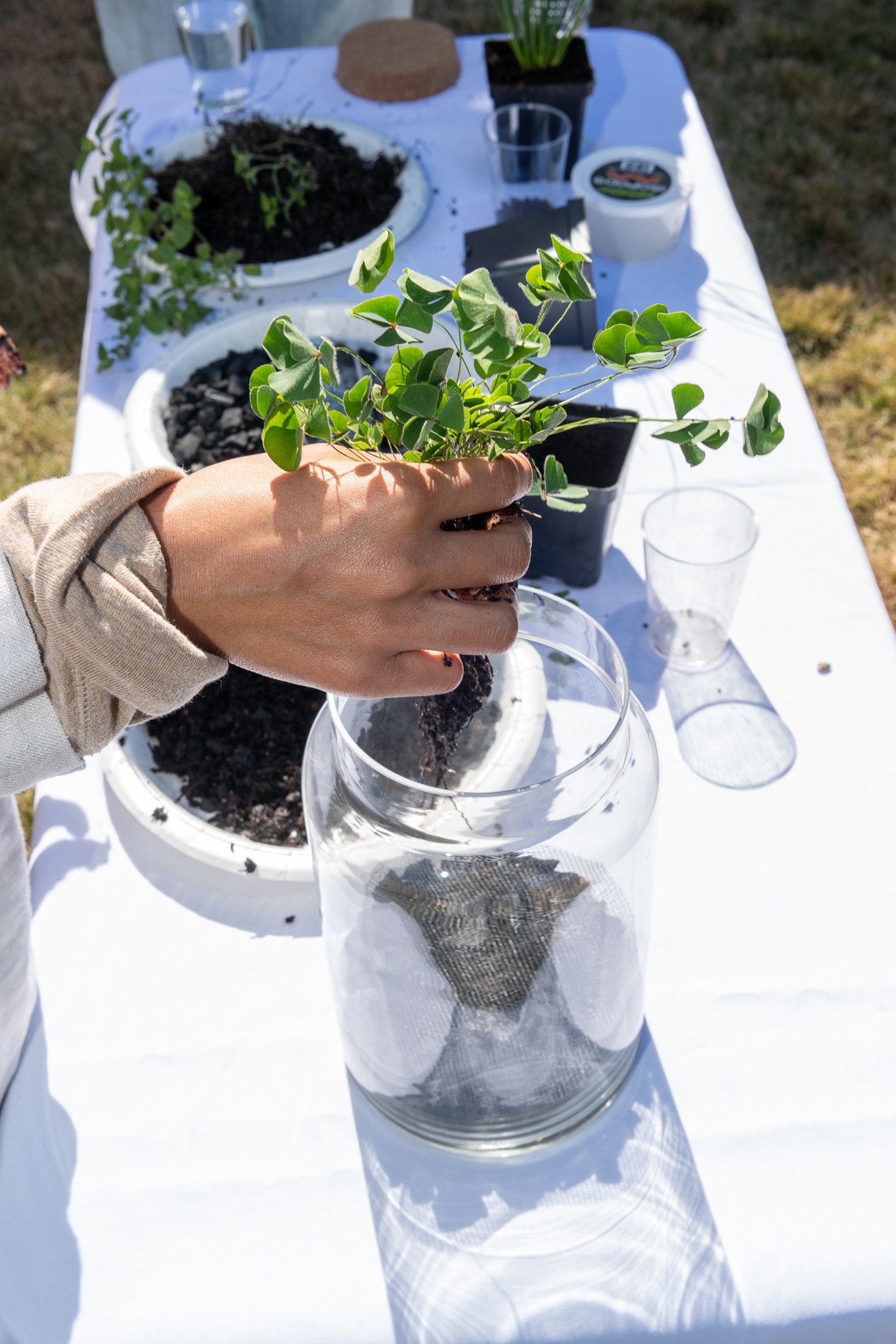
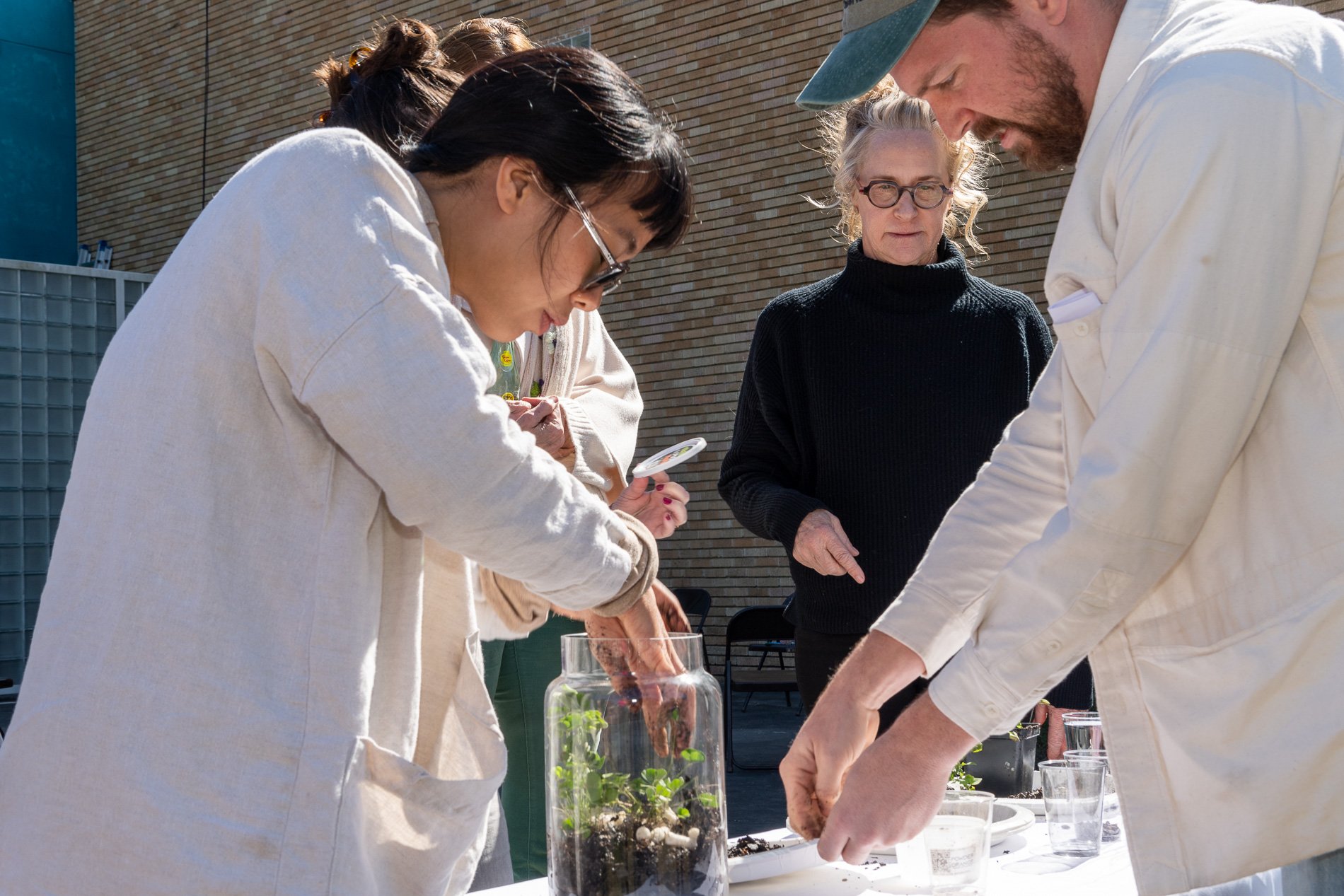
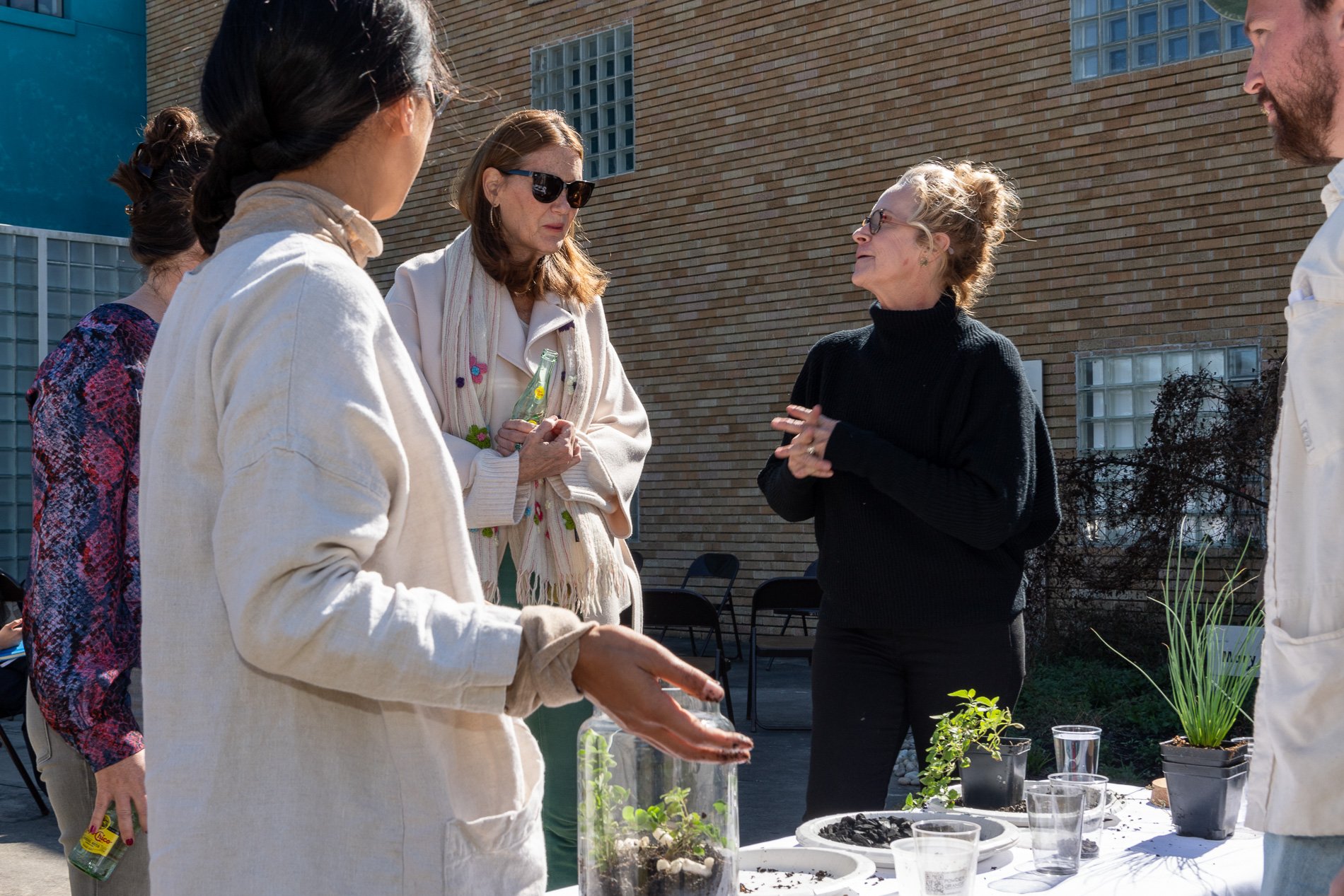
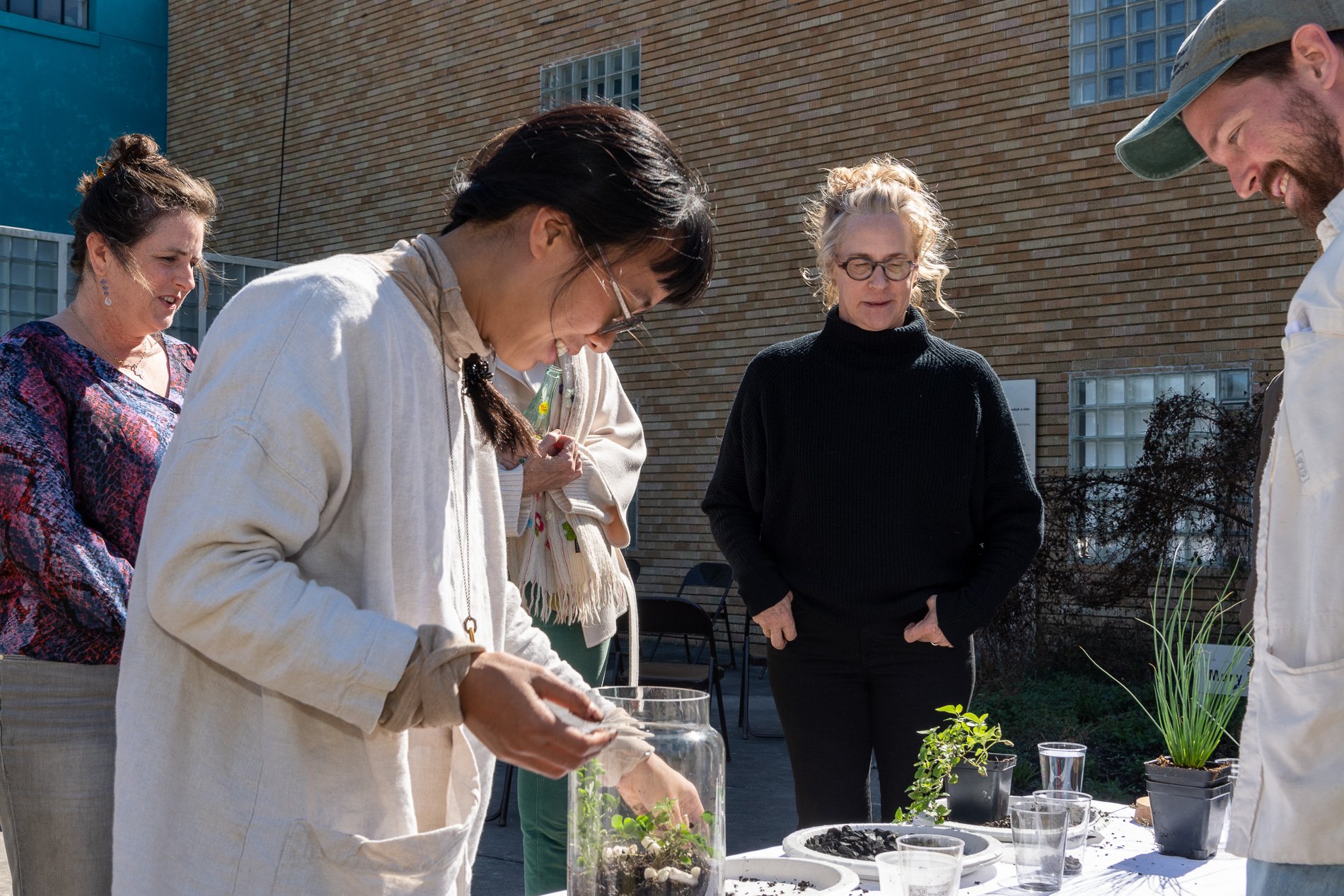
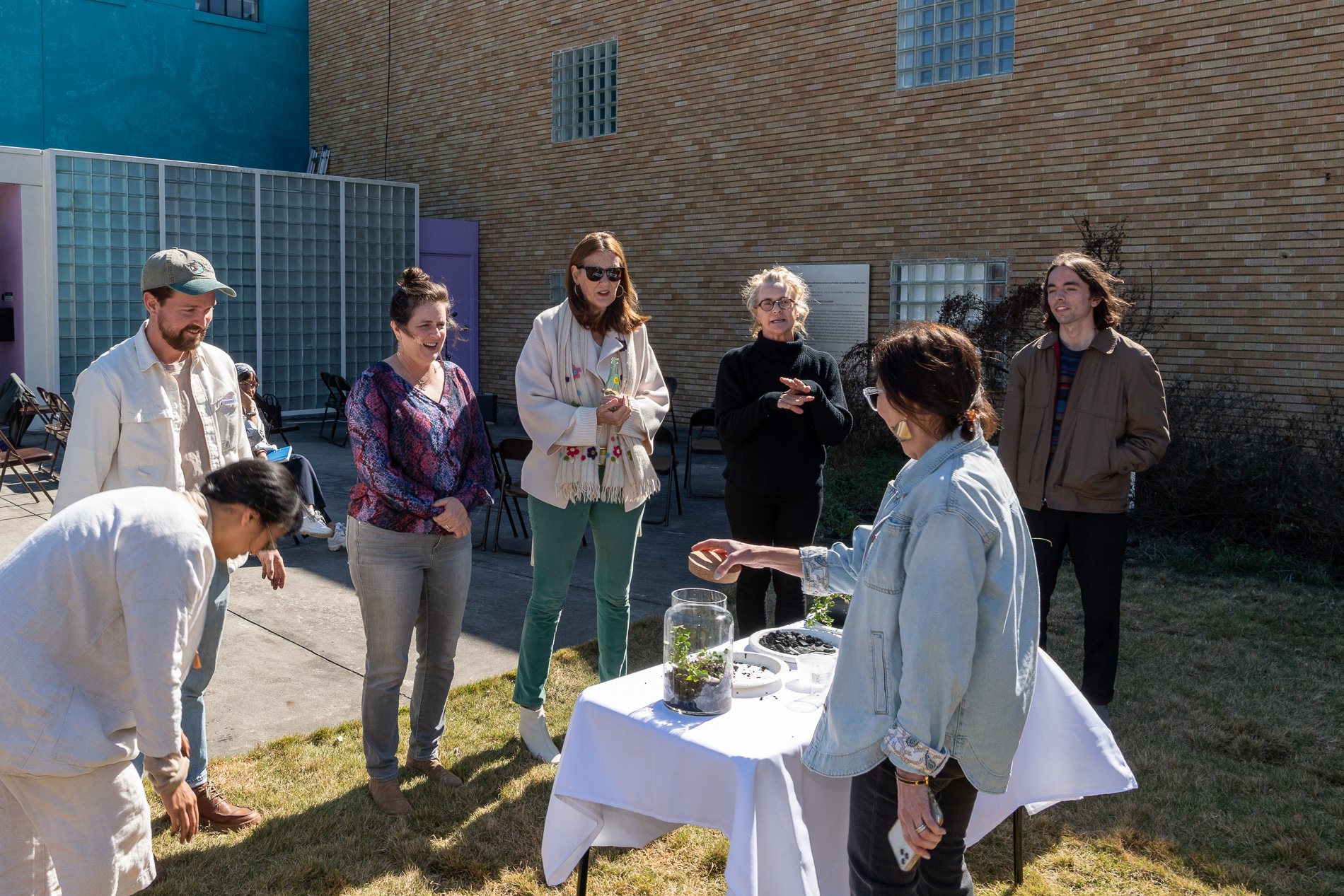
Found objects — a glass jar and cork lid, shale, charcoal, mesh, distilled water, Springtails, a Monarch carcass, living soil, Horseherb (Calyptocarpus vialis), Bigfoot Waterclover Marsilea macropoda, two chrysalides, two oyster shells, decaying bee balm bloom and a bird skeleton.
water + air + citizen
I documented the event by having the participants take a small step as a community to build a healthy functioning ecosystem collectively. Earth's water system is a closed water system. Although we can make soil, we cannot make more water.
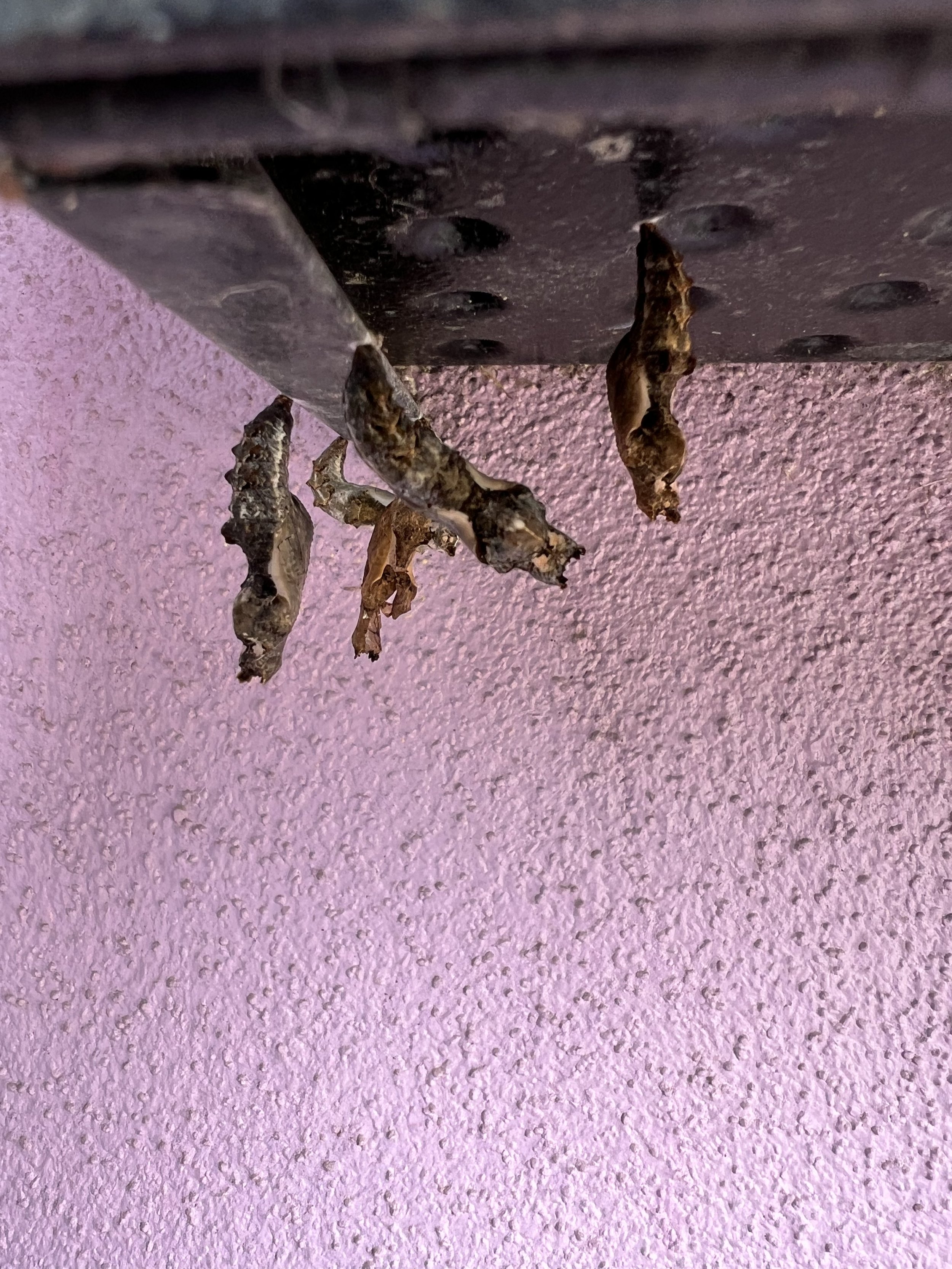
Before the discussions began as a symbolic gesture, each person added an element to provide the future with a water system to sustain life on Earth. The objects in the documentation are found objects — a glass jar and cork lid, shale, charcoal, mesh, distilled water, springtails to eat the fungus, and a Monarch carcass to envision the future. Sourced from Symbiosis, the piece includes living soil, Horseherb (Calyptocarpus vialis), Bigfoot Waterclover Marsilea macropoda, two chrysalides, two oyster shells, decaying plant matter and a bird skeleton.
After the event, I added elements present in urban earthly healthy ecosystems; the bird skeleton I found in Symbiosis last spring, two chrysalides vacated by butterflies and left on Lawndale's fence, a dried lemon bee balm bloom, and lastly, a past Monarch butterfly. Monarchs were not witnessed in Symbiosis' first year. I found this Monarch on the sidewalk of my neighborhood. To recover endangered species, we must envision them in our terrain, provide habitat and plants that give them nectar. I placed the terrarium on two broken concrete pavers. As an urban community, we took the first step we successfully built an ecosystem where our actions support natural systems that temper weather and provide clean water and air.
In 2021 I proposed to Lawndale a social Sculpture that addresses the three ways humans intersect soil in Houston. The way we treat our soil impacts two ingredients necessary to sustain life on Earth, water and air.
Public policy, Design industry, and Art activism.
Water + Air + Citizens is a discussion that looks at three ways Houstonians (humanity) impact these natural systems through urban landscapes.
Medians, yards, gardens, lots, parks, blocks are all surfaces of Earth. But, by any name, the skin of our planet purifies its water and regulates its atmosphere.
As the event grew close, I began to see a bigger picture, another layer to the work. In my sculpture practice, this is a common occurrence. In this case, I became aware that the title I chose for the sculpture is three of the most potent elements in weather. First, with water, we have floods and hurricanes. We are hit with hurricanes, tornadoes, and dust bowls in the air. Finally, citizens' power of public opinion is a tremendous force and often overcomes the common sense of individuals and leaders.
Symbiosis - Pollack
When I study the areas of the work that visibly support the most wildlife in Symbiosis I often think of the the most notable works of Pollock. I am presently reading The Extended Mind by A.M. Paul. In the chapter on thinking in natural spaces she wrote. - “Nature changed Pollocks thinking - gently tempering his raging in-tensity- and it also changed his art. In New York, Pollock worked at an easel, painting intricate, involved designs. In Springs, where he worked in a converted barn full of light and views of nature, he began spreading his canvases on the floor and pouring or flinging paint from above. Art critics view this period of Pollocks life as the high point of his career, the years when he produced "drip painting" masterpieces like Shimmering Substance (1946) and Autumn Rhythm” the extended Mind by A.M. Paul. I often see Pollockness in “Symbiosis”. This images especially reminds me of his Autumn Rhythm. In “symbiosis” it is winter shelter. This scarlet sage was damaged after the freeze.
Documenting the art of creating living soil. SOILED — Tighty-Whities 2021
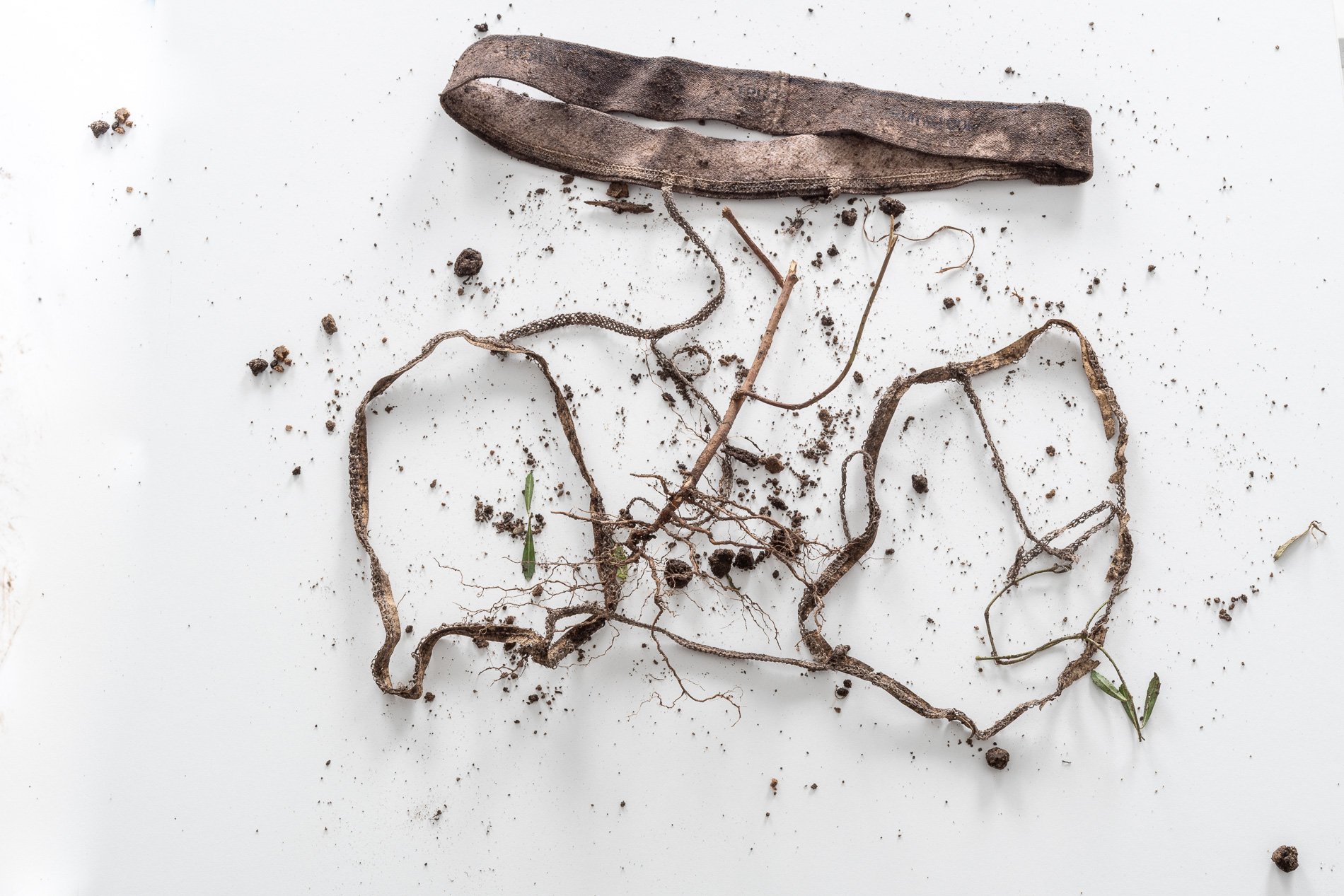
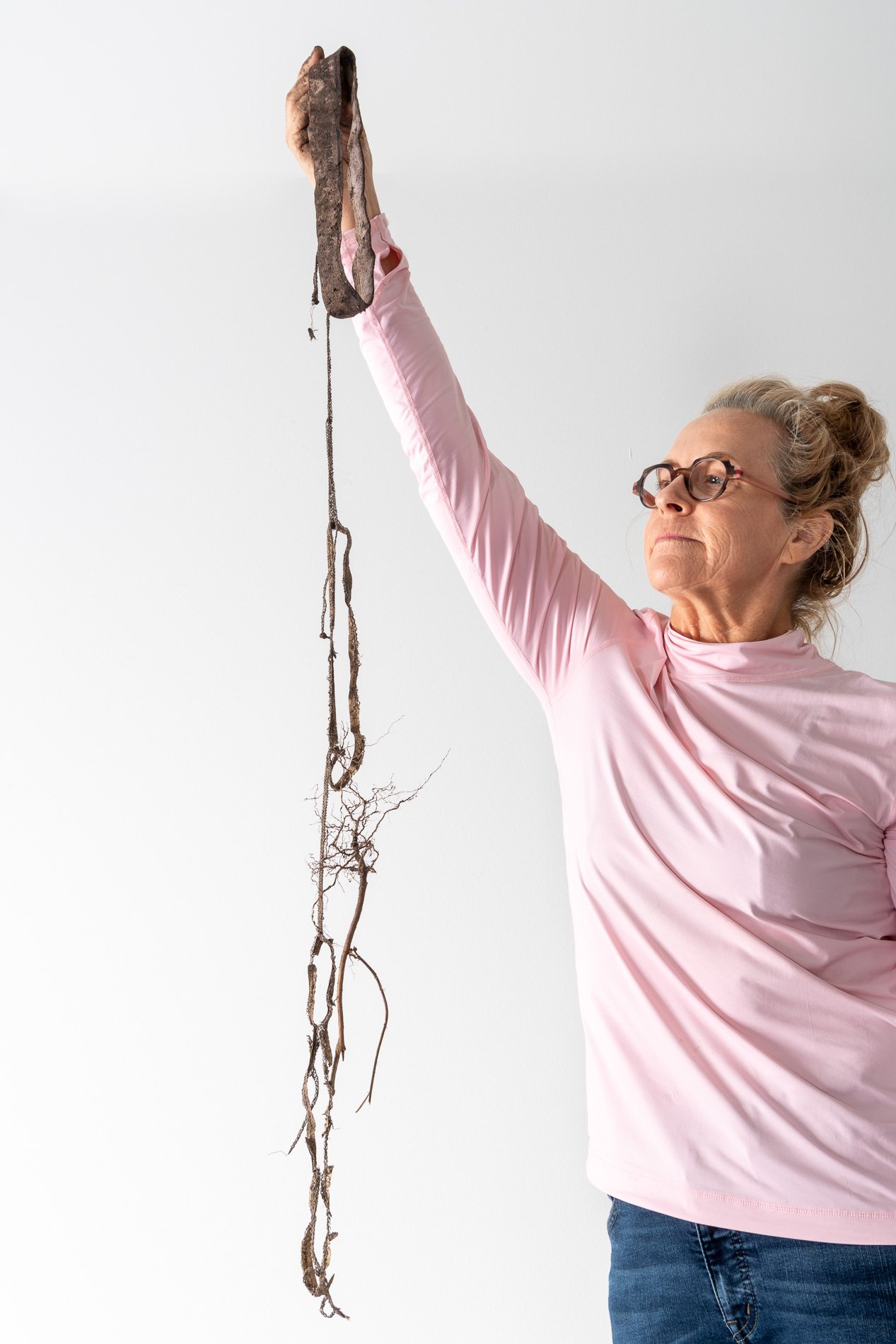
SOILED — Tighty-Whities 2021
Photograph by N. Baker
How do you document art that lives beneath our feet? Creating art beneath the Earth’s surface I am finding new ways to document the work and it's movement. This photograph is the result. Let me explain. To test soil for fungi that recycle wood and live on dead material soil, scientists buried cotton fabric. In Symbiosis, to document the Saprophytic fungi, I planted new, washed men's medium cotton briefs. This photograph demonstrates the results. In 2022 I will recreate the piece and grow the tighty-whities in a vertical column. This change will document that living soil, the diversity of microbes is built from the top down. In contrast, when my father farmed in the 50s and 60s, the farm bureau that advised him told him to invest in a new plow to dig deeper to access the richest soil.
The purpose of my work is to change how we see landscape. It isn’t just about creating beautiful gardens. Landscape can store carbon and soak up rainwater to cool the planet. It is the cheapest and fastest way to get our planet back on track.
Digging up the briefs I immediately knew I had made a mistake. I left them In the garden’s soil too long. Still, I dug them out with tender care. The petroleum-based elastic band was entwined with a plant root. The root took the elastic leg 6” deeper into the earth than I planted it. I left the elastic and the root as I found them. Laid them on a board and took them immediately to Nash’s photography studio to document the work.
First, I delicately untangled the elastic. The cotton had completely decayed. The elastic was not biodegradable.
Seeing that the briefs were still intact minus the cotton and plus the root I started reassembling the briefs and the added appendage.
In art many times you have to listen to the materials.
Symbiosis- invasive species
Hairy Crabweed Fatoua villosa is the only invasive species I have discovered in Symbiosis.
It gives me confidence in my landscape philosopies when I read research publications that support my observations of “Symbiosis.”
In July, Houston received an extraordinary amount of rain. That is when I discovered an invasion of Fatoua villos. Aware of the harmful effects of invasive species such as kudzu, I panicked. I went into industrial irradiacation gear. After two days of pulling the hairy-plant-beast from the beds, I noticed many of the native plants were suffering from too much water. I also noticed the native plants in the beds that I had not pulled we're not struggling. I stopped the pulling of the species. That is when I adopted a weed or invasive species management philosophy. Now I carefully observe how each species is impacting the naticve plants, the wildlife and the visual impact of the sculpture. Below is an article from Science Daily that supports my observation.
“The paper's implications suggest that faced with declining fisheries, threatened reef ecosystems, and changing climatic and oceanic conditions, the value of ecosystem services provided by some invasive species, e.g., mangroves, may outweigh their negative effects. Therefore, the decision-making process involved in managing some invasive species warrants more careful consideration of both costs and benefits provided to the ecosystem.
"In a static world, invasive species are bad because they disrupt ecosystems," Granek said. "But we're living in a world where the environment is changing. The climate is changing. The oceans are changing. That changes the calculus of how bad some invasive species are to the habitats they've been introduced into."
Carbon by the Yard - a weekly update
Carbon by the Yard
Zoysia Turfgrass relief
35' X 48'
Embedded within the installation Symbiosis, Carbon by the Yard is a temporary, living sculpture in the shape of the Carbon element symbol, C. The work consists of carving a 16 x 14-foot shape into the existing grass, and allowing the Zoysia grass to grow tall around it. A simple gesture, the letter brings attention to the role lawn-grass plays in climate change. In 2020, the Environmental Protection Agency estimated that grass uses up about a third of all public water: in the US, this translates to 9 billion gallons of water every day. Our mowers consume 200 million gallons of gas. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency estimates that, gas-powered lawn mowers produce 11 times as much pollution as a new car hour for hour. And, manicured lawns provide no livable habitats for pollinators or the other plants and animals necessary to maintain a healthy ecosystem. With Carbon by the Yard, artist-environmentalist Cindee Klement brings attention to the ways in which our daily decisions can help to reduce our carbon footprints.
Reducing nitrate leaching losses from turfgrass fertilization of residential lawns
The sketch for Lawndale approval
September 23, 2021
I sketched the C into the space with flags. Moving and adjusting them until I had the shape C right and in the right place.
Next I marked the C with a water base paint used to mark fields.
The C marked in water based paint.
October24th- The first cutting.
The yard maintenance company used their regular mower. The CO2, cost, time, and noise pollution of the gass lawn mower was not worth the result.
I was afraid that the following week the lawn maintenance company would not be able to see the relief enough to remow it. I remarked the C with the flags.
The second cutting was rained out.
I will update this blog post through out the process.
October 8th - week three cutting #2
October 18th - Week 4 cutting #3
October 22 - week 5 cutting #4
After 4 cuttings the C is now beginning srand out.
November 1- week 6 cutting #5
November 7- week #7cutting #6
November 12th, week #8 cutting #7
November 19th, week #9 cutting #8
November 26th, week #10 cutting #9
December 3rd, week #11 cutting #10
December 24th, week #14 cutting #13
January 9, week #16 cutting #15
March 30 - this would have been week 29……. Unfortunately, it is not.
I noticed the grass was growing exceptionally slow. Long story short Lawndale’s lawn maintenance company was mowing on a high setting.
I am starting over on counting weeks of emissions saved.
April 10th, week 1, not cutting the yard #1
Spring 2022
Symbiosis - where are the birds?
For several weeks I have noticed the neighborhood birds are not stopping into Symbiosis. I have asked the neighbors and they have noticed the birds were absent too. Today an article came out in the Houston chronicle, Songbirds Take a Break.
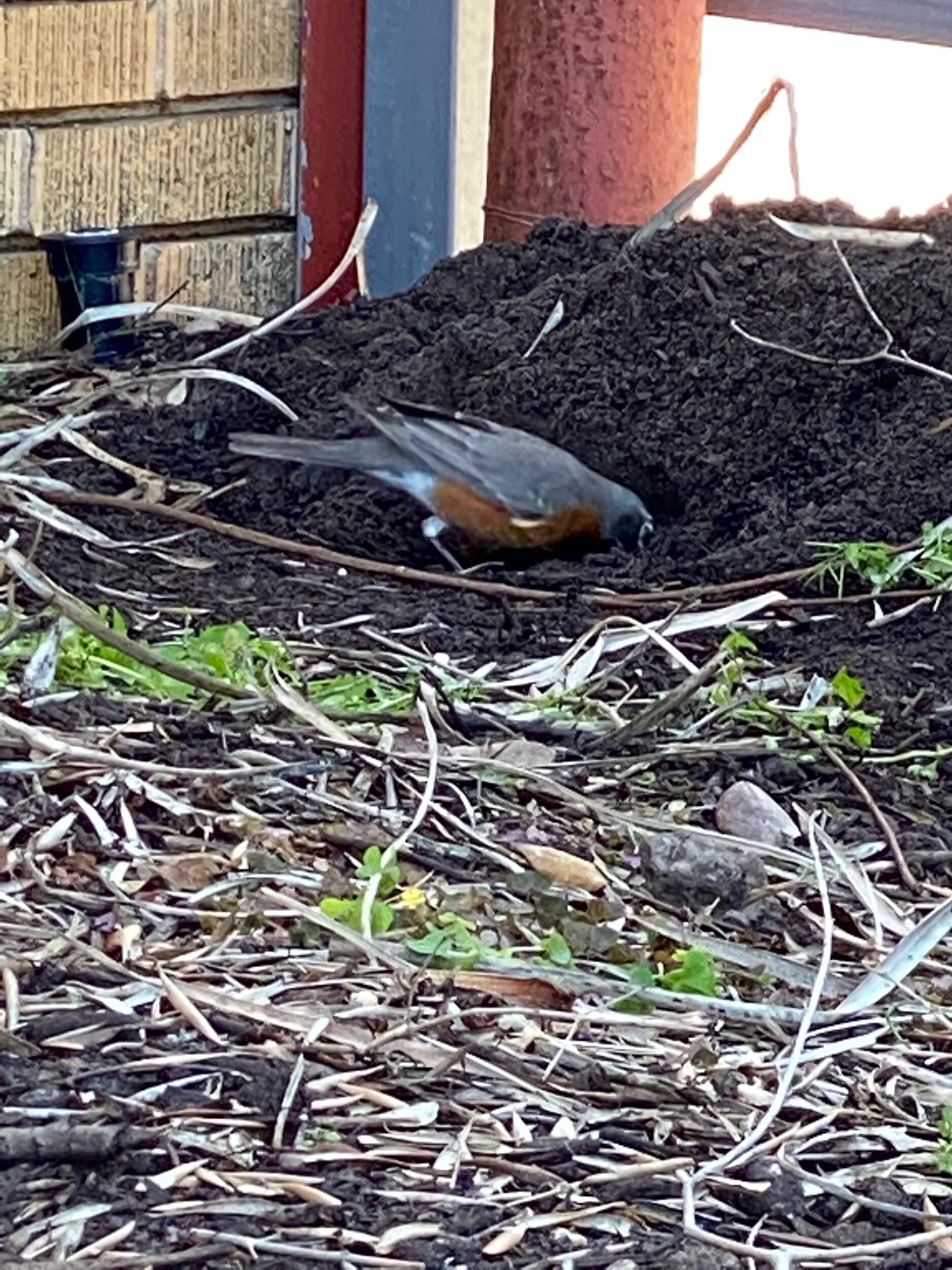
March 19th - first bird in garden. An Amerucan red robin foraging for insects, bugs, protein or seeds, poking it's beak into the newly installed living compost.
March 31, 2021 robin hunting for grubs as I install the American beautyberry.
April 9, 2021 robin on the oak stump. I installed rotting native tree stumps to give the birds a camouflaged lookout and hideout.
April 9, 2021 dove
May 22, 2021,
blue jay
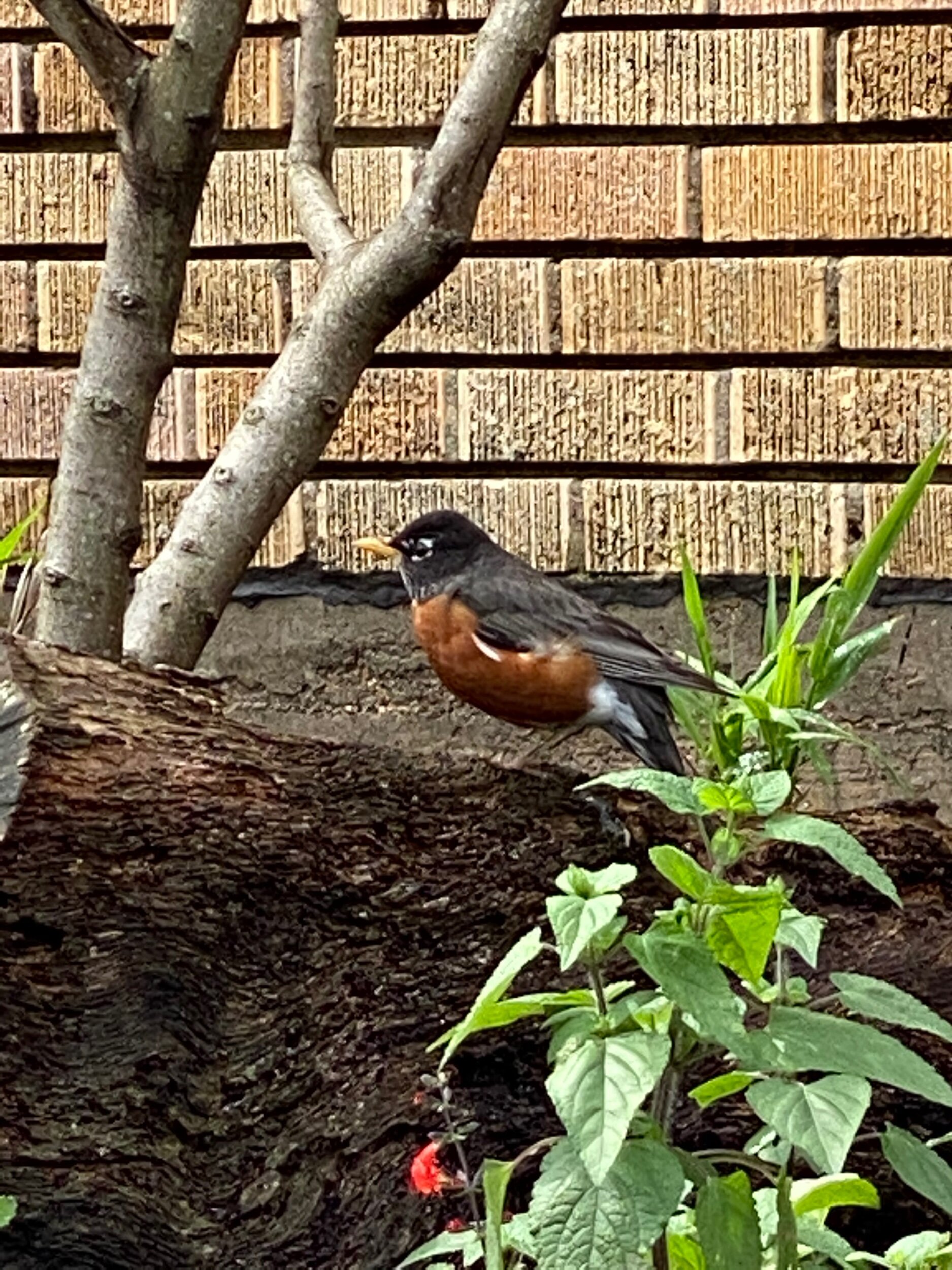
May 1, 2021 American red robin
June 19, 2021
June 22, 2021
Symbiosis- art activism
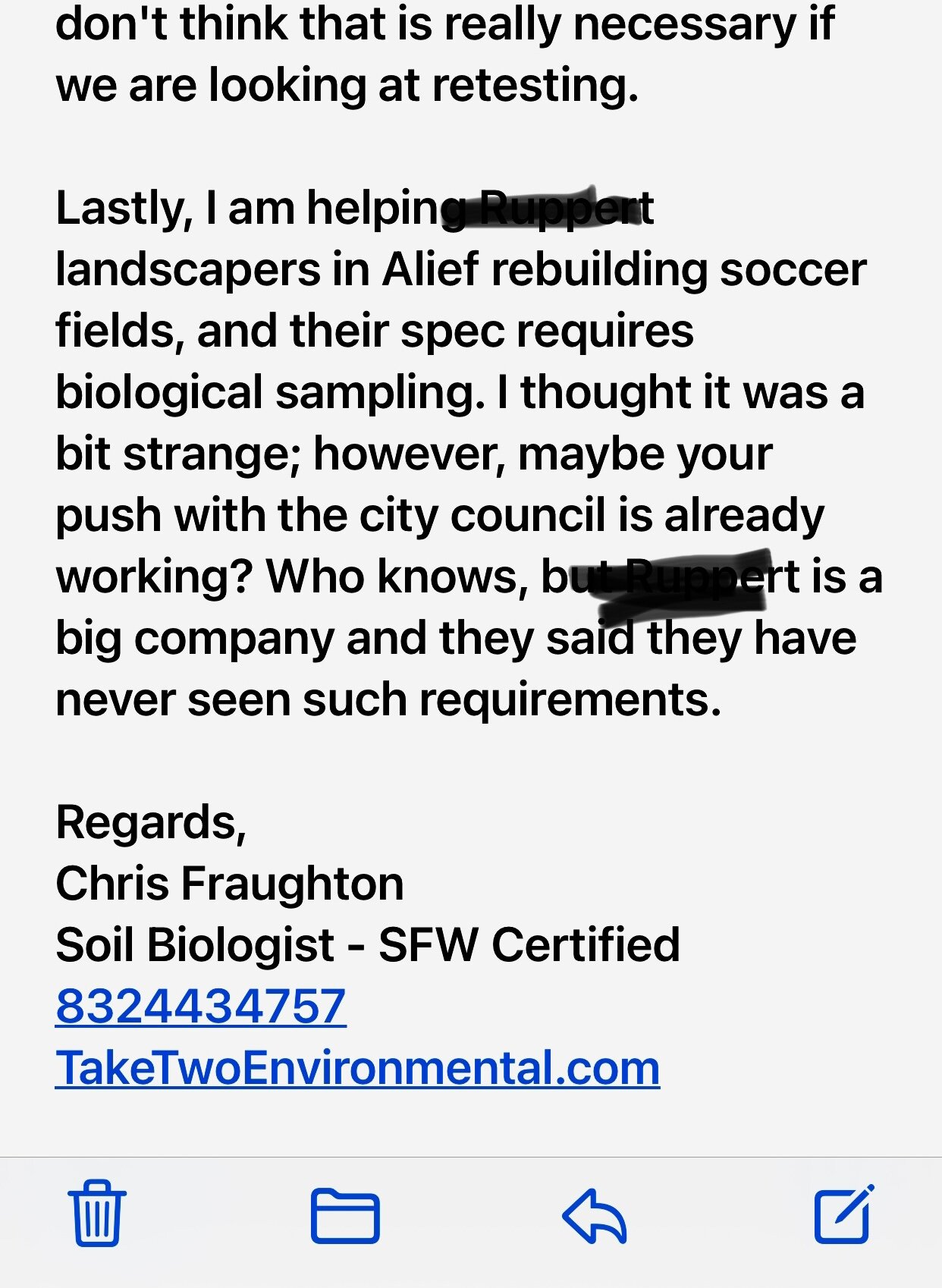
Can art activate change? It has in the past and global communication is easier than ever. I received the below email from Chris Mc Fraughton of Take Two environmental. :)
Chris was trained at Elain Ingram’s the Soil Food Web. He knows what he is doing.