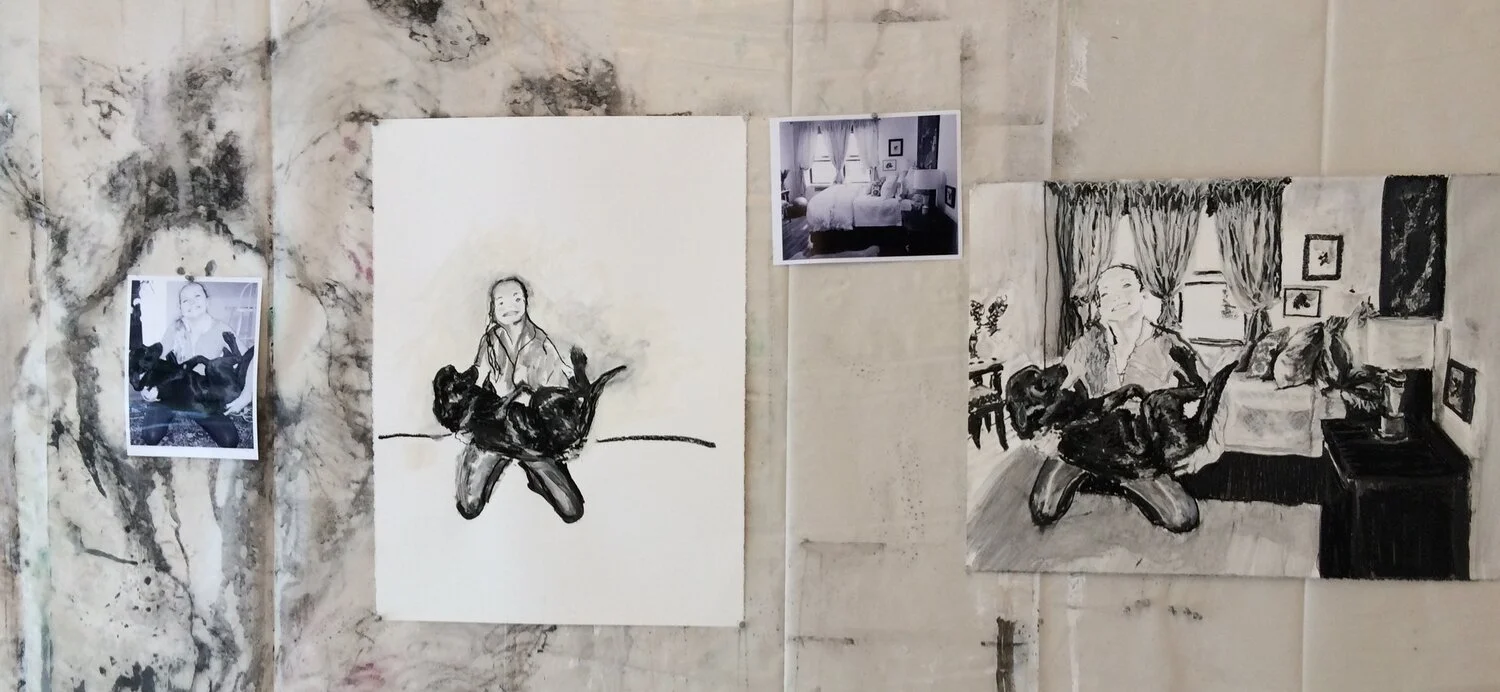
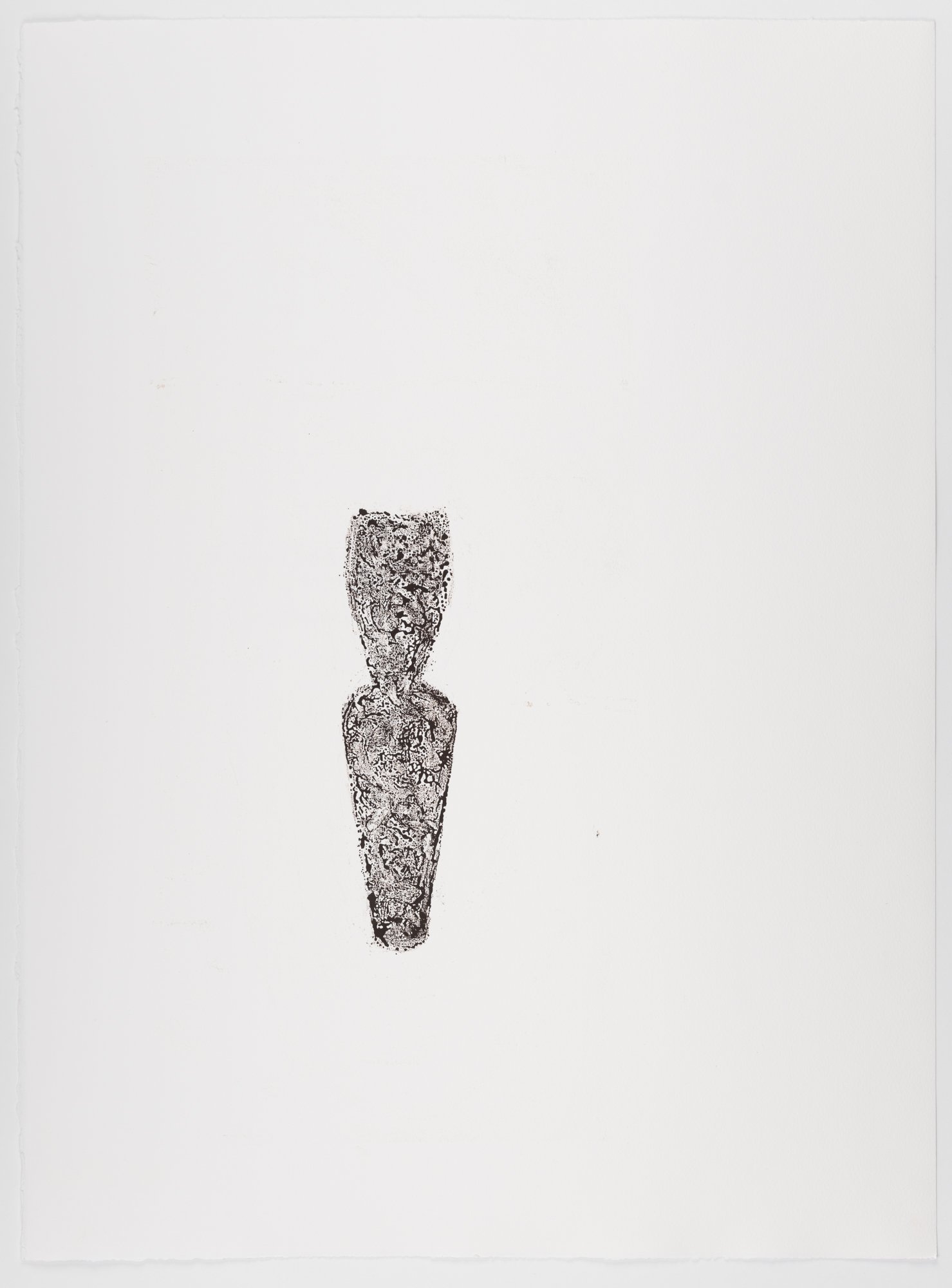
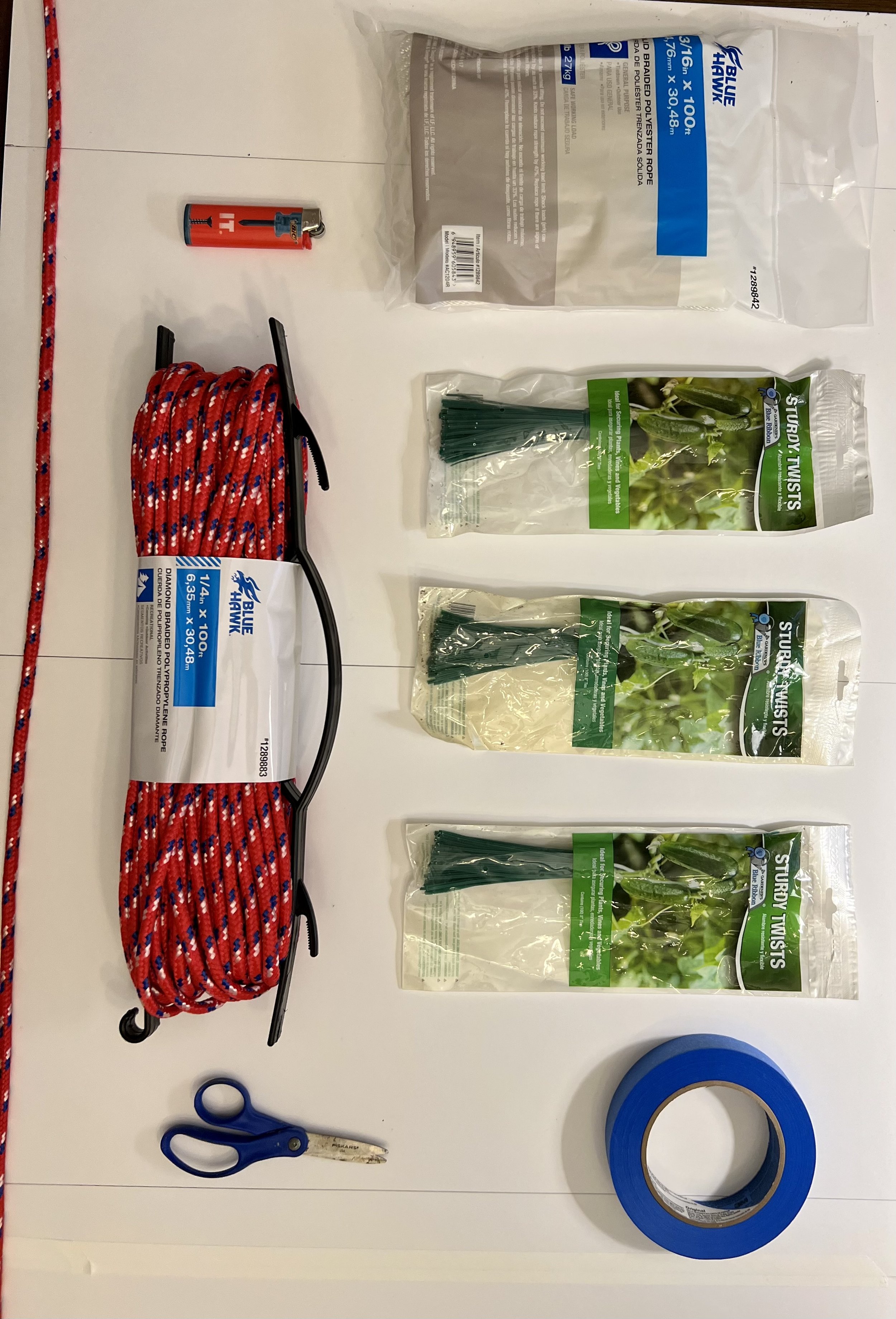
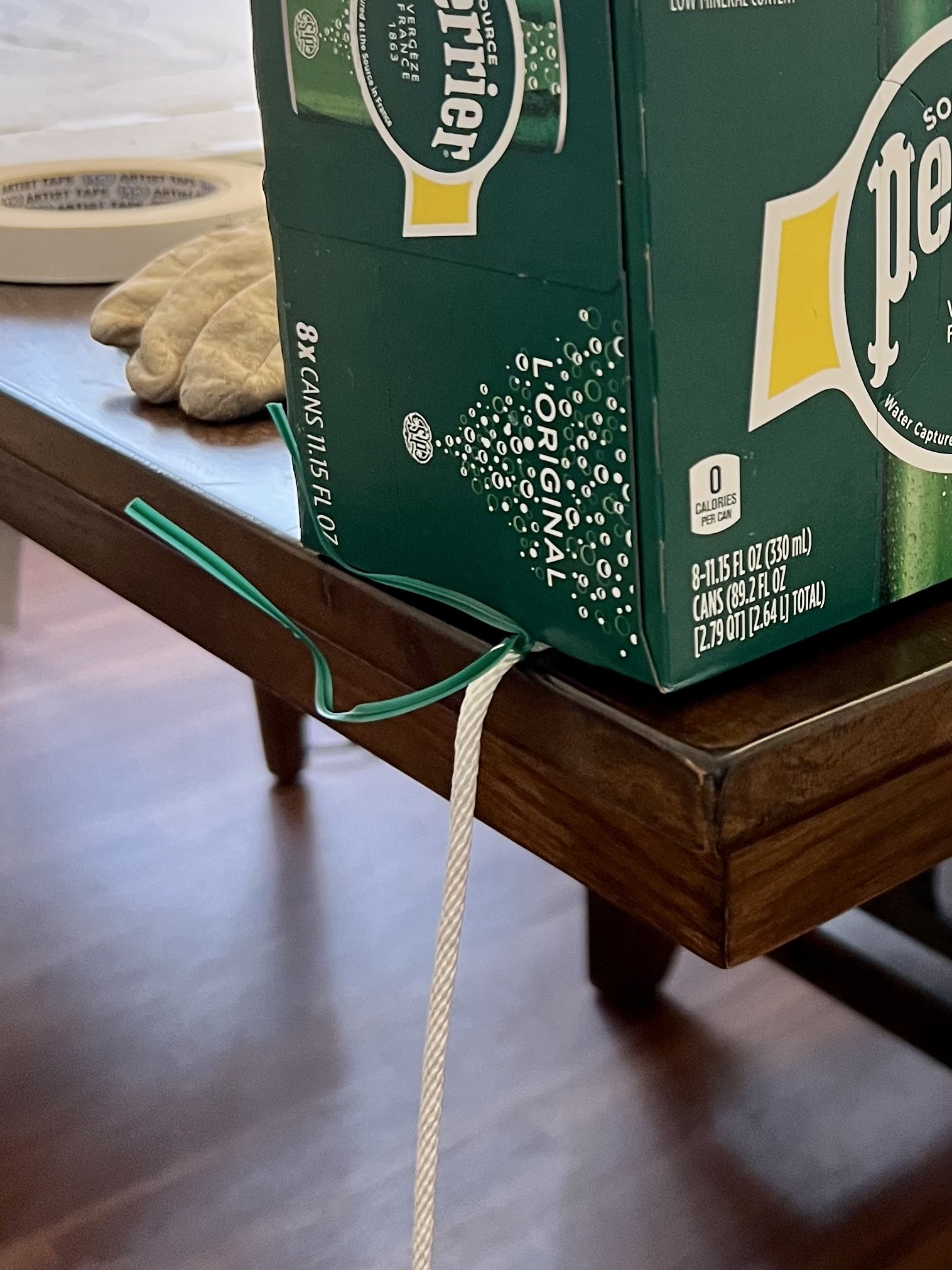
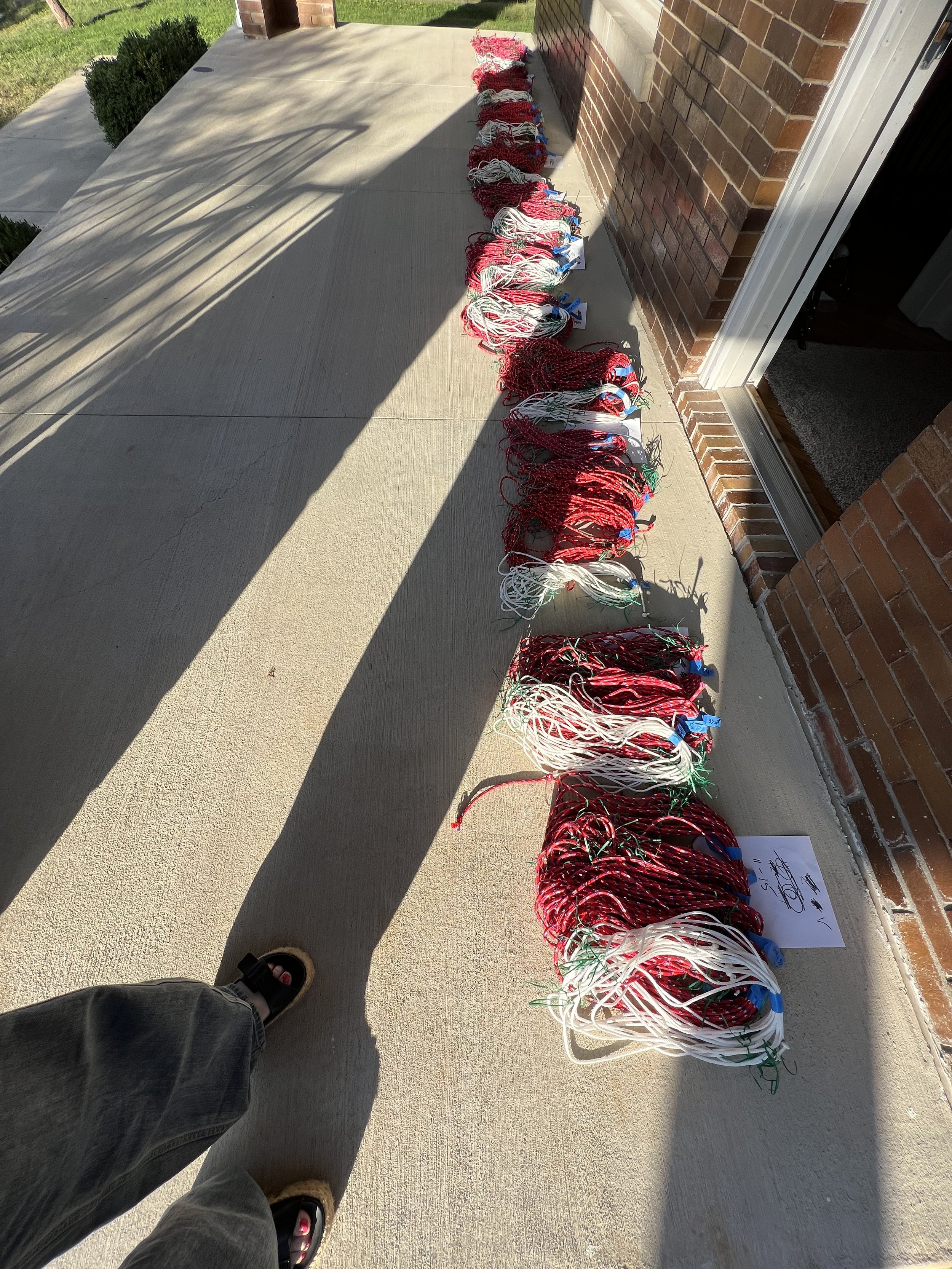
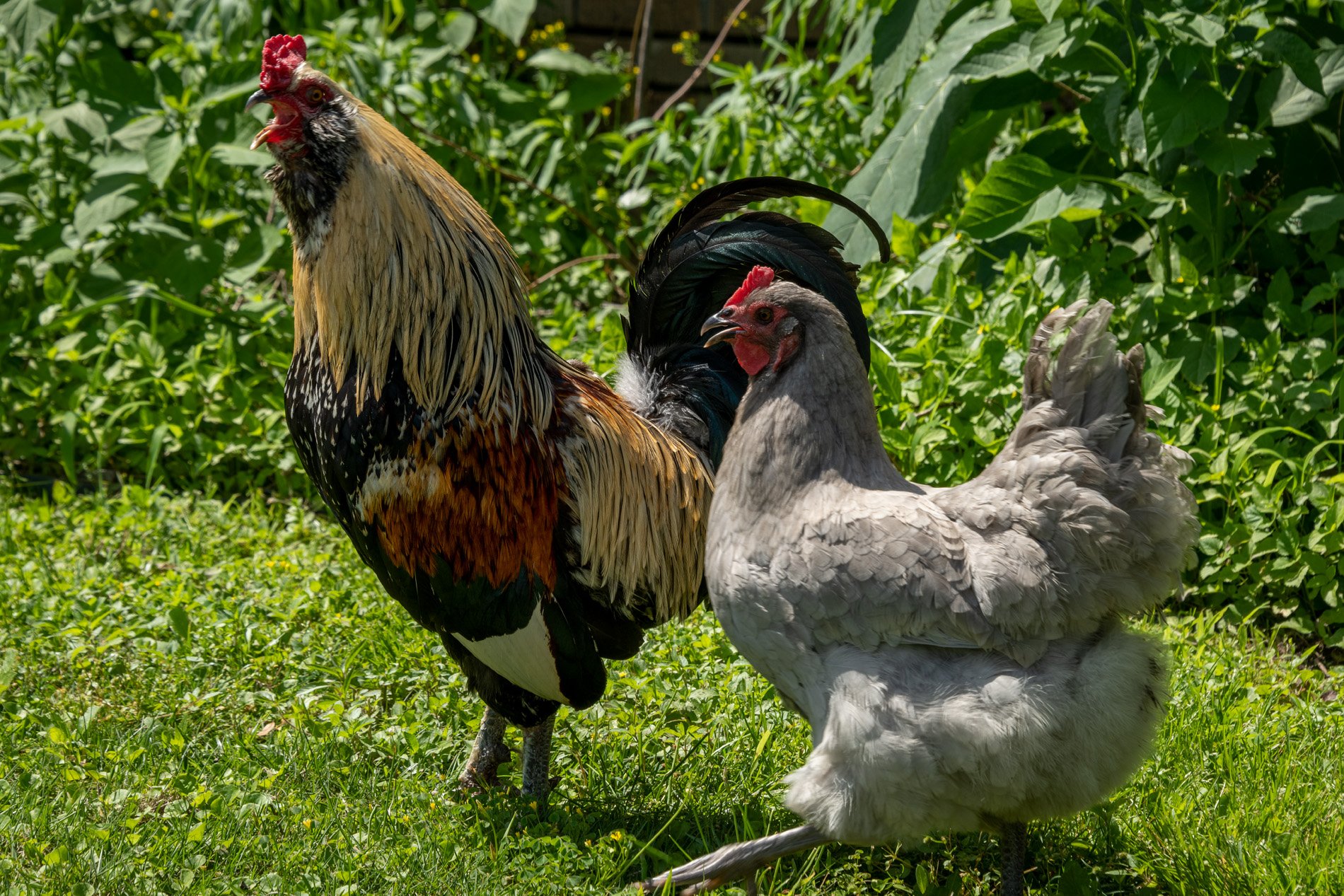
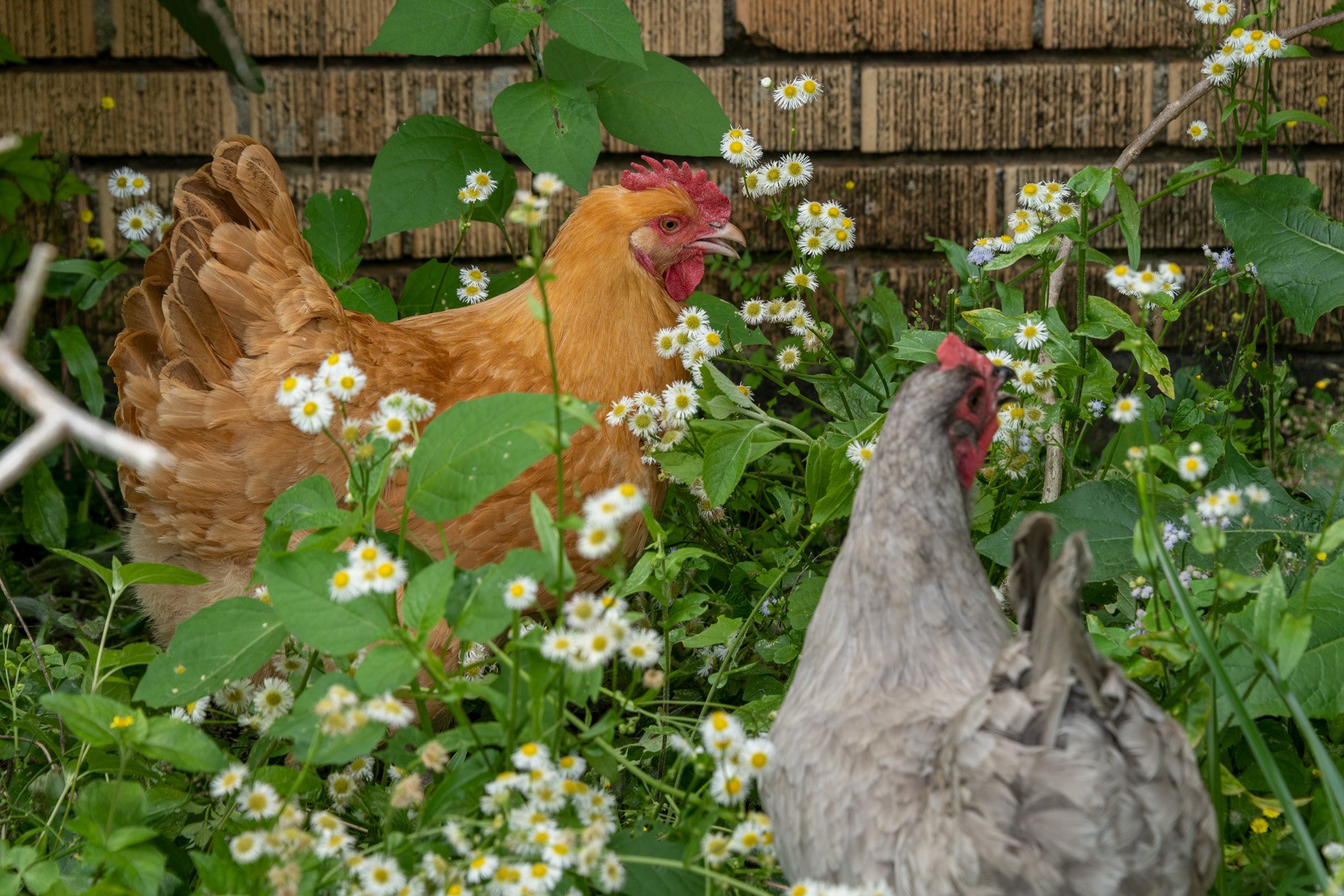
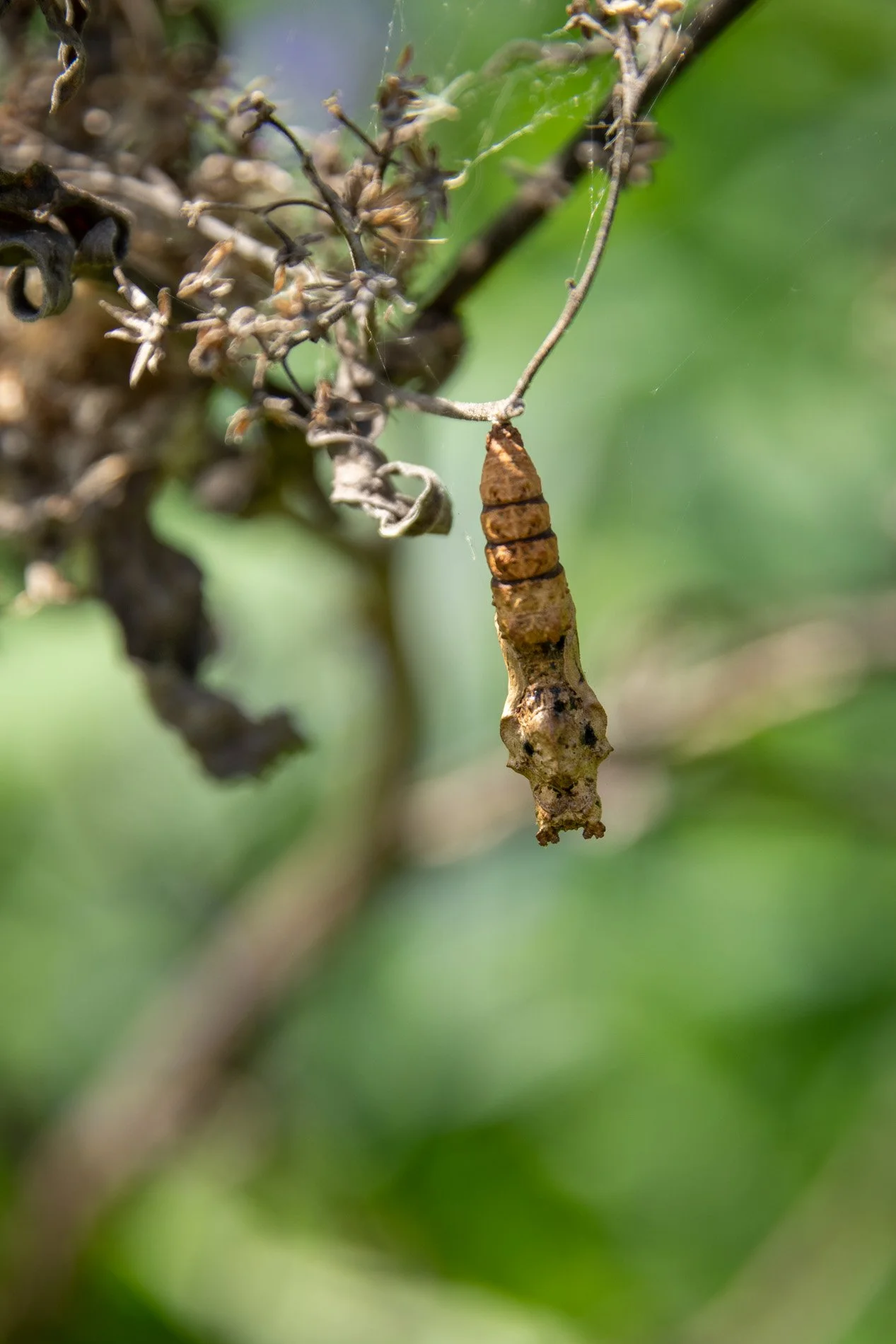
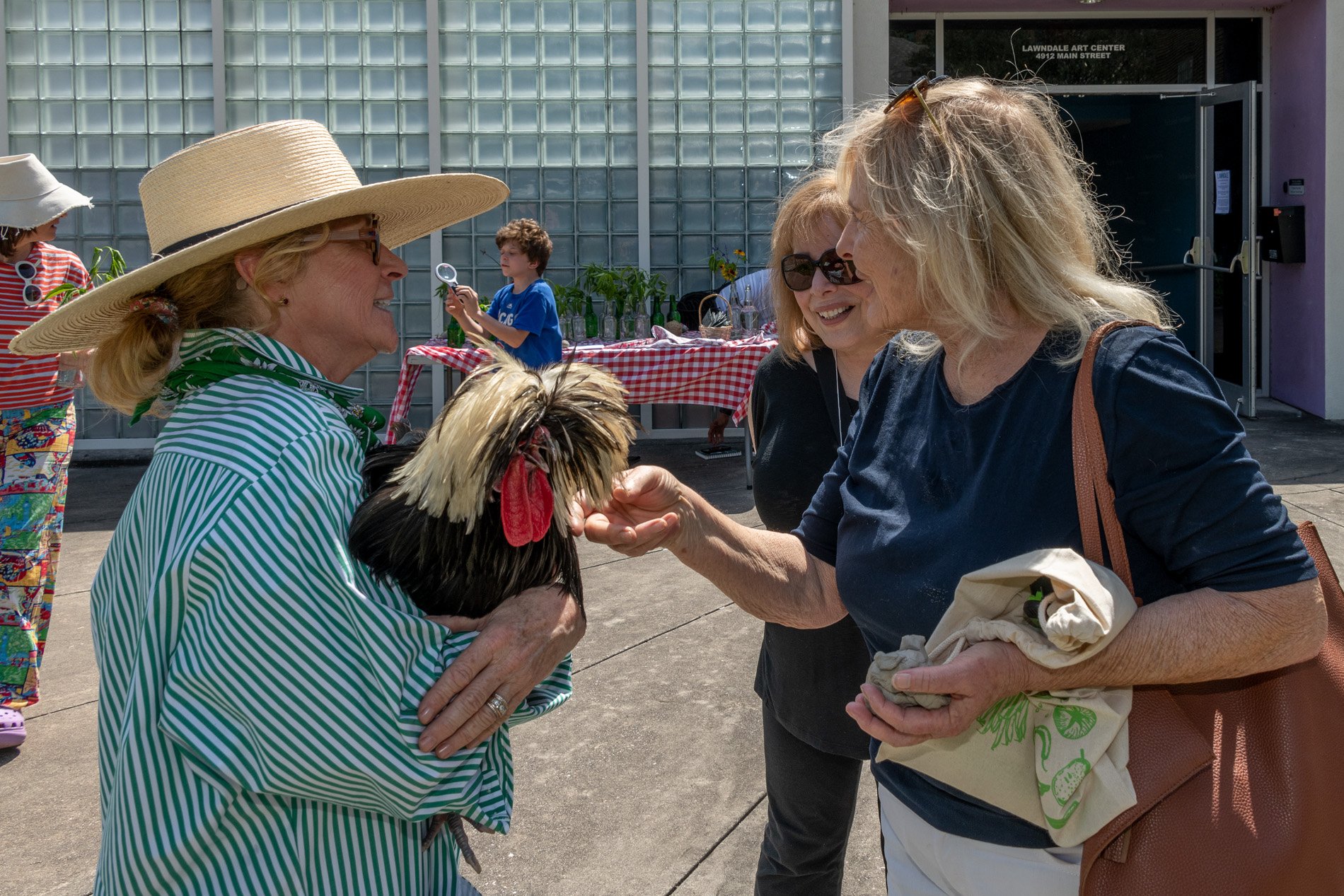
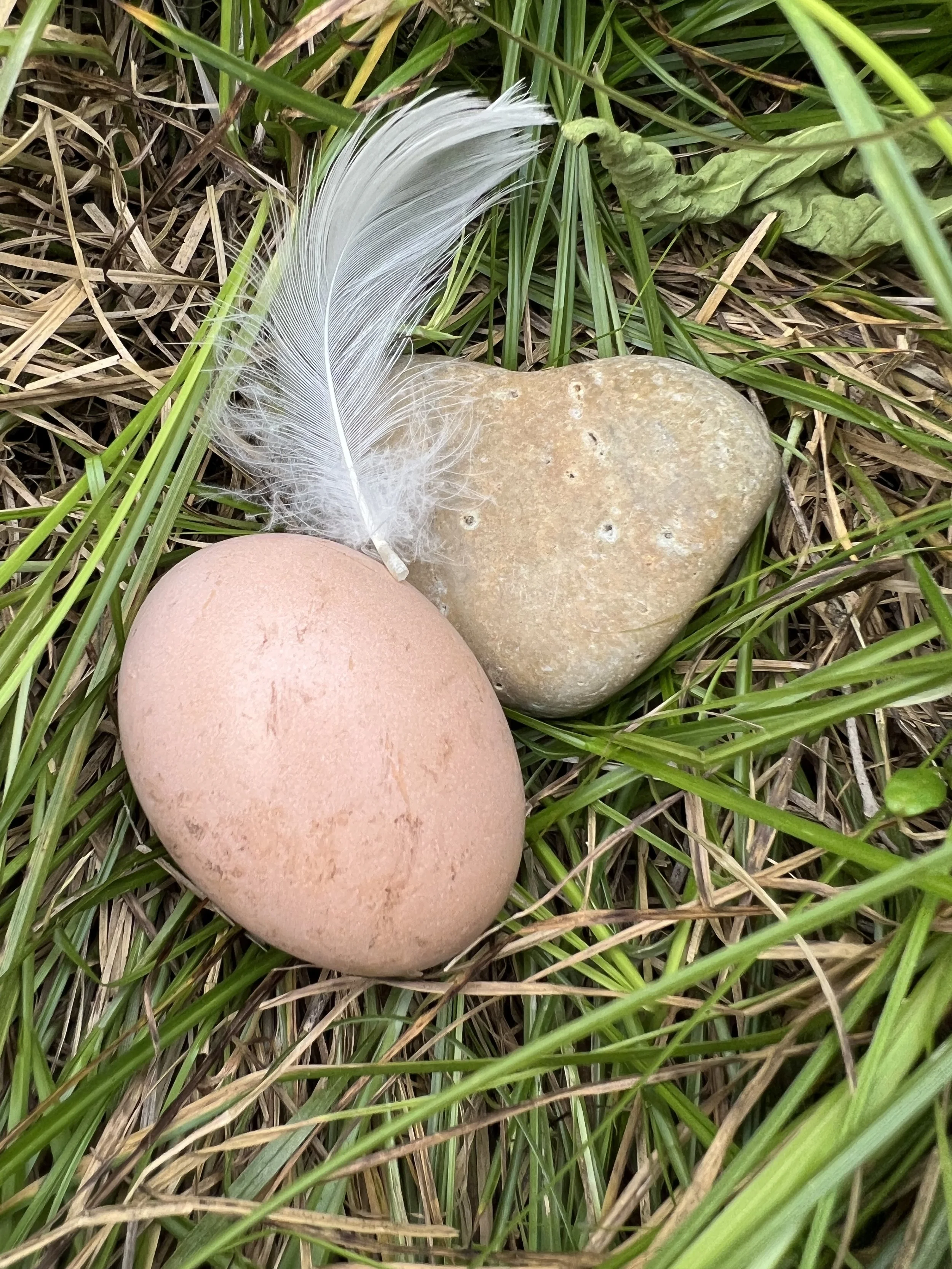
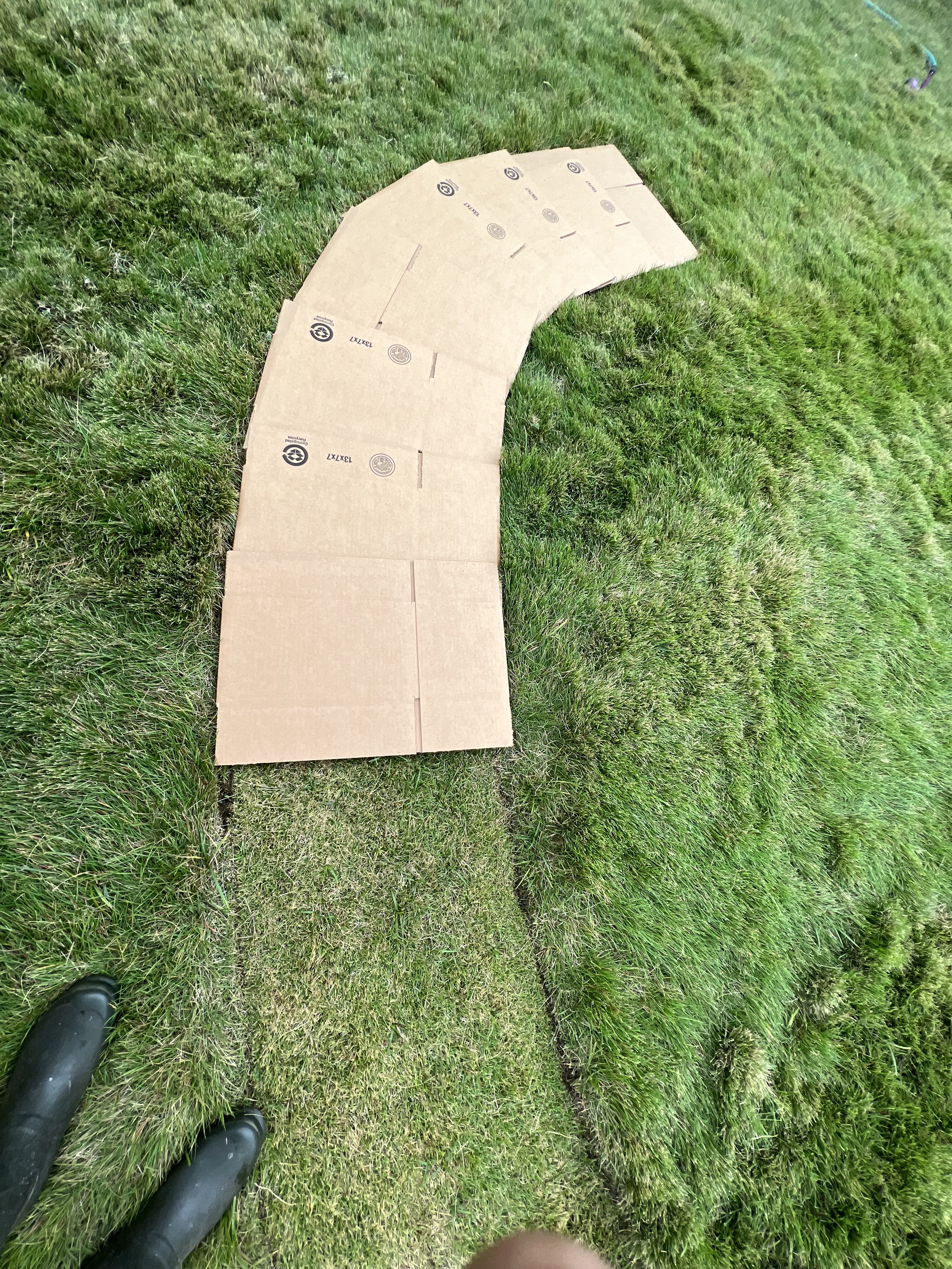
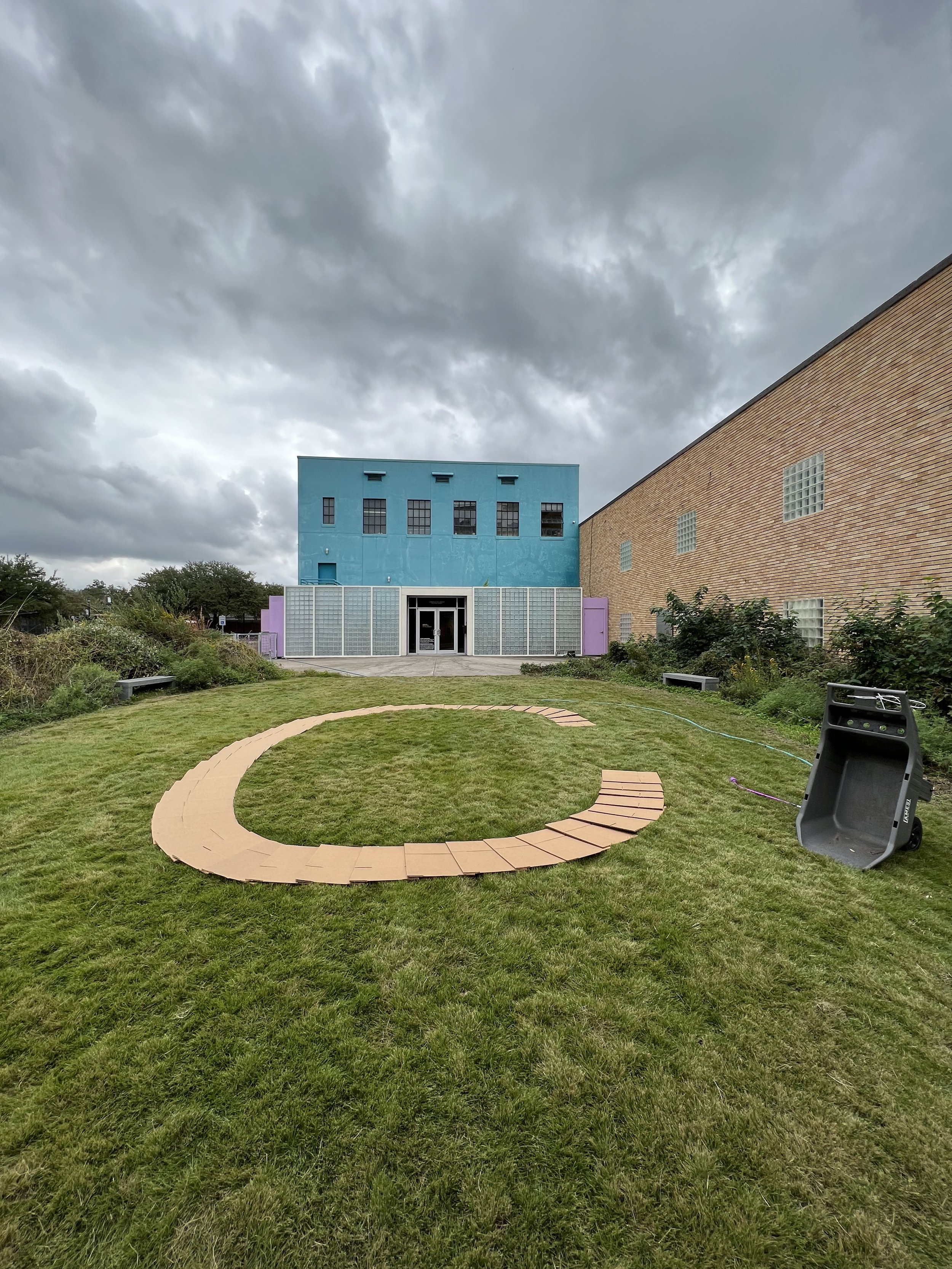
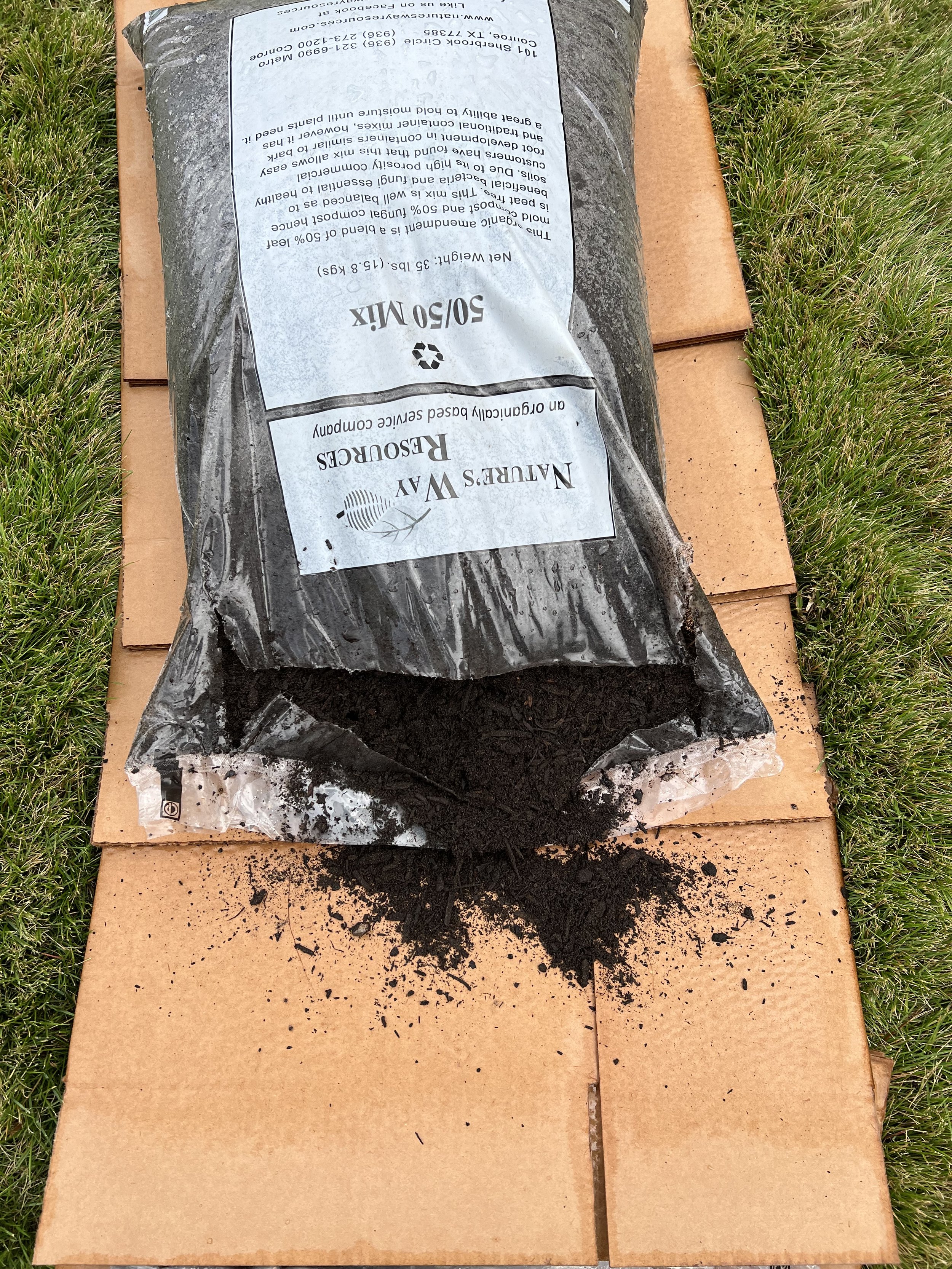
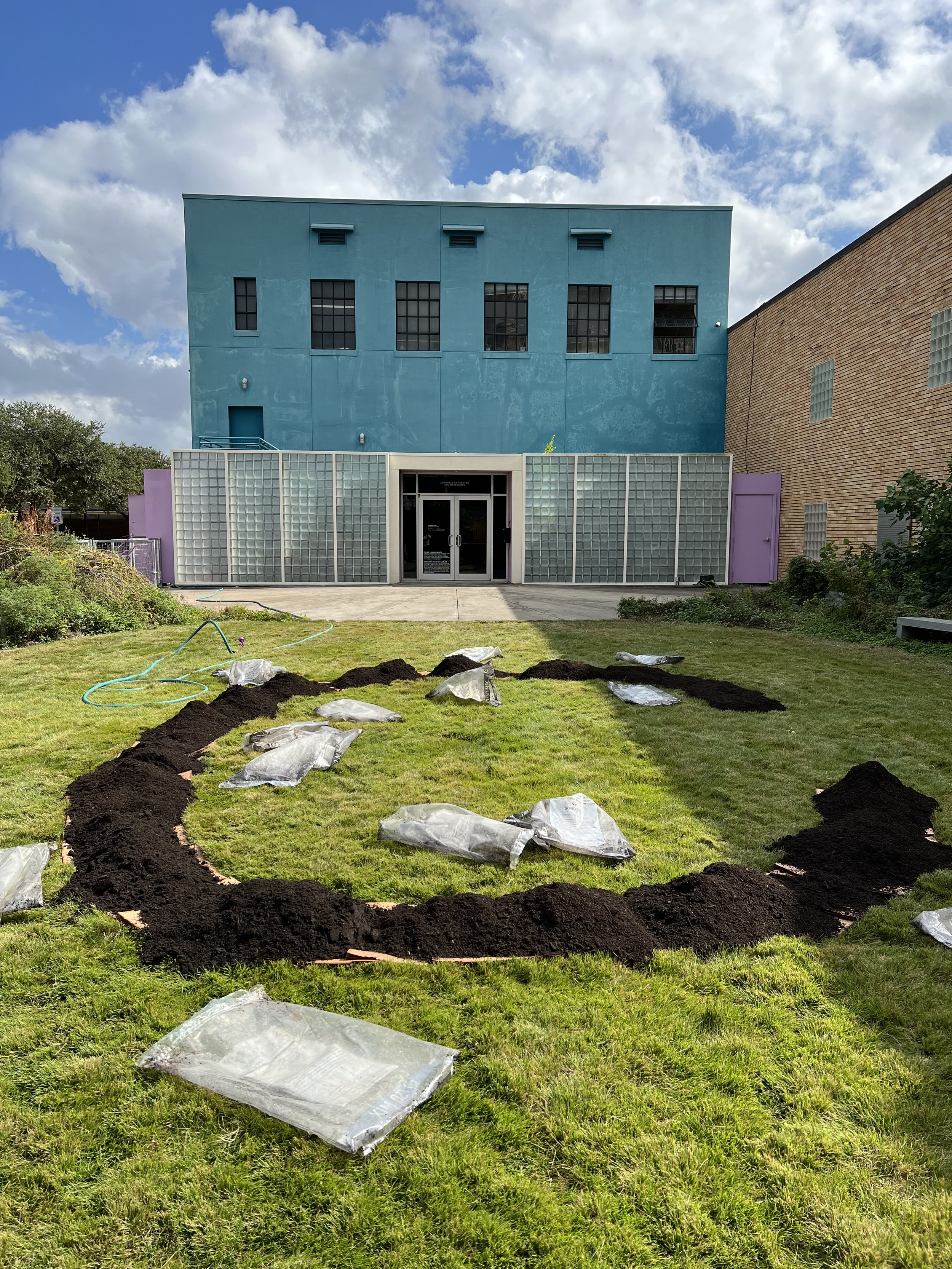
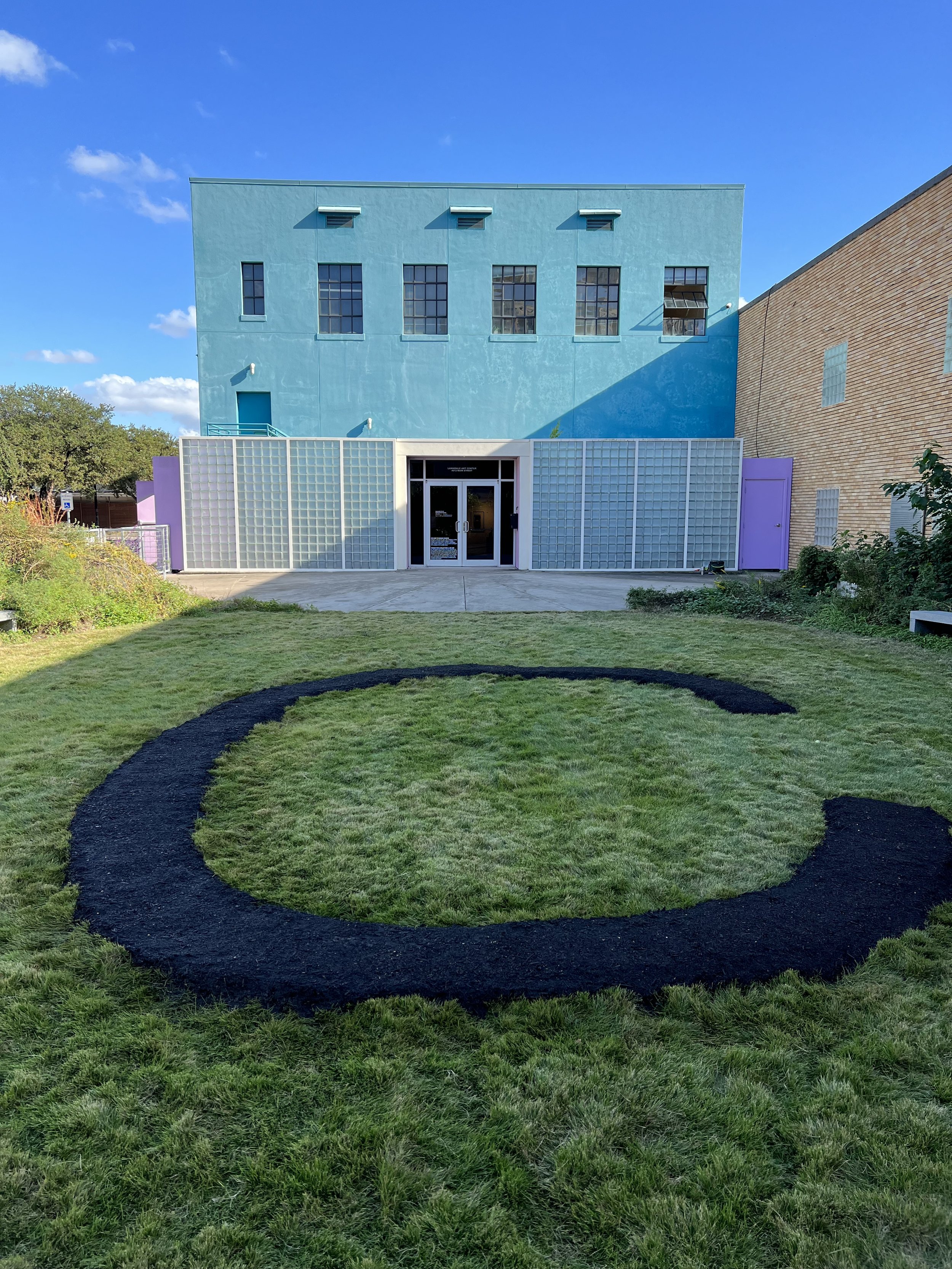
30” X 44” watercolor monotype.
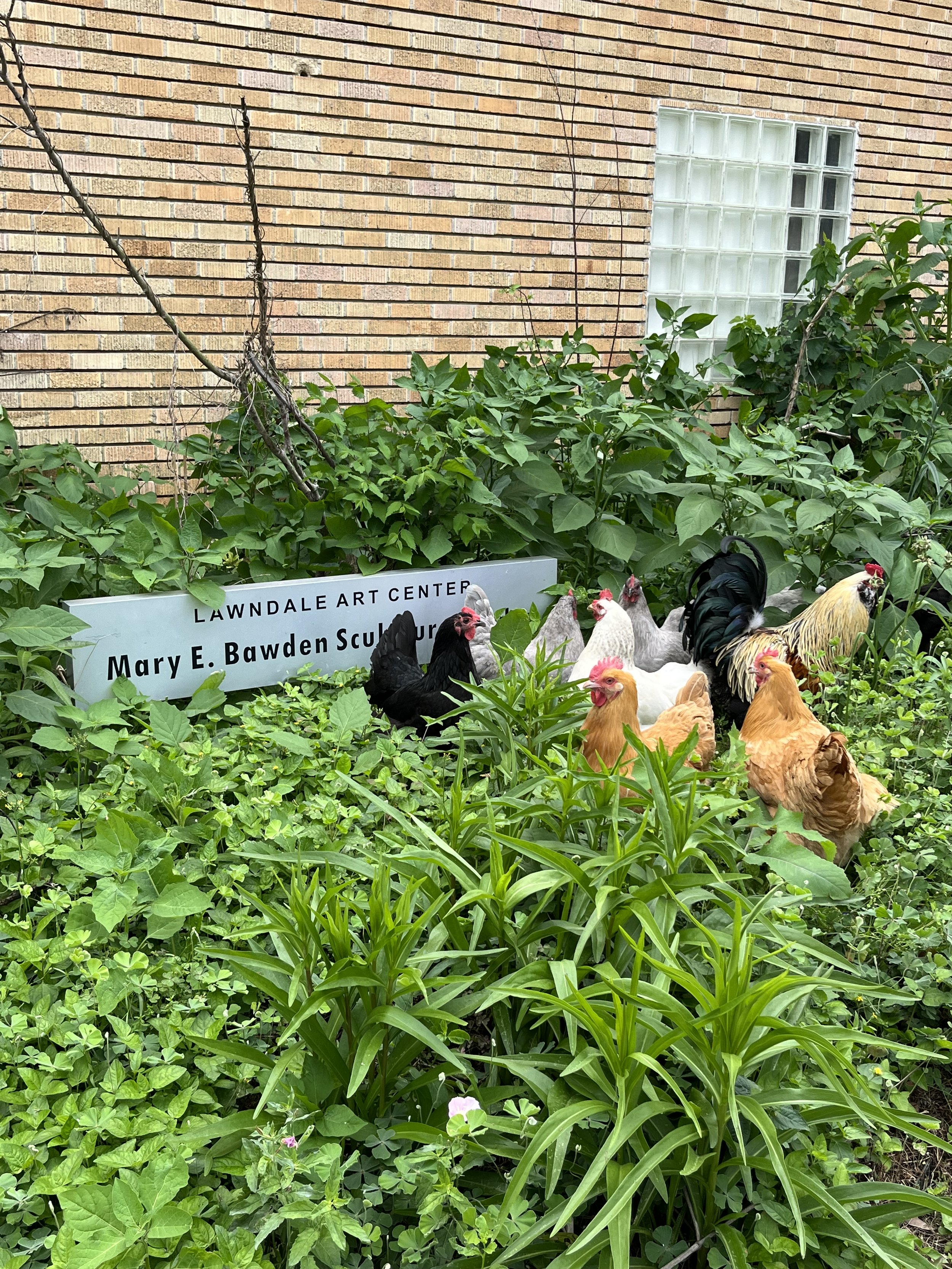
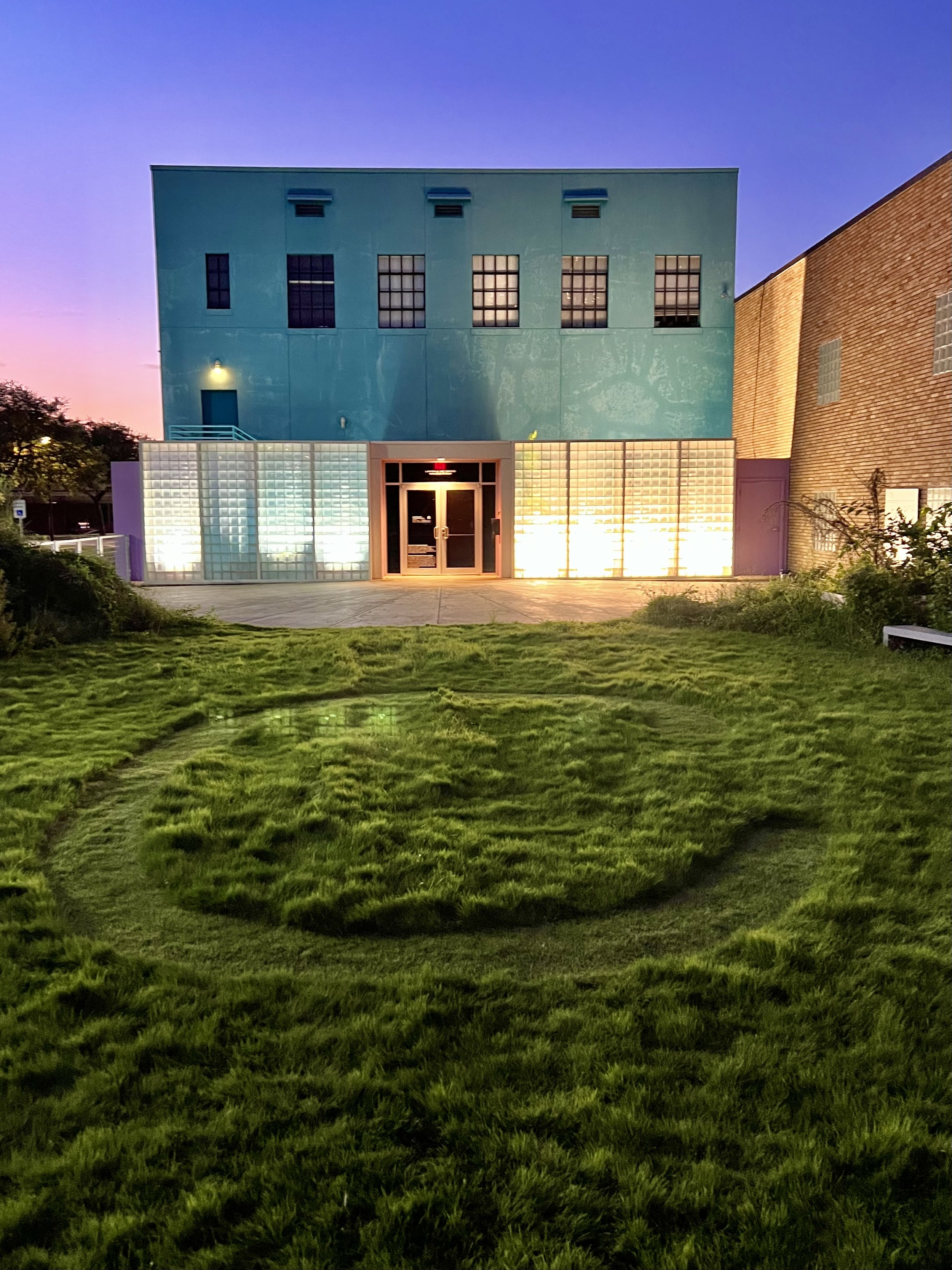
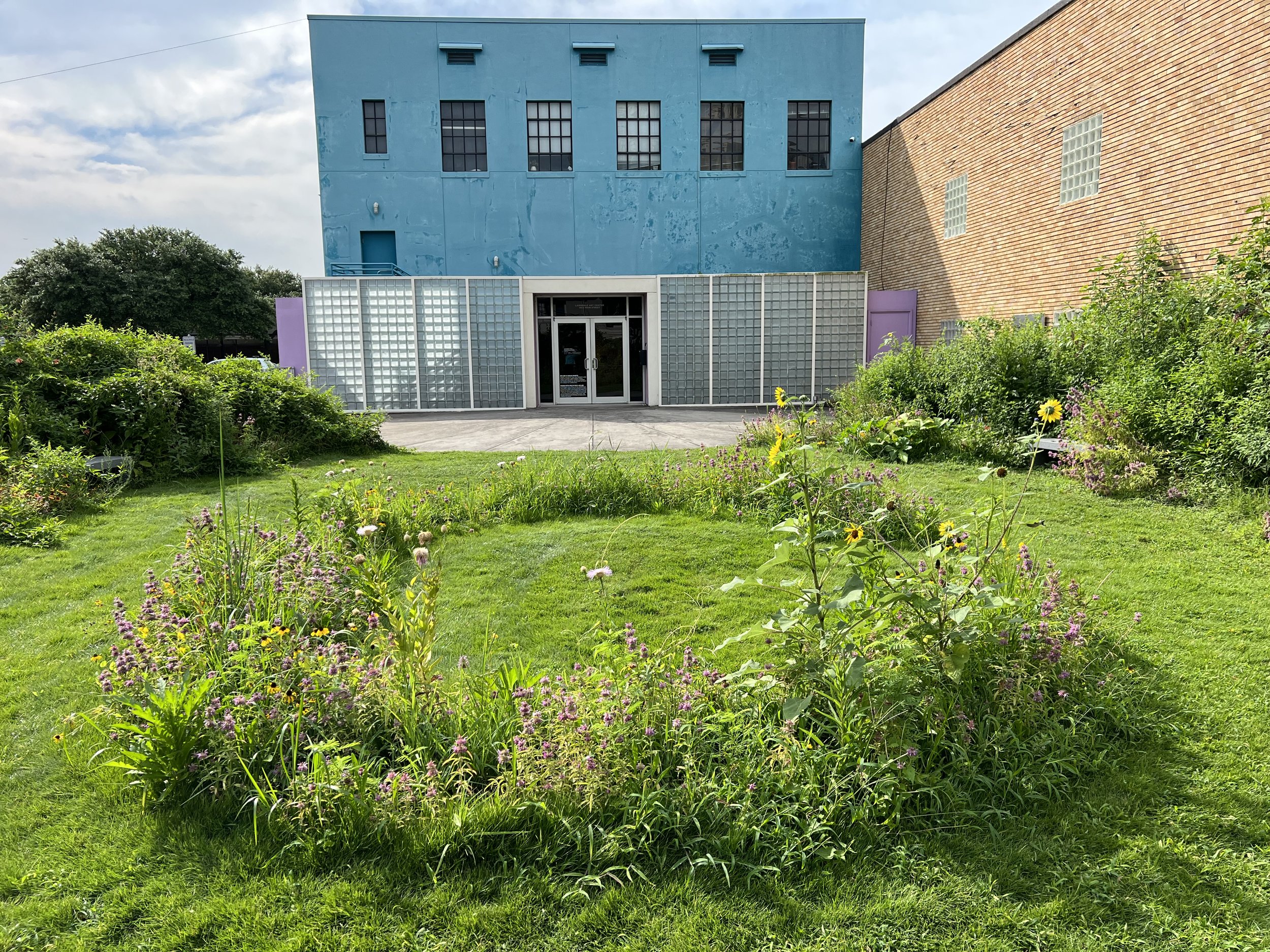
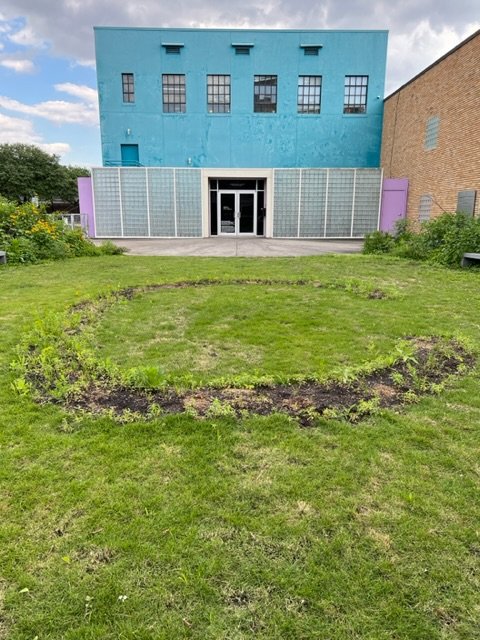
Exploring the beauty and artistry of urban rewilding is a central theme in my current living sculpture installation, Sequel. A key design element of Sequel is the mutual respect and reciprocity that value nature and all its inhabitants.
True beauty is derived from a respect for the environment and an understanding that humans are part of a larger, interconnected web of life which is not determined by the manicured and organized plantings on the site.
Part of my daily art practices is noticing the small changes as the seasons unfold. As volunteer plants rise above the ground I don’t reach for a herbicide I research the plant through multiple sources. Then I search for how the plant supports the Gulf Coast Ecosystem and the needs of permanent and migrating wildlife.
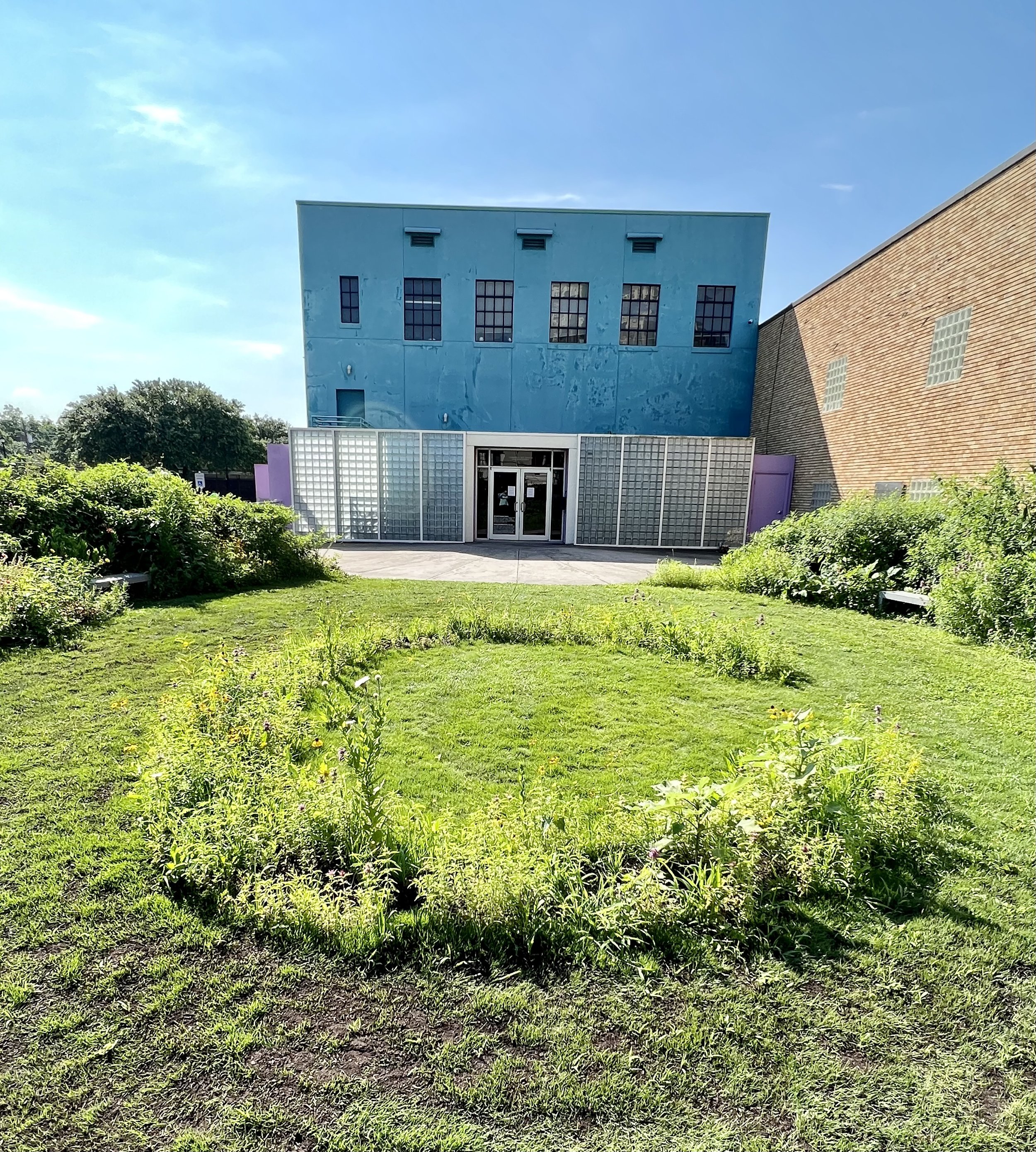
With longer days we humans are starting to clean up our outdoor spaces. By traditional values an unsightly spider web on the wall would be swept away. Dandelions and other tall skinny volunteer plants would be poisoned providing neatly groomed manicured lawns.
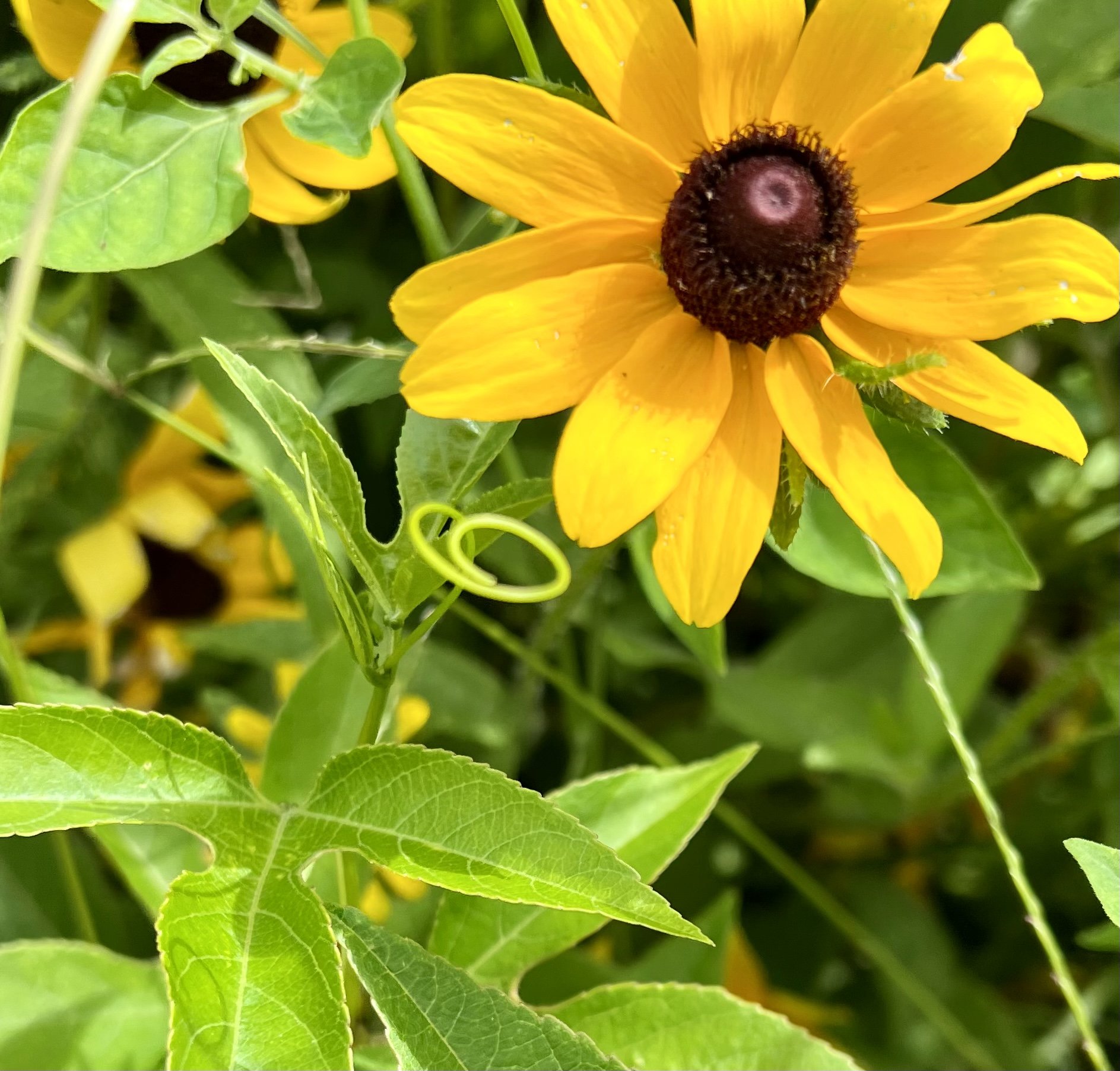
In Sequel I consider the longer days of spring summon the migrating humming birds and they too have needs that might surprise you. Over the years through research I've discovered that these tiny avian wonders greatly benefit from less manicured environments within our cities. Unfortunately, hummingbirds, which typically grace our urban areas from mid-March to mid-May, are on the decline. However, by allowing our urban landscapes to remain a bit "messy" and imperfect, we can support their numbers.
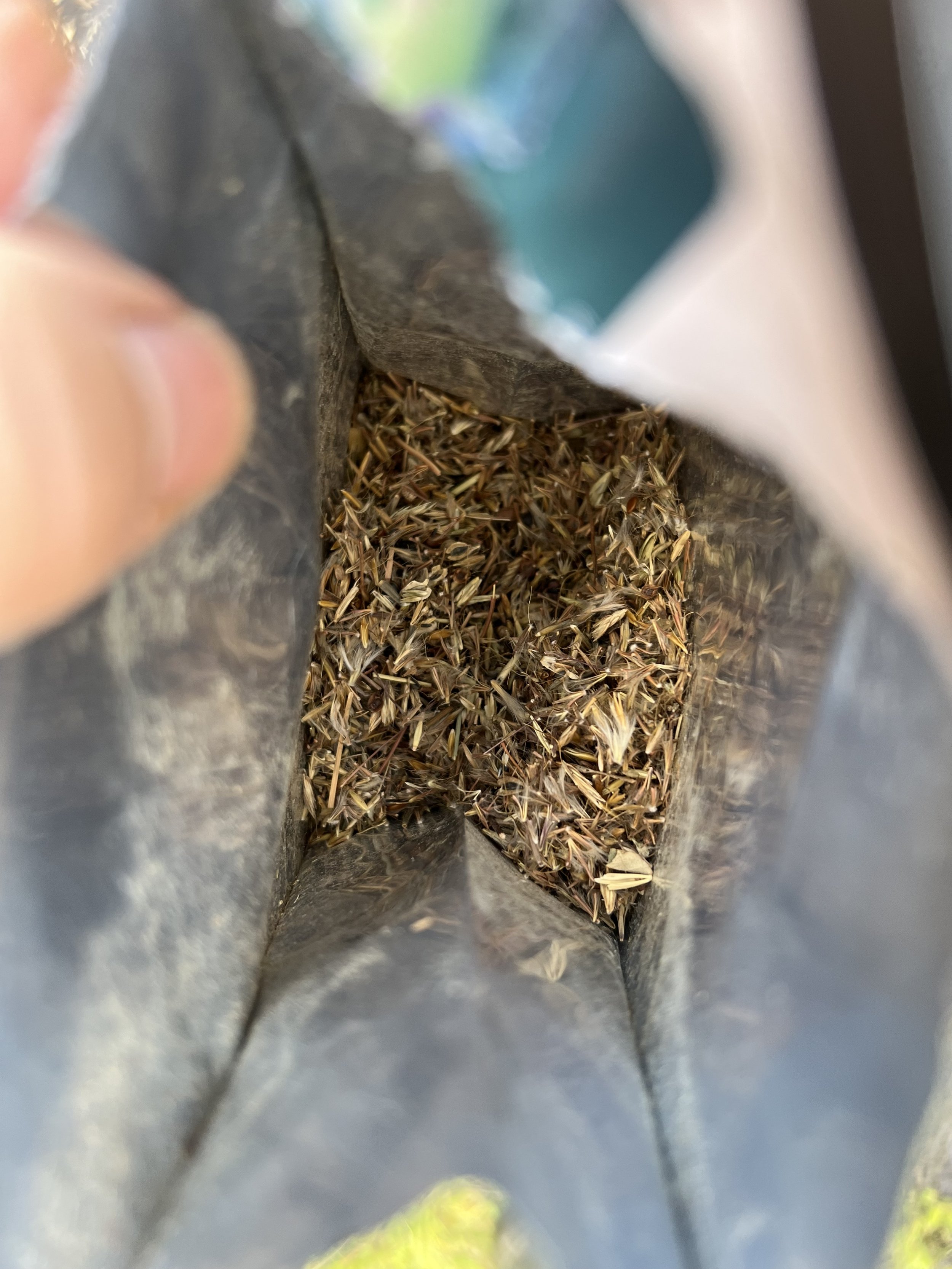
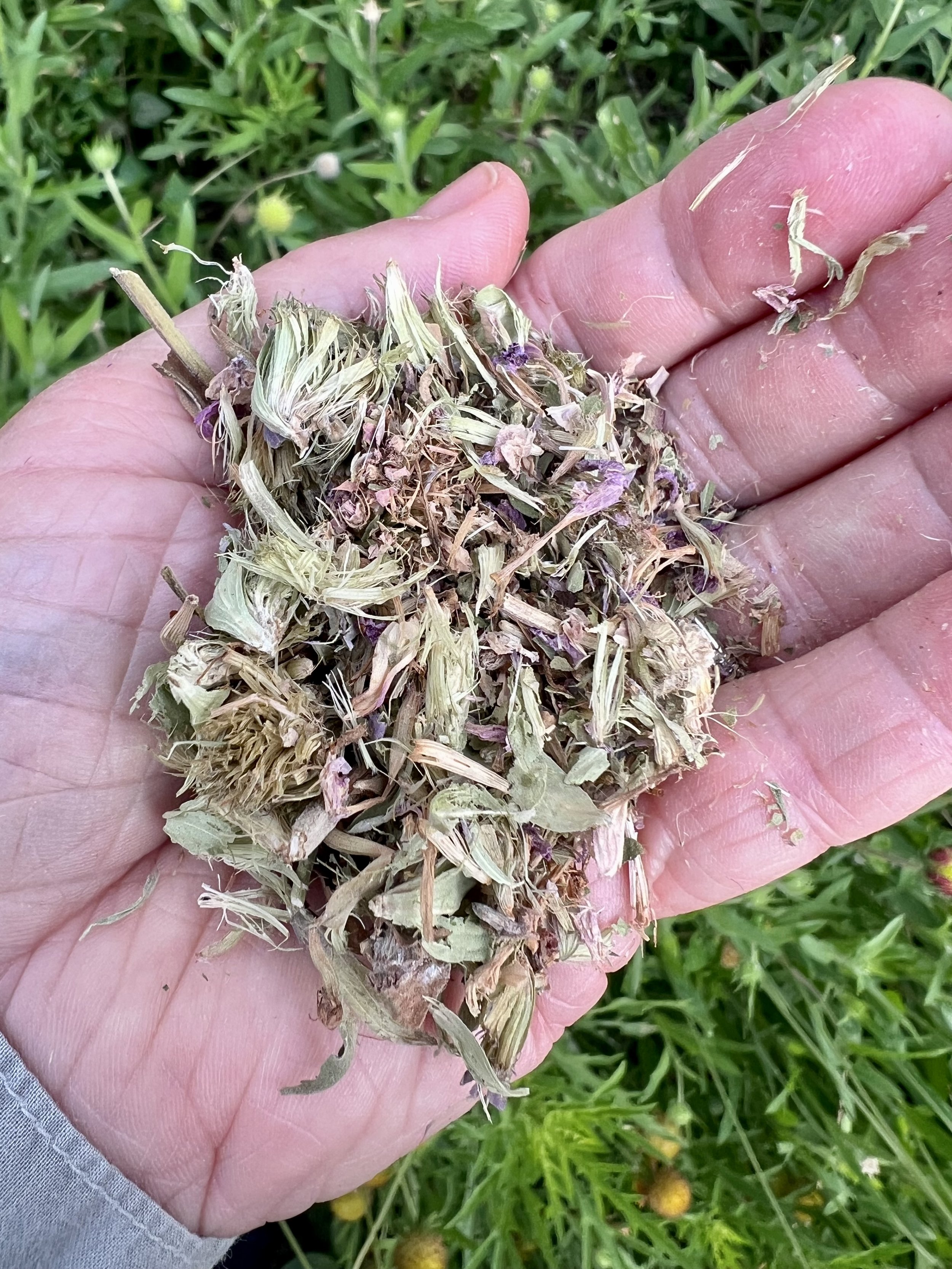
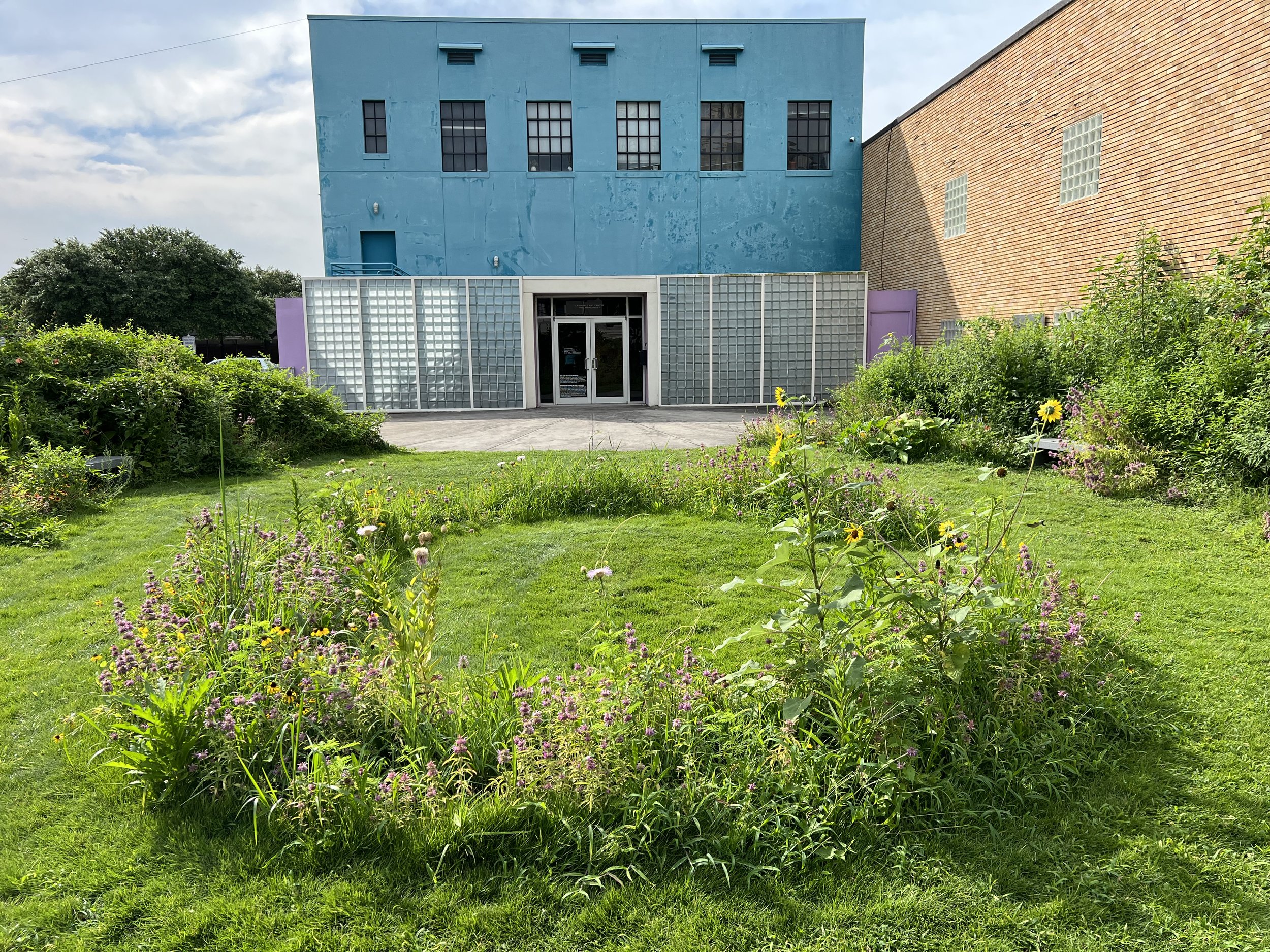
The benefits hummingbirds gain from such environments are substantial. As they prepare for nesting, they require unique materials for constructing their nests—materials often found only in less controlled, more natural settings. I find it fascinating how hummingbirds gather spider silk, dandelion puffs, thistle down, lichens, and moss. These elements help them create nests that are functional and aesthetically exemplify nature's perfect balance. These materials provide the necessary strength and structure for nest building, a critical aspect of their survival.
I believe buzzing hummingbirds swooping in and out of Sequel would be an incredibly beautiful addition to the installation. To support hummingbirds I've come to realize there are several practical actions we can all take as urban residents:
1. Allow dandelions and thistles to grow naturally. By avoiding mowing or spraying herbicides on them, we're providing the soft materials hummingbirds need for their nests.
2. Resist the urge to sweep away spider webs. Instead, let's recognize these webs as vital resources for nest building.
3. Appreciate the natural beauty of lichens and mossesand air pkants. Removing them disrupts their essential role in the ecological landscape that hummingbirds depend on.
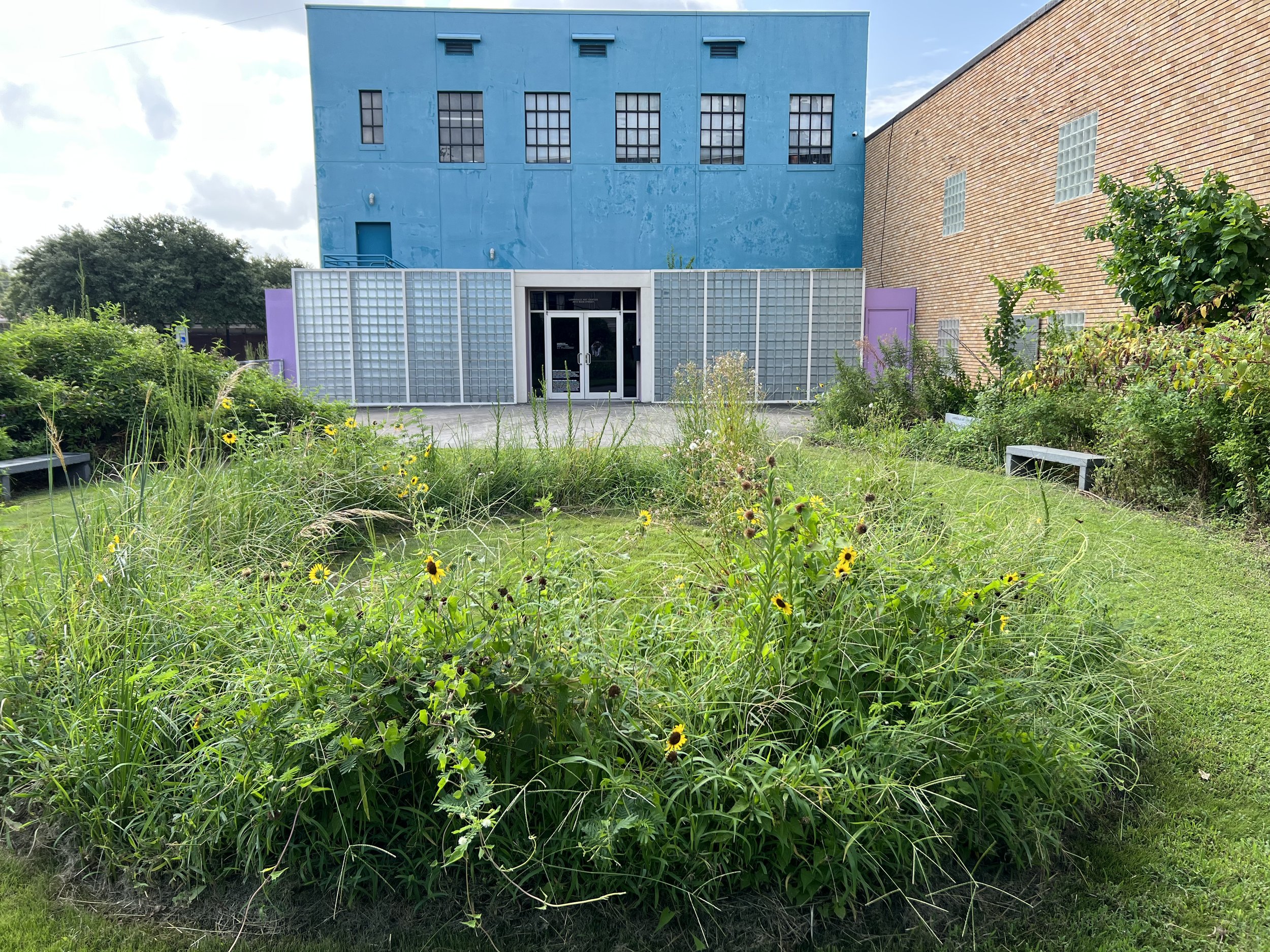
My journey as an eco-artist has deepened my personal connection to hummingbirds, revealing how these incredible creatures can add magic to our backyards, fostering a sense of wonder and connection to the natural world. By recognizing and valuing seemingly minor aspects of urban nature—like dandelions, spider webs, lichens, and moss—we can significantly contribute to the survival and flourishing of hummingbirds. This approach not only aids these delicate creatures but also highlights the intricate balance and resilience inherent in nature.
In balancing the aesthetics of urban landscapes with the ecological needs of hummingbirds, I envision cities that embrace natural elements rather than suppress them. This perspective encourages a harmonious coexistence between urban development and the ecological needs of wildlife, creating urban environments that are not only visually appealing but also ecologically supportive. The presence of hummingbirds in such settings becomes a testament to nature's resilience and the potential for urban spaces to contribute positively to biodiversity