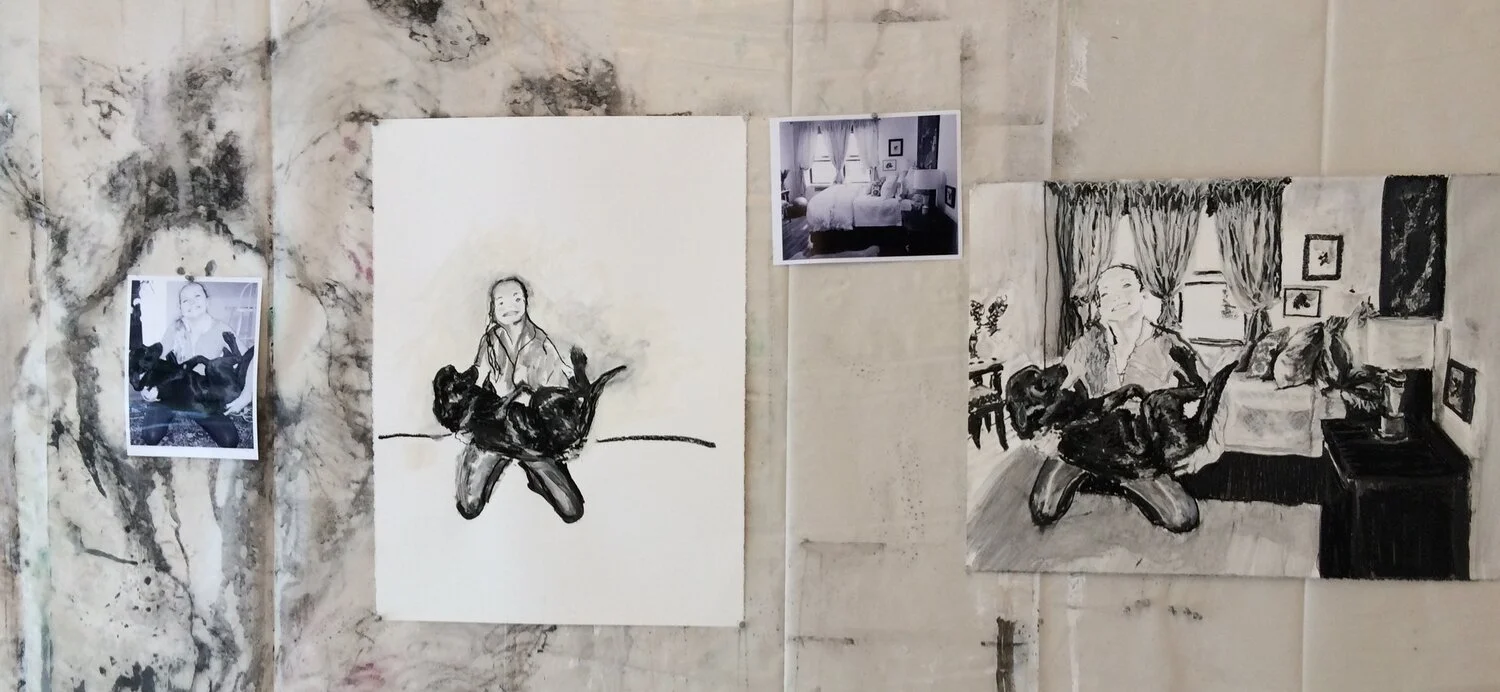
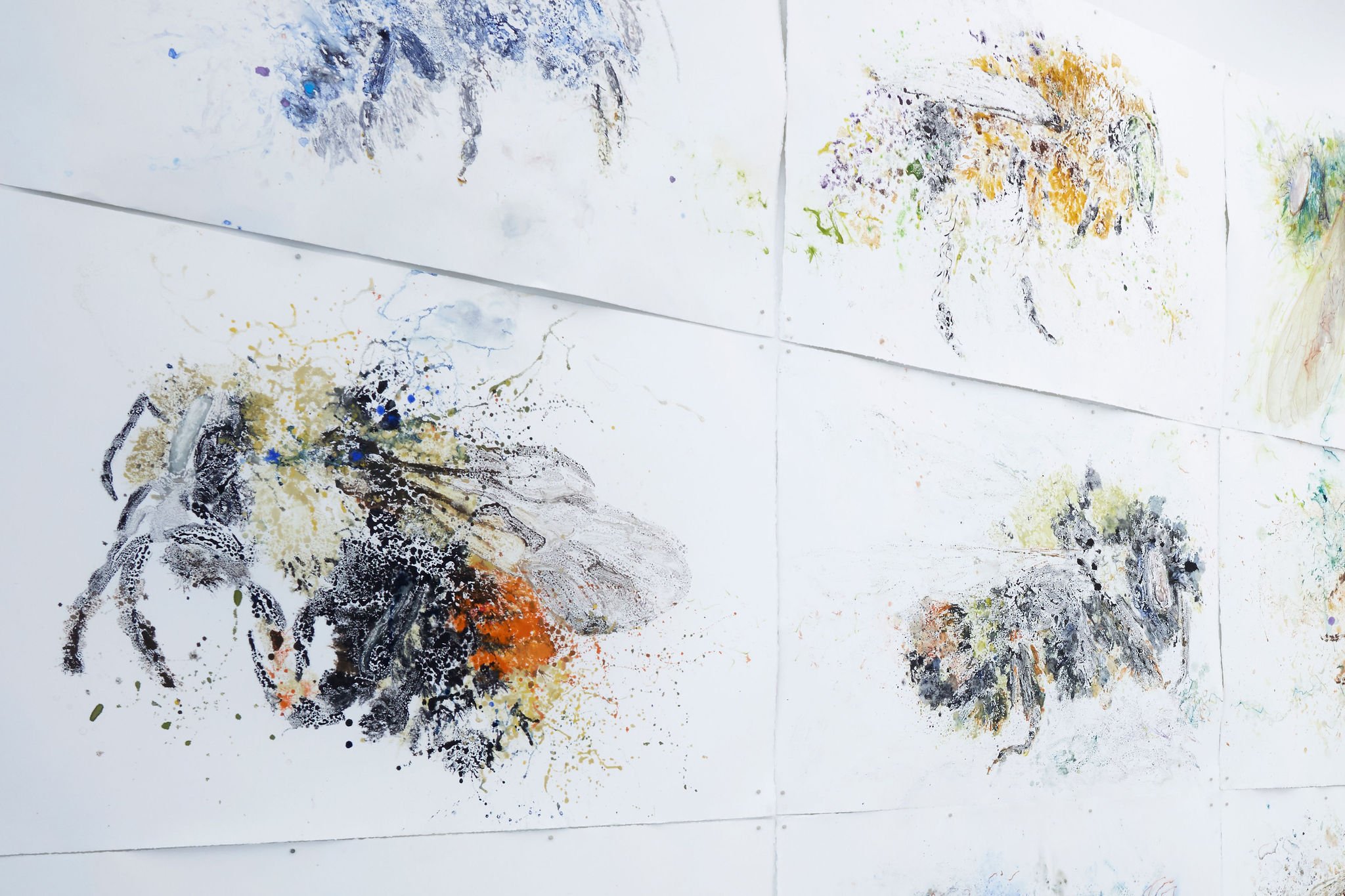
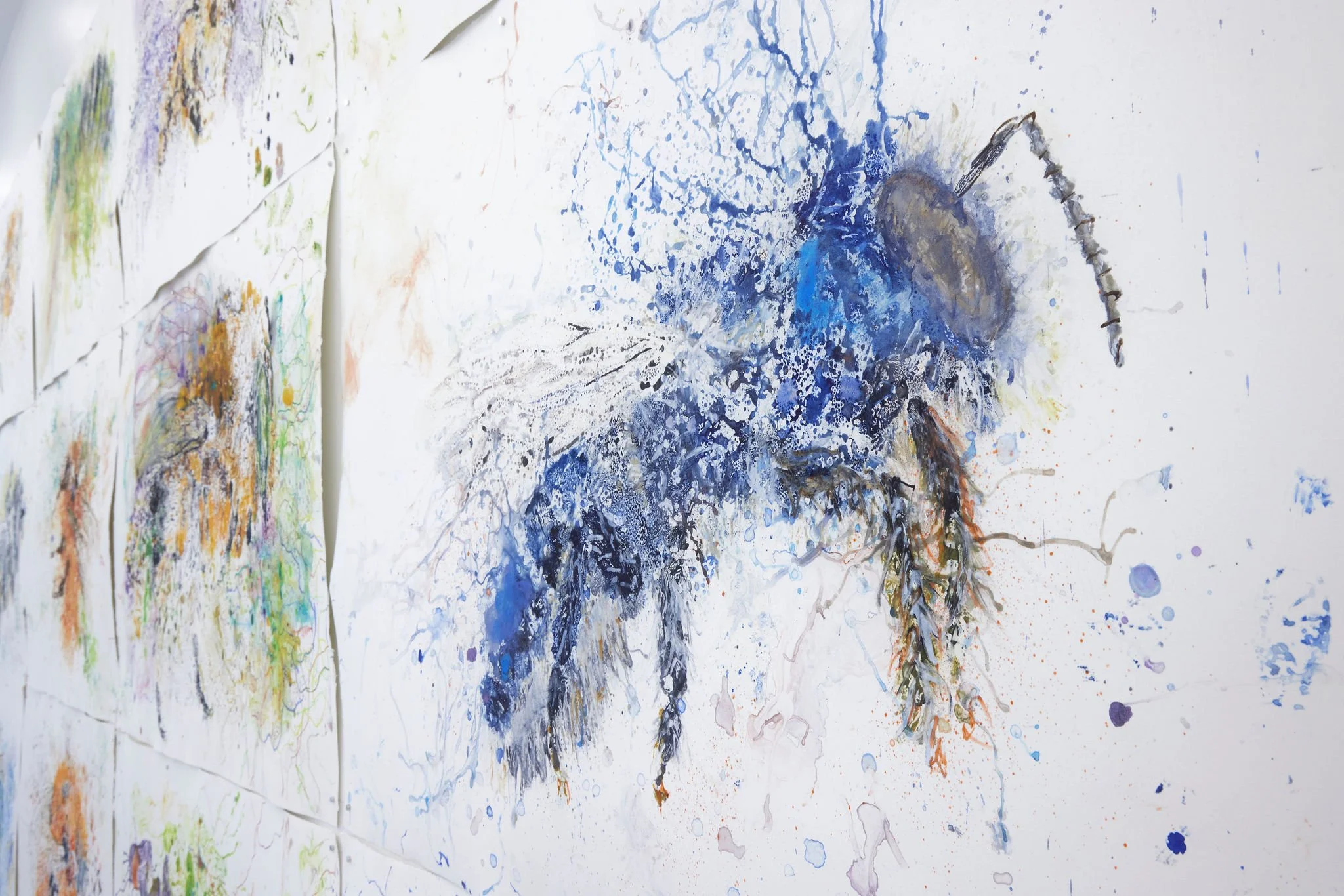
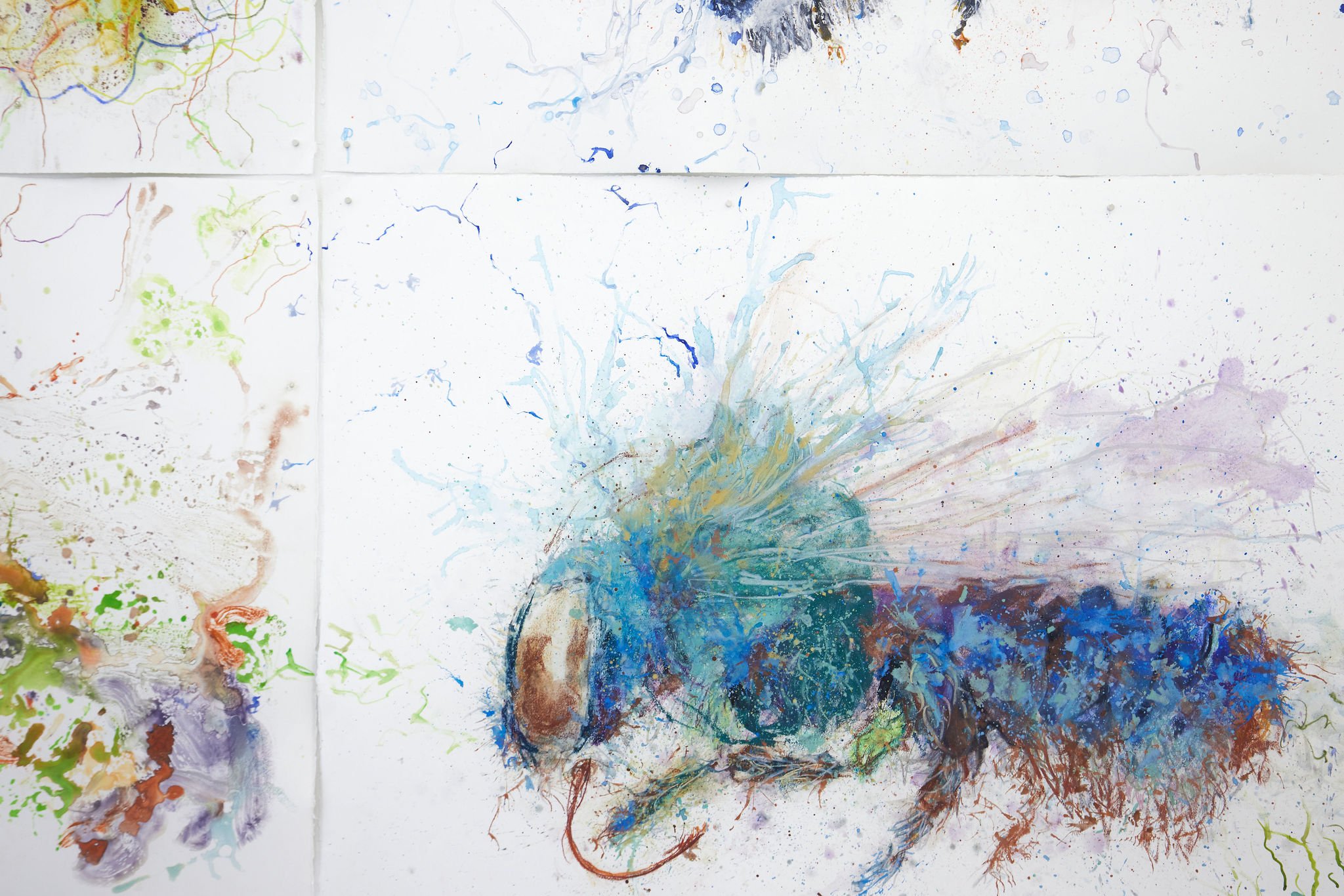
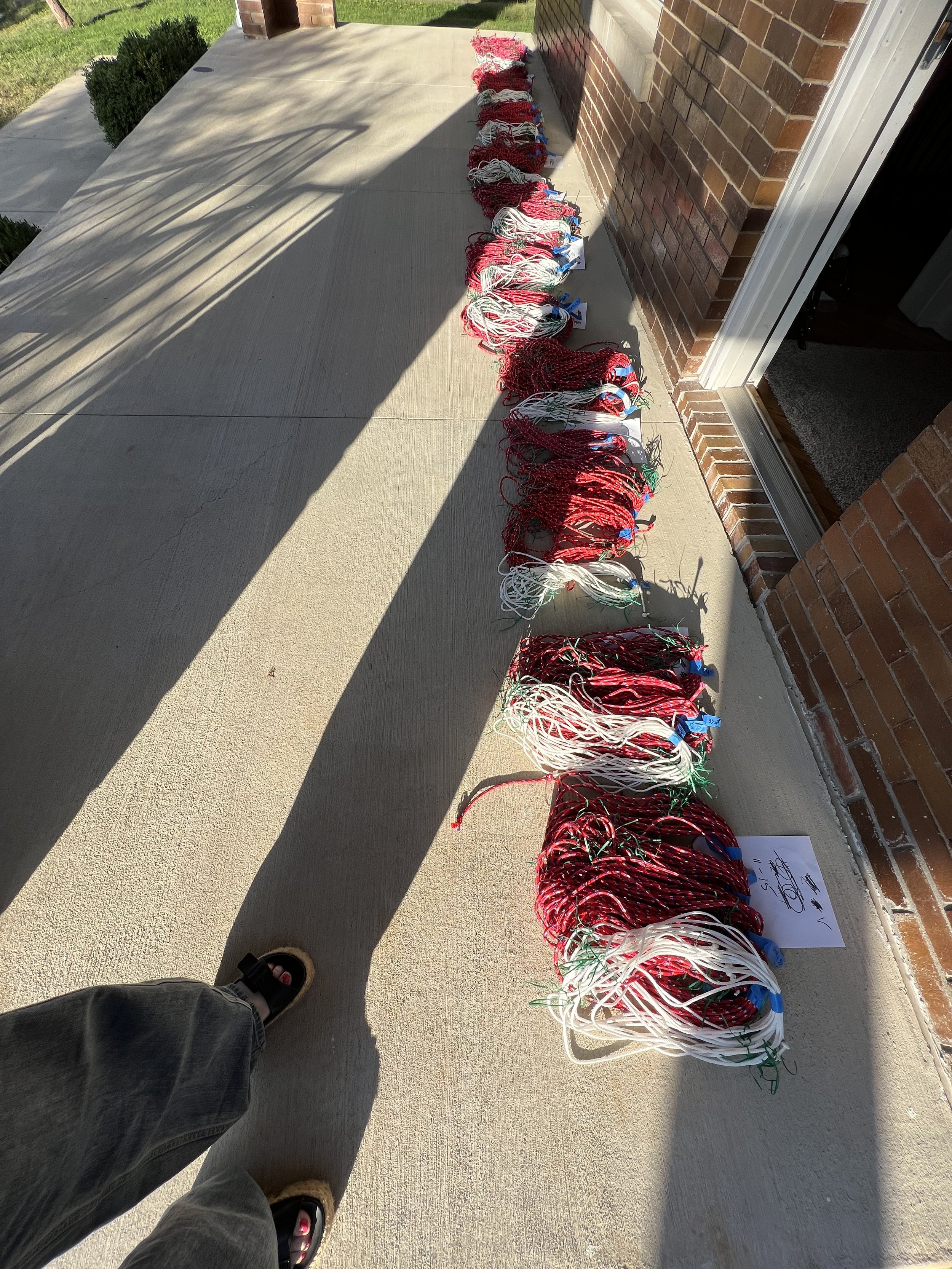
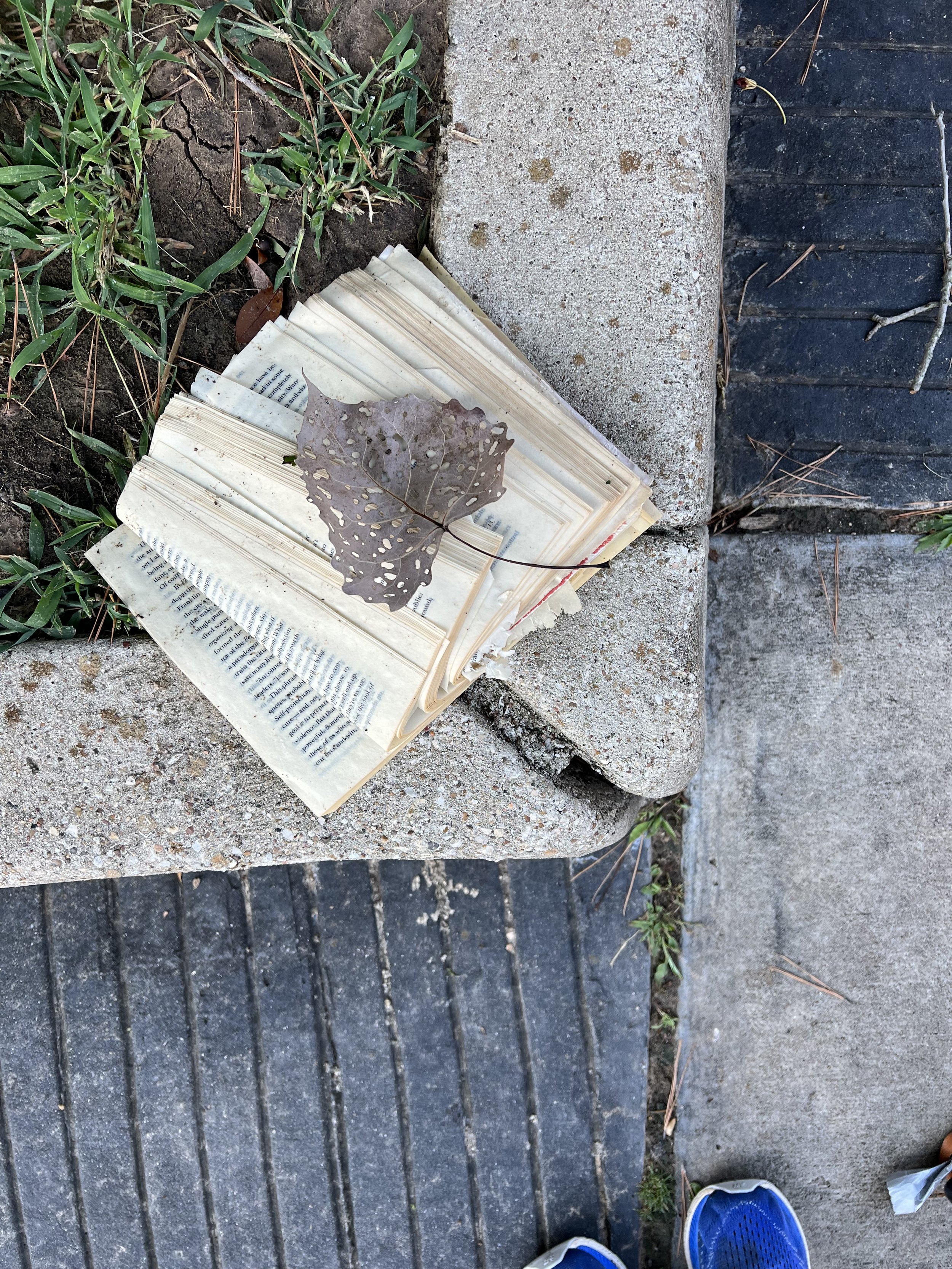
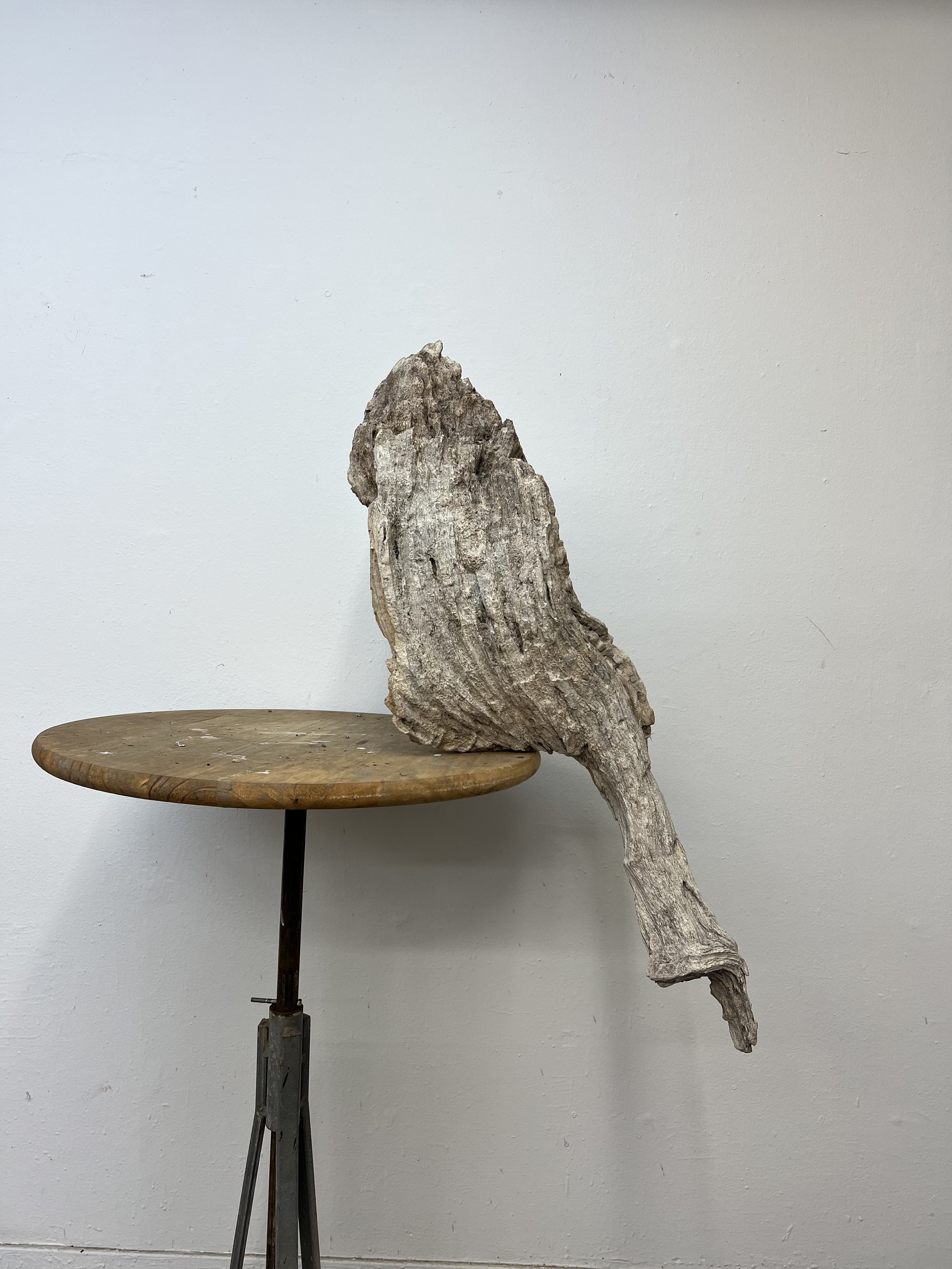
Lifeblood
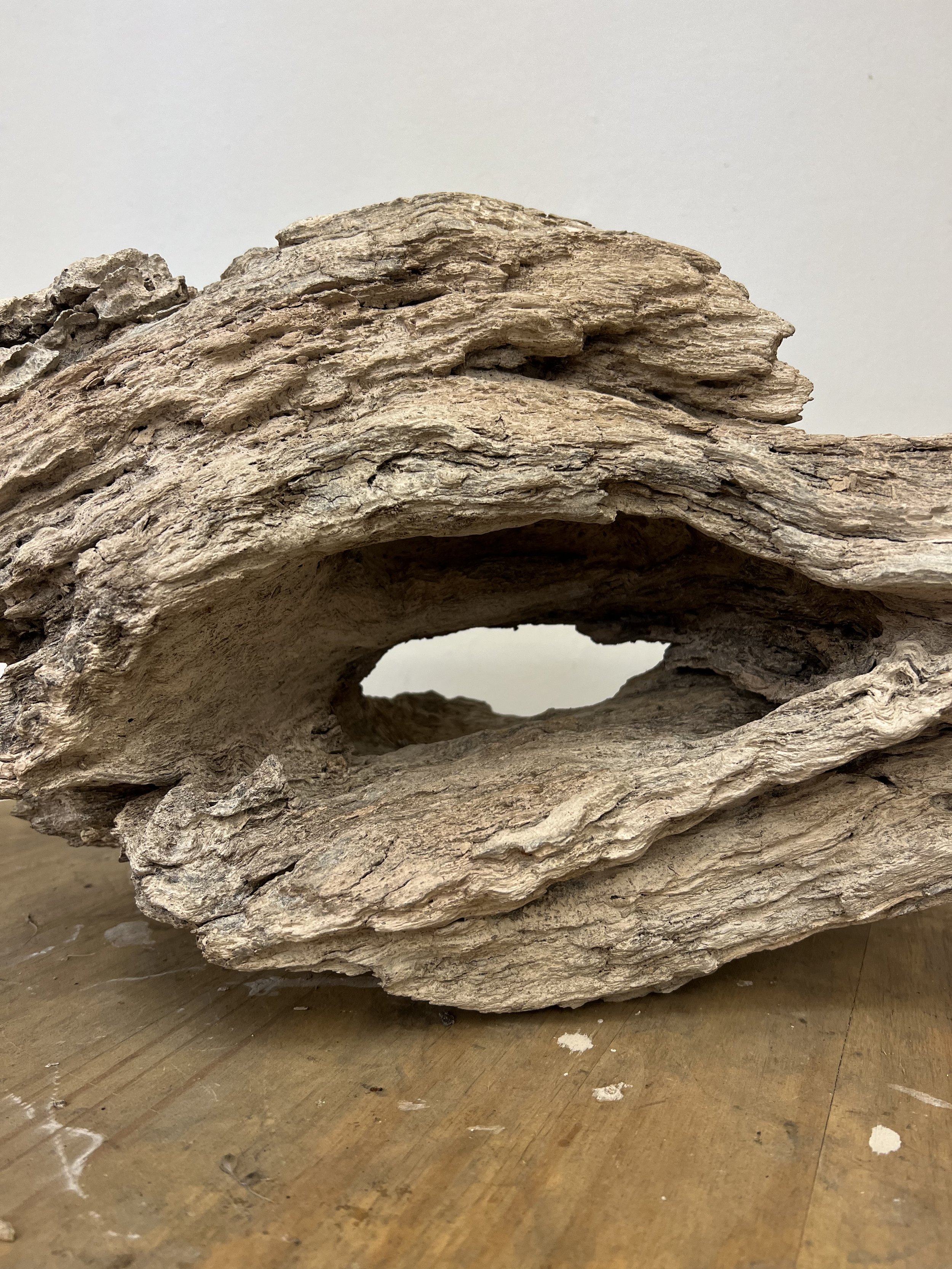
5.75 “ X 6” X 7”
bronze
Image by Jake Eshelman
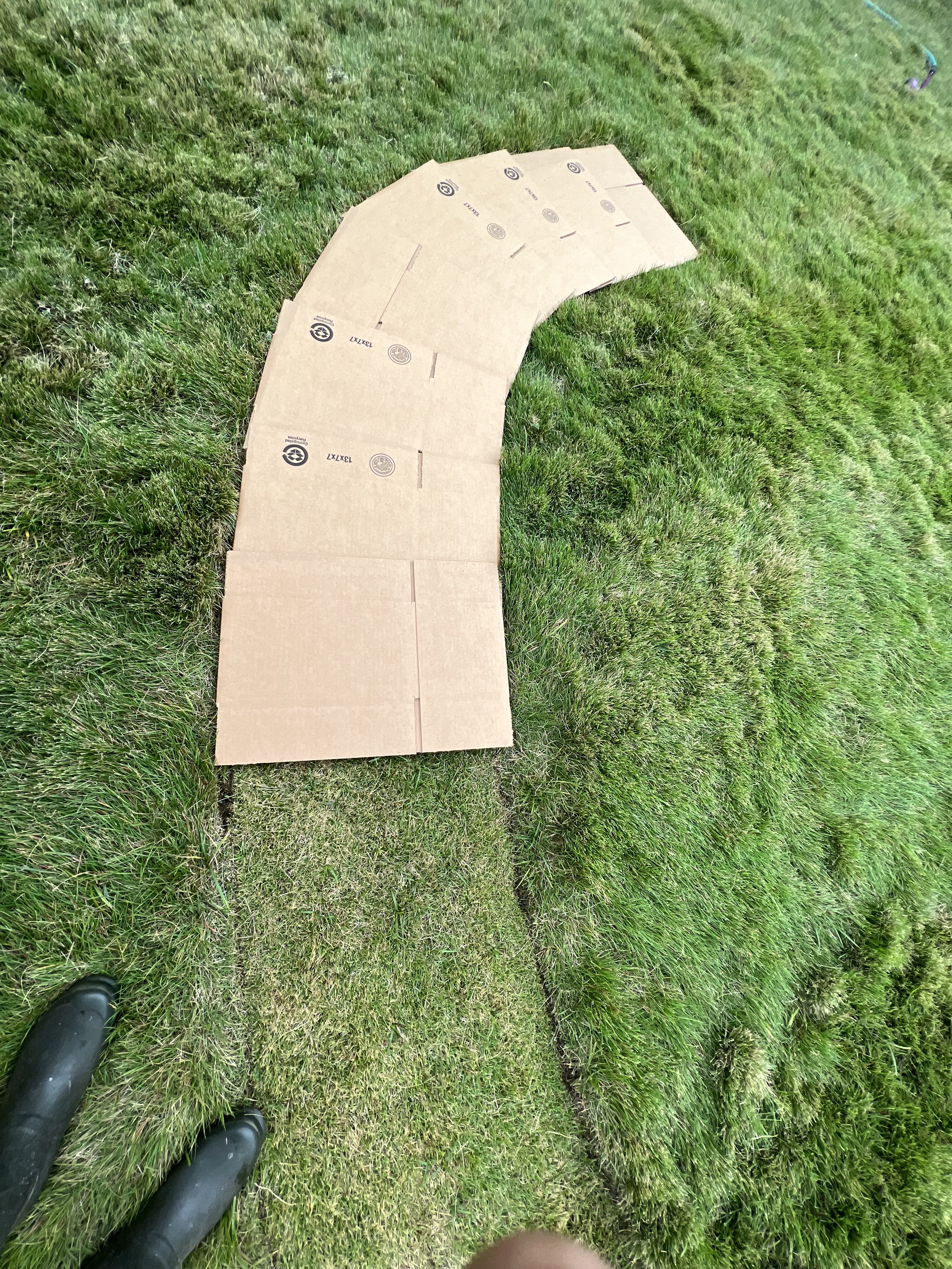
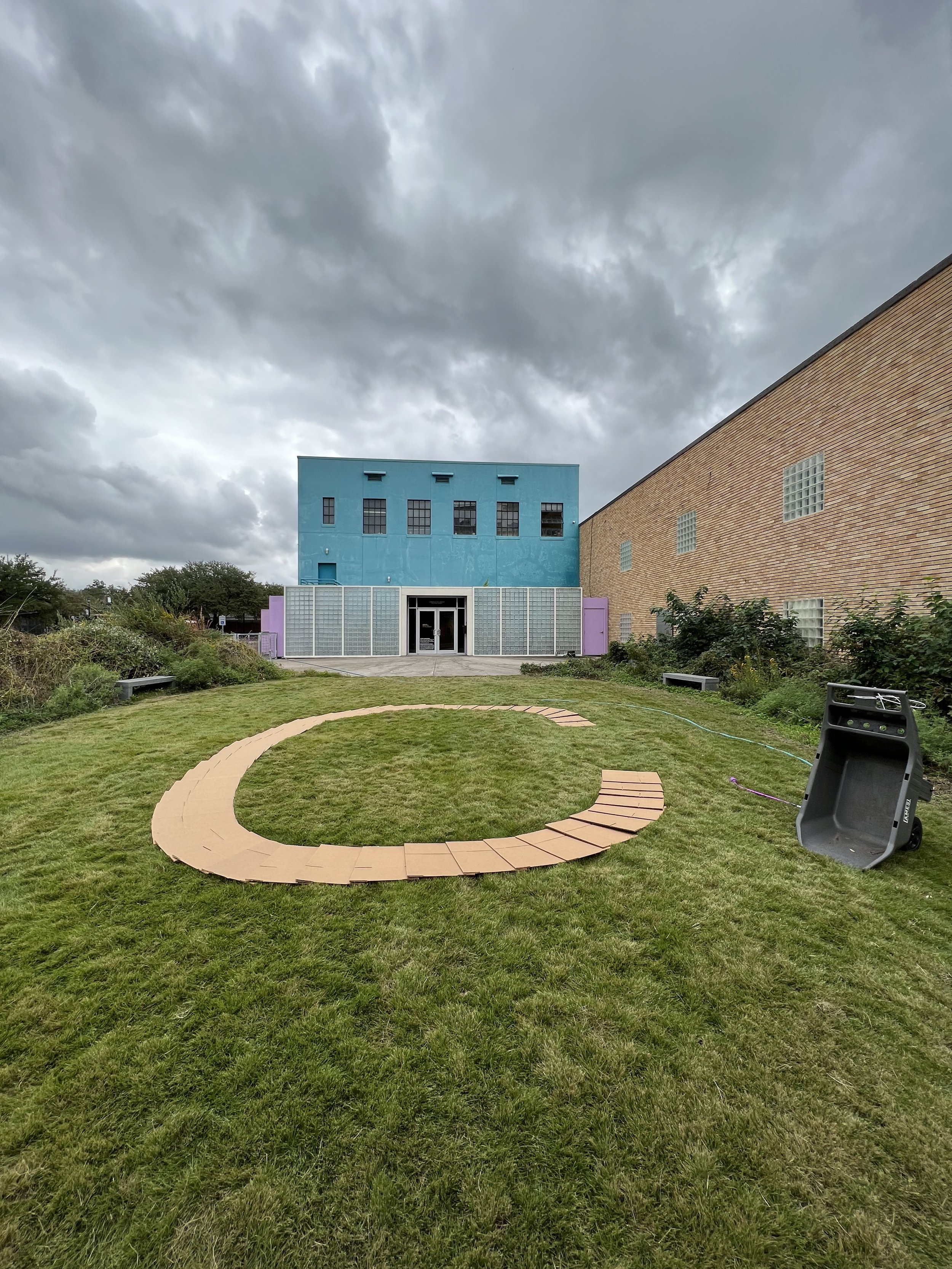
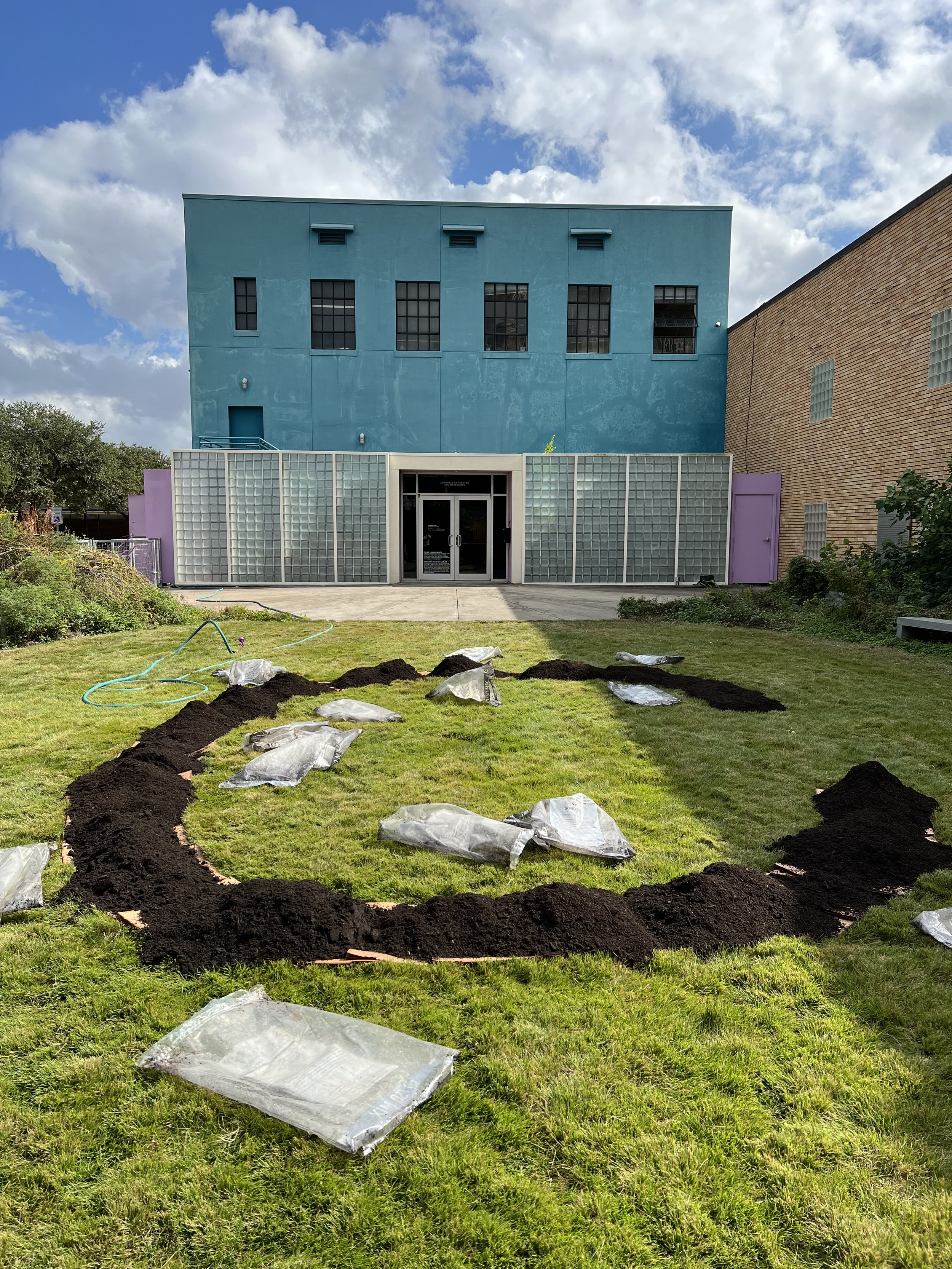
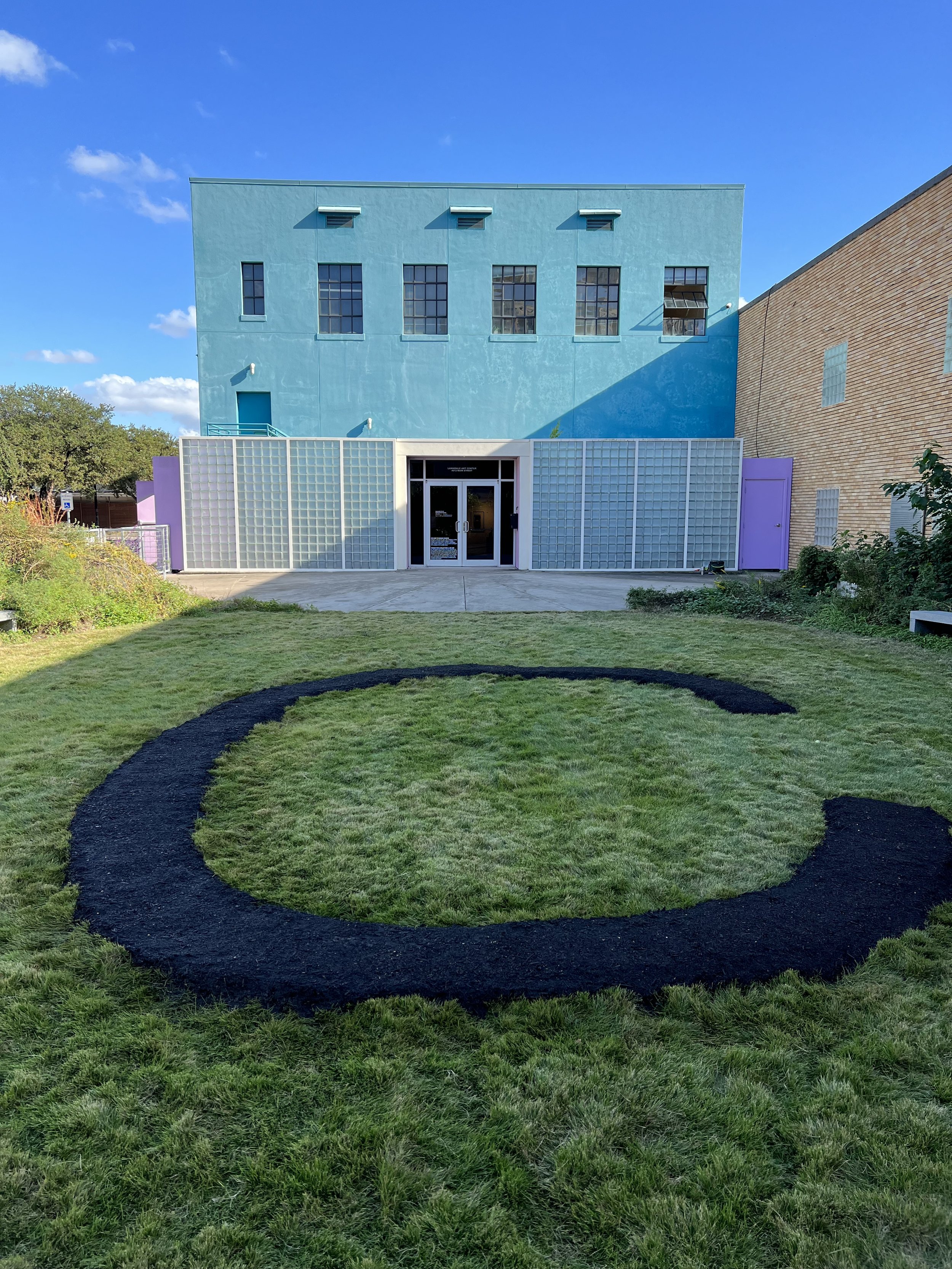
Lifeblood, Explores of the profound connection between humans and nature, conveyed through the visual metaphor of a root naturally occurring in the shape akin to the human heart. This piece is part of a larger body of work titled "Subterranean Secrets," which delves into the theme of roots. My work aims to invoke reflection on the unseen yet vital networks that sustain both plants and humans. By casting roots directly in bronze, I emphasize their resilience and permanence, highlighting the enduring significance of these natural systems.
The inspiration for "Lifeblood" arose from my studies on regenerative agriculture, focusing on the indispensable role roots play in countering extreme weather. My exploration into the fascinating world of roots began in 2017, unveiling striking visual similarities between roots and the human heart. These parallels reveal both biological and conceptual truths, as roots and the heart function as lifelines, circulating essential nutrients that sustain life.
Through "Lifeblood," I invite an examination of the often-overlooked relationships between human existence and the natural world. The act of casting these roots in bronze imparts permanence to these otherwise ephemeral forms, challenging perceptions of how we value the natural systems surrounding us. This sculpture contributes to the ongoing dialogue about our environment by emphasizing our dependence on nature and reinforcing the deep interconnection between humanity and the natural world.
In the end, "Lifeblood" serves as a call to acknowledge and appreciate the hidden yet crucial systems that support life. I believe that by understanding and valuing these networks, we can cultivate a deeper awareness of our roles within the broader ecological system, sparking actions to preserve and nurture the natural environment essential to human existence.