In a nutshell, this is what I hope to achieve with my site-specific piece, Symbiosis.
I am rethinking the uses of yard clippings.
Your Custom Text Here
In a nutshell, this is what I hope to achieve with my site-specific piece, Symbiosis.

I am rethinking the uses of yard clippings.
Symbiosis is a long term art installation. A piece of dirt in the middle of a large US city, an ecosystem that serves the local art community. Through pairing my intuitive sculptural practice, and natural history research I am sculpting the garden into an ecosystem that balances the needs of the Homo sapien art community and the urban natural world. I spend much of my time filtering through biologist research, inspirational documentaries and interviews of individuals that are leading the way. New Year’s Day I listened to a remarkable podcast an interview of Nora Bateson who is an award-winning filmmaker, writer and educator, The podcast was taped before the pandemic. She knows what she is talking about. Here are two quotes from the podcast that gave me pause and reminded me how grateful I am for my opportunity to make a difference through Symbiosis at Lawndale
“ In my little fantasy there is a great big pause button, and we can say hold everything, let’s regroup, let's turn this titanic around”
“One way or another the systems that we are within are going to change.”
A very enlightening podcast regarding how change and regeneration happens. It is haunting to consider this came out before the Covid 19 quarantine of 2020. Everything Nora talks about addresses the things I am thinking about. She is most definitely an influencer. I will continue to follow and monitor her work.
You can find the interview at The Regenarration podcast on Soundcloud Solve Everything at once.

Checking on the garden I found a moth that was still alive laying in the Pond. I rescued him and laid him out to dry.
How beautiful droplets of dew or rainwater puddle on the waxy leaf surfaces? They provide the watering holes for nature’s tiniest creatures.🐞🐛🕸️🦎🐌🐸🐜🦋🐝
What do you see when you see a leaf? ☘️🌿🌱🍀
I see a unique natural system. Leaves multi-functioning as micro reservoirs, coats of armor protecting the soil, and micro floodgates slowing rainwater. 💦🌊💧
On the Coastal prairie, leaves function to protect the soil from being compacted by the pelting raindrops. If the heavy raindrops fall is not broken by layers of leaves and organic matter, the tiny cavities in living soil collapse, and rainwater moves horizontally across our landscape instead of into the tiny reservoirs in the soil. We need these small cavities to allow water to penetrate deep into the soil. Leaves also slow rain droplets giving the soil time to transport the rain to its deepest roots. Once the rain is in the ground cooling our planet leaves protect the soil from the heat of the day. This multilayered ground cover gives rain more time to trickle into the aquifer. Purifying our water and cooling our planet. How amazing are leaves? As an artist my how we see urban landscapes
My work records endangered knowledge to the collective memory and reimagines urban landscapes to holistically balance the needs of humanity and wildlife.
In Symbiosis I am stretching my practice and creating a living piece of site-specific art activism that will reimagine a 53.5’ X 48’ traditional urban landscape/sculpture garden and answer the question: how do we holistically restore an ecological balance in Houston? Symbiosis is a collaboration with Lawndale Art Center’s community, neighbors, urban wildlife, and the coastal prairies carbon cycle. #symbiosis #lawndaleartcenter #urbanlandscapes #artadia #coastalprairie #water #leaves #conservation art #bioart #nature #contemporaryart #modernart #artactivism #cindeeklementart #texasart #houstonart


Rural areas are highly impacted by the unanticipated consequences of our industrial agriculture’s dependence on chemicals that weaken bee’s immune systems. Urban bee populations can be more diverse than in rural areas. Researchers are finding in cities such as Chicago, Berlin, Berkley, and Melbourne that have reimagined their parks, neighborhoods, city centers, vacant lots, street medians, and rooftops planted with native flowers, grasses, and fruit, and vegetables support healthy, vibrant wild native bee populations.
In the US, there are four thousand native bee species. They pollinate over three hundred times more effectively than honey bees. For example, A single female Leafcutter Bee visits 100,000 plus blossoms per day whereas a honey bee visits 50-1000.
Houston covers 600 square miles of land and has one of the longest growing seasons in the U.S. As it continues to sprawl across Texas, its gardens must increasingly become a refuge for native plants and animals. With 2.3 million people living in the most vital economic, cultural center of the south, we can become the most critical urban native bee habitat in the United States.
I have spent the last year and a half studying the bee situation as it pertains to my art and my interest in regenerative agriculture. I am determined to take this knowledge and save the bee in urban settings.
With Houston's land size, population, and location in the Sunbelt like it or not-we are impacting the bee population.
ADDITIONAL LINKS
If Cuba can create urban gardens to feed its poor can you imagine what we can do
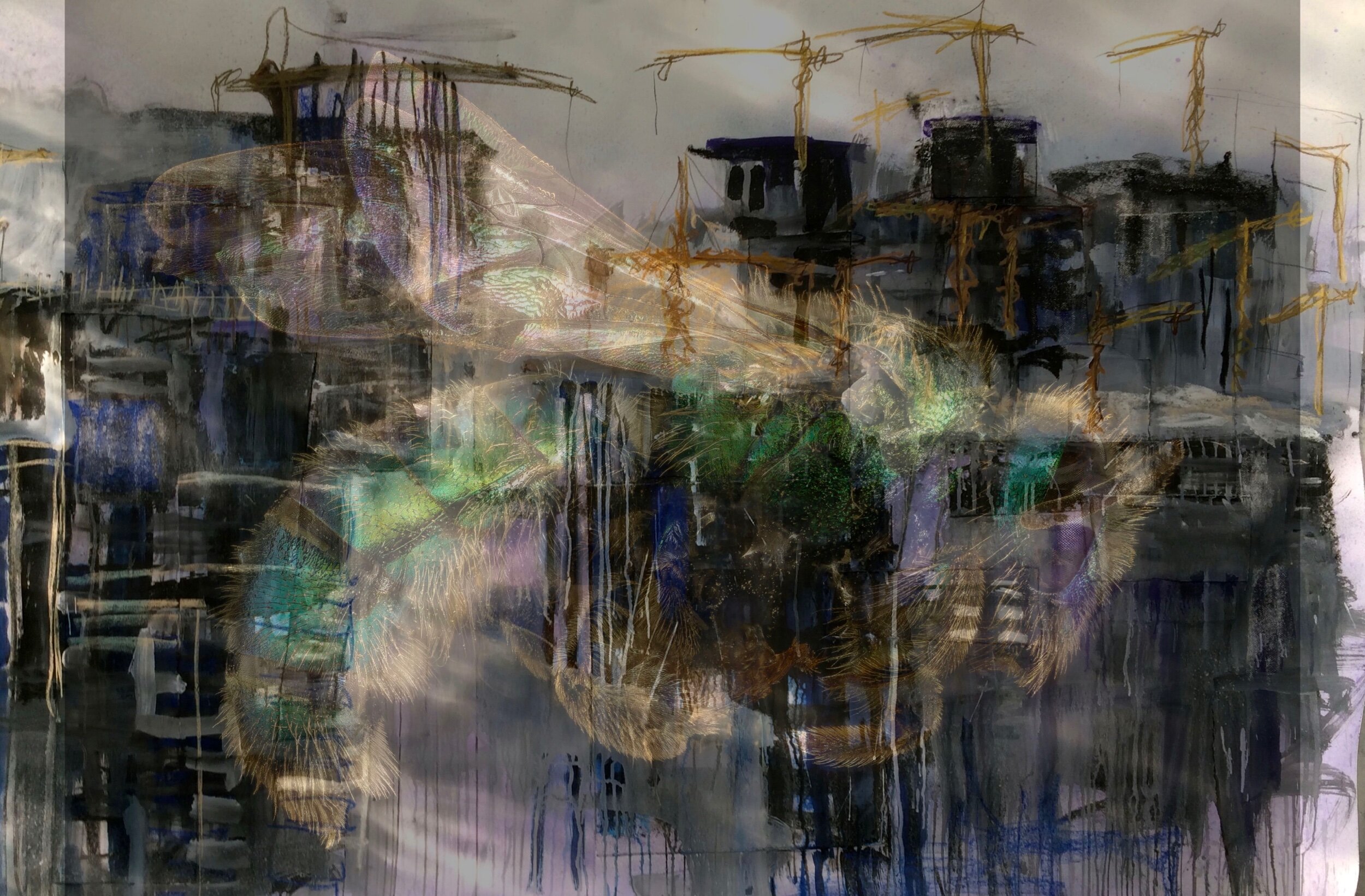


A male southern carpenter bee- This bee was sleeping on my Salvia the morning of July 4th. The male wild bees do not live in nests. When they emerge they fly out looking for females to breed with. When the females return to their nest to sleep the males curl up to an petal.

Xylocopa micans I

Xylocopa micans II

Xylocopa micans II ghost

Image from my video
Sometime in 2019 or late 2018 I discovered the USGS photographic library of wild bees. I was overwhelmed at the number of species and their individual beauty. They are jewels of the insect world. These facts combined with the reality that most well educated people believe that there is just one bee species - the honey bee. There are 20,000 species. How a creature who is responsible for our food could be misunderstood to this existent is baffling. Scientist just started realizing the error in their studies last summer. Committing to telling the story of the plight of the most important being on the planet is a worthy story. I have always felt the need to support underdogs.
Below us the artist statement for the project as I incusion it today. Artist statements remain fluid as I work on big projects.
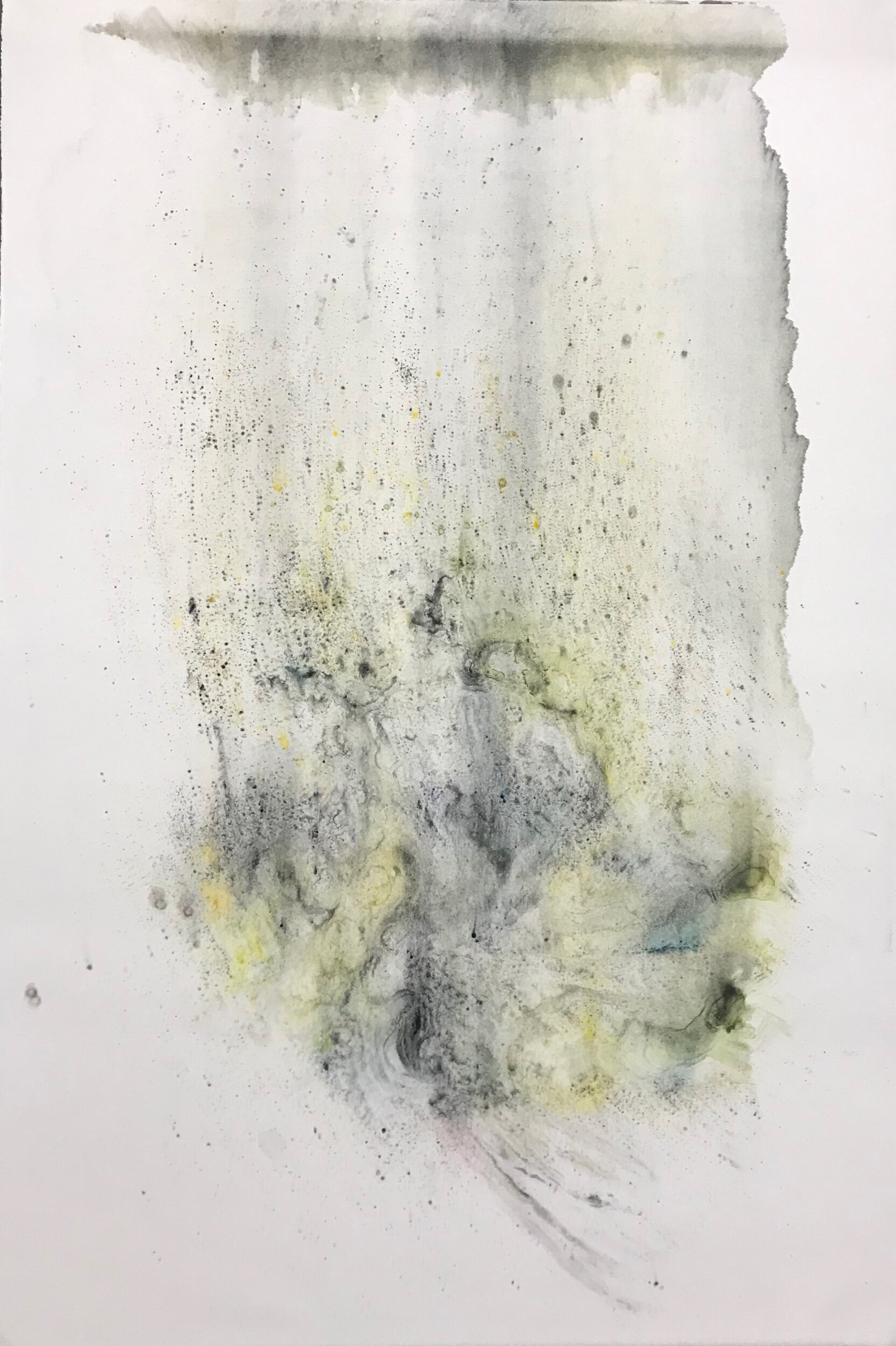
RUMBLINGSA rumbling in the distance is nature's way to alert living creatures to their environment. Rumblings; monumentally draws attention to the 20,000 unknown species of threatened wild solitary bees. The bees that can not bee industrialized. The watercolor ink carefully manipulated on the fifty interconnected monotypes to reflect the synergistic, aqueous effect of; the unexplored bee species superior magnetic attraction of golden dust, the movement of the anonymous Keystone species dedication to pollinate, and their fragility due to the applied chemicals that flood industrial agriculture. With Rumblings, there is knowledge and knowledge is power; it is a resounding call to all for action.
The COVID 19 quarantine in March was a huge buzz kill to this series. These are all monotyoes. I use the plexiglass surface to create my water effect that I then press into the paper. I am very attached to this method as the best way to communicate this work for a few reasons. 1. It is a process I created and as far as I know no one else creates monotyoes with this type of mark making., 2. The watery look suggest the use if pesticides that are impacting their extension and lastly the tiny details that make up the bee is suggestive of pollen dust. I have been creating this pieces in MFAH beautiful Glassell studio school printmaking studio. With COVID that us not an option for me.
Since March, I have stitched bees and tried to be open-minded to another process to complete the series. I finally decided to see if I could hand press a 30” X 44” print in my studio.

Here I am applying the ink to the plexiglass. On the wall is a photo of Bombus Dahlbomii, the largest humble bee in the world at 2” long and endangered if it us not already extinct. The photographs are stunning. The photographs are taken if dead bees. In ny pieces, I try to put movement and energy back into the buzz pollinator.


Here I have just pressed the plexiglass with the watercolor ink bee image onto the wet paper. And surprise surprise surprise.

Bombus Dahlbomii IV
I have made three other attempts to print this monsterous fluffy ginger and not been happy with the results.
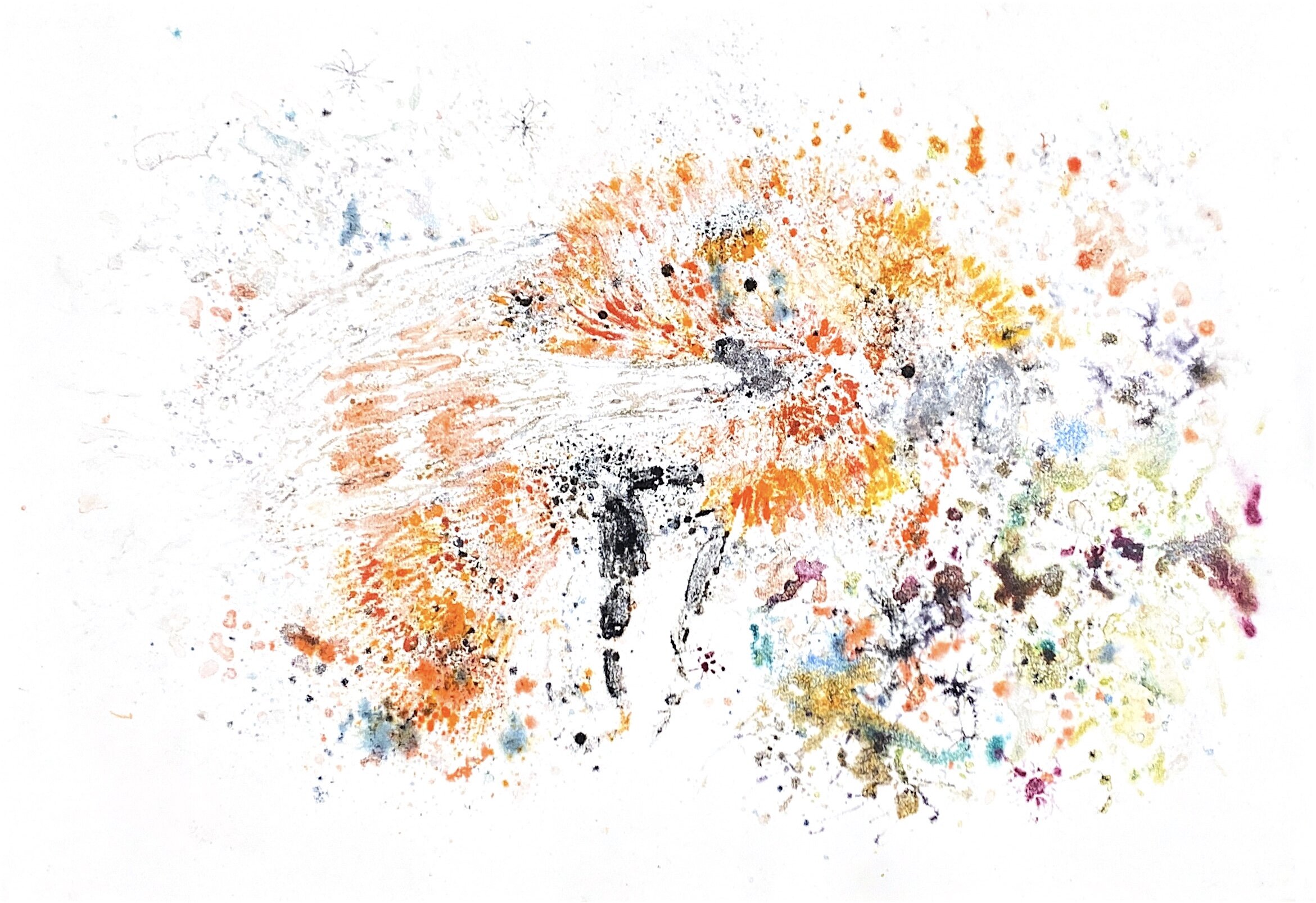
Bombus Dahlbomii IV Ghost.
The prior attempt are below. Getting a mono-colored fluffy bee with out muddying the ink was tricky.
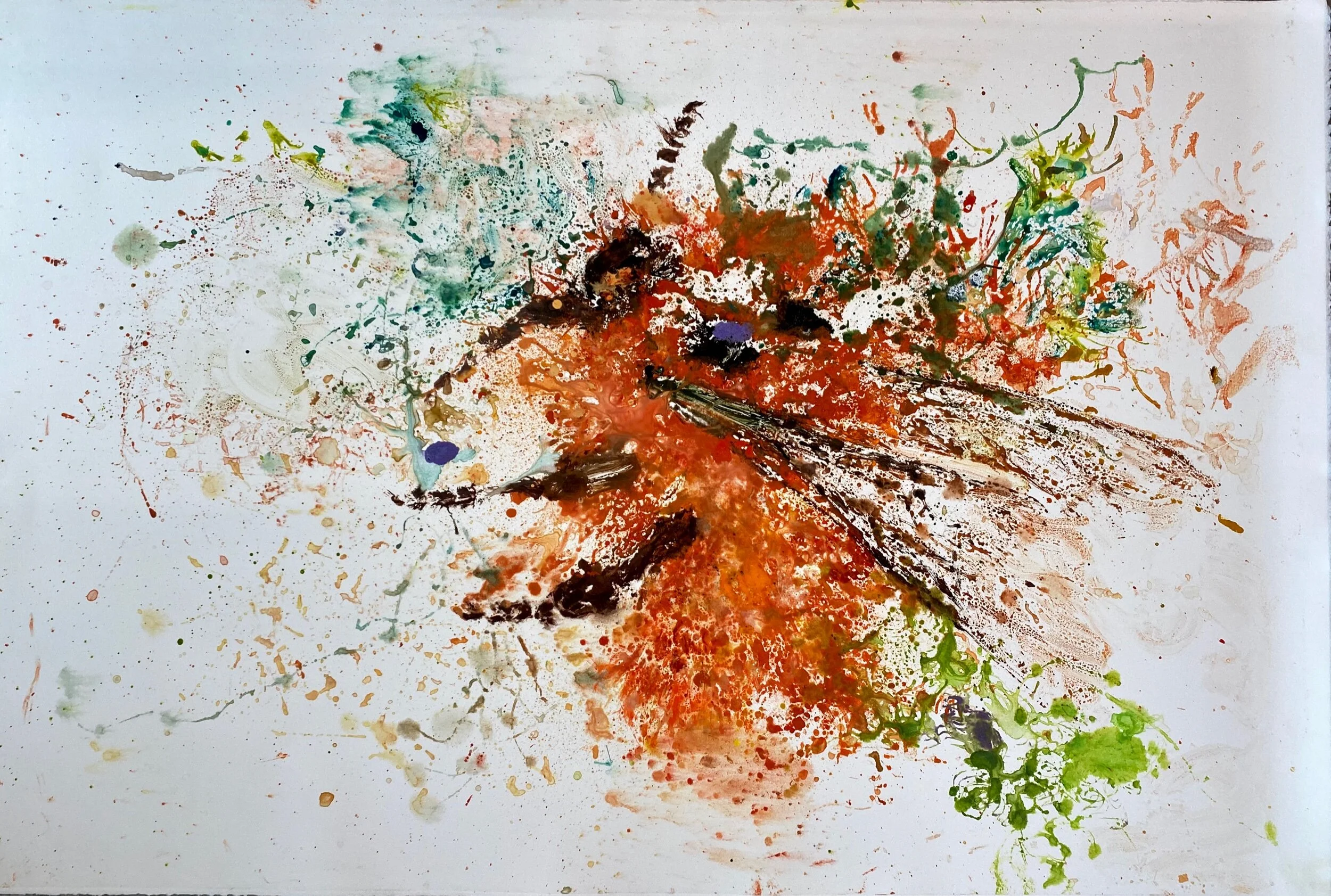

Bombus Dahlbomii Day I

Bombus Dahlbomii Day I ghost

Bombus Dahlbomii Day II

Bombus Dahlbomii Day II ghost

Bombus Dahlbomii Day III

Bombus Dahlbomii Day I'll ghost
I am hoping the Bombus Dahlbomii day IV pieces cut the mustard. I am feeling hopeful and extremely excited that I can create monotypes without a press Is this non-verbal size.
I just read an intesting article; how Cowbirds are hedging their bets when choosing surrogate birds to hatch and raise their young. Another instance that supports the theory that diversity is the ticket when it comes to the survival of a species.
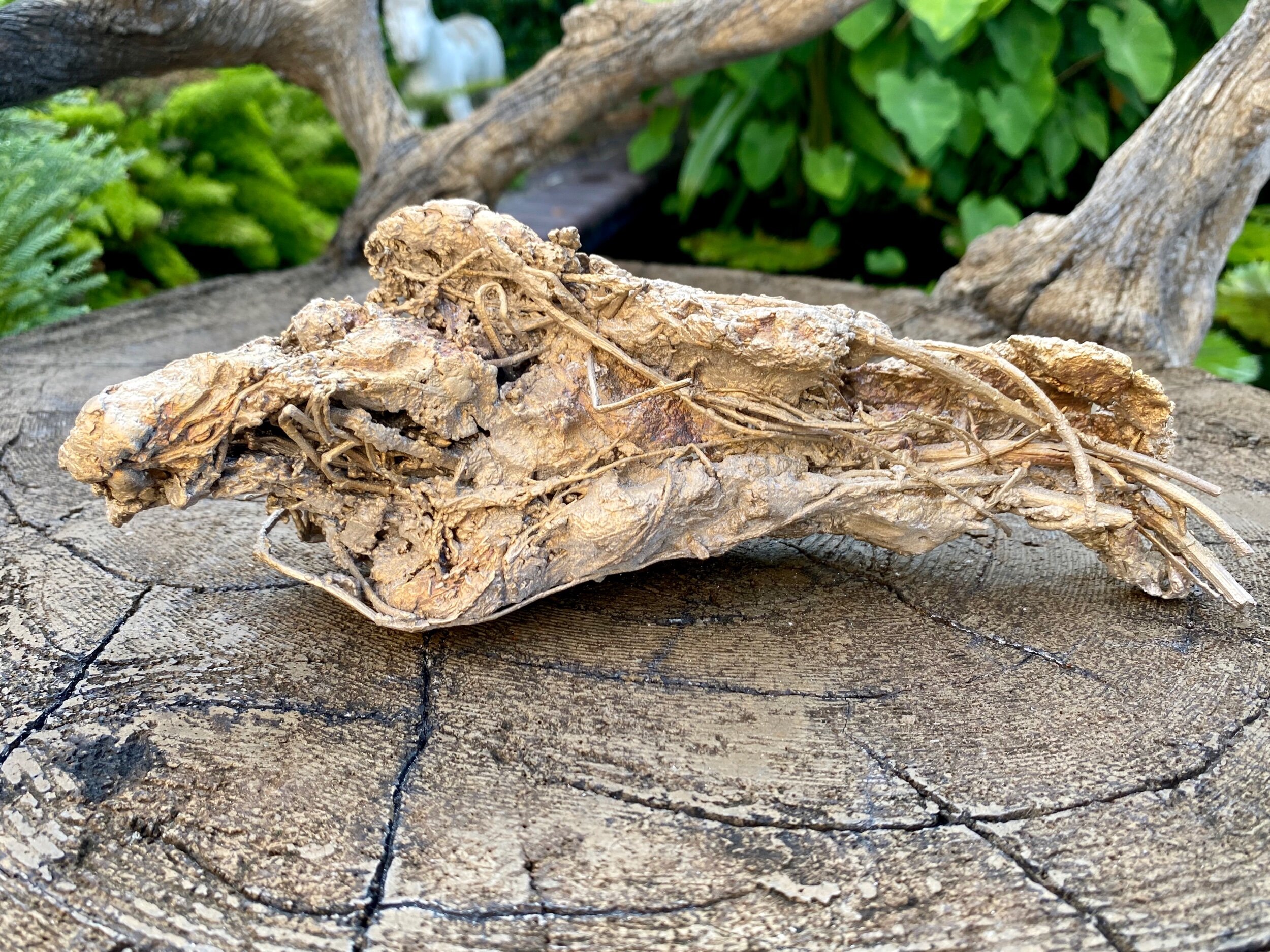
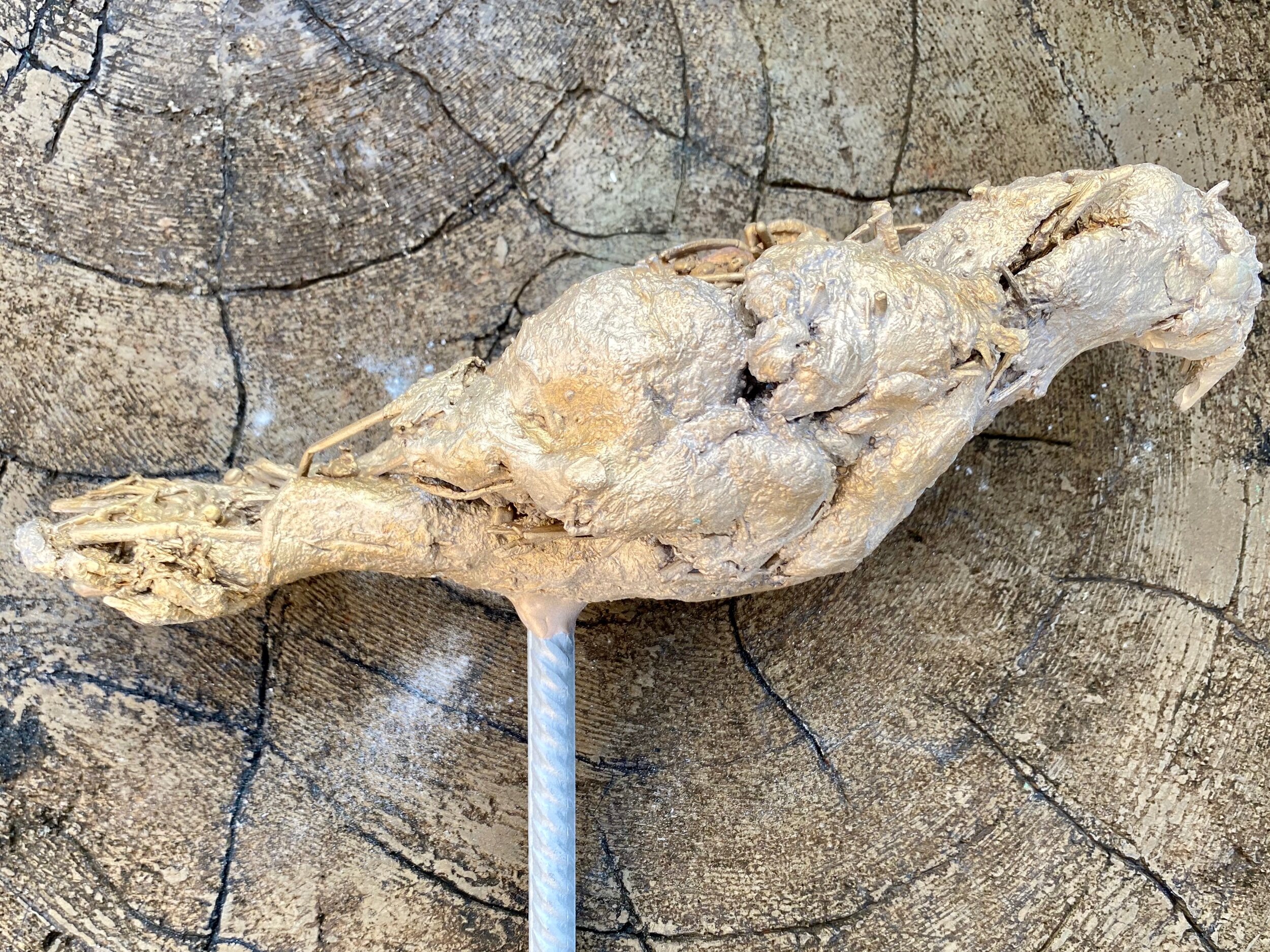
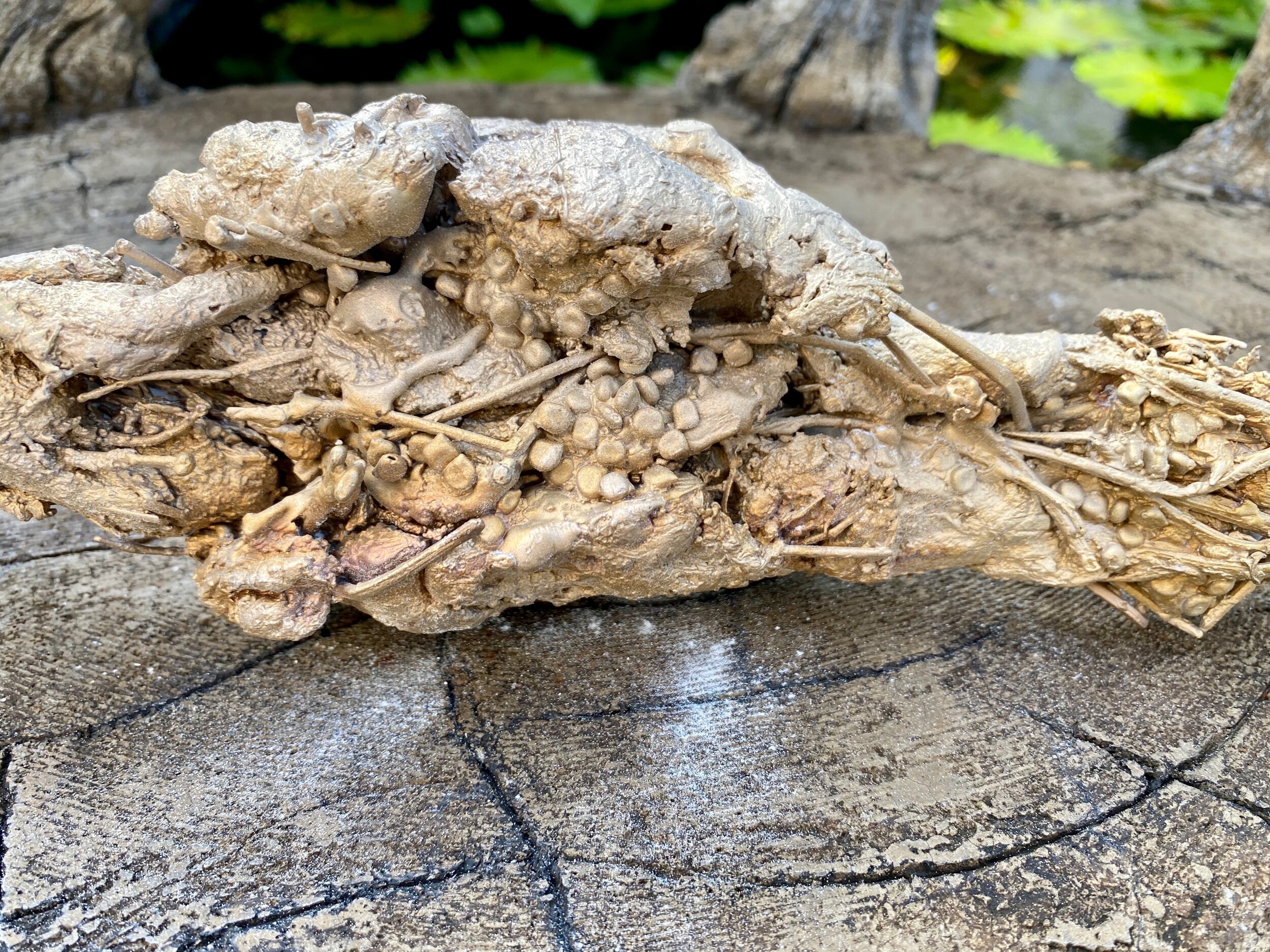
Coincidently I picked up the bronze Cowbirds yesterday. They are ready for me to recreate the texture where they were damaged during the spruing process. Once that is complete I will deal with their patina. I should wait and decide on their finish once the abstract bison is further developed. That said I am excited to see how the materials will look in a polished finish. Below are closeups of each bird - just for the record.
The finishes are very powdery looking and flat because they were just sandblasted. When I decide on the patiba the textures will really show up.
I took a risk when I decided on the manner in which I would create the birds. The Cowbirds are constructed in a primitive manner. And they look extra primitive laying on the faux bois chair. Context impacts the way we see. I feel hopeful the organic and rough construction will work on the abstract beast they will be attached to. Roughly constructed they support the story, polished perfectly detailed birds would not relay their connection to the geography and mammals. I realize I have not taken the safe root and hope I didn’t need to hedge my by as the Cowbirds did theirs.
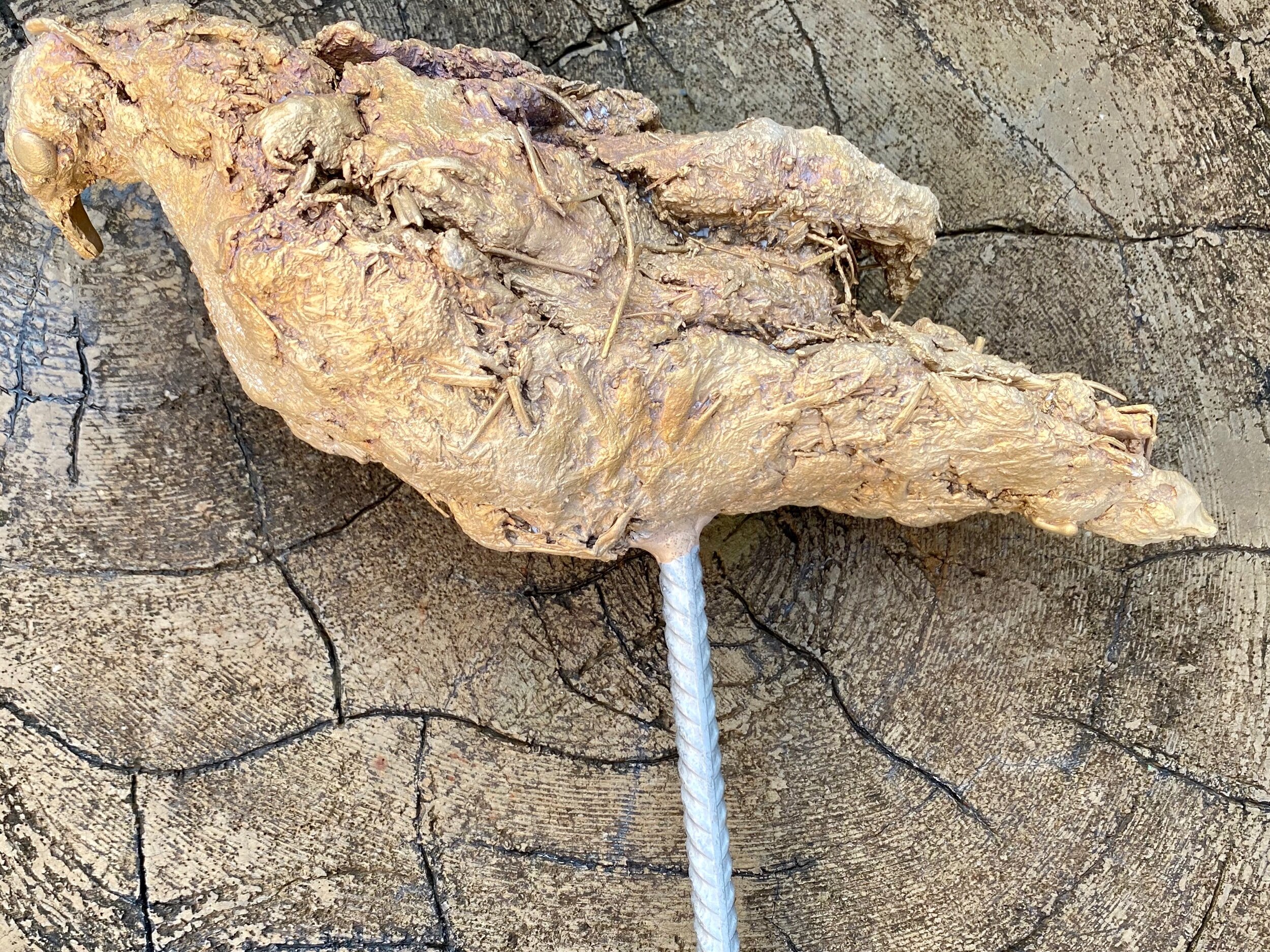

The big bird side 1
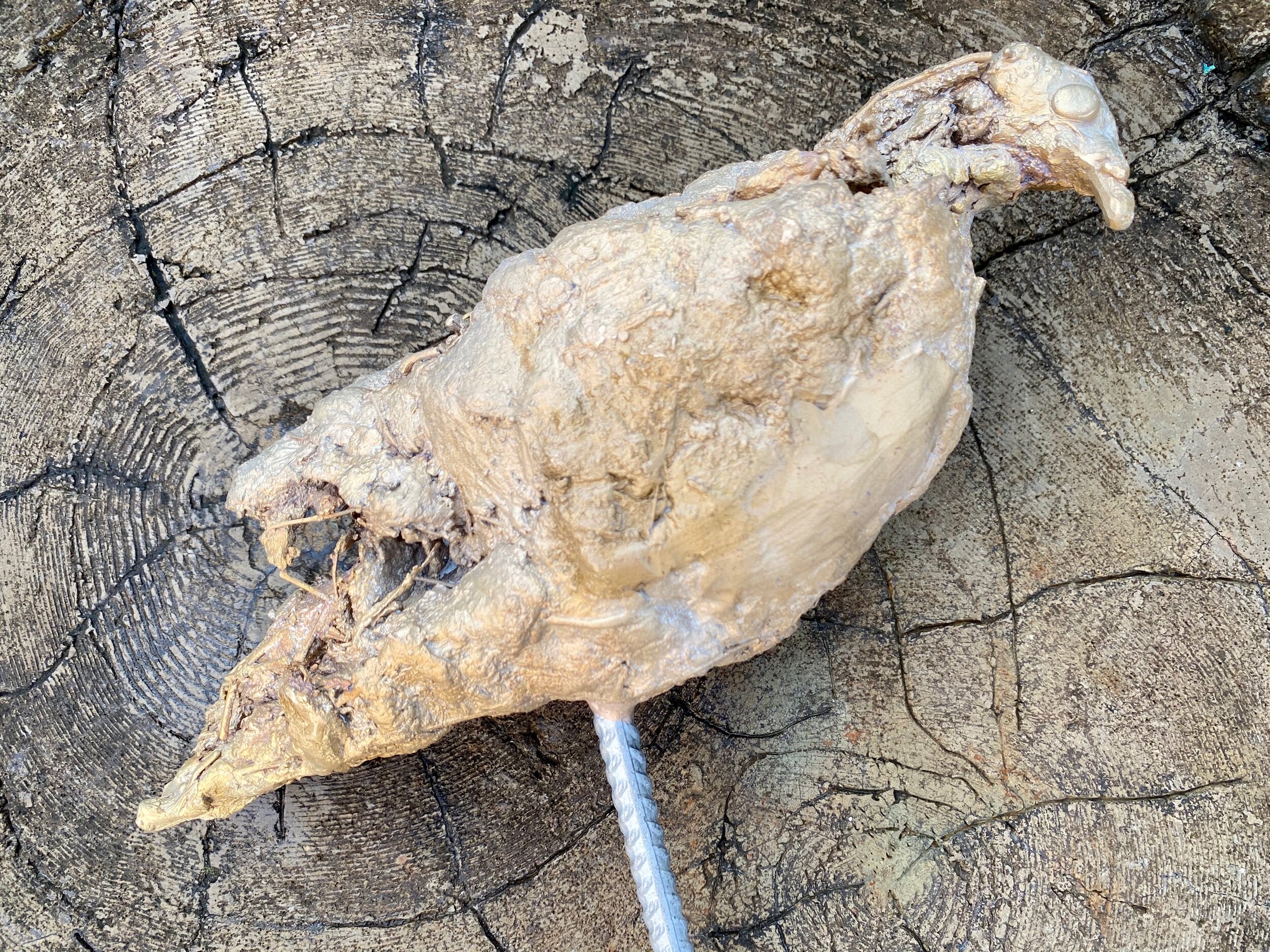

Opposite side.
On this image you can see a smooth surface from where the sprue was cur off. One spots the I will retexture.

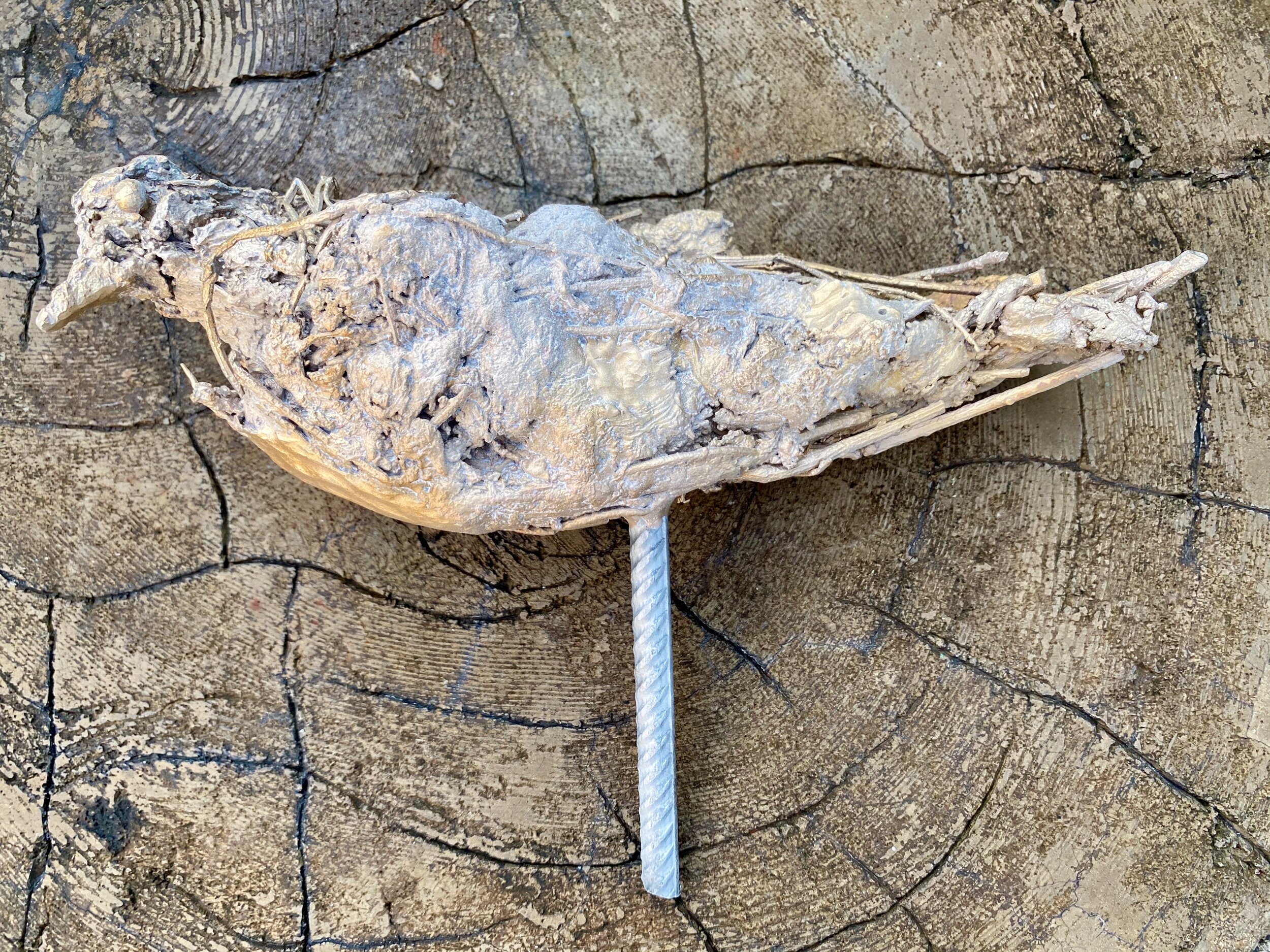
From the top

Bird 2



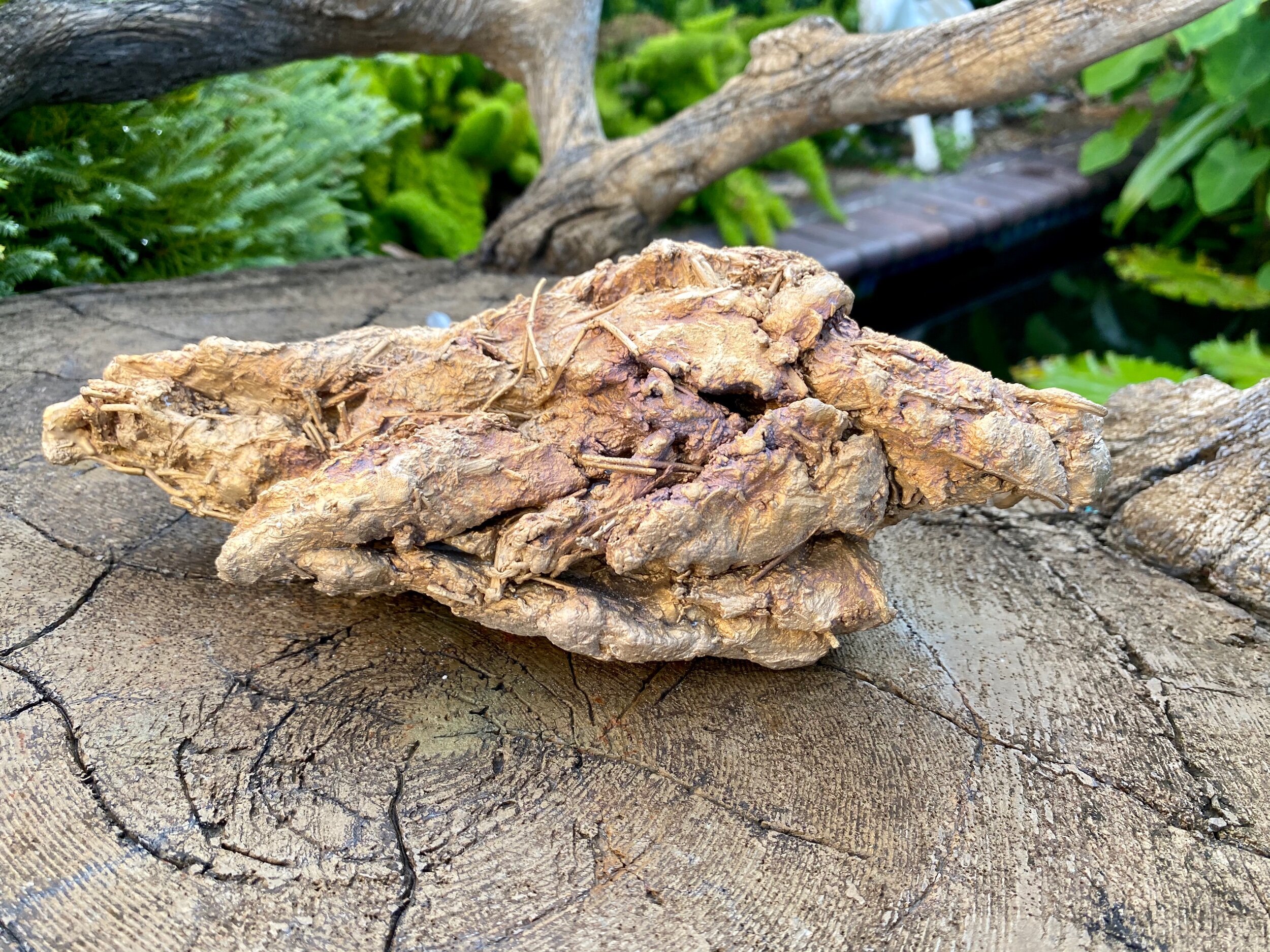
Bird 3



Derail shot of bird 3 - you can see the seeds and grass stems.
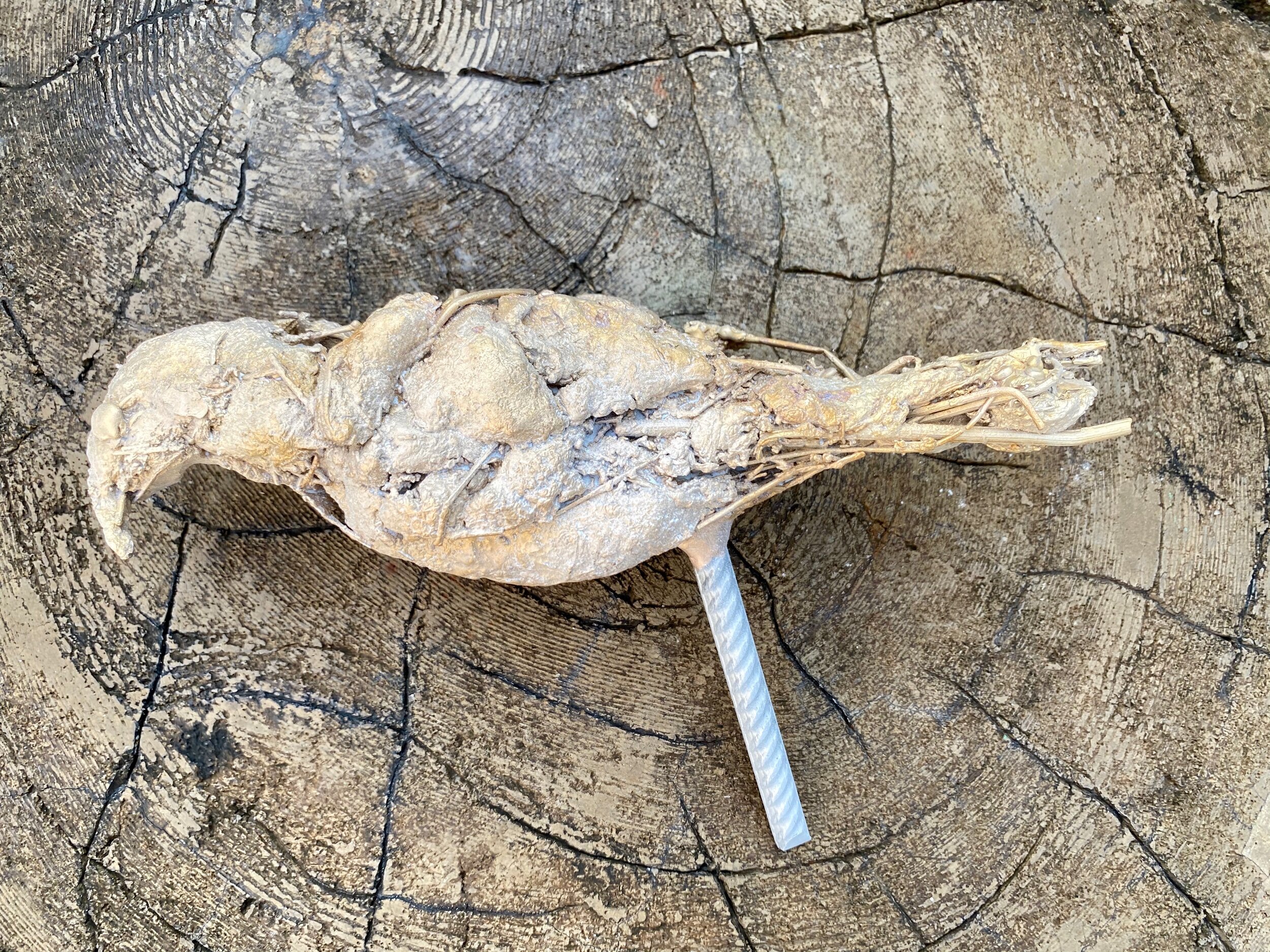

Bird 4
As I recall this one gas some bluebonbet seeds in it's back feathers.
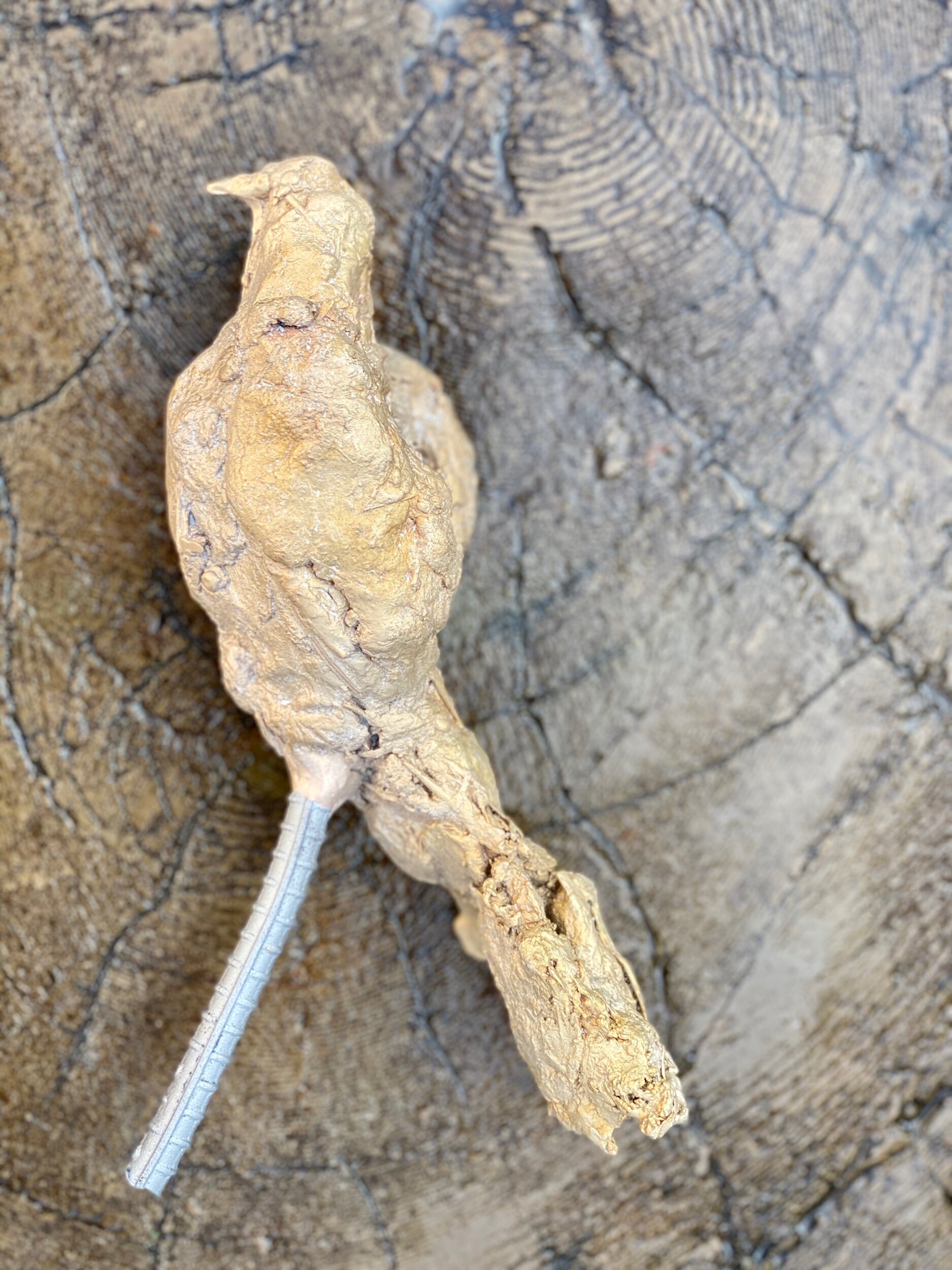

Bird 5


Texture gives me good goosebumps.
I am in love with these textures and I can hardly wait to incorporate them into my Endangered Knowledge piece. I do need to figure out how to fade the green out. I do not want a green bison. I think the answer is sunlight.
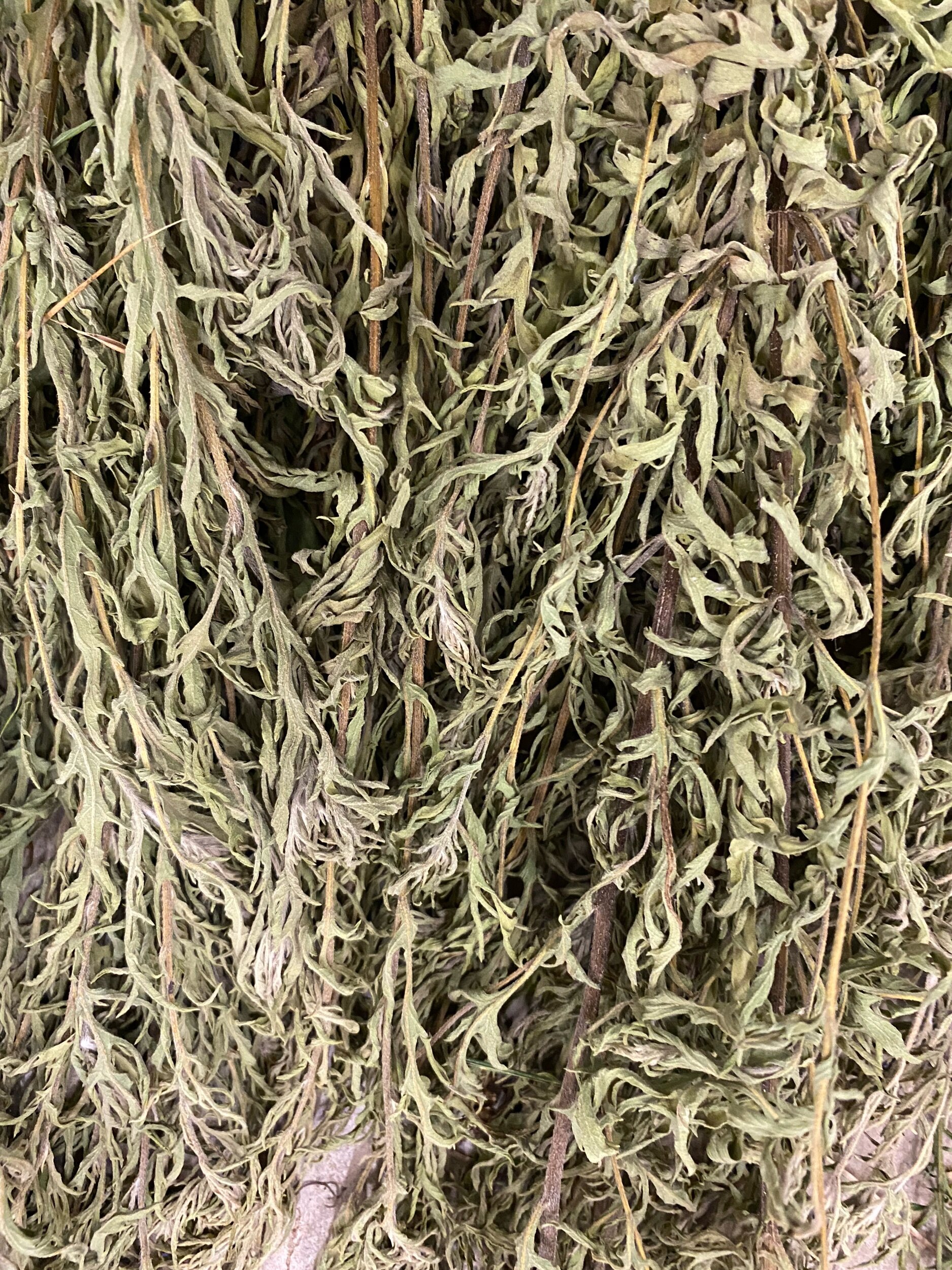
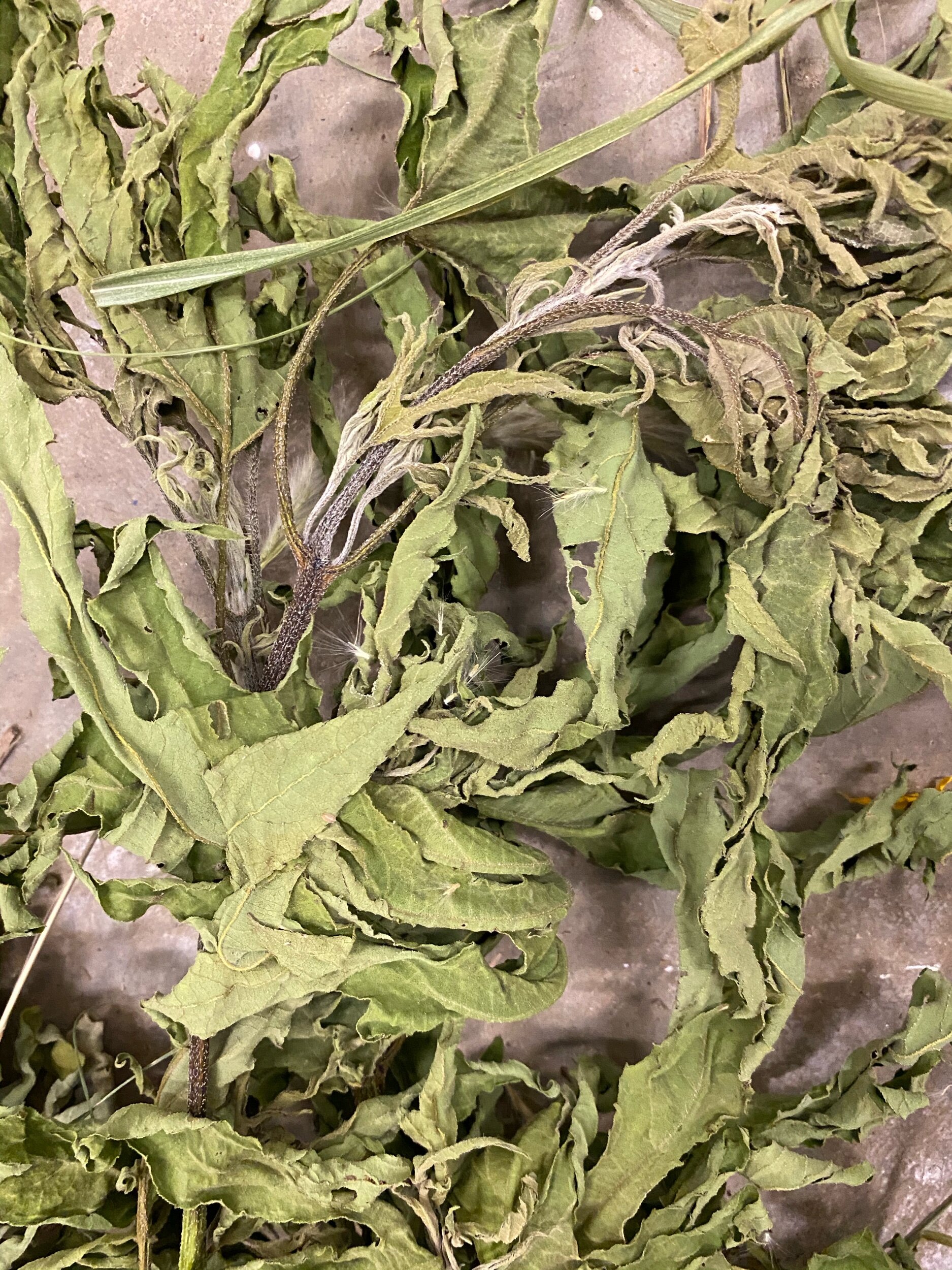
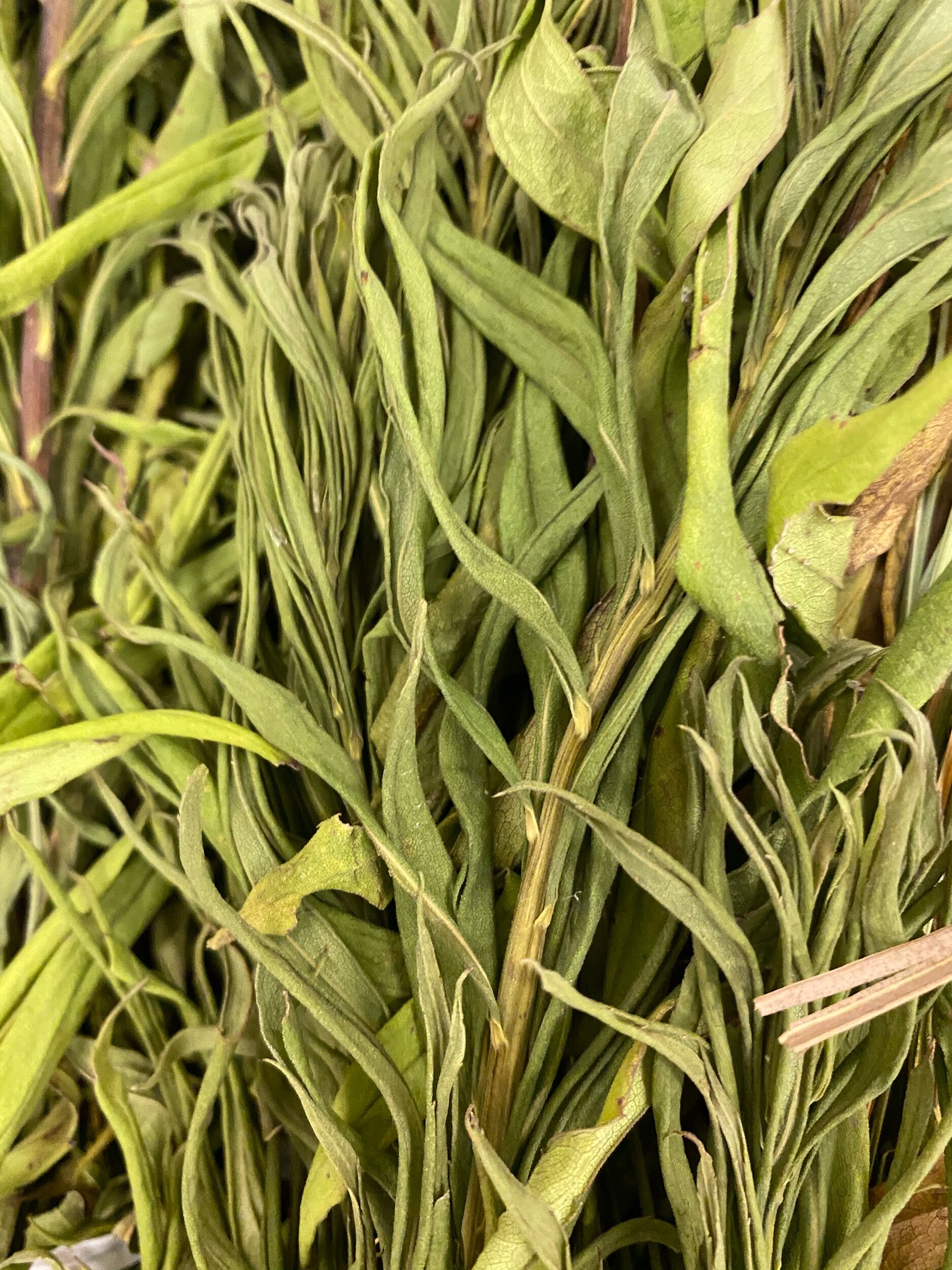








A peak in n my studio rich with native plants drying
I reached out to the Katy Prairie Conservancy, and they put me in touch with Bill Stransky with the Texas Rice Coalition, Bill a founder of the Katy Prairie Conservancy is a rock star in the nature Conservancy world. He very kindly offered to help me identify native grasses. He met me on a Sunday morning with his college-age daughters and not only pointed out native plants, but they helped me cut and bag them. It was such an honor to meet him and have him support my environmental work. I can not finish these piece without help in accessing native plants. It was a great day. I am hoping to meet Bill again in the fall when the rice plants are ready to harvest. It is important I have rice grasses since the exhibitiion space is a Success rice grain silo. The plants we harvested are presently drying in ny studio. My studio smells like heaven covered in plants. It is also the new home to a few spiders.

Bill Stransky and his daughters.

A bag of prairie seed mix. - donated by Bill to my project

The mix-

A new studio mate.

This is just the beginning, I need a lot more plants to dry for this large old male beast.

Since last November I have been dropping hints to Houston Chronicle writer Molly Glentzer to write a native bee article. Earlier this week she called to talk about native bees. Some of the information I talk about when I talk about bees is alarming. She asked if I knew a locacal native bee athaurity, I did not. She said she could find one.
Here article came out today. Sadly she did not mention my bee art activism but the native bee specialist confirmed everything I have been saying. And yes It is alarming. Knowledge is power. - plant native non hybrid plants, blue, purple, yellow and white primarily. Starting the conversation with art activism.
her awesome article is below.
https://www.houstonchronicle.com/life/gardening/article/Your-Houston-garden-needs-native-bees-15287310.php

In a moment of global uncertainty, I ask myself, what materials would I use to leave a message for future civilizations? As I think of artists who painted caves, of muralists from the past, of artifacts from ancient civilizations, I am curious about how we leave a mark. My answer is tied to the natural world: much of my previous work has been about conservation issues, looking specifically at bees, at waterways, at recovery from Hurricane Harvey, at bison and now, at grass. And so, if I were to write a message to the future, I would use grass to write it, and bison to carry the message.
Endangered Knowledge: The Soul of Humus
For this year's Sculpture Month, I propose a site-specific sculpture of a bison, made from a welded steel armature, a work of land art covered in topsoil and dried native grasses. This is part of a comprehensive installation that I am currently developing, which considers the role of the American bison within Houston's specific soil ecological history. The work is titled Endangered Knowledge: The Soul of Humus.
It is inspired by the words of M. Thomashow, who writes, "Record natural history to the collective memory so that it is no longer endangered knowledge." For several years, I have been researching grass-fed food production, attending soil conferences, and visiting regenerative ranches. Research in these fields show how to fight desertification and reverse climate change through regenerative agriculture practices. Interestingly, this natural history of living soil, how it evolved in the Houston Coastal Prairie, and its essential part within microbial communities in human health, is not common knowledge.
Description of Work
In the hide of a sculpture, I tell the narrative of soil health. My sculpture will record this endangered natural history through the dense coat of the powerful humus-built bison, that will be dripping in the armor of locally sourced dried native grasses and sedges, seeds, and pods. The male bison will be supported by a welded steel armature, covered in a stainless-steel lath. The bison's skin, made from these dried grasses, will be attached to the lath with a Houston mud composite. I propose the 11' long bison be exhibited in the center of a large grain silo, the bison in an actively grazing stance, head down in plow position, his hump rising robust and bushy out of his heavy forequarters to 6.5' tall. Lighted from inside the grain silo funnel, viewers can approach the bison and intimately inspect the diversity of the native plants implanted in its pelt.
Ecological History
Historically B. bison functioned as the first farm equipment. The grass seeds clinging to their burly coats were carried across the plains as they migrated north to south and back between seasons, like tractors up and down fields. Herds of tractors not green, but a rich brown harvested the plains with their appetites, each bite stimulating new root growth. The old roots withered into cavities that served as dwellings for a variety of keystone species, and became underground cisterns collecting floodwaters for drier seasons. Their coats dropped kernels and cuttings as the winds ruffled their beards and chaps, and when they took dirt baths in buffalo wallows dug with their horns. Massive roaming compostors, a single bison cow daily dumping 40 lbs. of fresh manure onto these seeds and drilling them into the earth with their spade-like hooves, sprinkling them with the perfect prescription of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium-rich urine and then moving in a predator safe tight herd on to the next buffet. With time the newly sowed fields sprouted new growth of blades, stems, and leaves of countless shapes, sizes, and heights. This diversity of leaves fit like puzzle pieces into dense living solar blankets, harnessing carbon from the air and returning it as sugars to feed the dynamic root microbiomes below the earth’s skin. The complicated relationship between the soil microbiome and the human intestinal microbiome is one of the most dynamic topics in biomedical research. Flocks of birds mutualistically
living off the pests harbored on the bison followed the herds, drinking from and bathing in rainwaters that collected in the bison wallows, building their nests from clumps of bison fur. Recent studies show the fur provides a health benefit to unborn chicks. Bird and butterfly habitats were abundant when the bison roamed.
Relevance
Global warming, food security, drought/flooding, wildlife habitats, economic instability, and health – these problems are not new to humankind. The archeology of ancient civilizations has recorded connections between the longevity of civilizations and the health of their soil. The United Nations reported in 2014 that the world's topsoil would only last 60 more growing seasons. Soil scientists around the globe agree that solutions to these issues are rooted in our treatment of soil—the skin that covers our planet.
Message to the Future
The armor that protects the epidermis in the Gulf Coast prairie is grass. The animal whose population peaked at 30 million, is B. Bison. Combine native grasses with ruminants and the grasslands decompose into rich organic matter; for every 1% increase per acre of biological organic material, the soil can hold an additional 20,000 gallons of water. Restoring native prairie vegetation decreases water runoff and flooding, increasing soil absorption of water and slowing floodwaters on land. With extreme building practices and concrete hardscaping, reimagining the landscape of Houston's 600 square miles of real estate can make a significant impact on the region’s flooding. The prairie grasses' roots can extend from eight to fourteen feet deep: these roots sequester carbon like an upside-down rainforest. Changing our agricultural practices is an important step towards turning global warming right side up. Telling the dynamic story about these relationships between the grazing herds, the living soil, and finding ways to reimagine urban landscapes and agricultural practices in holistic and regenerative ways are the center of my current research and sculptural practice.
The impact of the bison on sustaining topsoil—and, therefore, life—need not be Endangered Knowledge. The role bison play within the prairie ecosystem—their ability to increase photosynthesis, reduce competition for water, and regenerate depleted, unsalvageable, lifeless prairies back to productive and bountiful, nutrient-producing land and wildlife habitats—needs to be carved into our modern systems. Recording this Endangered Knowledge into the consciousness of humankind will stimulate grassroots efforts and stop the cultivation of soil depletion and return the natural process to the treatment of the skin of our planet. A Parietal artist in 2020, I will use grass to record the Soul of Humus so that it will no longer be Endangered Knowledge.
Additional work
Soul of Humus will be the first piece in my Endangered Knowledge body of work. The complete body of work will eventually consist of the following sculptures: 4 pedestal-shaped sculptures of roots and soil, measuring approximately 12" X 12" X 36"; installations made from native grasses and their roots (size and number to be determined); 1-5 bronze castings of bison dung with their spade-shaped hoof prints, dung beetles, and mushrooms. I am also currently in conversation with a bison rancher to secure a bison heart to float in a glass case of formaldehyde: the bison, the largest mammal of the western continent, is the heart of our soil diversity, it is the western symbol of a healthy planet. The health and longevity of civilization, as we know it, is dependent on finding ways to mimic the natural process stampeded into the bayous of Houston. In this sculptural series, I look closely at the components of this process and the environmental interrelationships unique to the Houston area and world health.
Footnote-
Bison vs Buffalo which name is correct? The common name Buffalo has been widely used, since early settlers were naming them as their European and Asian counterparts. The correct name of the last American surviving bison is B. Bison.
Further Reading and information –
- Allan Savory on how to fight desertification and reverse climate change
- Soil as Carbon Storehouse: New Weapon in Climate Fight? - Yale E360
- A Prehistory of Houston and Southeast Texas,– D. Worrall, coming fall 2020
- Can Livestock Grazing Stop Desertification?
https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/can-livestock-grazing-stop-desertification/
- Dirt: The Erosion of Civilizations, by David R. Montgomery
- Soil Biology and Land Management https://www.nrcs.usda.gov/Internet/FSE_DOCUMENTS/nrcs142p2_052489.pdf
- Wildlife that Depend on Bison
Sample Work and Visual Support Materials for Proposed Sculpture
Two small sculptures that are made with the same structure, process, and made with native plants-
The bison will be furrier than these small birds are and would be dripping in a thick coat of textured dried grasses.

Hay Day Peace Pigeon 2016
15” X 12” X 8”
welded steel armature, plaster and hay

Feathery Finery Peace Pigeon 2016
12” X 12” X 6”
steel armature, steel lath, plaster and plants
Three large sculptures that are made with the same armature and process, but I have used metal instead of dried plant cuttings on the surface for texture.

Broken 2018
40” X 29” X 55”
Welded steel armature, stainless steel lath, concrete, wire cloths and wire

Sonata in 4D 2018
6’6” X 5’5” X 5’
steel welded armature, stainless steel lath, plaster, wire cloths and wire

Bringing Home the Bacon 2019
66” X 42” 60”
welded steel armature, stainless steel lath, hydro stoner, wire cloths and wire
There are many textures of native grasses at the Katy Prairie Conservancy and Buffalo Bayou.
If you accept my proposal, I plan on asking the Katy Prairie Conservancy and the Buffalo Bayou Partnership to allow me to source my grasses and plants from their properties.

Sample of one of the many amazing textures on the various grasses and plants in the coastal prairies.

This shows the movement I am visualizing on the coat of the Bison
Below are Some of the source images I will use while sculpting the bison.
most of these I took doing research at Roam Ranch this summer, fall and winter.

This shows the position of the head I am looking for, it is grazing but you can see the face. This is a cow (female) My piece will be a burly big old male.

This is a large bull but it is not very old. My sculpture will be an old male that will have scrapped up and chipped horns from fighting and digging wallows and a massive thick (and dripping with dried grasses) big beard and chaps. This side view is pretty close to what I have in my head. I might have his head turned slightly to one side. That could be determined by which side of the building the silo would be on. The face will be more interesting and textured than the back side of the bison will be. My sculpture would be grazing on taller grasses. I would also raise his head for more eye contact

This is a good image of a bull’s face. Not my photo.

another view- not my image
It was never my intent to become an environmental activist – I am beginning to wonder if that is what I am. Since the below email I have had one meeting with Sally Alcorn and her assistant Hannah Cobb. They are on board with my thoughts and want to help. We decided the first step is to look at the citi’s present landscape ordinance, and then Coronavirus 19 hit Houston.
I guess even in a pandemic certain things have to continue, such as city budget planning. I received an Instagram message from Sally April 27th at about 11:00 pm regarding a video of the City Council meeting and the City Parks budget. I will make another blog post summing up the results of that meeting. Maybe this pandemic will open some doors that normally would not budge.
TO: Sally Alcorn salliealcorn@comcast.net
Dec 27, 2019, 10:14 AM
RE: Houston’s impact on bees.
Sally,
It was great to run into you at the mother-daughter Christmas party. I appreciate your interest in positioning Houston to become the leading city in the U.S., addressing the native bee environmental issue. You have a lot on your plate with your new elected position, so I thought I would recap a few of the important topics we discussed.
Scientists predict that without pollinators, human life can only continue for four years. In 2017, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service listed the Rusty Patch Bumble Bee on the endangered species list. The campaign to list a species as endangered is lengthy and complicated. With this system, it is difficult to gauge how many species are actually endangered.
Bees are responsible for pollinating 75% of the world's flowering plants; they are crucial for the production of most fruits, nuts, and berries – our agriculture depends on pollination by bees.
Rural areas are highly impacted by the unanticipated consequences of our industrial agriculture’s dependence on chemicals that weaken bee’s immune systems. Urban bee populations can be more diverse than in rural areas. Researchers are finding in cities such as Chicago, Berlin, Berkley, and Melbourne that have reimagined their parks, neighborhoods, city centers, vacant lots, street medians, and rooftops planted with native flowers, grasses, and fruit, and vegetables support healthy, vibrant wild native bee populations.
In the US, there are four thousand native bee species. They pollinate over three hundred times more effectively than honey bees. For example, A single female Leafcutter Bee visits 100,000 plus blossoms per day whereas a honey bee visits 50-1000.
Unlike the honey bee, Native bees do not swarm, are not aggressive. Native bees are perfect for urban population centers.
Houston covers 600 square miles of land and has one of the longest growing seasons in the U.S. As it continues to sprawl across Texas, its gardens must increasingly become a refuge for native plants and animals. With 2.3 million people living in the most vital economic, cultural center of the south, we can become the most critical urban native bee habitat in the United States.
I have spent the last year and a half studying the bee situation as it pertains to my art and my interest in regenerative agriculture. I am determined to take this knowledge and save the bee in urban settings.
With Houston's land size, population, and location in the Sunbelt like it or not-we are impacting the bee population.
I realize we will have to start with baby steps. Let's put our creative minds together, save the native bees, and build a better energy capital. This is a great opportunity for our new city council.
I am very flexible are weekdays or weekends better for you to get together?
Best,
Cindee
P.S.
If Cuba can create urban gardens to feed it’s poor can you imagine what we can do.



Things are now going smoothly maybe too smoothly. All the work I did this summer is paying off.

Close up of support system
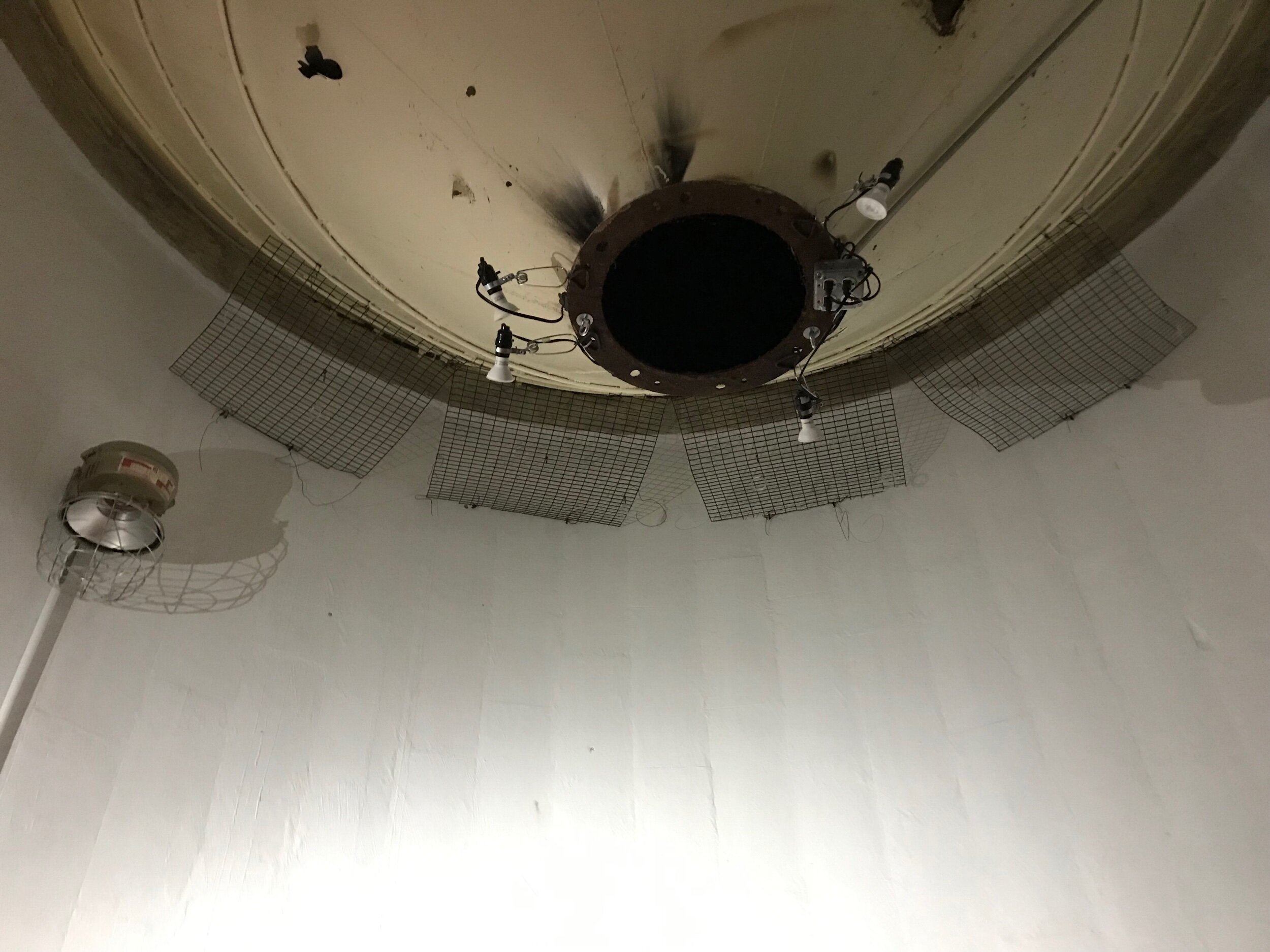

The moment I got off the scissor lift and looked up at my support system, I realized I had made a big mistake. I should have painted them white. The black stood out too much on the white walls. I could not sleep that night trying to decide if I should repaint them... It was not easy, but I spent the next half day painting the system 19’ in the air white.
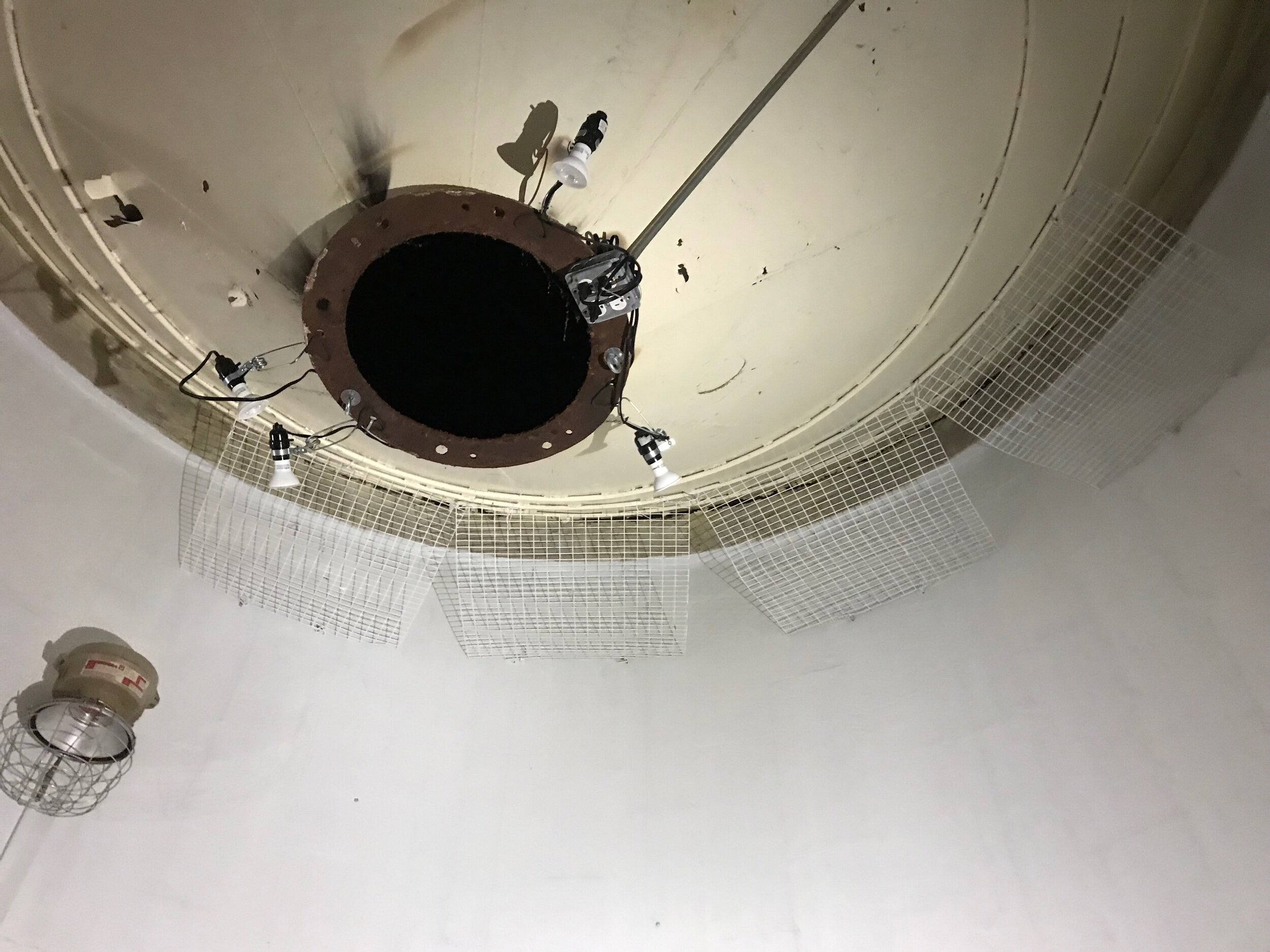

I think it was worth it, the support system is much less intrusive.
I hung from the support system 8 fishing tackle swivels with 25 lb filament attached to each swivel. Four of the swivels are 36” apart 18” from the wall. At these distances the pieces will not touch each other or the wall. Everything should move independently. These are for the big pieces. The other swivels are for smaller pieces and are spaced randomly. I am guesstimating where I want these. Tomorrow I will start hanging work.
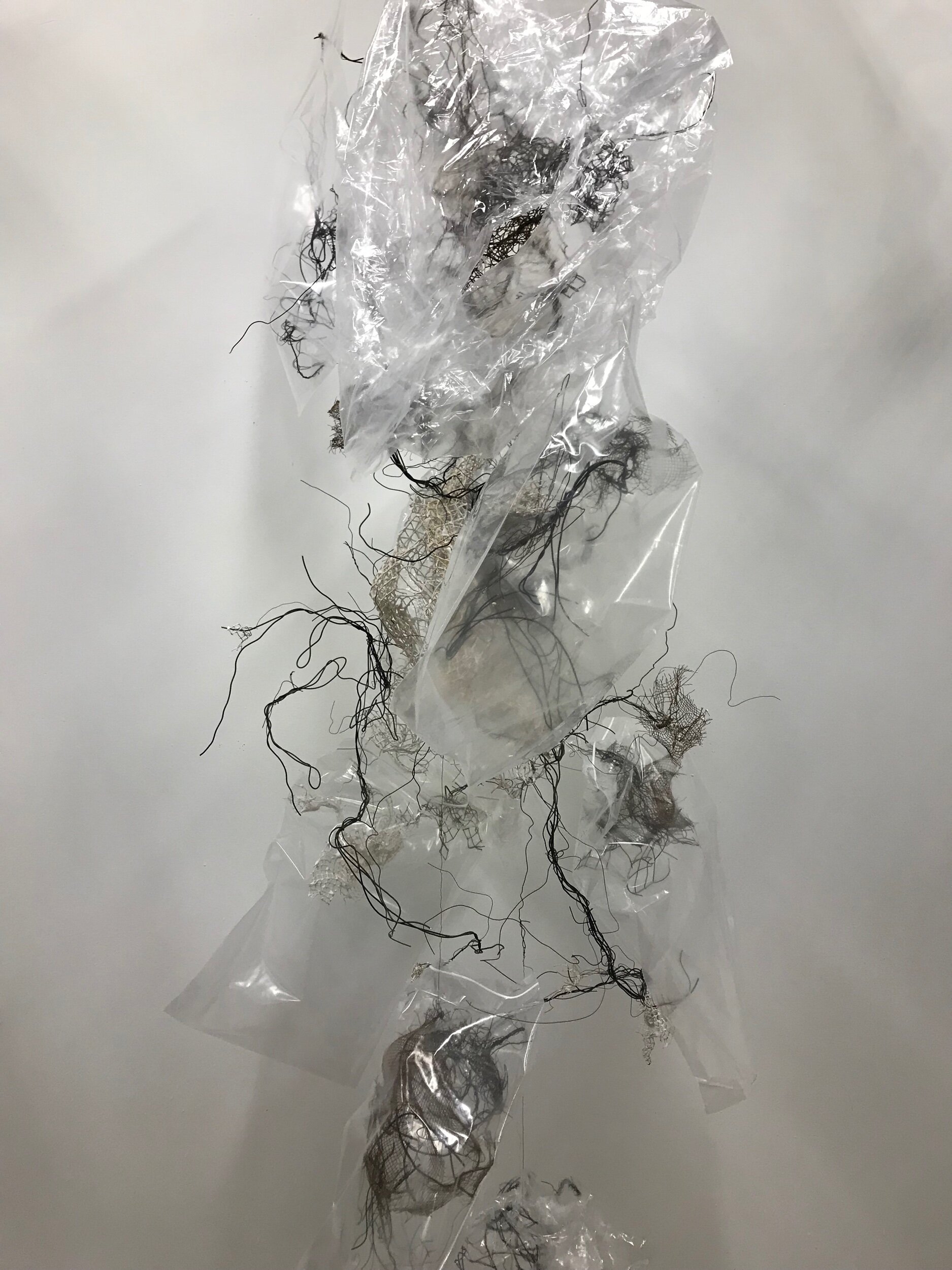

Each small element bagged separately making bouquet of bee cocoons
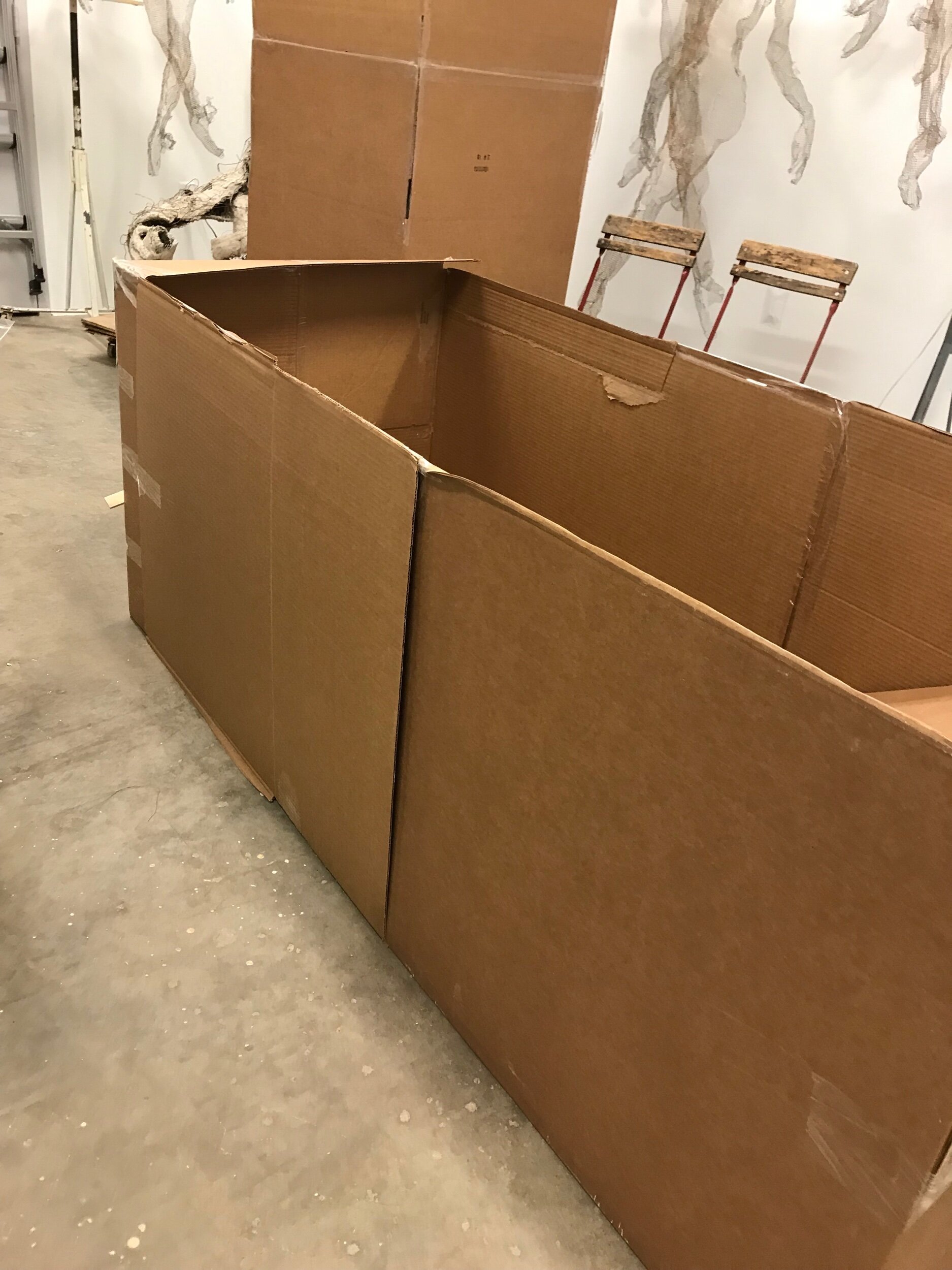

Making my own wardrobe style boxes.

My pieces hang from the top of the boxes. I needed something to support the top of the box. Southland hardware yard sticks were the cheapest thing I could find. I think they will work.
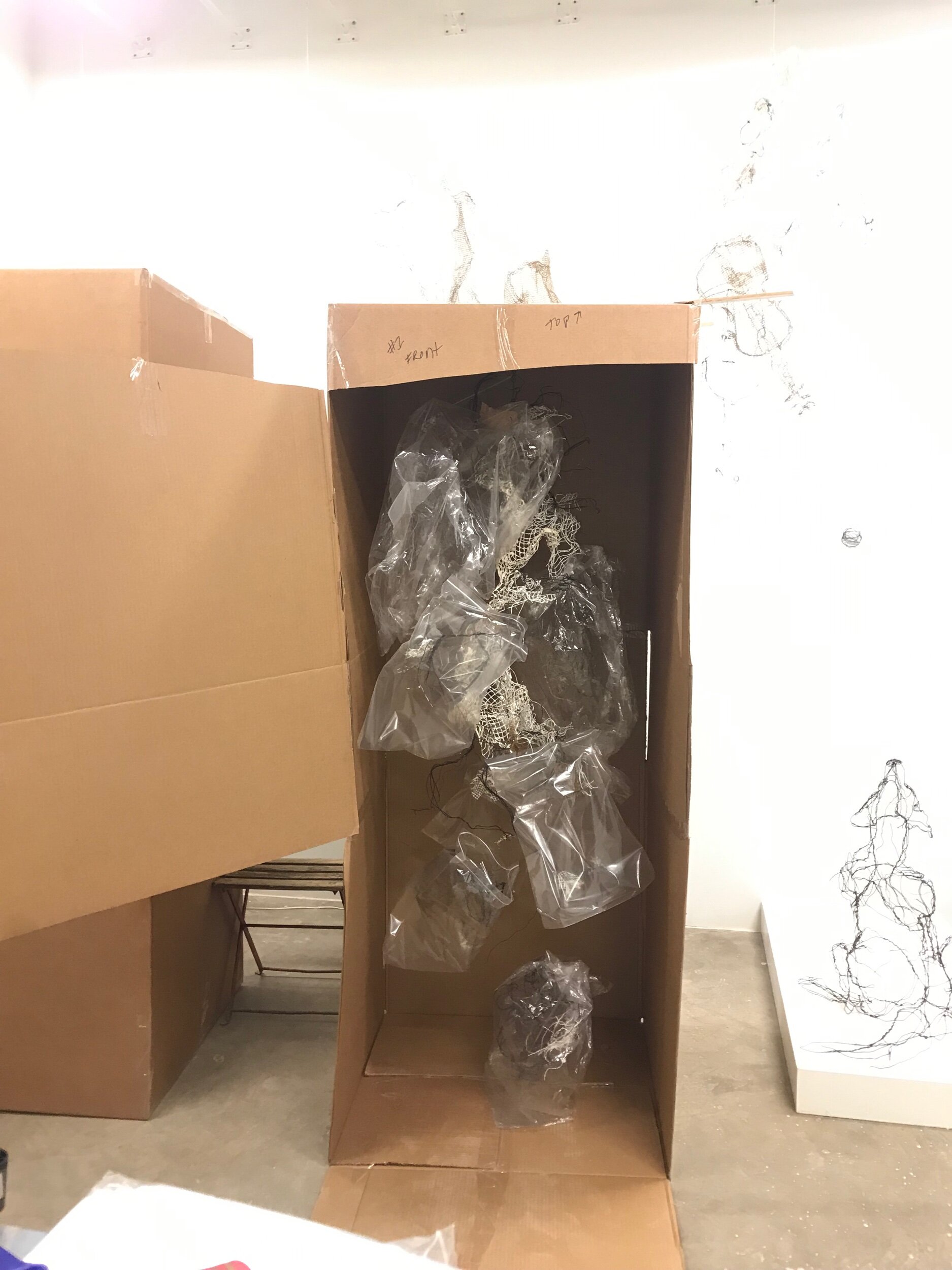

My sculpture wardrobe boxes have doors.
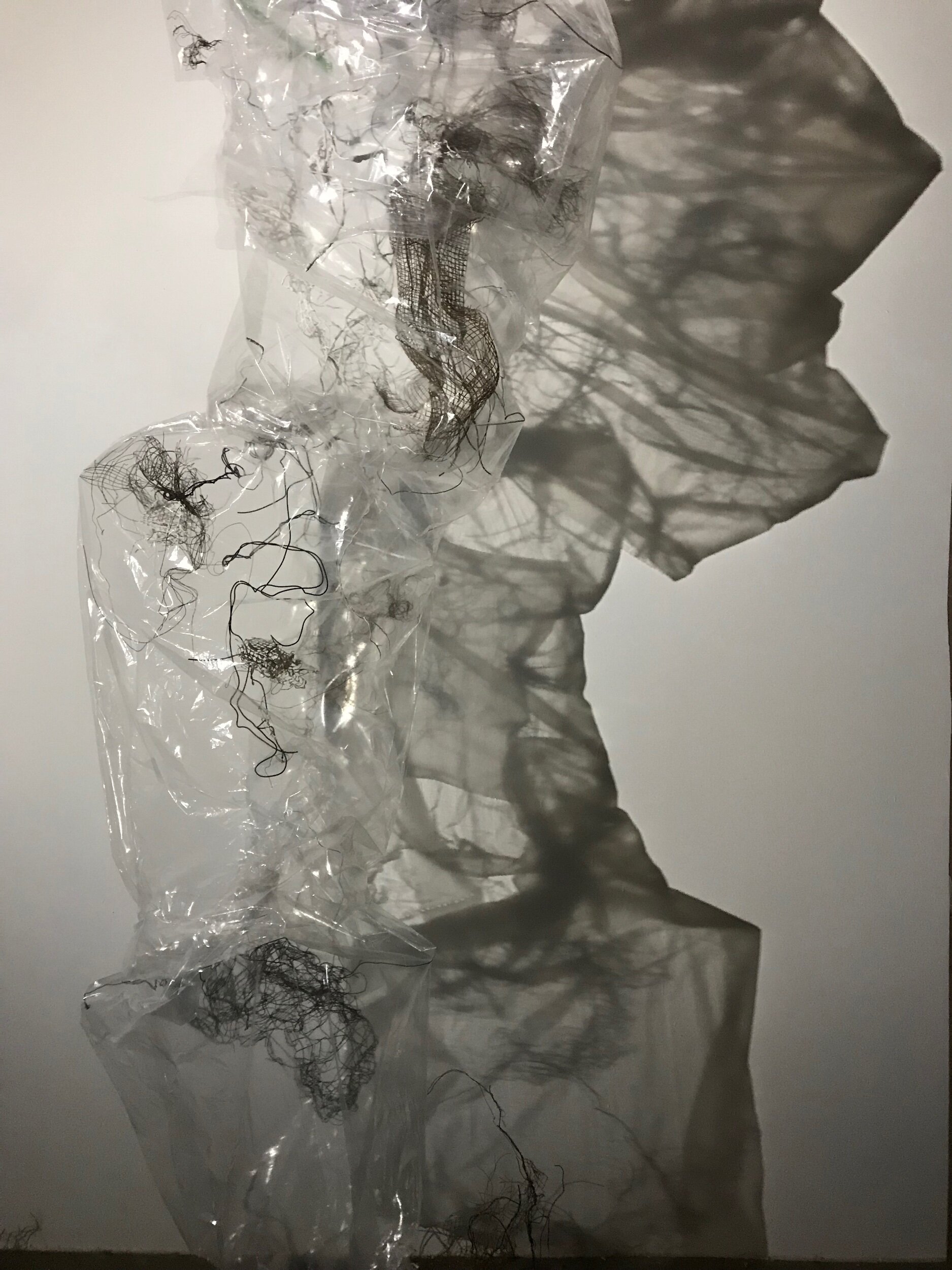

The pieces in bags make awesome amnion shadows

7 boxes ready to go.

Behind and attached to the Silos at Sawyer Yards

The lobby of the SITE Gallery Houston with the mechanicals of the grain silo in place. Just the coolest

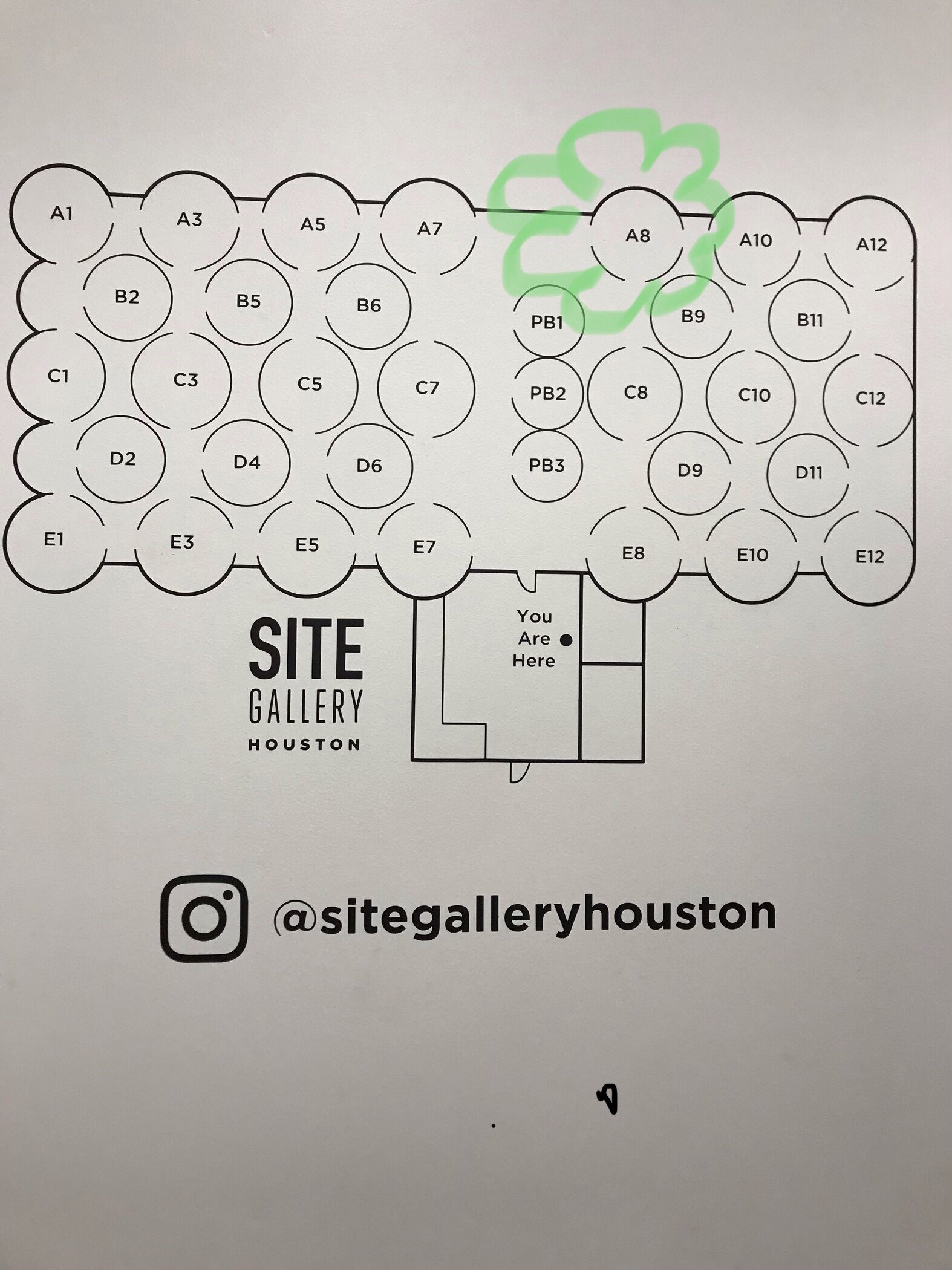
Green marks the spot

In May I started seeking a space to exhibit new environmental, 4D kinetic sculptures. I hoped to use this new work as a start to an art installation inspiring conversations about topics I am very passionate about; the unexpected consequences of forcing natural processes into an industrial model and the complex relationships between humans, plants, and animals.
The stars aligned in July when Sculpture Month Houston’s founder and curator, Volker Eisele, invited me to be one of the 19 artists asked to create a site-specific sculpture in the historic Success Rice Grain Silos behind the Sawyer yard’s artist studios. In the 50th anniversary year of man landing on the moon, this year’s exhibit title is Outta Space from the 2012 Van Halen album A Different Kind of Truth. Outta Space will combine two curatorial themes: one features work focused on environmental degradation issues and the other focuses on interpretations and explorations of Alternative Worlds as envisioned in the fantasies of the artists.
I have passionately committed myself to this installation every day since July. My passion comes from spending my early years on a farm in west Texas, from my concerns regarding industrialized food and its effect on our health, from my love for historic buildings and, most importantly, from my desire to make an impact on the return of our most important keystone species.
As a site specific installation artist my aspiration is to create a piece that is unique to the silo’s space and true to my work. My silo is a circular space constructed from cinder blocks, 18’ in diameter and spans 20’ in height. It has, in the center of the space a 10’ tall funnel suspended from the ceiling. There are a few old, large light fixtures, conduit runs vertical and perpendicular on the walls and there are three entrances to the space. I have three weeks to install the work that I have assembled to date. My mantra as an artist is “if I am not nervous to take on a new project then I am not stretching myself”. I am slightly anxious, yet happy to embrace the butterflies and honored to have my name listed among this year’s SMH artists.
In celebration of the opening there will be food trucks, a bar and music provided by Chapel In The Sky with projections by Michael Walrond - SHDWSOFDUST.
Public Opening for the Exhibition
SITE Gallery Houston,
1502 Sawyer St. Houston, TX 77007,
(The multi-story building behind the artist studios facility).
https://glasstire.com/2016/11/04/the-problems-and-rewards-of-houstons-silos/
https://glasstire.com/2017/10/30/a-conversation-about-art-and-the-silos-on-sawyer/

7 days left to rip and wrangle rusted wire cloth, then delicately stitch the wire fragments into biospheres of frail and vulnerable abstract wild bees and organic shapes. Then coat hydro stone and cast shadows, to kinetically unveil the unintended consequences of forcing natural processes into an industrial model. Then pack, transport, unpack, install for 21 days, and open........ find more locations to install......... rinse and repeat.


