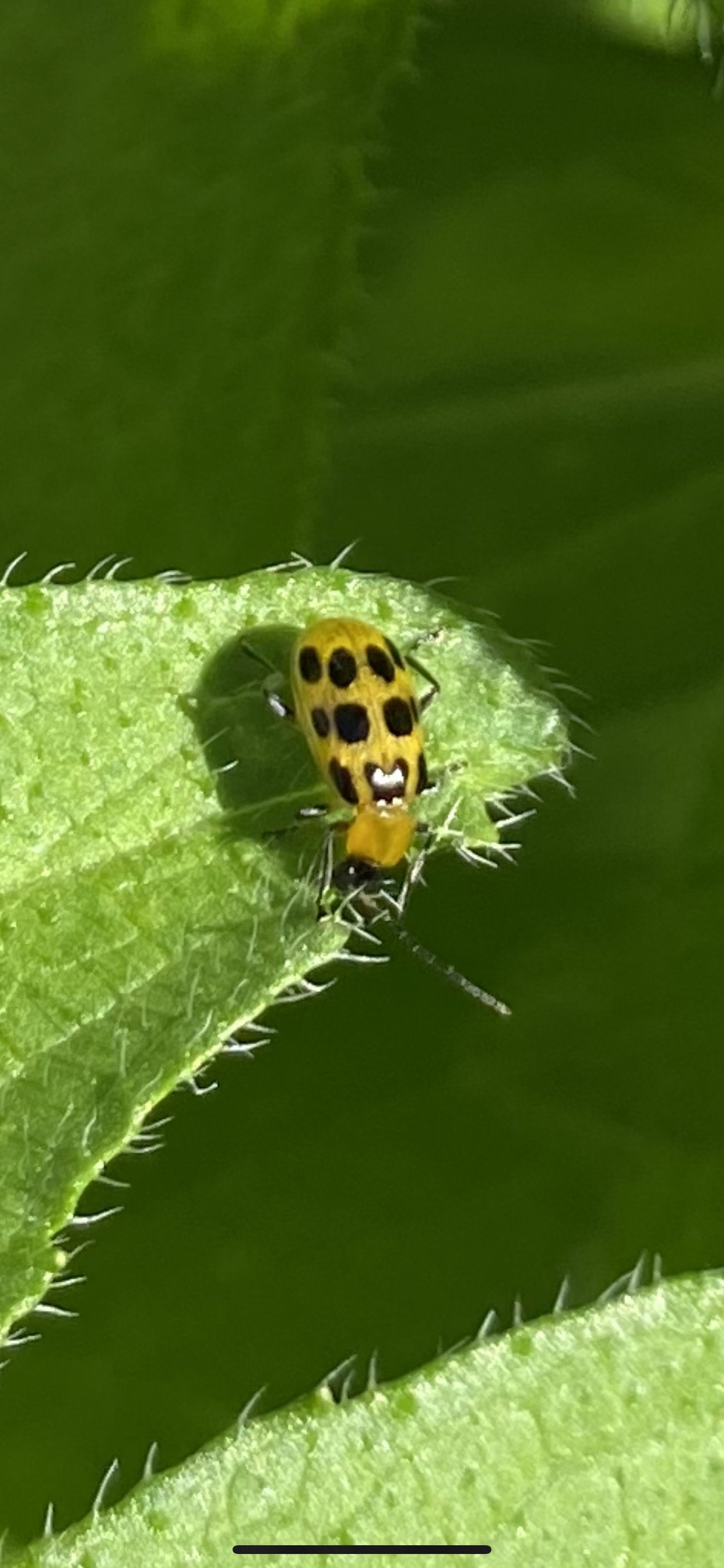
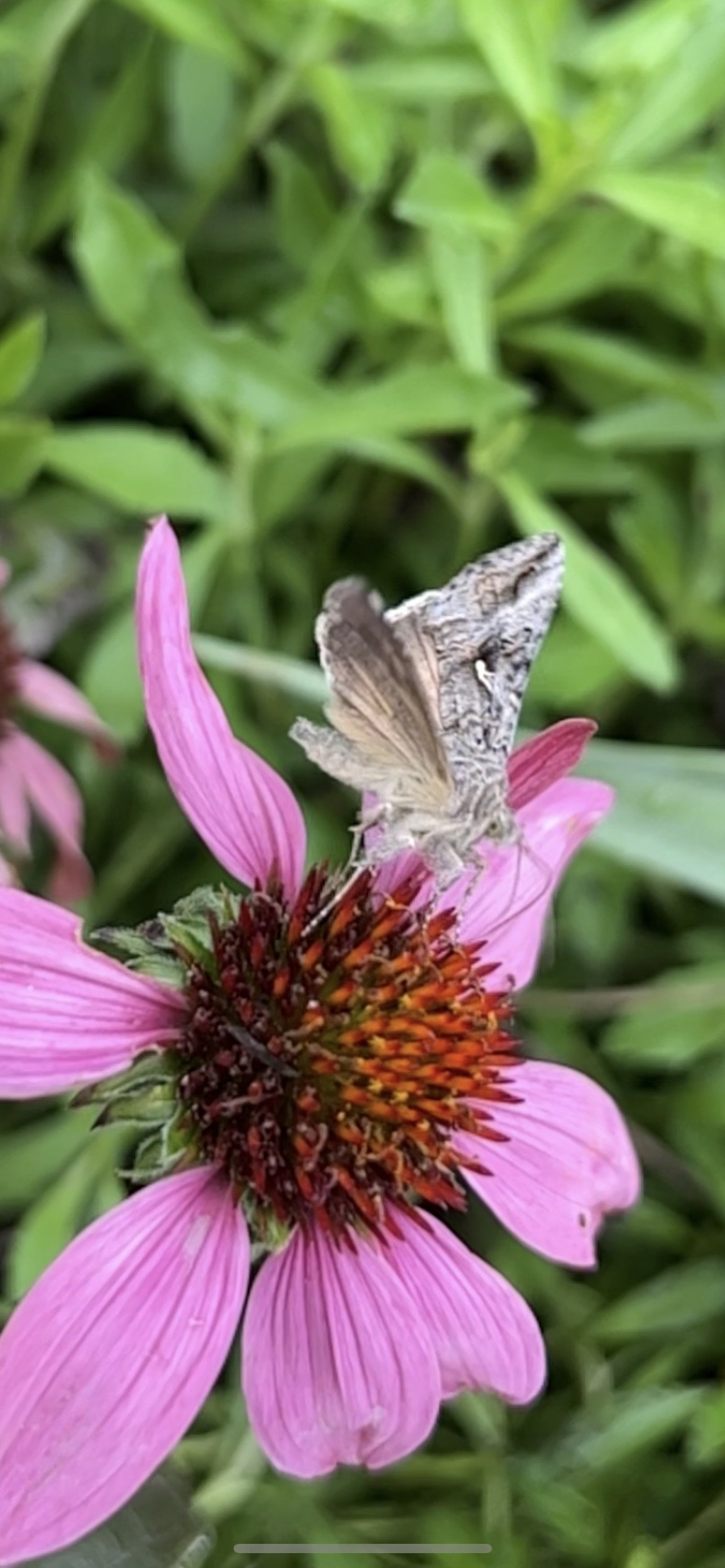
Tiny spent sunflower bloom/seed head-the colors - suttle and faded, still rich and deep. The shapes of the seeds as they dried ❤️ The beauty of the natural world when you stop and look. I studied this dried object probably 4 minutes turning it in my fingers watching the white blooms from the crepe myrtle attached by the thread of a spider and then turning it over hiding underneath- a creature. As we enter the Anthropocene, saving insects is a priority in “Symbiosis.” When I edit out any materials such as this elegant, delicate, dried Rosinweed sunflower head from the garden, I do not bag them and put them in a trash can. I chop and drop. This tiny spider is evidence that chopping and dropping not only builds soil and saves money it also saves insects.
Green Tree Frog Eggs
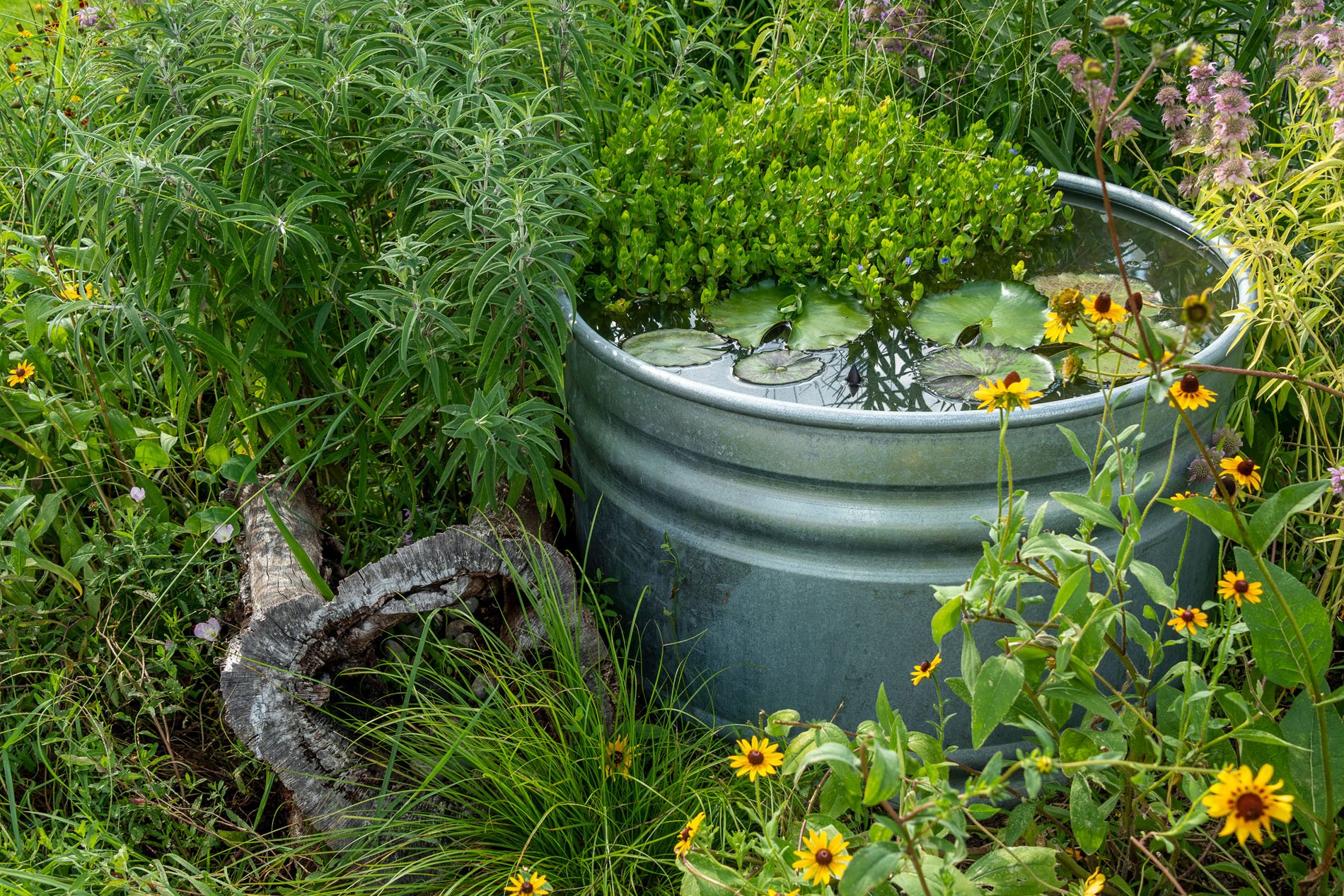
We had the first big spring rain the week before Mother’s Day. That Saturday , I stopped in "Symbiosis" to check out the wildlife and chat with anyone visiting the exhibitions. To my surprise, the pond is now a green tree frog nursery. The trough pond is surrounded by tall native plants that tree frogs love. I have not seen the green tree frogs since last year, I thought I heard them one night few weeks ago. Mother toads and tree frogs have to have water to lay their eggs. I believe tree frogs lay their eggs on limbs where they fall in the water.
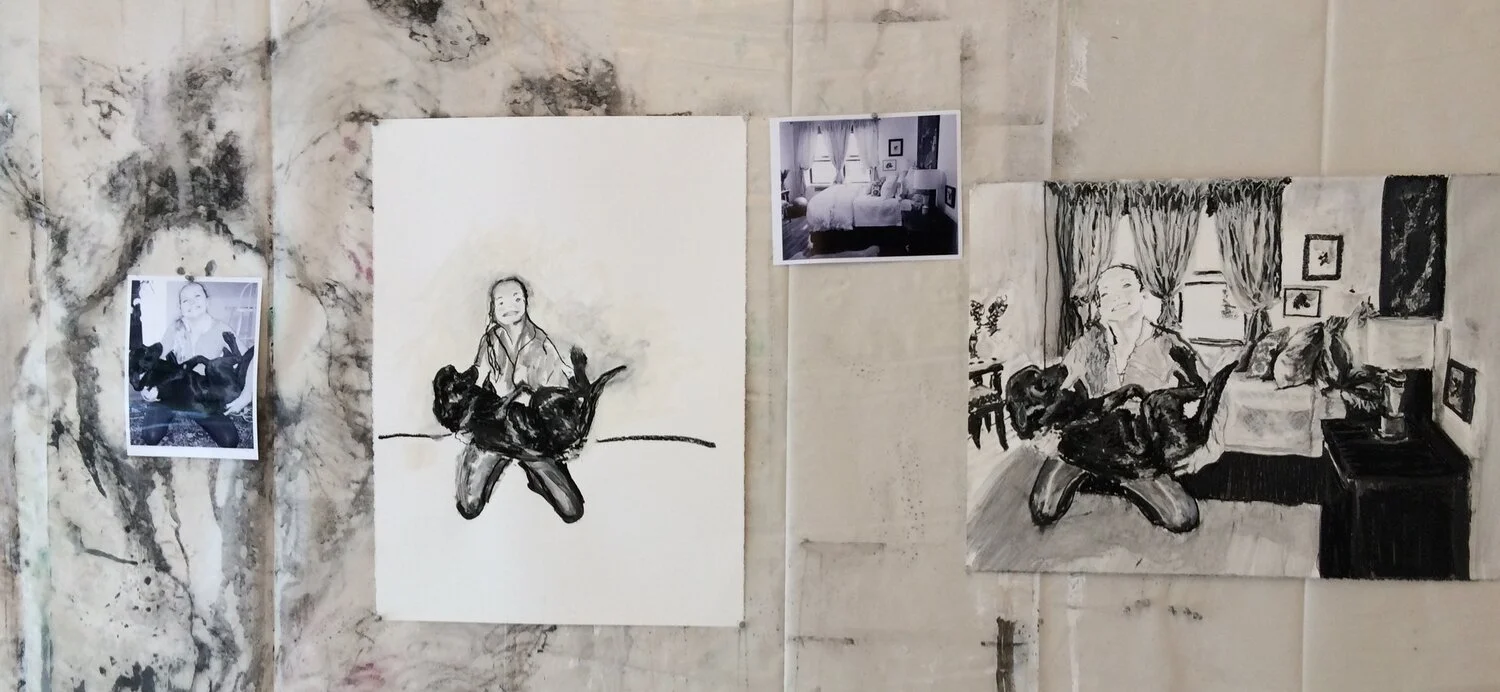
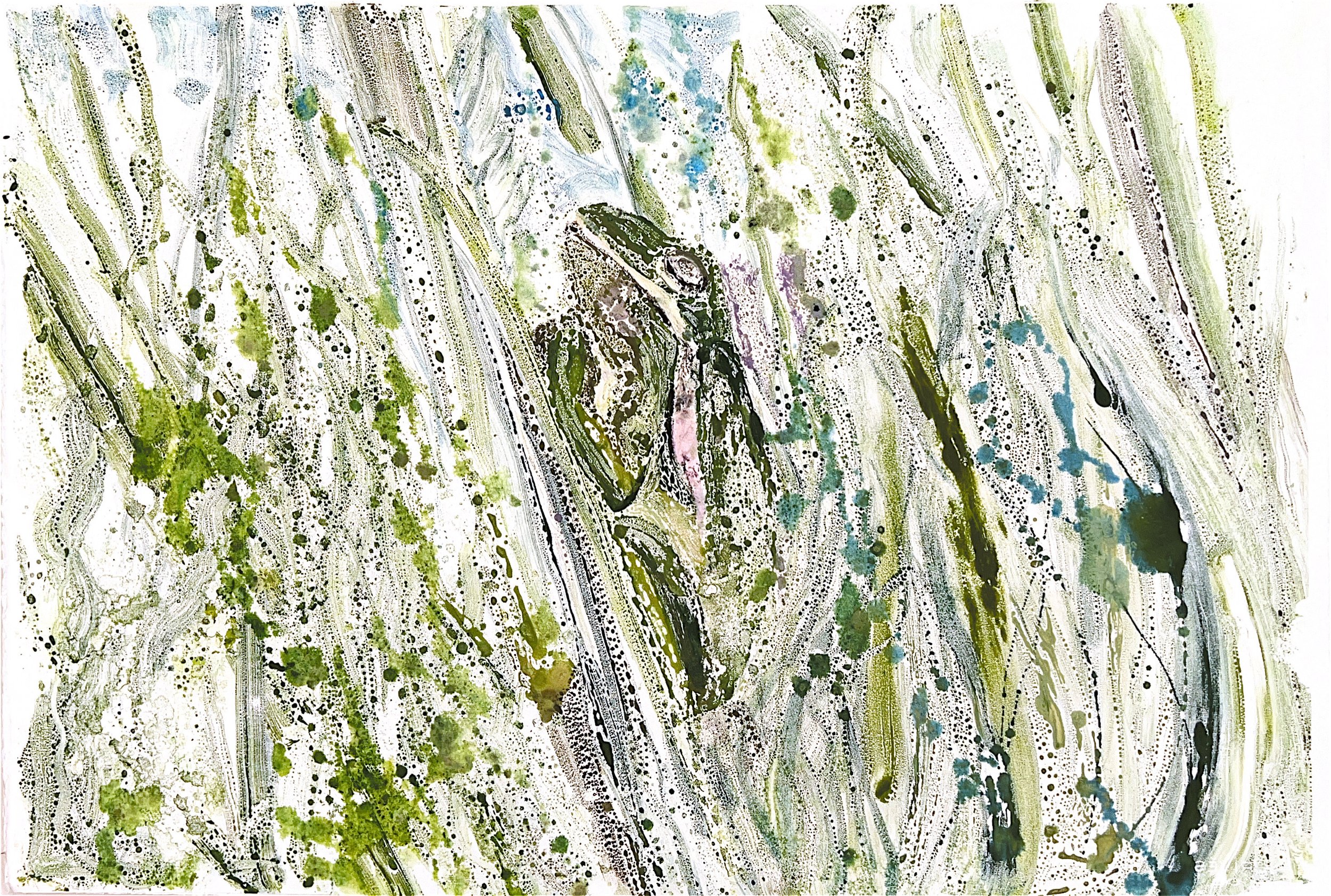
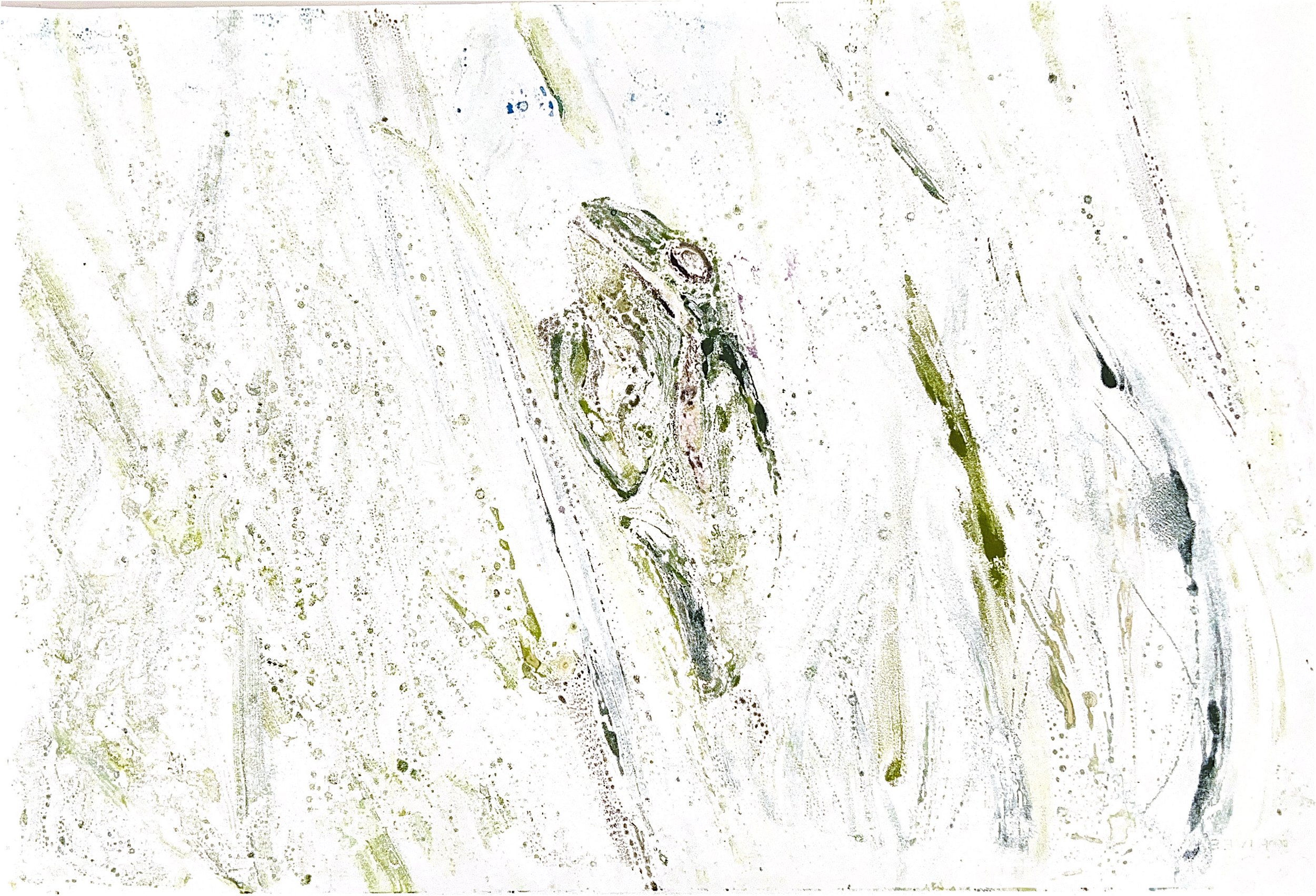
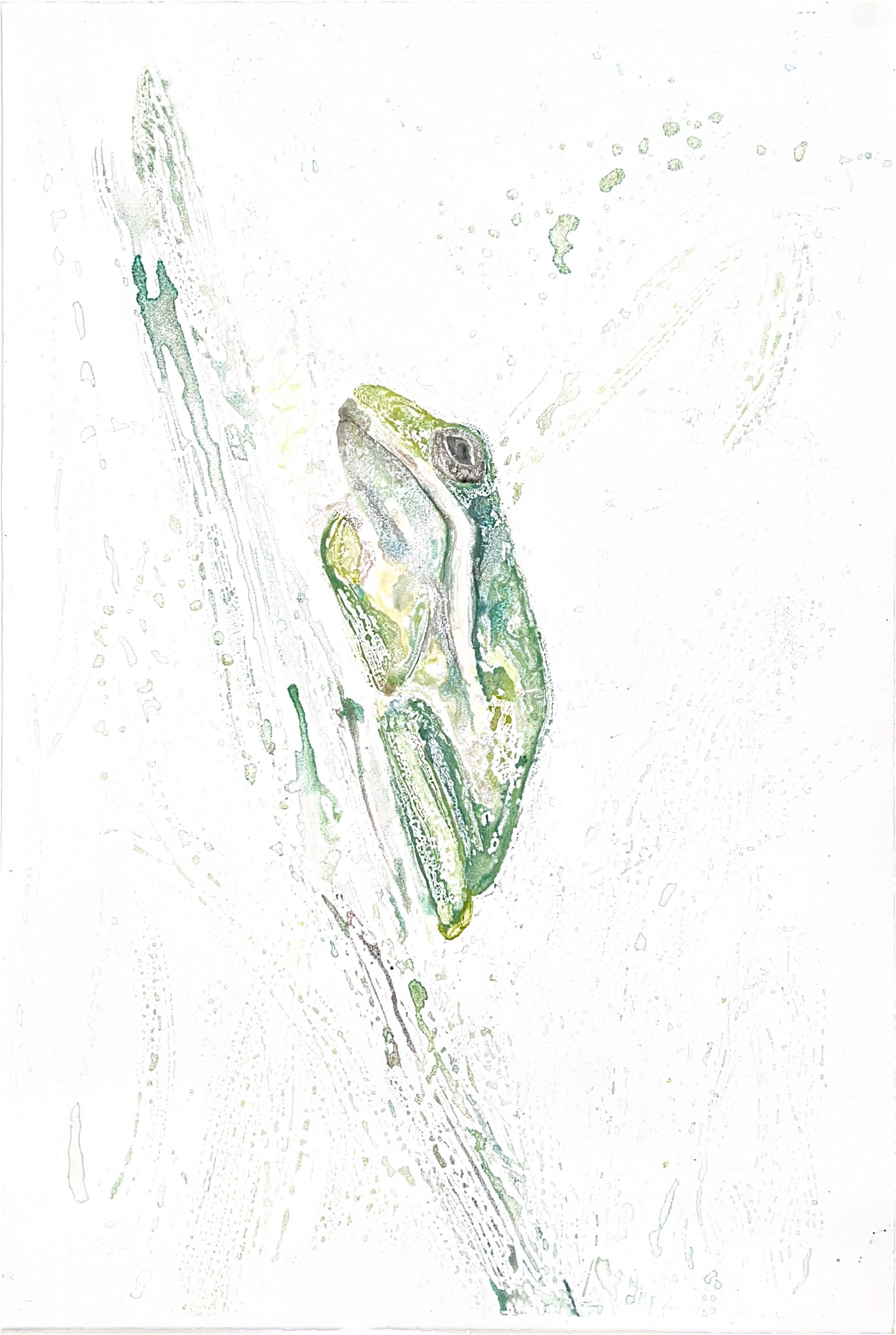
Above are a few watercolor monotypes I did of the tree frog.
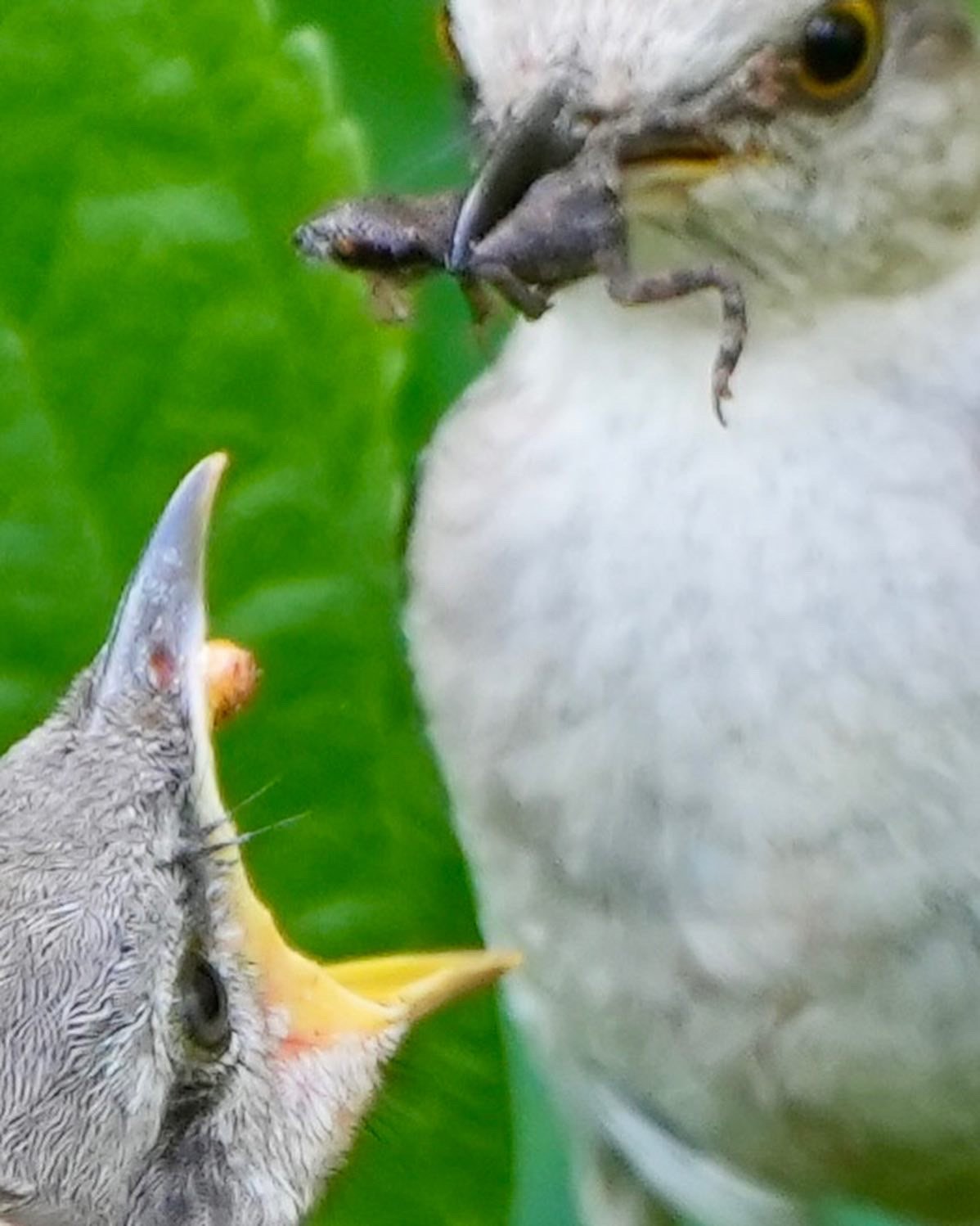
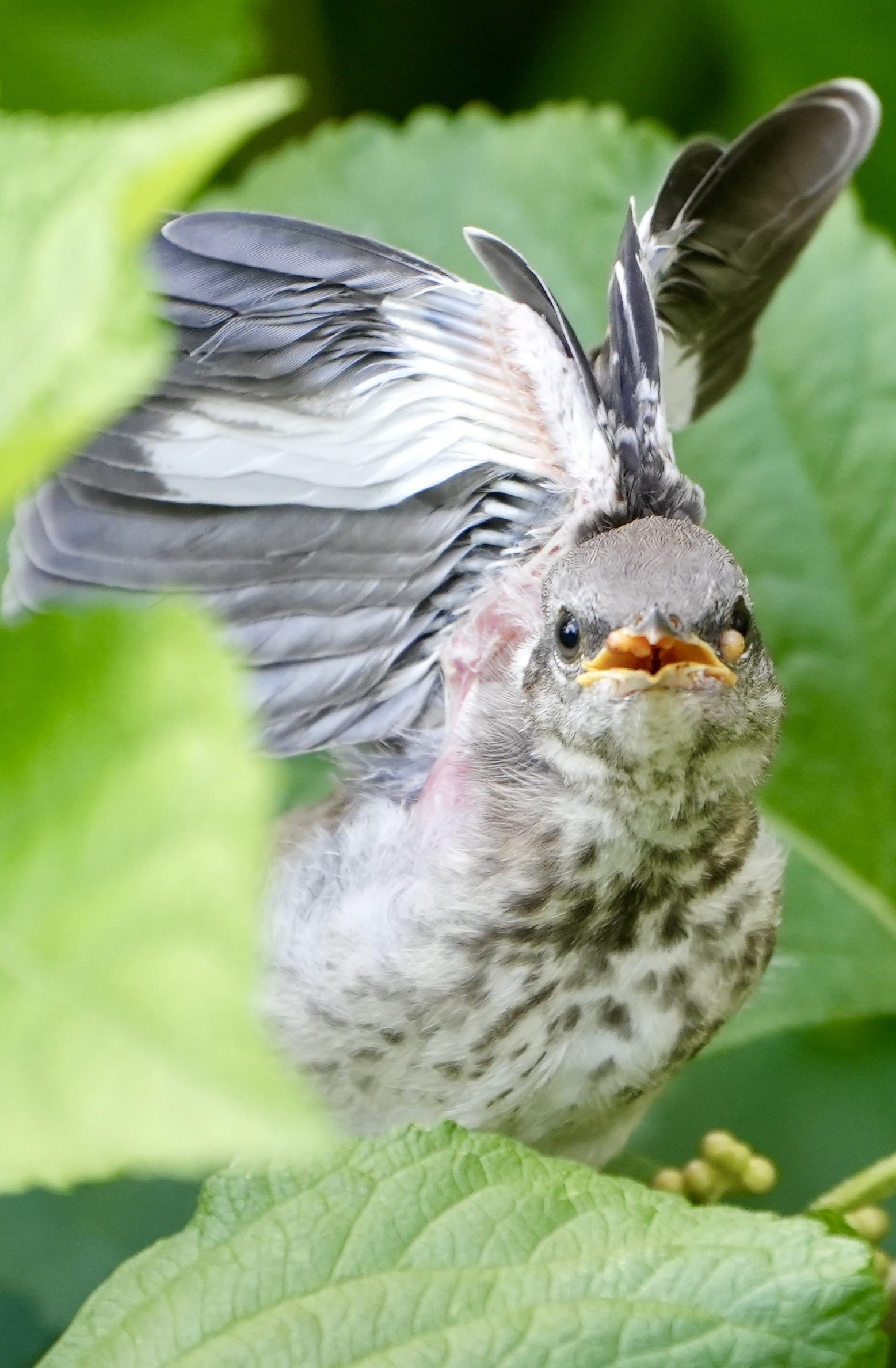
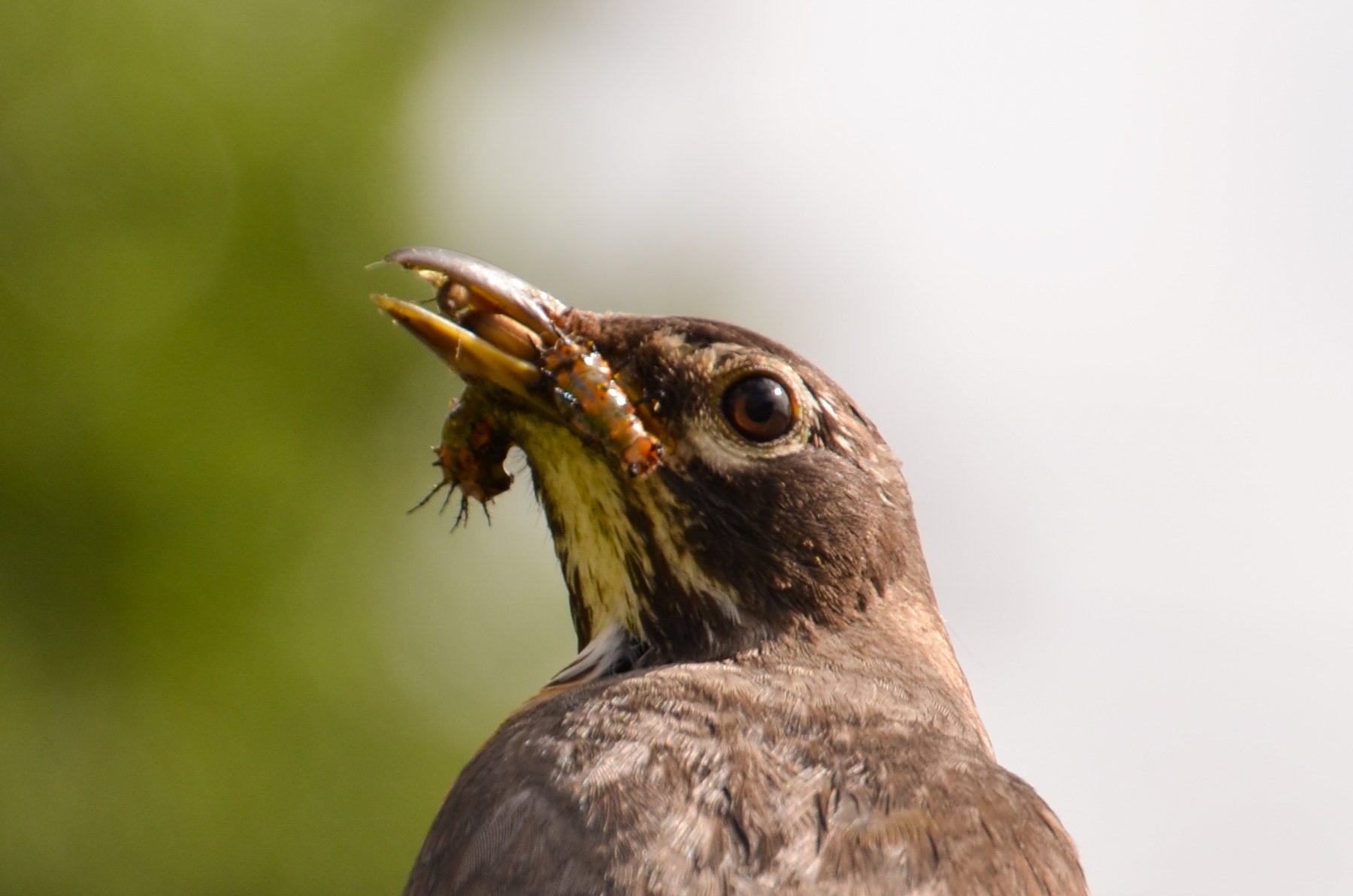
Symbiosis- Food chain - Mockingbirds and Toads
On an early July morning, with a new camera in my hands, I was hopeful the zoom lens would document unseen details in Symbiosis. I focused the lens on the “feed me” gesture of the juvenile bird. Later zooming in on the image on my computer revealed the middle of the food chain — A Mockingbird feeding a juvenile, not a caterpillar, wasp, or an insect but a slight blurry silhouette of a toad. On my laptop, I witnessed the middle of the food chain, a moment in a living sculpture, evidence of a healthy ecosystem and hope in a sea of asphalt on the Gulf Coast.
In Symbiosis building, a food chain that has not been exposed to chemicals or pesticides is crucial to building a base and armature that supports the more visible kinetic elements — wildlife and humans, the upper food chain. Its strength is critical to the success of the whole.
I use systems thinking to plan and organize my sculptural additions and extractions to the piece. In this case, not using pesticides to control insect pests or unruly vegetation is a priority. The water feature in the garden invites mosquitos, dragonflies, frogs, toads, and aquatic insects to lay their eggs in the still water. The tadpoles, nymphs, and Texas mosquito fish eat the mosquito larvae.
In the work, all of the individual species are linked by the health and abundance of the lower species. “Symbiosis” is an element of the “living” Earth, a community of organisms existing within the Art center's sculpture garden and social sculpture.
That Was Then This is Now.
July 2020 - the sculpture garden as it was when Stephanie and I first discussed the project.
February 2021. After the Texas freeze
May 2022 - 12 months from installation.
I ❤️Aphids and what insects tell us.
I Leave aphids be. It may look alarming but It is a necessary step in regaining a balance of good bugs and bad in "Symbiosis". I am looking forward to see which beneficial insects show up to help the planet manage the aphids. Aphids feed through a needle-like mouthpart. After they insert their mouthpart into a plant's tissue, they then use it like a straw to suck out plant juices. The do not kill the host plant. Aphids aid benefical bugs they are food for thousands of different species of predatory insects. As protein Aphids help build a broad diversity of beneficial bugs in nature.
After writing this post I came across one of the most interesting insect control articles.
We have so much to unlearn.
Land Art vs Living Sculpture
Land art or earth art has paved the way for what I hope will become a new art movement.
The Tate defines Land art or earth art as the art made directly in the landscape, sculpting the land itself into earthworks or making structures in the landscape using natural materials such as rocks or twigs. With the Tate's definitions, Symbiosis is land art, a part of the conceptual art movement, and environmental art.
What separates Symbiosis from these traditional classifications of art are the concepts I apply to my creative decision-making process and the materials I use support and regenerate life. It values all living creatures as participants in the creative process.
My process for creating a living sculpture involves holistic decision-making. First, I incorporate a systems thinking approach to create a functional balance between the healthy ecosystem, human economics and societal landscape norms. For example, contemporary landscape designs are structured in monocrop rows or groupings separated with bare earth. To maintain the manicured design, weed-killing chemicals and gas-operated mowers and edgers are the most economical. This lack of plant diversity, geometric-in-shape groomed plantings, and chemical inputs make these landscapes uninhabitable for a diversity of wildlife other than a few lizards. For many valuable insects and microorganisms, the inputs are deadly. These designs do not consider supporting the food chain necessary in a healthy ecosystem. In Symbiosis, I keep the ground covered with a diversity of plantings that drift in and out of each other and with the seasons; this provides camouflage from predators, nesting materials, and a variety of nourishment all year. Weeds fit into this landscape and help build the microorganisms and structure or armature in the soil. This less structured planting design is balanced with a classical symmetrical layout. Symbiosis is designed to build the food chain. The maintenance required is easily accomplished with handheld clippers. The clippings are put back into the garden to decompose by insects and natural systems that build the soil health and retain water and carbon, or into a vase to be enjoyed. Ultimately Lawndale benefits economically through lower maintenance, chemical inputs, and utility costs, while enjoying a toxin-free environment—living sculpture.
I use materials that support plants and wildlife specific to the site's ecological history. I begin with a water source, animal waste and decaying plant materials native to the area. These materials build habitat and nourishment for microorganisms in the soil, in the water feature and up the food chain to sustain each other in extreme Texas weather. When combined with our clay soil they: store carbon, cool and return water to the aquifer, support life beneficial to humans and keep harmful pests at bay. In addition, they assist in cleaning the air, slowing rainwater, and reducing land erosion.
For example, I have created symbiotic relationships between humans, mosquitos, dragonflies, fish, and chemical-free water. In a hot environment, animals need a freshwater source to drink and reproduce. I installed a small pond without a filter or pump. Using plants to filter the water, I utilize the eating and waste habits of the Texas Mosquitofish to control the algae and build the water's biology. Mosquitos and dragonflies are attracted to still water with a balance of healthy bacteria and algae to deposit their larvae. The larvae become protein for the fish. Attracted by the water source, the dragonflies hover above the garden and on dried plant materials hunting mosquitos, supporting human health. Lawndale benefits economically by not utilizing an electric pump, needing a mosquito misting machine or pesticides and enjoys the beauty of the water feature and a kinetic, ephemeral rainbow of dragonflies hovering and darting over the living sculpture.
In Symbiosis, as the lower food chains develop, it begins to regenerate life and recover what is lost. Perpetual, it is art for now and future generations. In a living sculpture, the ways to evaluate it are space, shape, line, color, texture and regeneration.
I submit below images and descriptions of symbiotic relationships, ephemeral parts of the installation from April 2021-April 2022.
Dung loving birds nest fungus
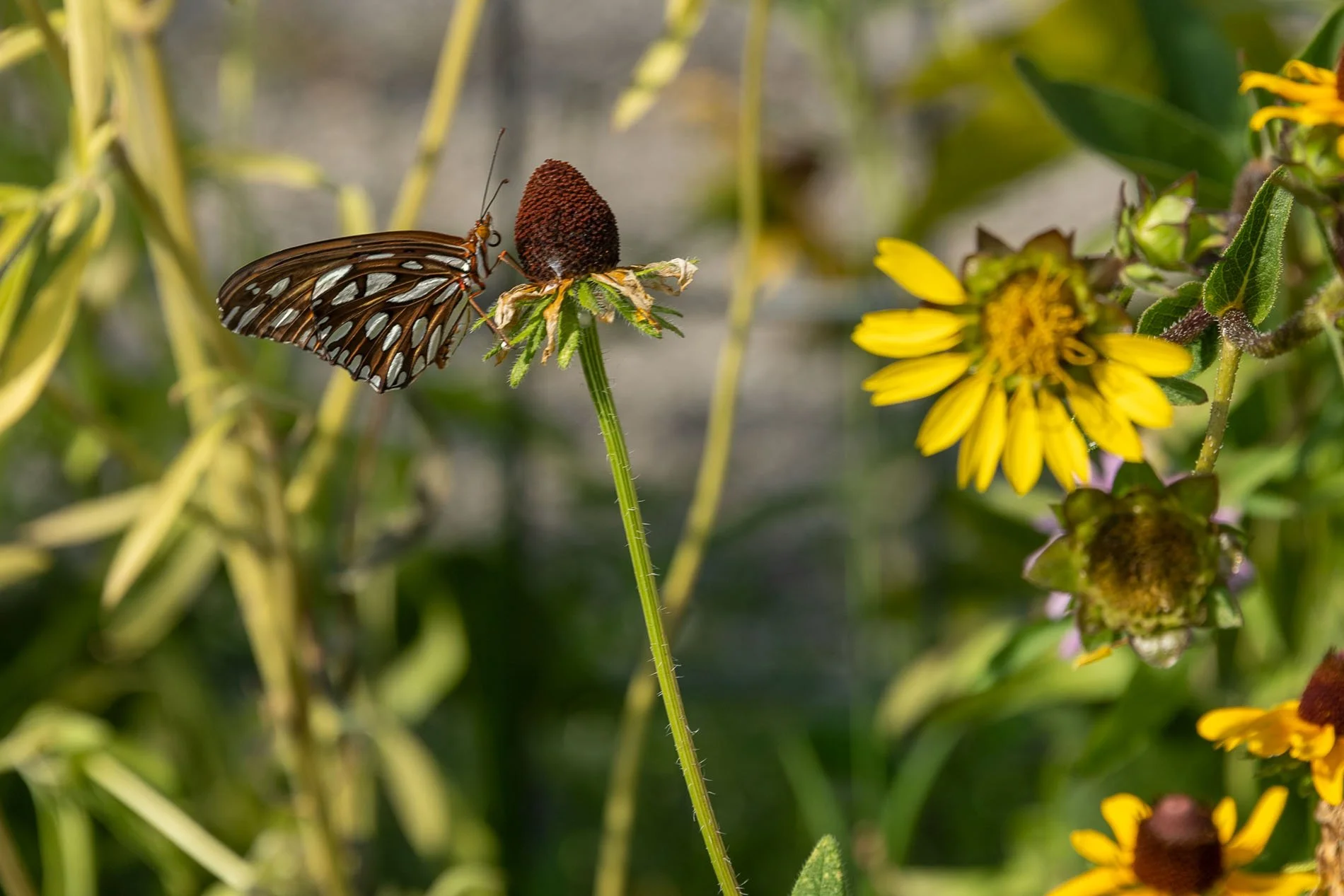
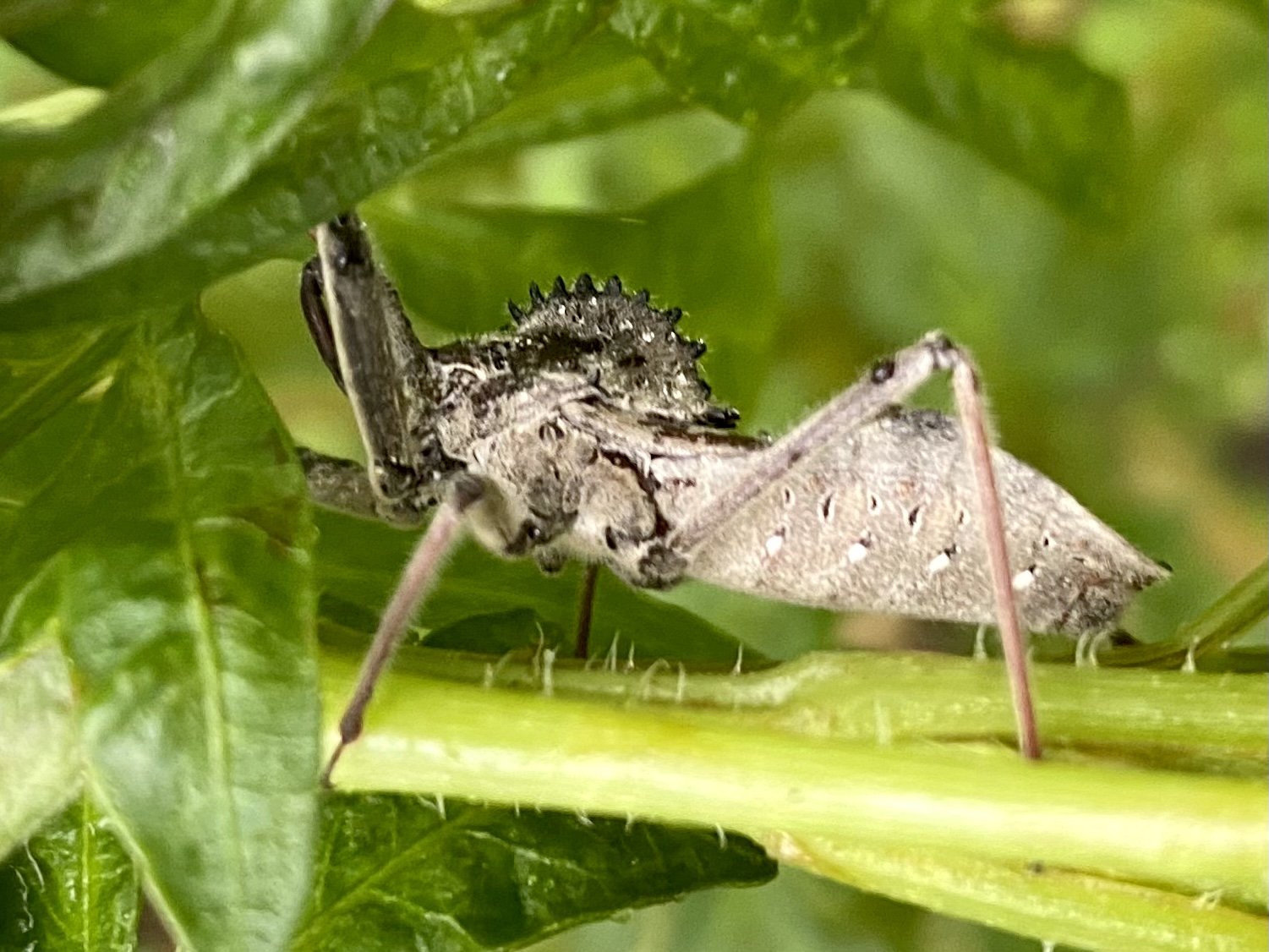
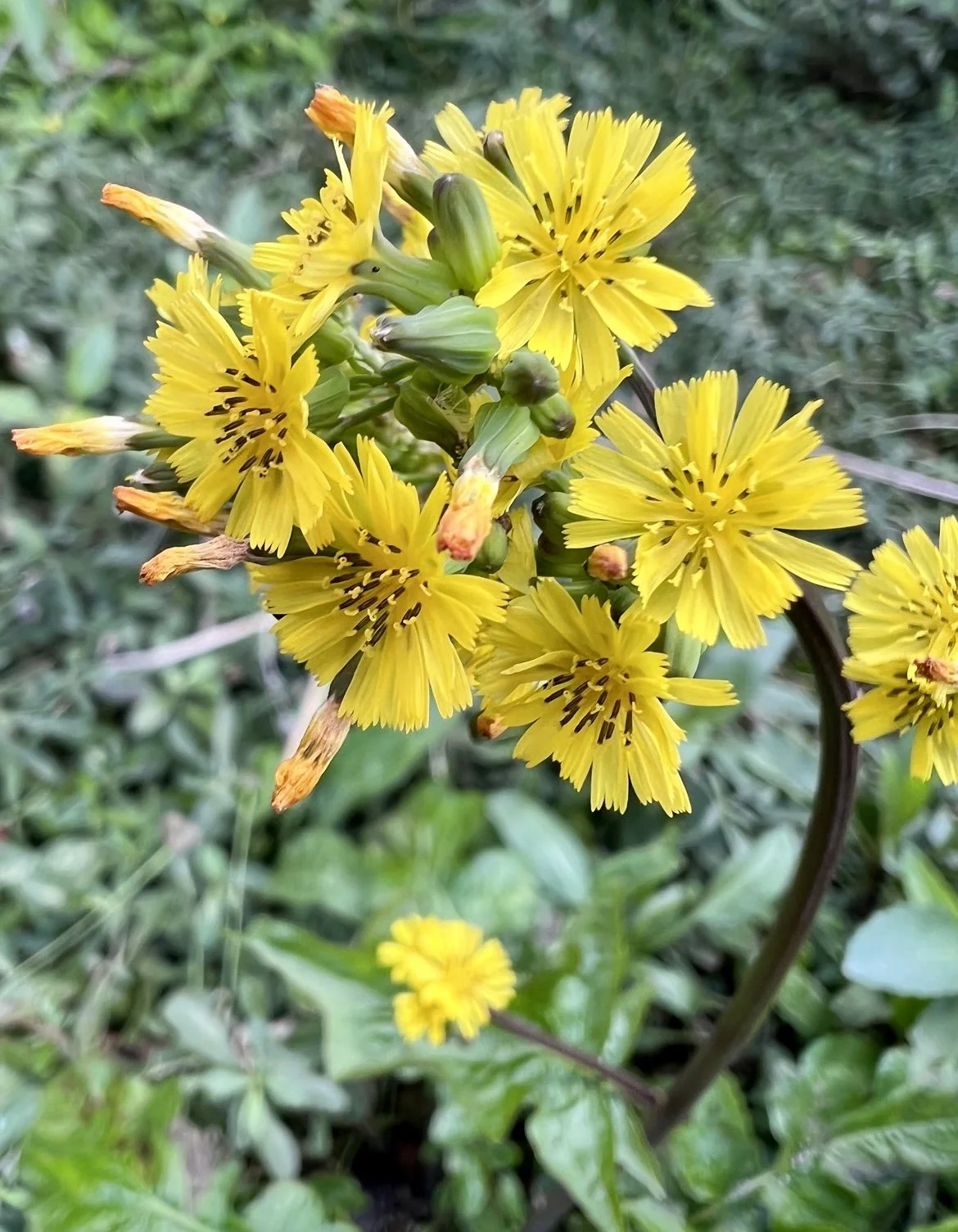
Gulf Fritillary butterfly on rosin weed sunflower. It roots can extend 16’.
image by Nash Baker courtesy of Lawndale Art Center
Black Swallowtail (Papilio polyxenes) on Monarda citriodora lemon beebalm image by Nash Baker courtesy of Lawndale Art Center.
Gulf fritillary butterfly on Gulf verain Verbena xutha image by Nash Baker courtesy of Lawndale Art Center
Battus philenor a pipevine swallowtail
Gulf fritillary on Rudkeckia hirta
Long-tailed skipper Urbanus proteus on Salvia azure
Junonia coenia the common buckeye butterfly on a blanket flower Gaillardia puchella with dew drops.
Black Swallowtail (Papilio polyxenes) on scarlet sage Salvia coccinea.
Gulf Fritillary butterfly on purple cone flower
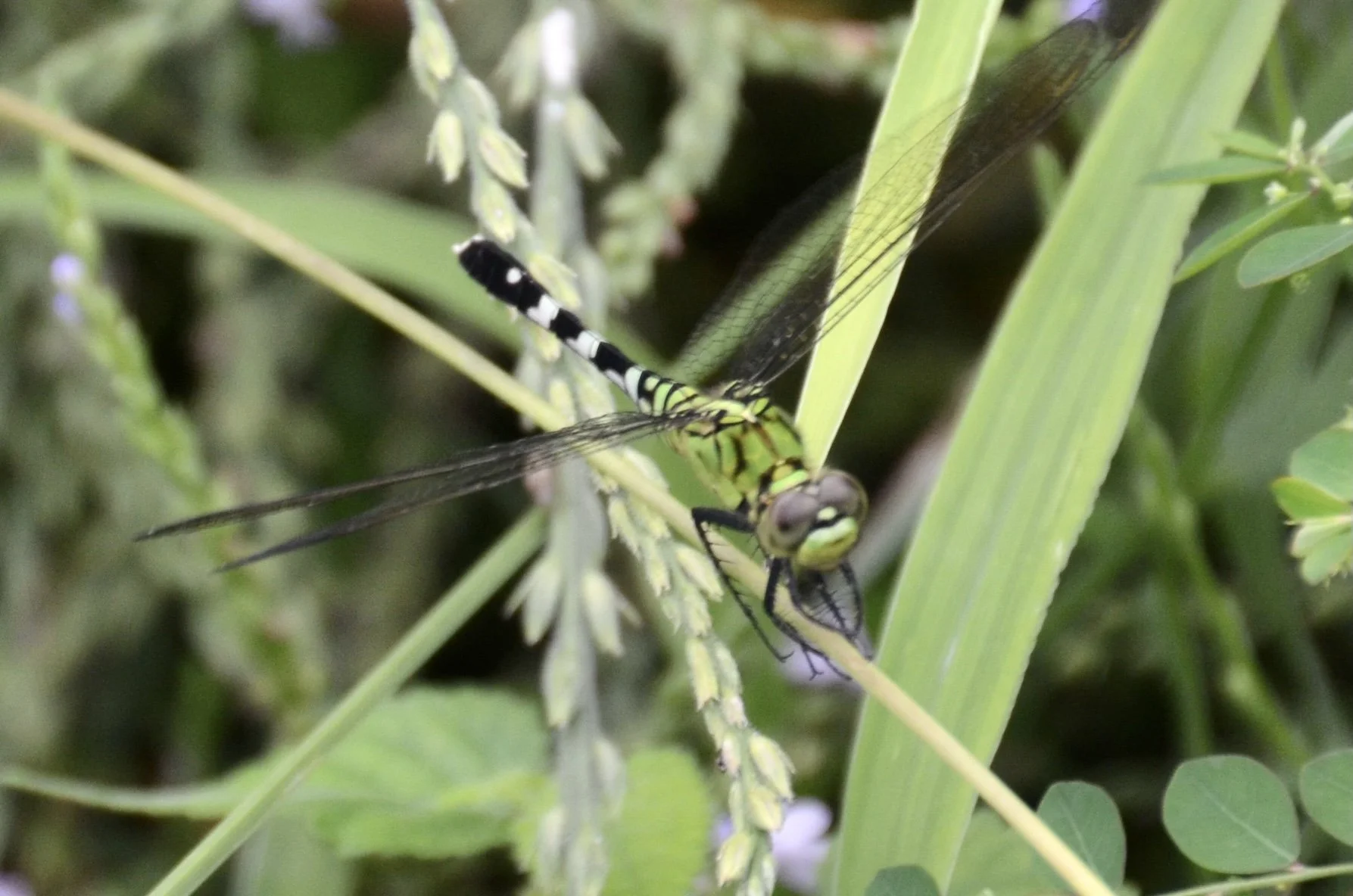
Red arrow Rhodothemis lieftincki on dead olive tree limb.
Mosquito control and water source for winged species.
Past bushy blue stem and Seaside Golden rod. I leave them through March so the winds can spread their seeds to other gardens, and to provide shelter for birds, tree frogs, toads, and field mice.
Plathemis Whitetail Skimmer
Mosquito control and water source for winged species.
Past bushy blue stem and Seaside Golden rod. I leave them through March so the winds can spread their seeds to other gardens, and to provide shelter for birds, tree frogs, toads, and field mice.
Brown skipper and Rudbeckia hirta
Symbiosis - Pollack
When I study the areas of the work that visibly support the most wildlife in Symbiosis I often think of the the most notable works of Pollock. I am presently reading The Extended Mind by A.M. Paul. In the chapter on thinking in natural spaces she wrote. - “Nature changed Pollocks thinking - gently tempering his raging in-tensity- and it also changed his art. In New York, Pollock worked at an easel, painting intricate, involved designs. In Springs, where he worked in a converted barn full of light and views of nature, he began spreading his canvases on the floor and pouring or flinging paint from above. Art critics view this period of Pollocks life as the high point of his career, the years when he produced "drip painting" masterpieces like Shimmering Substance (1946) and Autumn Rhythm” the extended Mind by A.M. Paul. I often see Pollockness in “Symbiosis”. This images especially reminds me of his Autumn Rhythm. In “symbiosis” it is winter shelter. This scarlet sage was damaged after the freeze.
Symbiosis - dead plants
The February freeze left its mark in the garden. Above ground, the Scarlet salvia, Salvia coccinea, was left in the form of crispy brown twigs and leaves. Below ground, the roots were protected by the moisture and living organisms in the soil. The beauty of a perennial is the roots are weather tough and will sprout new life this spring.
In our present culture, these dead limbs would be removed from the site immediately. They remove these dead plants when the weather is still harsh, leaving the ground bare the life that lives in and on it vulnerable. In Symbiosis, these bronze arched stems, and their bi-petaled crumpled leaves are sheltered from downpours, wind, and predators. I leave them. Their leaves and stems may not be a beautiful green, drawing energy from sunlight and water from the earth producing sugar to boost growth and oxygen released into the air. They absorb heat, warm, and protect the ground and living organisms. When March winds come, their seeds fly to new gardens and bare spots ground. When our weather warms, I will chop these dried elements to return to dust. They will become sustenance for bacteria, nematodes, fungi, and earthworms. In life and death, the plants are valuable in landscapes.
Water + Air + Citizens- social sculpture
Water + Air + Citizens
February 19th, 2022, at 2:00 pm
—social sculpture—
Reshaping soil in Houston: Public policy, Design industry, and Art
Lawndale Art Center's Mary E. Bawden Sculpture Garden
Dear friends and family,
Lawndale and I invite you to a public conversation with Sallie Alcorn (Houston City Councilmember), Maggie Tsang (2021-2023 Wortham Fellow at Rice School of Architecture, Managing Principal, Co-Founder of Dept.), Isaac Stein (Design Principal and Co-Founder of Dept.), and myself (exhibiting artist).
I have organized a social sculpture event, a conversation that will explore Houston's landscape practices and ecologies. Together, the speakers and I will consider the diverse ways that Houstonians can positively impact the local environment, looking closely at the design and development of medians, yards, gardens, lots, parks, and blocks.
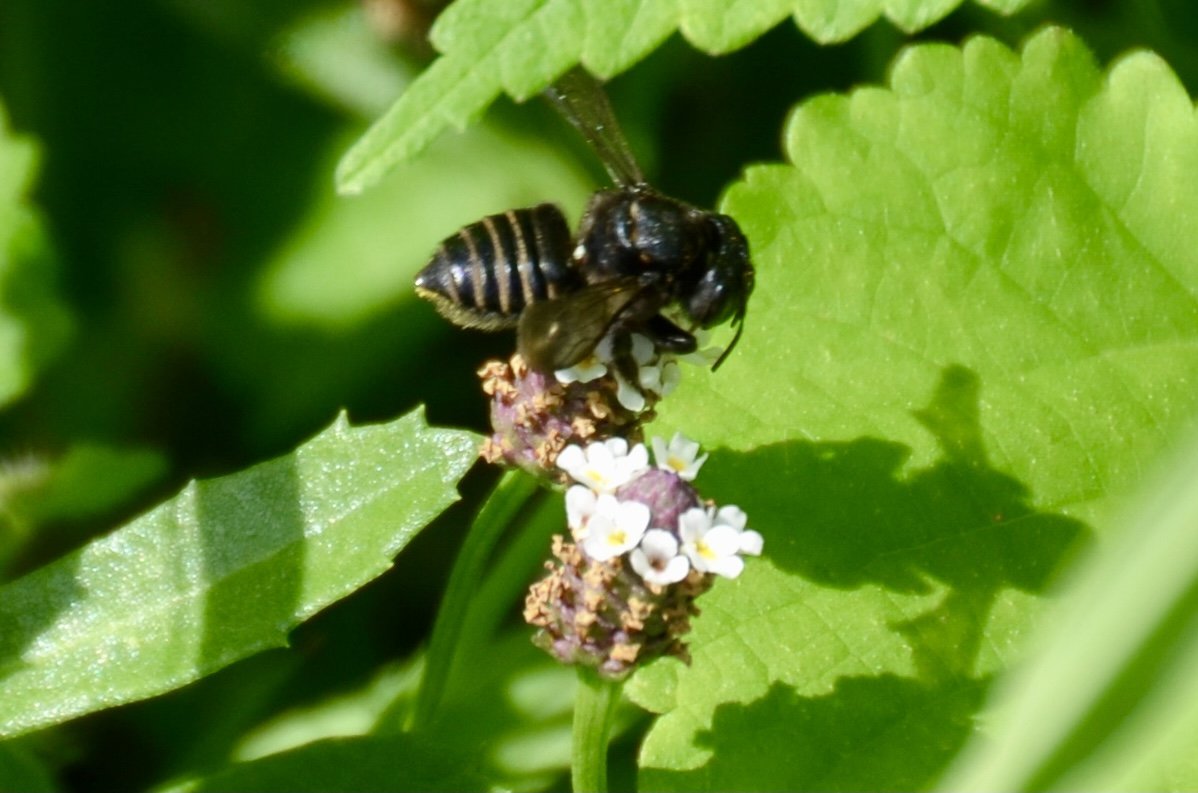
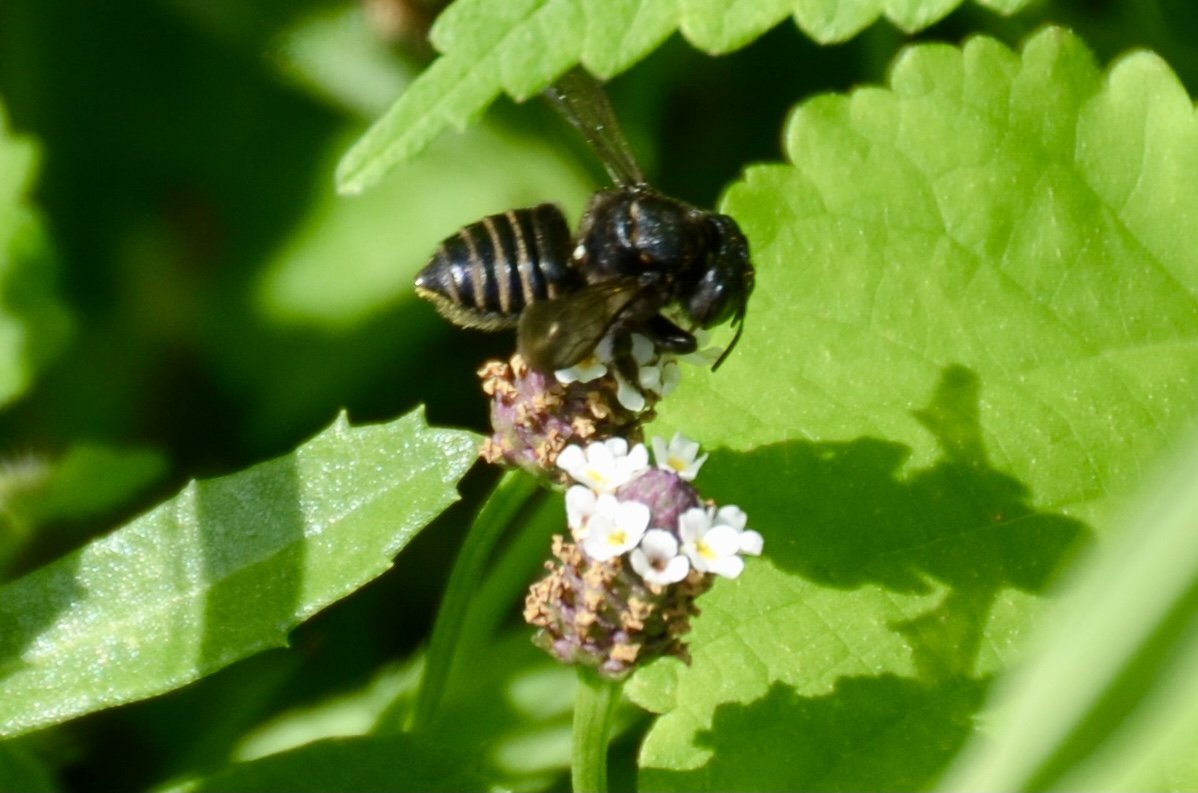
Image - Symbiosis, Spotted Horsemint, a volunteer Texas native plant, and a Texas native wild bee. The bee is a Two-spotted Longhorn Bee, Melissodes bimaculatus one of the threatened 400 native bee species of Texas.
Weed Out
As geologists and environmentalists battle, “are we in the Holocene epoch or have we made our mark on Earth and entered a new geological period, the Anthropocene?”, I ponder weeds.
The term weed, in the Holocene, is a plant that sticks out in a monoculture. From a bipedal primate’s perspective, a weed isn’t like all the surrounding plants: we undervalue it—because it “looks” different. From a human who spells her name Cindee with two ee’s, I have to say I am attracted to weeds and not just because of the ees. Since my first installation in Symbiosis, on February 14, 2021, I have thought a lot about the word, verb, and the thing weed, asking myself so many questions and finding answers in this urban garden.
In nature and in Symbiosis, I observe weeds and now see them as Earth’s first responders to large or small ecological disasters. Weeds are seeds, roots, stems, leaves, berries, and blooms—organic matter. Weeds are vegetative volunteers in the ecological services division of Earth; they provide emergency services for its living organisms above and below ground. Hear me out — when the Earth’s green skin is left bare, tilled, stripped, eroded, poisoned, burned, flooded, neglected, or disturbed by natural or human occurrences, Mother Earth cherry-picks from embryos sleeping in the soil her first responders—our weeds-seeds. Like our own“compounded prescriptions,” seeds are biologically programmed for the site’s specific ecological condition—temperature, moisture, and daylight—to grow fast and spread quickly; they are speed healers. As they mature, I see emergency room physicians administering oxygen masks for underground organisms, protective bandages for the Earth’s epidermis, and poison antidotes. Their organic matter lowers the Earth’stemperatures, thereby keeping soil and its living microorganisms alive. And they provide shelter, food, and nectar for the site’s microorganisms, wildlife, and humans. These ecological first responders are full-service providers, slowing rainwater, reducing soil erosion, replenishing the aquifer, cooling the planet, sequestering carbon, and stabilizing it in the ground for those debating geological periods to come.
From a sculptural perspective, if the shape, texture, or color of a volunteer first responder “weed” does not satisfy my artistic vision, I no longer yank it out of the ground in a knee-jerk response. I stop—look—think, why was it sent in? I take a holistic approach. I weigh the service it is providing our above and below ground micro-ecosystem, the armature that supports the life of the sculpture. I then consider what human adjustments I might implement to holistically balance these roles nature’s first responders are providing to achieve my artistic vision, supporting my sculpture. I consider the needs of other species from the bacteria, fungi, nematodes, and insects to the small mammals, birds, and humans whose life work supports my work. I know that the small systems have to be right for the global systems to run smoothly and I see that too much is at risk to resort to pesticides. I create ways that weeds’ delicately shaped blooms can work in my living land art.
From a practical standpoint, weeds are convenient, cost-effective tools in my human-made nature scape, a catalyst for environmental change, Symbiosis. So, while intellectuals debate the ages, I get out of weeds way, pull over to the right and let the weeds do their job.
In Wikipedia, weed is “of unknown origin.” Ironically, weeds are of unknown origins in most landscapes. So I break down the word weed into three parts.
We – all of us, me, you and I.
ee – In the English language, double e’s are a tool to
denote one connected.
ed – denotes verb, performs an action.
Holocene or Anthropocene? In this age of uncertainty, if humans “weed out” weeding, can all species win the battle? — I wonder…
Additional Weed Readings
WEEDS Control Without Poisons, by Charles Walters.
WHEN WEEDS TALK, by Jay, L. McCaman — includes charts with the functions of each species.
I purchased my copies on Acres USA.
Wood-sorrel exhibits nyctinasty, likely helping the plant conserve energy. It forms a taproot and is upright when young, but as it grows, its long, multibranched stems eventually flop over and trail out along the ground for as much as two feet, extending rootlets from nodes along the stem. This root is beneficial in breaking up the clay. Sorrels contain oxalates, a naturally occurring molecules that bind with calcium. If your soil needs calcium, keep the wood-sorrel.
Youngia japonica a member of the aster family and related to the dandelions. Dandelions Taraxacum officinale shows up when soil is low in calcium and compacted. The local bees, butterflies, birds, and I enjoy the blooms while the dandelion roots break up the clay. Their leaves are loaded with antioxidants and used by herbalists for many health issues.
I believe the above plant to be Cudweed. Cudweed is host for the American painted lady butterfly.
Why we shouldn’t rag on ragweed? The seeds of ragweed are rich in fatty oils. Fats are not only Ebut also is for fattening up birds and small mammals such as Eastern Cottontail, Meadow Vole, grasshoppers which eat the leaves, Dark-eyed Junco, Brown-headed Cowbird, Northern Bobwhite, Purple Finch, Mourning Dove, American Goldfinch, and the Red-bellied Woodpeckers to get them through the lean winter months.
It is an ancient grain for humans and ragweed is a valuable food source for the caterpillars of many butterflies and moths including the striking wavy-lined emerald and the uniquely adapted bird dropping moths. The seeds of ragweed are rich in fatty oils. Birds and small mammals readily consume ragweed seeds to help fatten up for the lean months to come.
I will use this post to document my experiences with weeds.
Documenting the art of creating living soil. SOILED — Tighty-Whities 2021
SOILED — Tighty-Whities 2021
Photograph by N. Baker
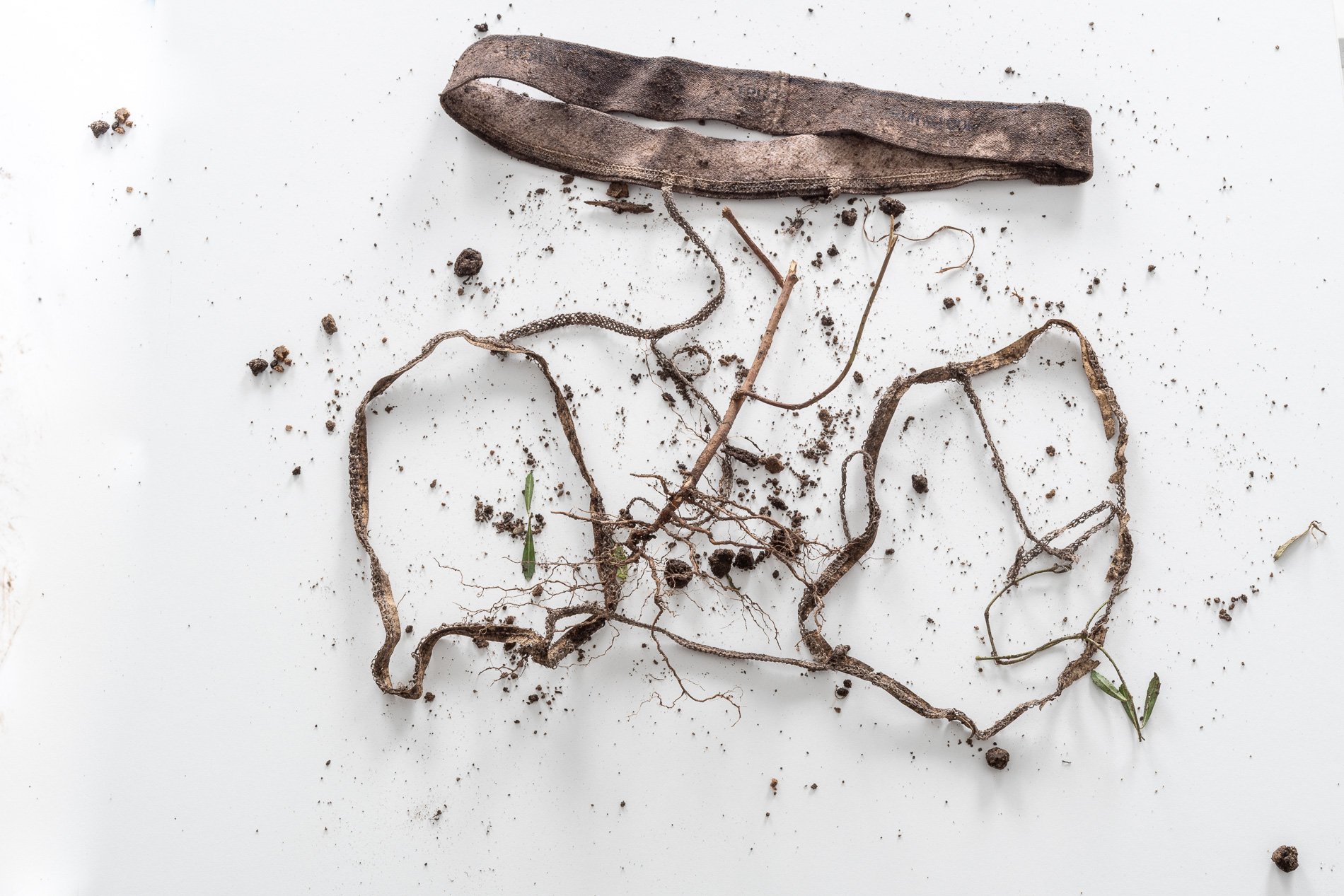
How do you document art that lives beneath our feet? Creating art beneath the Earth’s surface I am finding new ways to document the work and it's movement. This photograph is the result. Let me explain. To test soil for fungi that recycle wood and live on dead material soil, scientists buried cotton fabric. In Symbiosis, to document the Saprophytic fungi, I planted new, washed men's medium cotton briefs. This photograph demonstrates the results. In 2022 I will recreate the piece and grow the tighty-whities in a vertical column. This change will document that living soil, the diversity of microbes is built from the top down. In contrast, when my father farmed in the 50s and 60s, the farm bureau that advised him told him to invest in a new plow to dig deeper to access the richest soil.
The purpose of my work is to change how we see landscape. It isn’t just about creating beautiful gardens. Landscape can store carbon and soak up rainwater to cool the planet. It is the cheapest and fastest way to get our planet back on track.
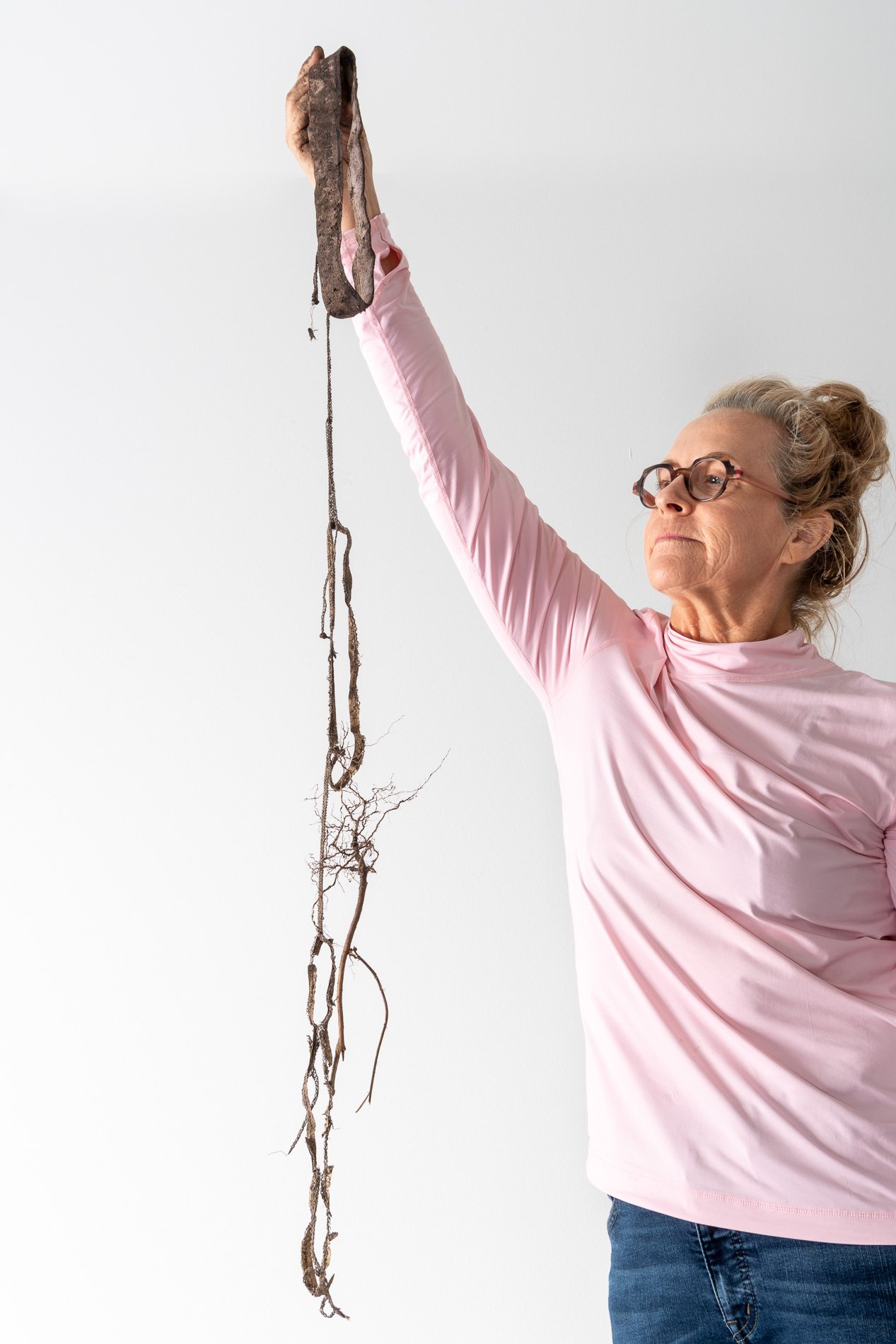
Digging up the briefs I immediately knew I had made a mistake. I left them In the garden’s soil too long. Still, I dug them out with tender care. The petroleum-based elastic band was entwined with a plant root. The root took the elastic leg 6” deeper into the earth than I planted it. I left the elastic and the root as I found them. Laid them on a board and took them immediately to Nash’s photography studio to document the work.
First, I delicately untangled the elastic. The cotton had completely decayed. The elastic was not biodegradable.
Seeing that the briefs were still intact minus the cotton and plus the root I started reassembling the briefs and the added appendage.
In art many times you have to listen to the materials.
Artadia 2021 Finalist
In early November I was notified that I was one of 6 artists in the Houston are selected by Artadia’s curators. It is hard to describe the feeling of having my work recognized by such an esteem organization.
See the full article here.
It never hurts to get a Glasstire shout out. In art every moment of support is a BIG moment. Many thanks to Glasstire for acknowledging my efforts and accomplishments.
Symbiosis- scientific research that support the living sculpture.
“All is not doom and gloom, though, according to Dr Rodger. Many plants are long-lived, opening a window of opportunity to restore pollinators before plant extinctions occur from lack of pollinators.”- First global estimate of importance of pollinators for seed production in plants
Symbiosis
4.5 cubic yards of compost ( living organic material), 200 plus Texas Native plants installed to support the return of Houston’s urban wildlife.
Summer 2021
Image by Nash Baker
Symbiosis- invasive species
Hairy Crabweed Fatoua villosa is the only invasive species I have discovered in Symbiosis.
It gives me confidence in my landscape philosopies when I read research publications that support my observations of “Symbiosis.”
In July, Houston received an extraordinary amount of rain. That is when I discovered an invasion of Fatoua villos. Aware of the harmful effects of invasive species such as kudzu, I panicked. I went into industrial irradiacation gear. After two days of pulling the hairy-plant-beast from the beds, I noticed many of the native plants were suffering from too much water. I also noticed the native plants in the beds that I had not pulled we're not struggling. I stopped the pulling of the species. That is when I adopted a weed or invasive species management philosophy. Now I carefully observe how each species is impacting the naticve plants, the wildlife and the visual impact of the sculpture. Below is an article from Science Daily that supports my observation.
“The paper's implications suggest that faced with declining fisheries, threatened reef ecosystems, and changing climatic and oceanic conditions, the value of ecosystem services provided by some invasive species, e.g., mangroves, may outweigh their negative effects. Therefore, the decision-making process involved in managing some invasive species warrants more careful consideration of both costs and benefits provided to the ecosystem.
"In a static world, invasive species are bad because they disrupt ecosystems," Granek said. "But we're living in a world where the environment is changing. The climate is changing. The oceans are changing. That changes the calculus of how bad some invasive species are to the habitats they've been introduced into."
Carbon by the Yard - a weekly update
Carbon by the Yard
Zoysia Turfgrass relief
35' X 48'
Embedded within the installation Symbiosis, Carbon by the Yard is a temporary, living sculpture in the shape of the Carbon element symbol, C. The work consists of carving a 16 x 14-foot shape into the existing grass, and allowing the Zoysia grass to grow tall around it. A simple gesture, the letter brings attention to the role lawn-grass plays in climate change. In 2020, the Environmental Protection Agency estimated that grass uses up about a third of all public water: in the US, this translates to 9 billion gallons of water every day. Our mowers consume 200 million gallons of gas. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency estimates that, gas-powered lawn mowers produce 11 times as much pollution as a new car hour for hour. And, manicured lawns provide no livable habitats for pollinators or the other plants and animals necessary to maintain a healthy ecosystem. With Carbon by the Yard, artist-environmentalist Cindee Klement brings attention to the ways in which our daily decisions can help to reduce our carbon footprints.
Reducing nitrate leaching losses from turfgrass fertilization of residential lawns
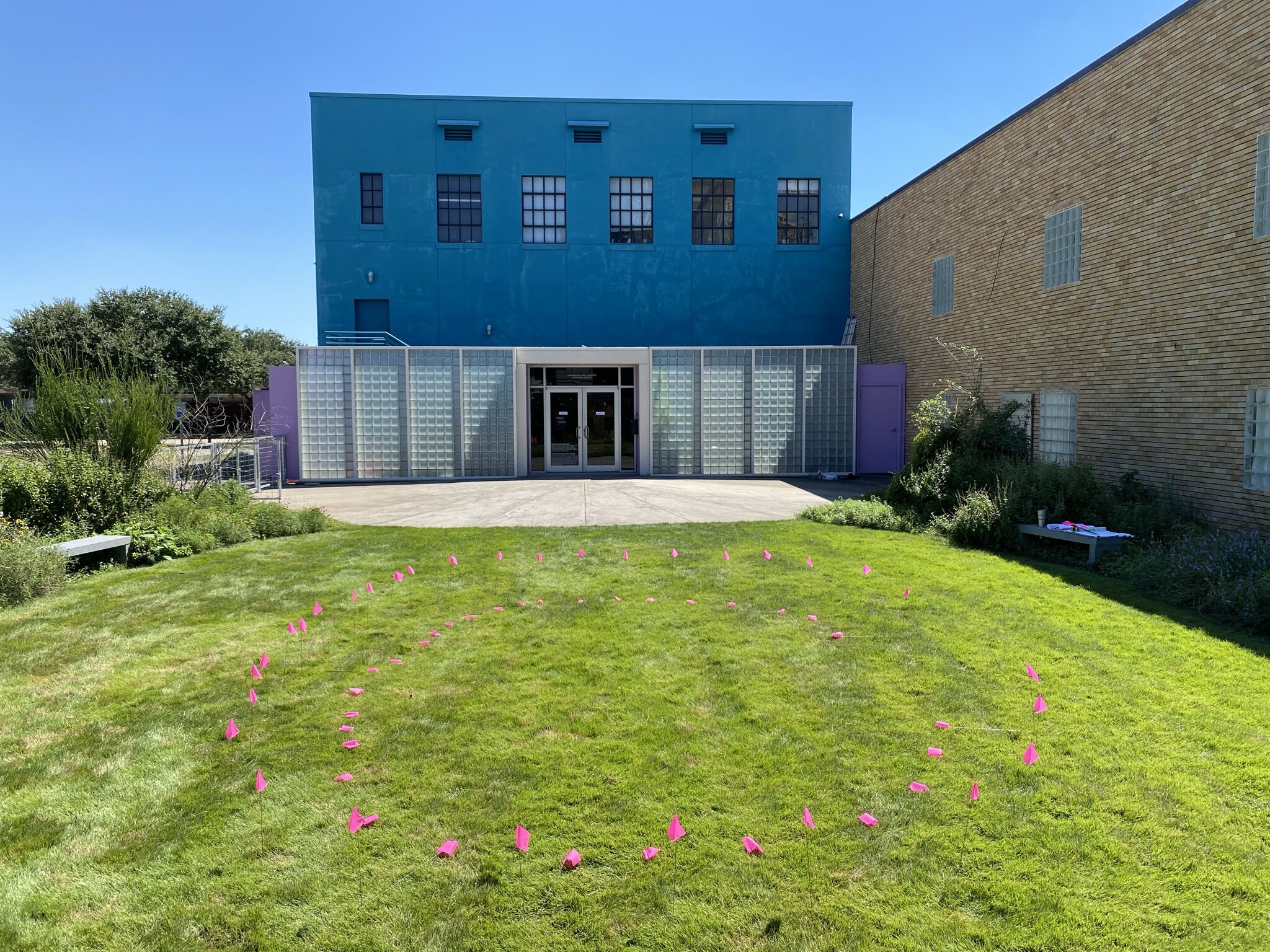
The sketch for Lawndale approval
September 23, 2021
I sketched the C into the space with flags. Moving and adjusting them until I had the shape C right and in the right place.
Next I marked the C with a water base paint used to mark fields.
The C marked in water based paint.
October24th- The first cutting.
The yard maintenance company used their regular mower. The CO2, cost, time, and noise pollution of the gass lawn mower was not worth the result.
I was afraid that the following week the lawn maintenance company would not be able to see the relief enough to remow it. I remarked the C with the flags.
The second cutting was rained out.
I will update this blog post through out the process.
October 8th - week three cutting #2
October 18th - Week 4 cutting #3
October 22 - week 5 cutting #4
After 4 cuttings the C is now beginning srand out.
November 1- week 6 cutting #5
November 7- week #7cutting #6
November 12th, week #8 cutting #7
November 19th, week #9 cutting #8
November 26th, week #10 cutting #9
December 3rd, week #11 cutting #10
December 24th, week #14 cutting #13
January 9, week #16 cutting #15
March 30 - this would have been week 29……. Unfortunately, it is not.
I noticed the grass was growing exceptionally slow. Long story short Lawndale’s lawn maintenance company was mowing on a high setting.
I am starting over on counting weeks of emissions saved.
April 10th, week 1, not cutting the yard #1
Spring 2022
Symbiosis - where are the birds?
For several weeks I have noticed the neighborhood birds are not stopping into Symbiosis. I have asked the neighbors and they have noticed the birds were absent too. Today an article came out in the Houston chronicle, Songbirds Take a Break.
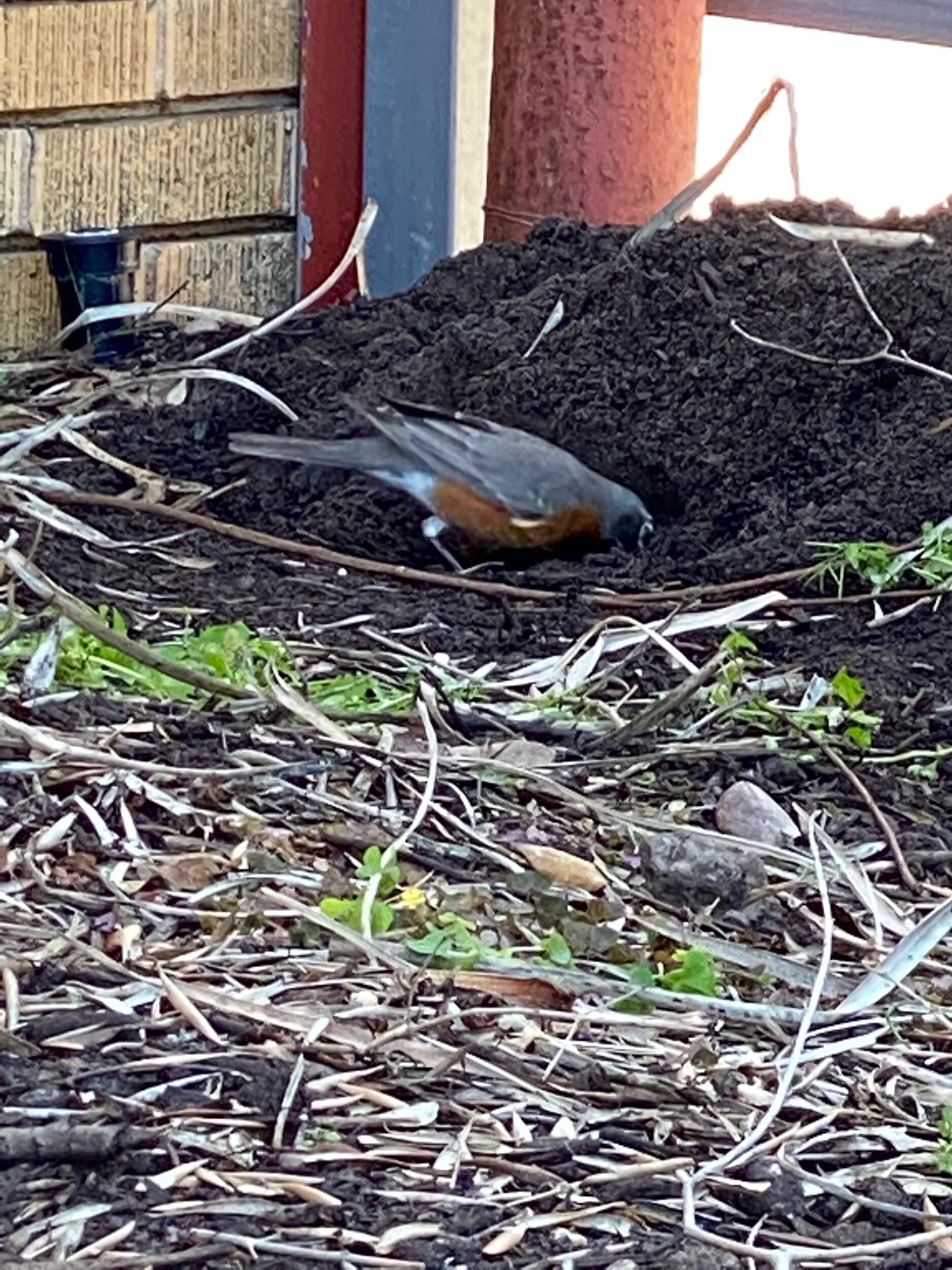
March 19th - first bird in garden. An Amerucan red robin foraging for insects, bugs, protein or seeds, poking it's beak into the newly installed living compost.
March 31, 2021 robin hunting for grubs as I install the American beautyberry.
April 9, 2021 robin on the oak stump. I installed rotting native tree stumps to give the birds a camouflaged lookout and hideout.
April 9, 2021 dove
May 22, 2021,
blue jay
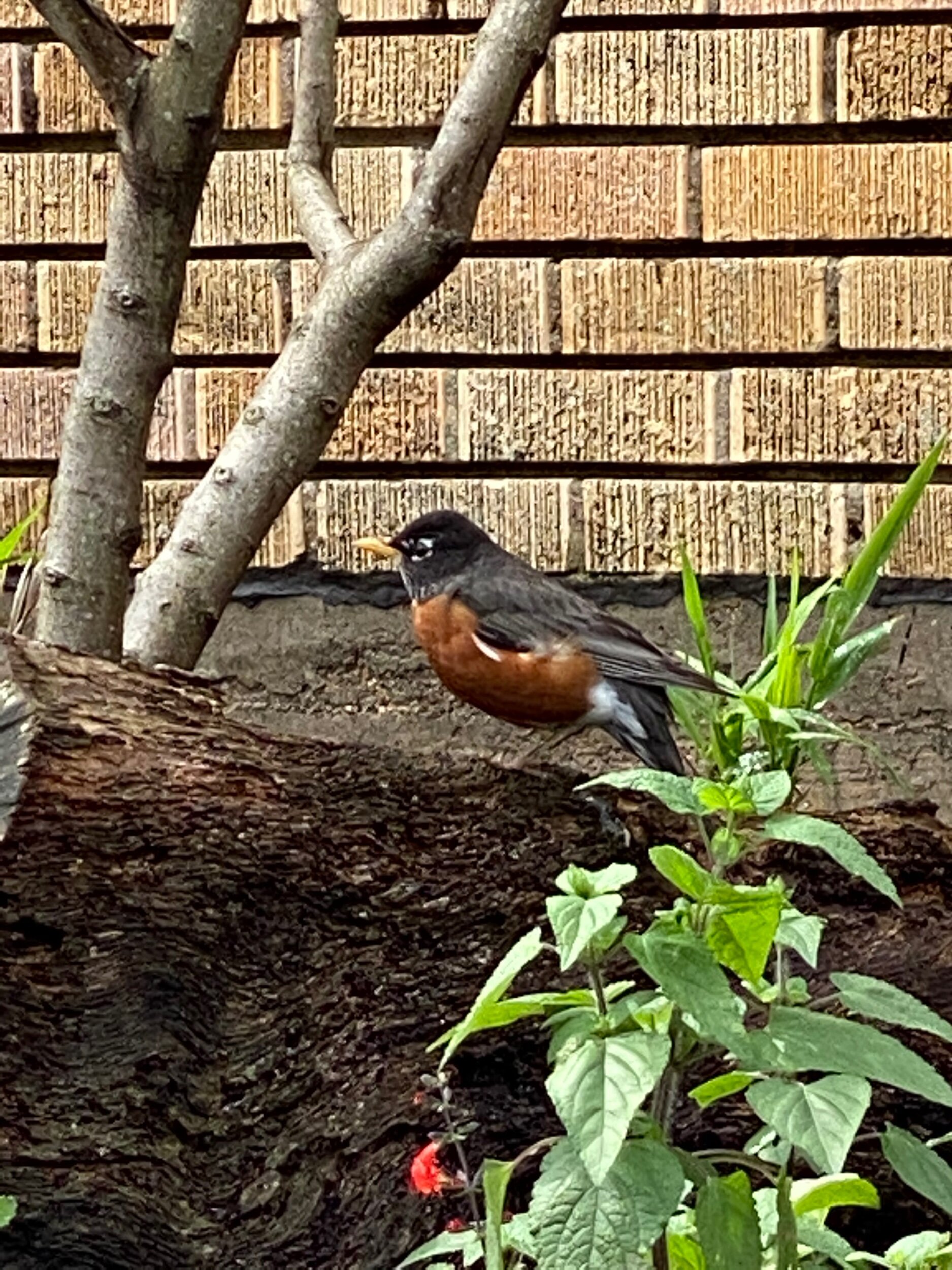
May 1, 2021 American red robin
June 19, 2021
June 22, 2021
Symbiosis - extraction from a different view
Passiflora incarnata is a boisterous Texas native vine. I placed it at the entrance for a few reasons, to grow across the gate to soften the concrete patio. The patio concrete will help contain Passiflora from self-propagating itself. It is a host for the passion butterfly larvae that will greet the art patrons. Without any chemicals in the garden the caterpillars exceled at digesting the passiflora incarnate leaves. Chewed to the stems adds an element of excitement to the composition. There is an additional beauty of knowing the life it has hosted.
Passiflora incarnata with extraction from a seasons worth of Gulf fritillary caterpillars
Detail
Not a leaf left. I will miss walking up to the gate and startling the resting Gulf Fritillary butterflies, causing them to flutter in and out of the welded wire fence circling me as I enter.
Symbiosis- art activism
Can art activate change? It has in the past and global communication is easier than ever. I received the below email from Chris Mc Fraughton of Take Two environmental. :)
Chris was trained at Elain Ingram’s the Soil Food Web. He knows what he is doing.
Symbiosis - Nash Prairie - seed collecting
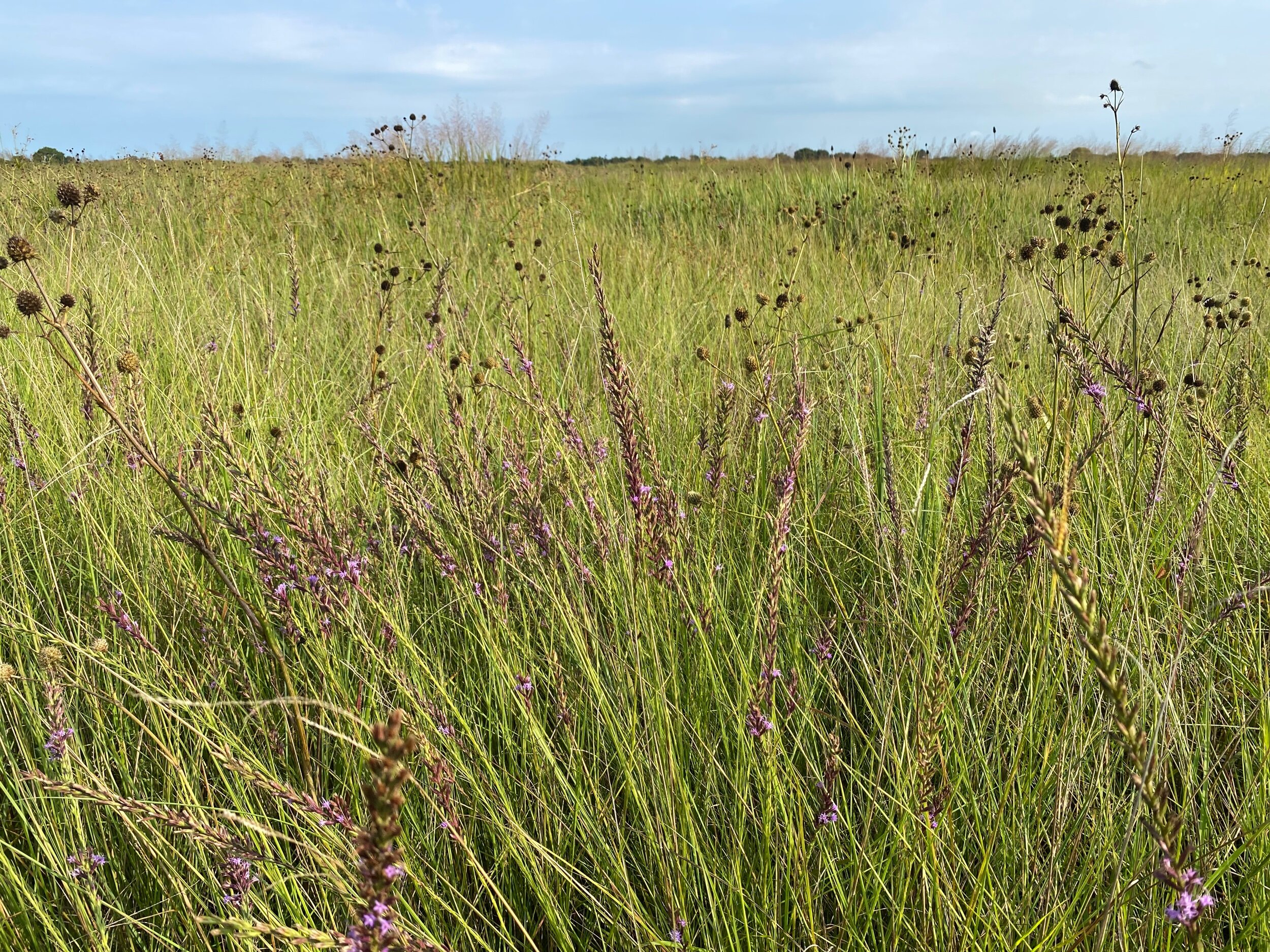
Mark Morganstern of Morning Star Prairie Plants invited me to join him to collect seeds for Symbiosis at the Nature Concervancy’s Nash Prairie Preserve. “The 400-acre tract is one of the last remaining segments of the Great Coastal Prairie, which once encompassed six million acres between Lafayette, Louisiana and Corpus Christi, Texas. Nash is a pristine piece of prairieland, largely unaltered by man or machine. More than 300 plant species have been documented there, including several rare species and at least one type of grass thought to be extinct in Texas since the 1800s.“
I will plant the seeds in Symbiosis this fall. Next summer I will collect seeds and share them with other properties.
Green tree frog on a Rattlesnake master. The rattlesnake master reportedly supports 250 species of wildlife.
Rattlesnake master seeds
The prairie
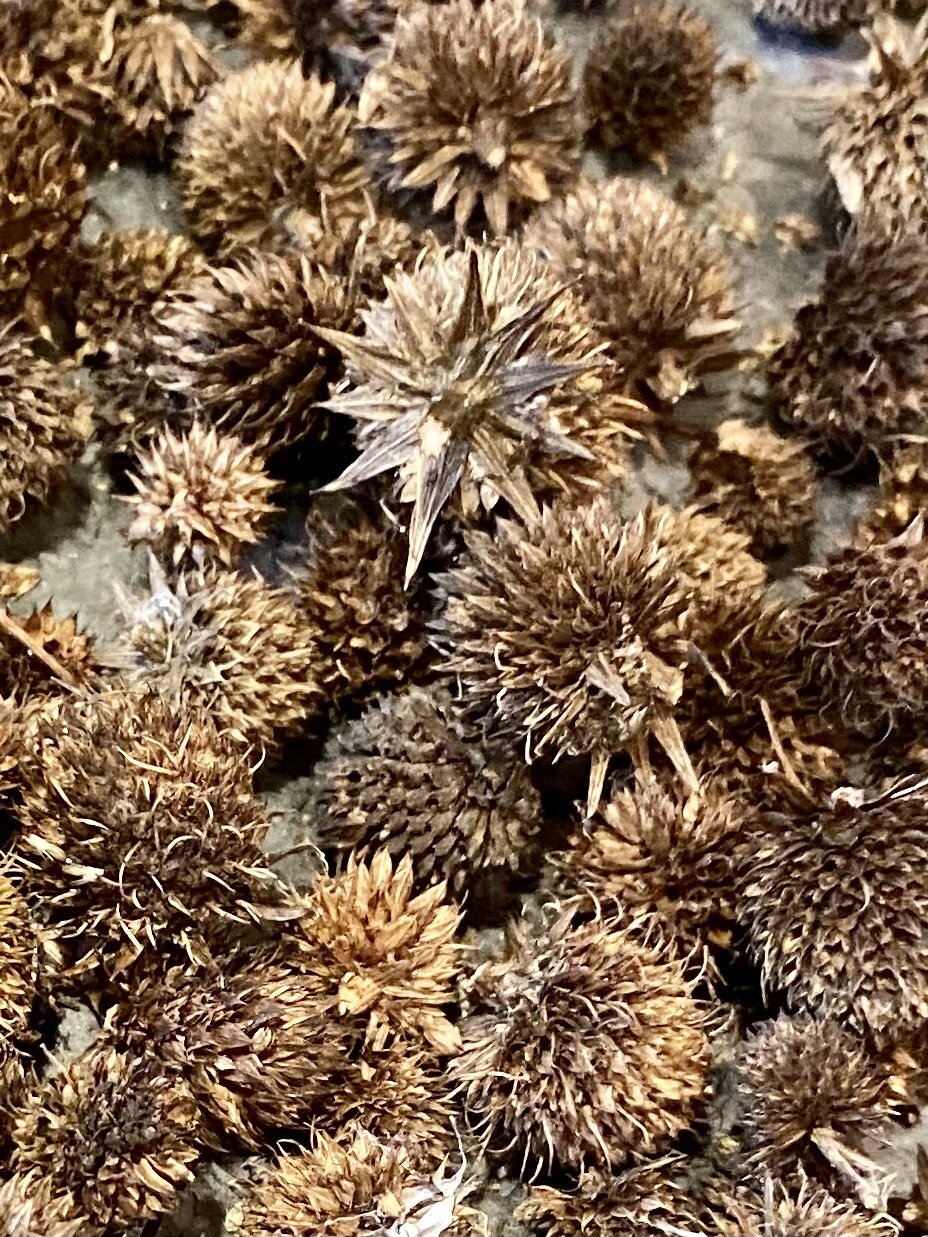
Coneflower seeds
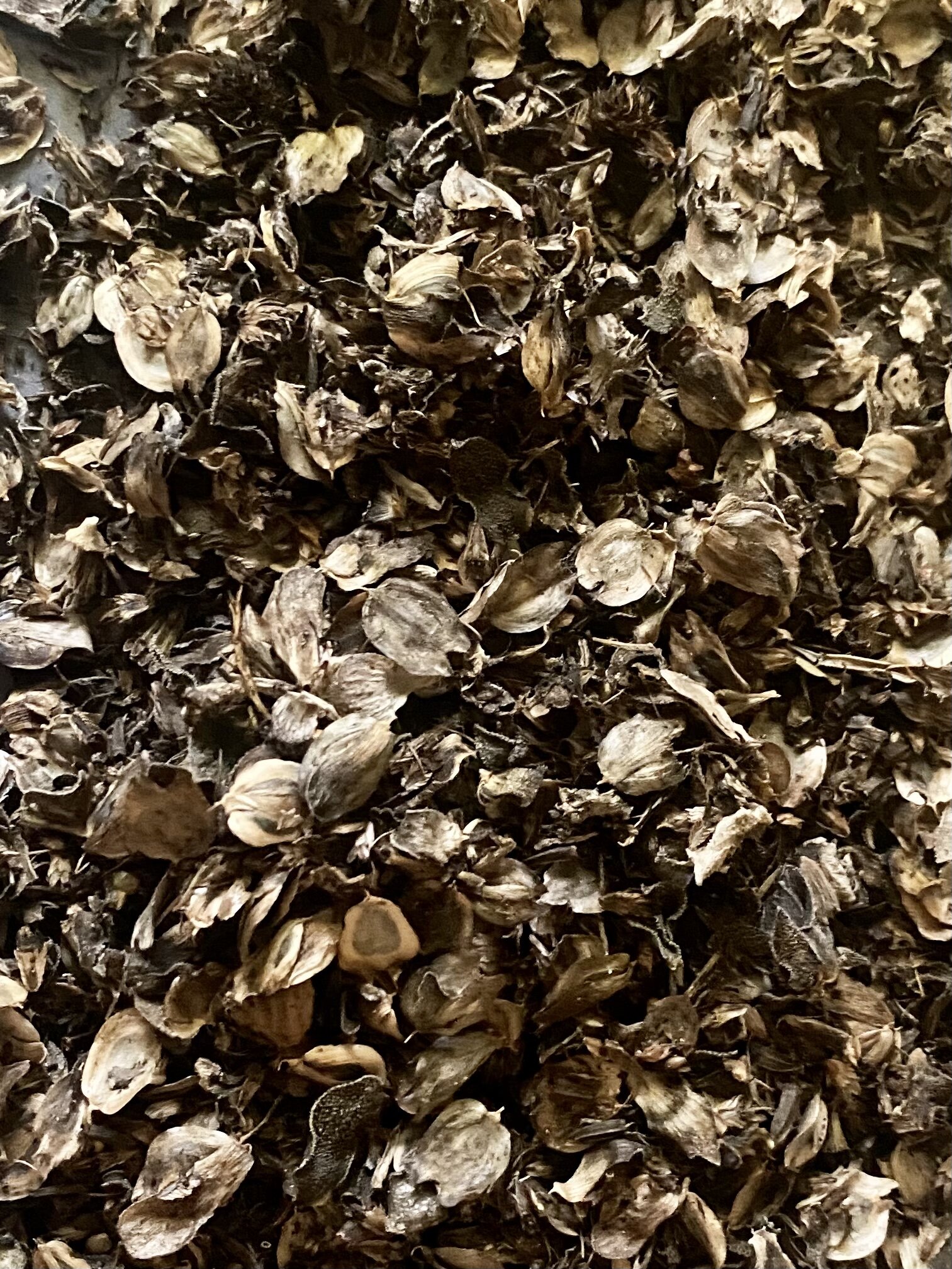
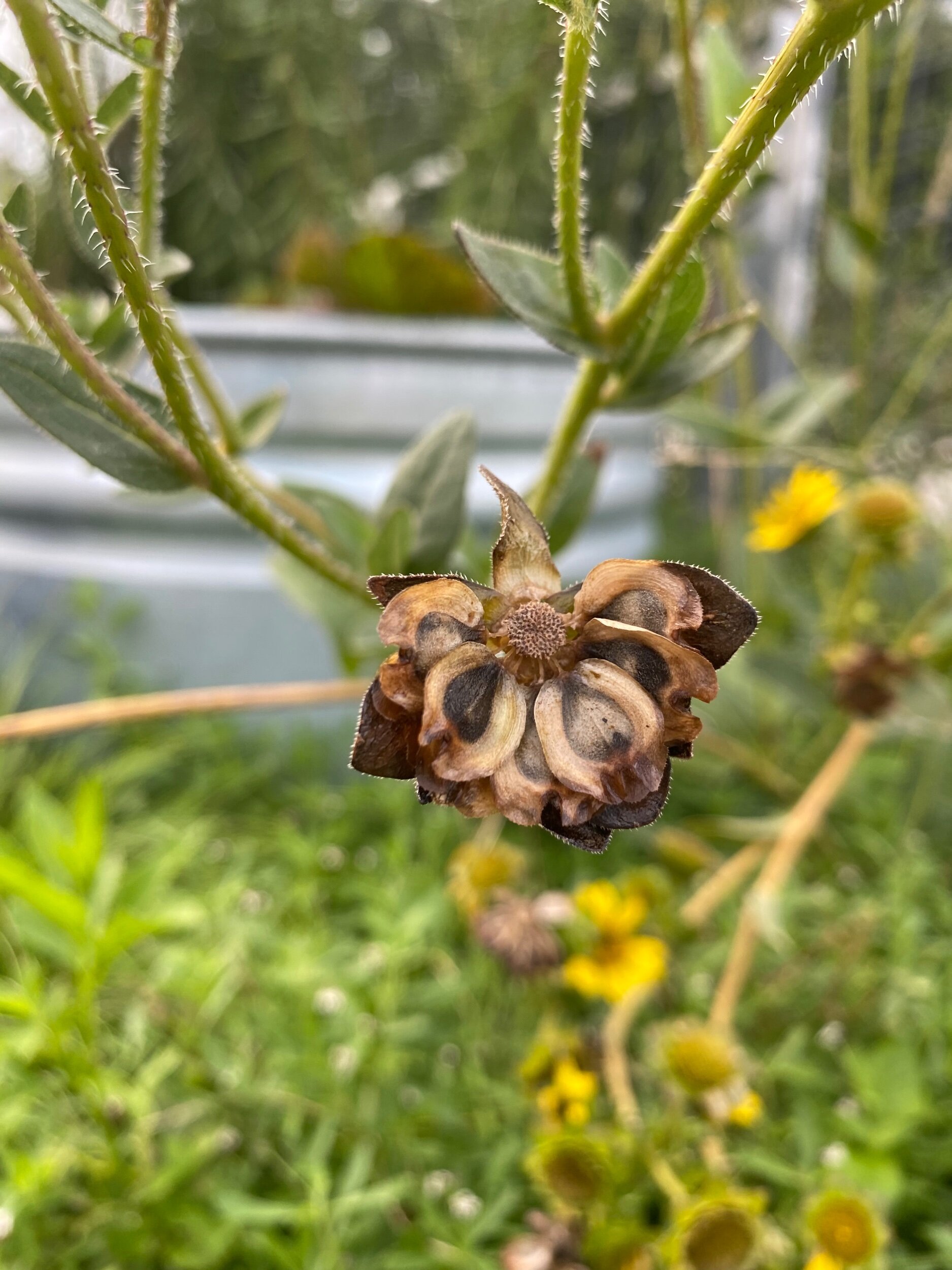
Rosinweed Sunflower seeds
Rosinweed sunflower
These are the seeds on the plant
Endangered Knowledge: The Soul of Humus
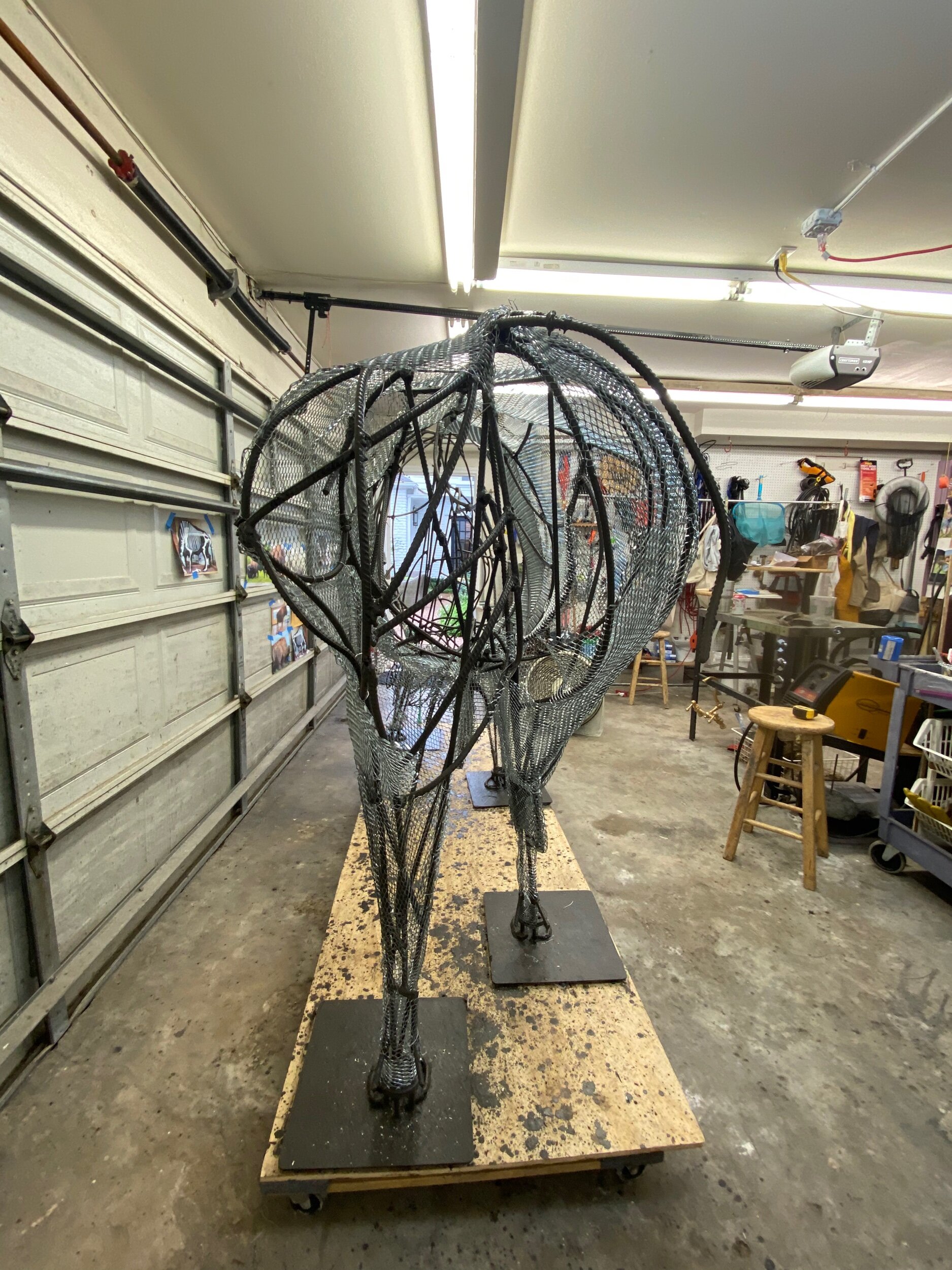
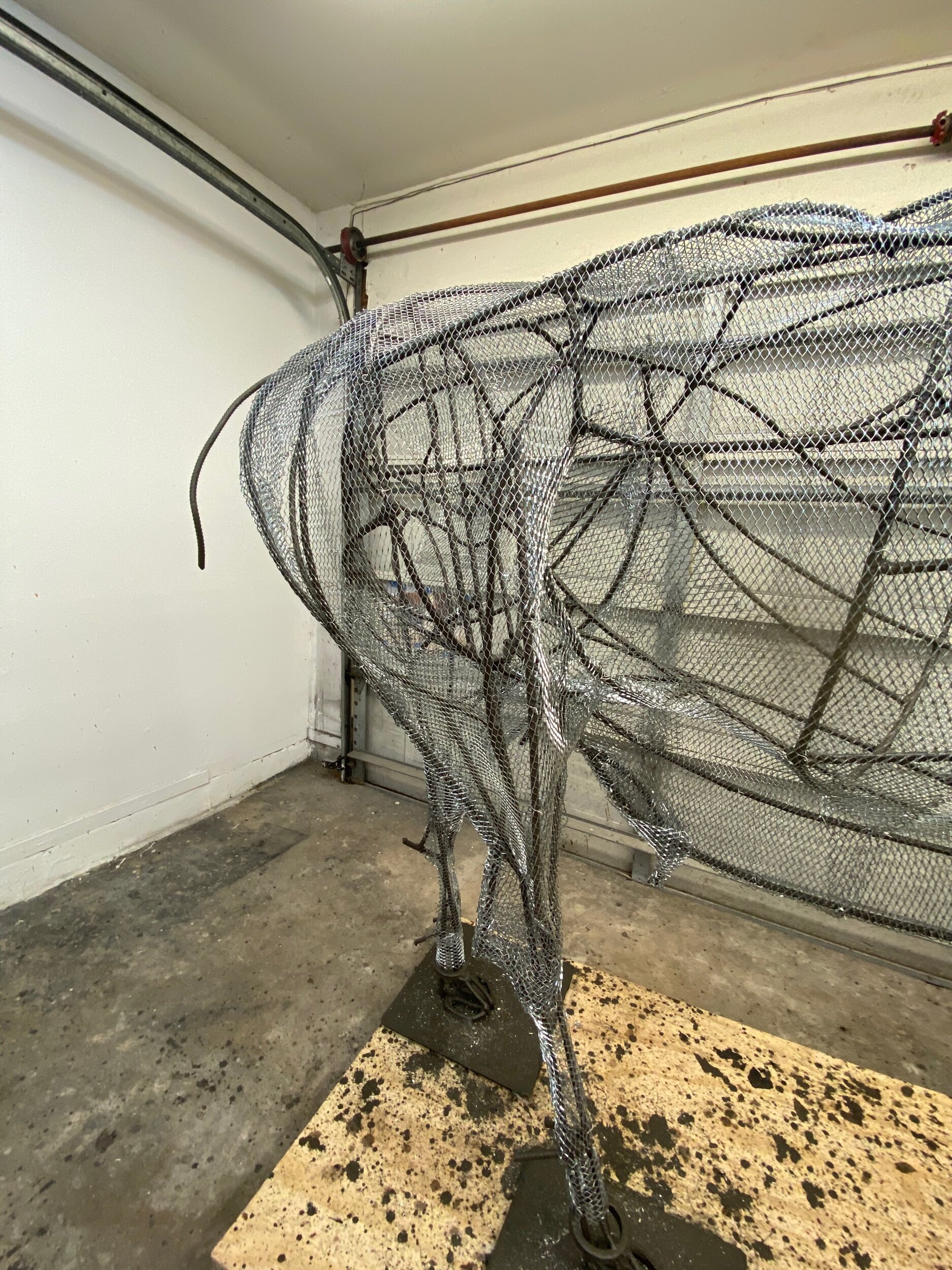
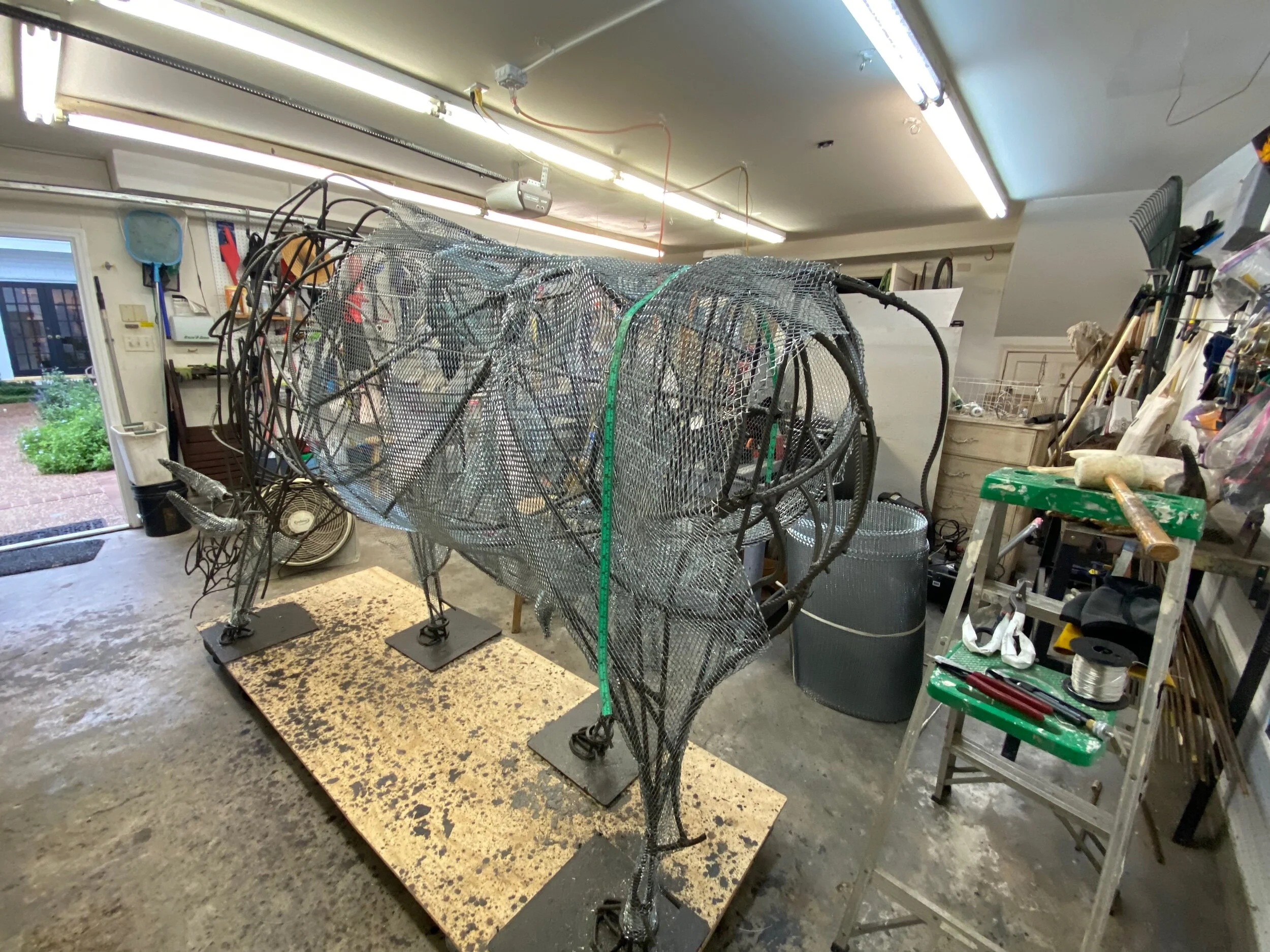
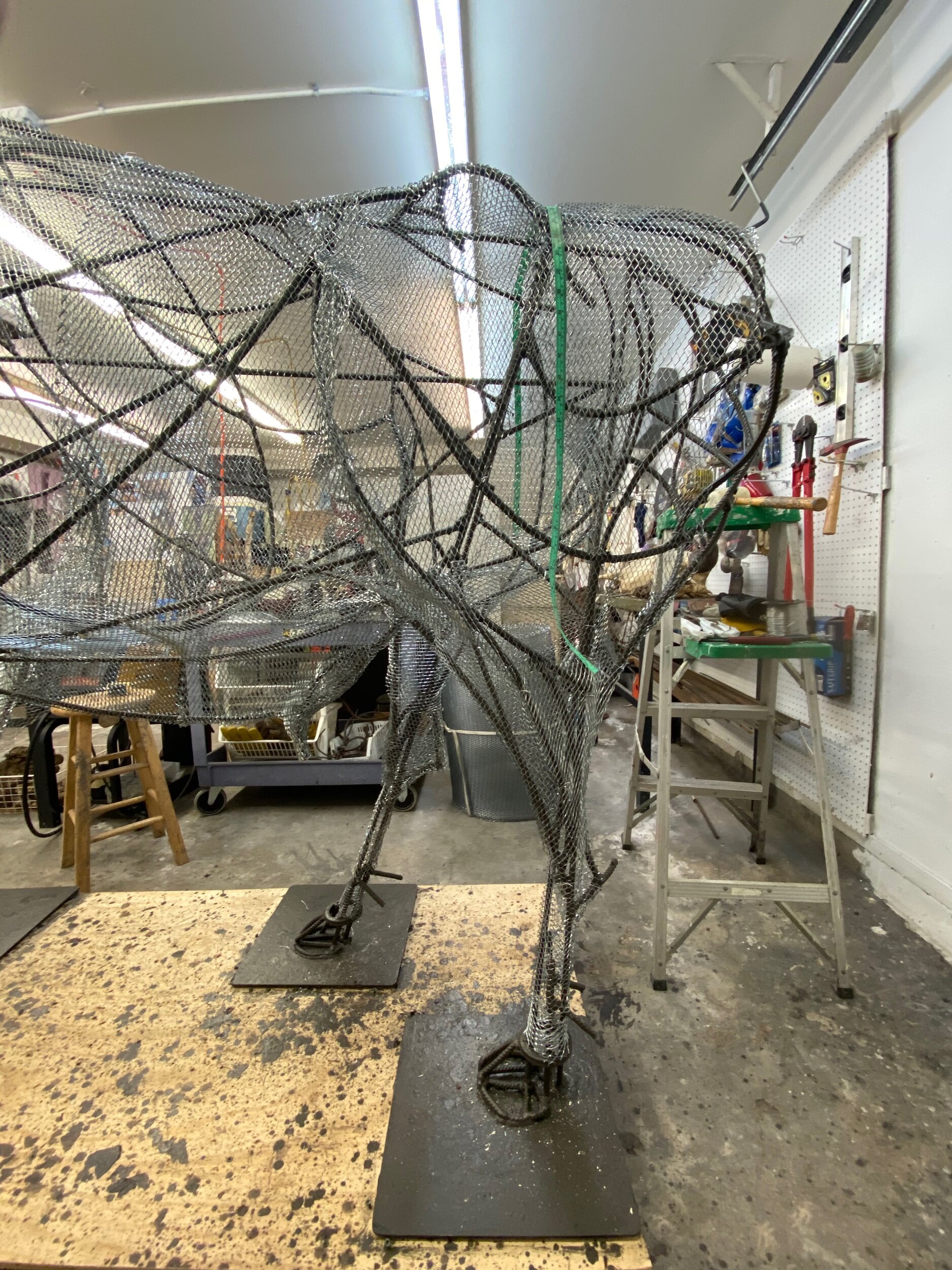
Today‘s progress may not look like much, however I worked 7 hours. I was focused on filling the tiny spaces in the groin, inside its flanks and rear end. And I was careful not to catch my skin on the sharp edges of the late. It is razor-sharp and requires careful deliberate moves.