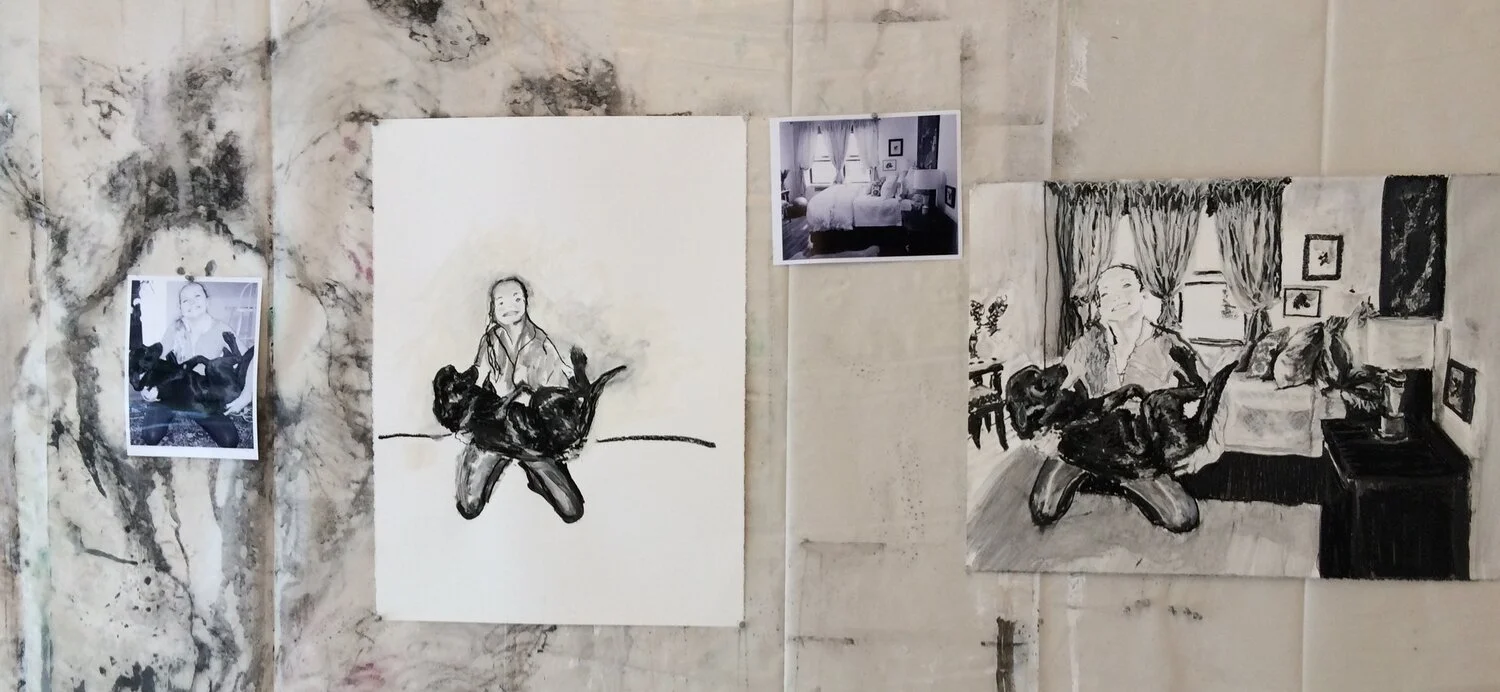
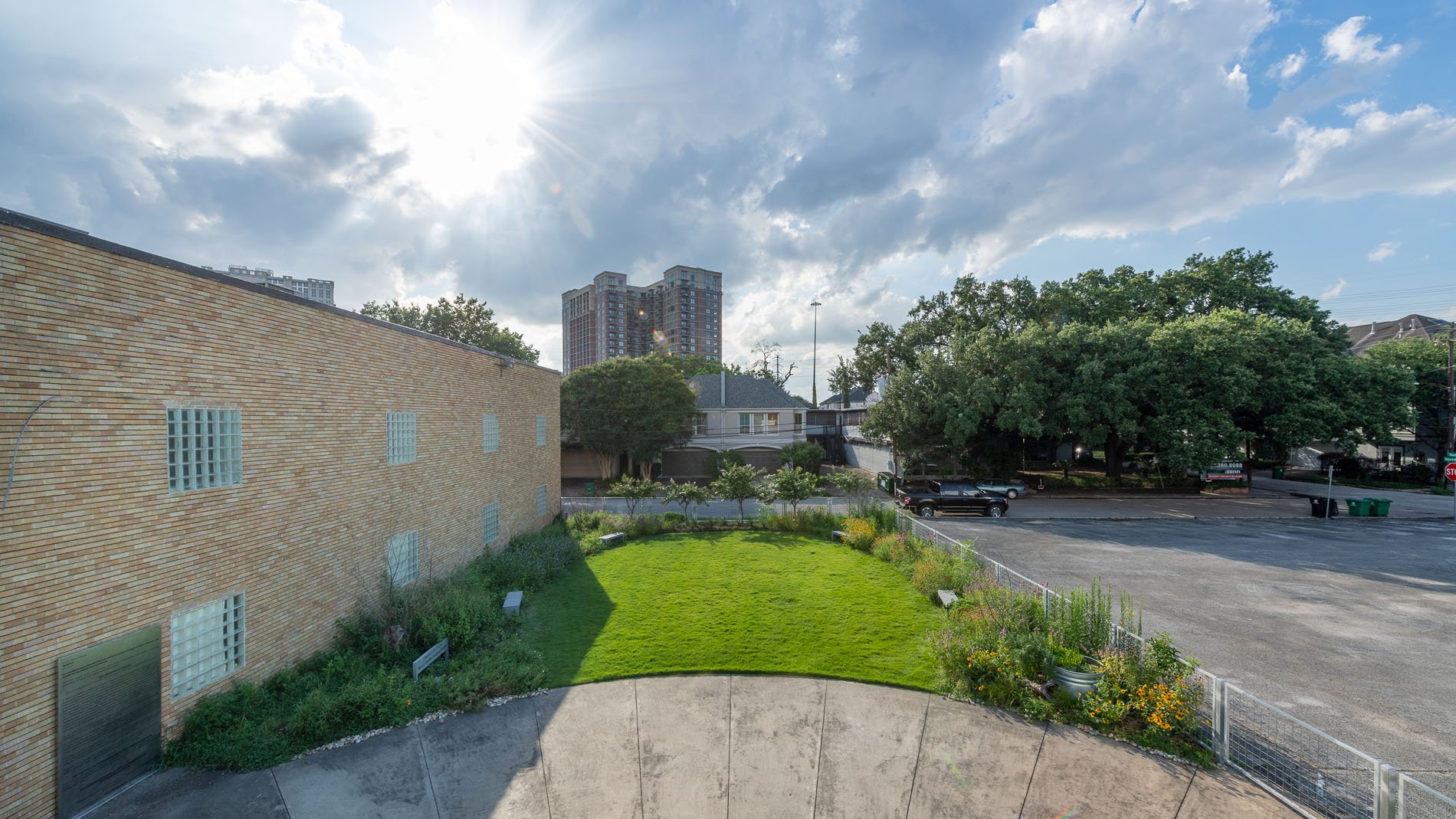
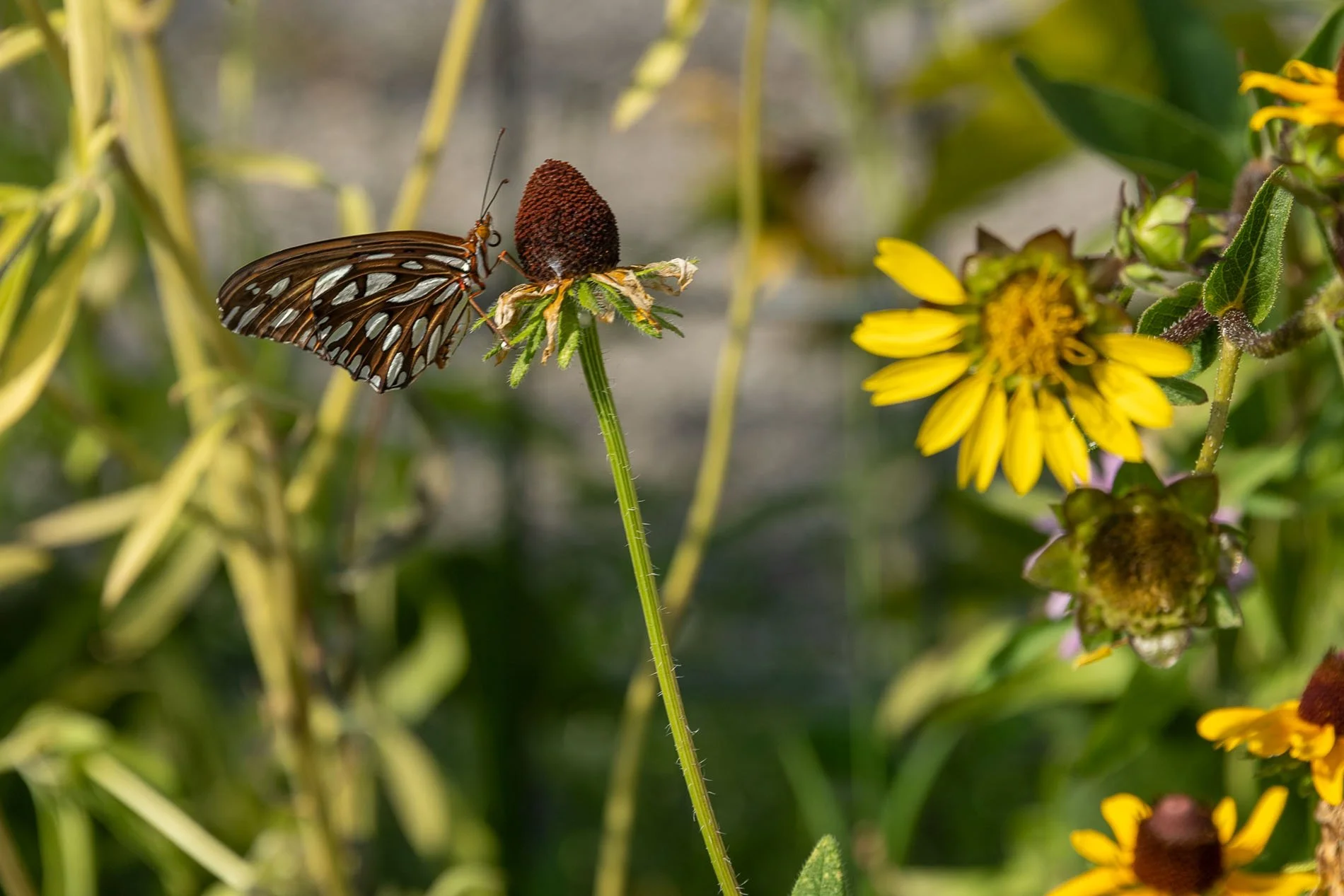
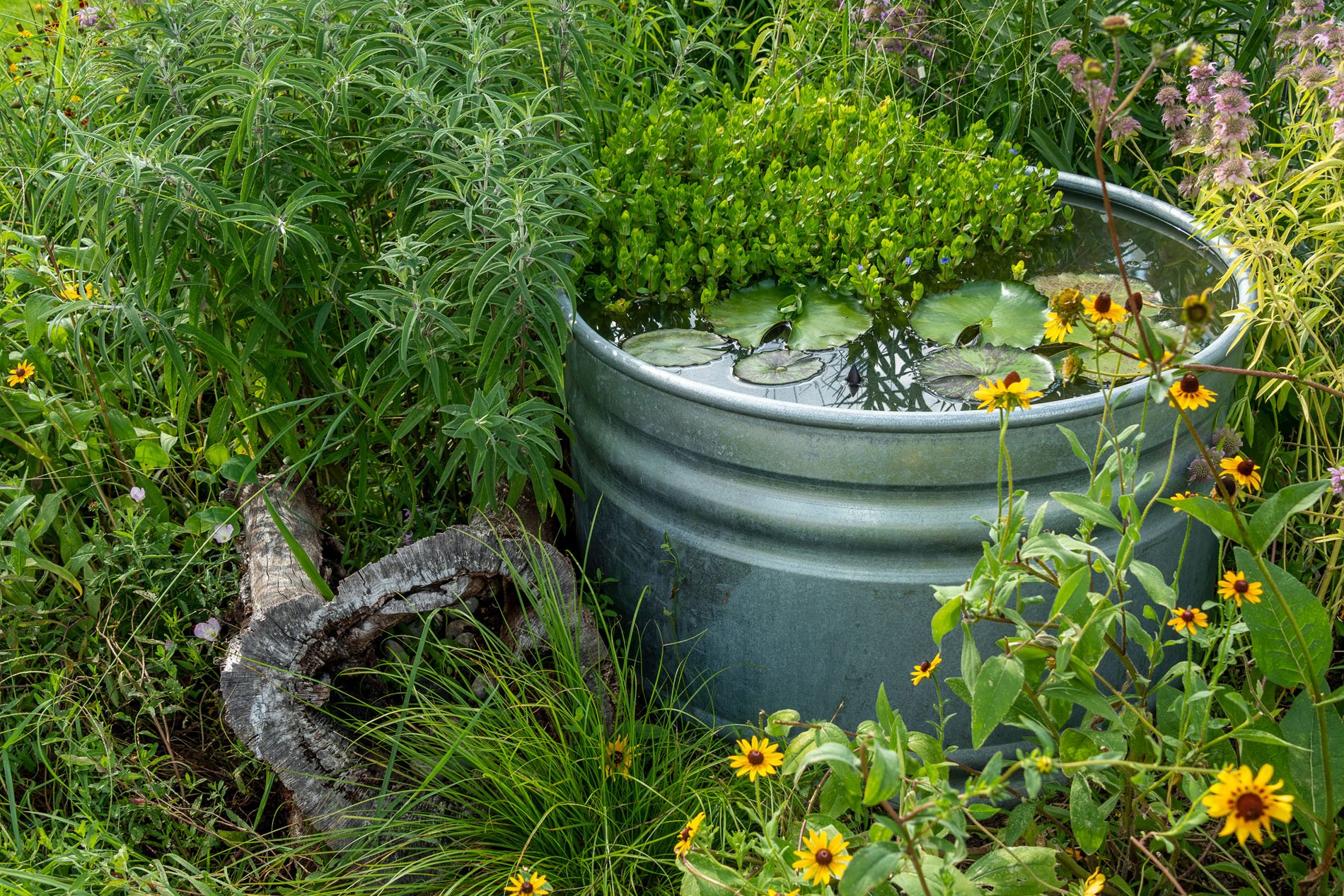
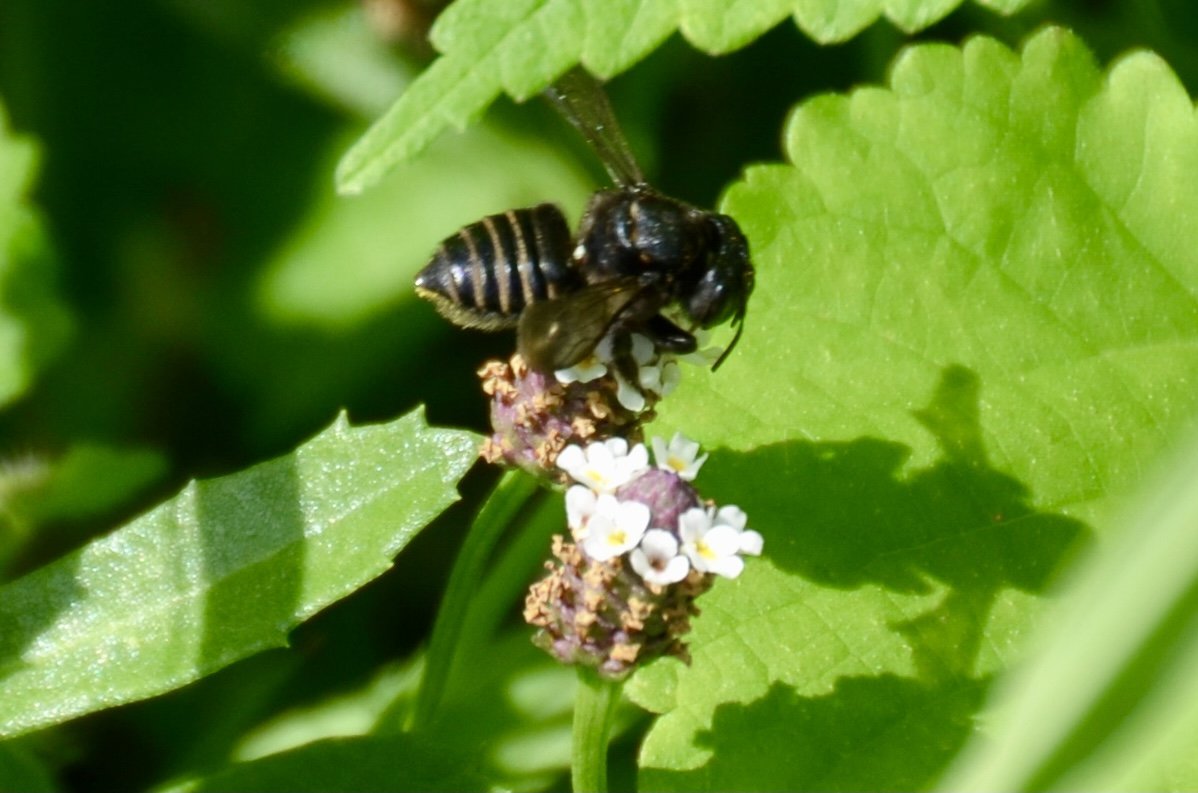
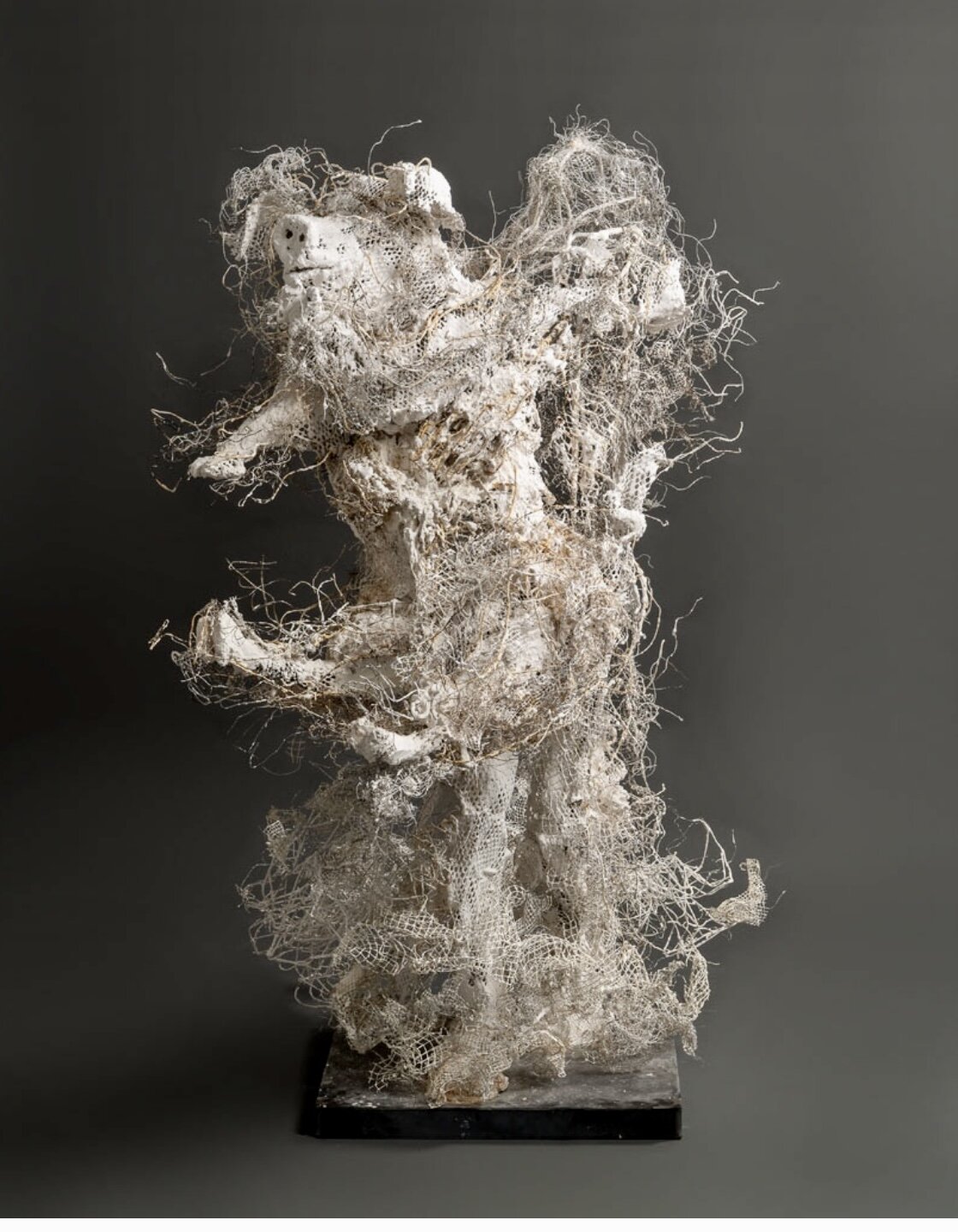
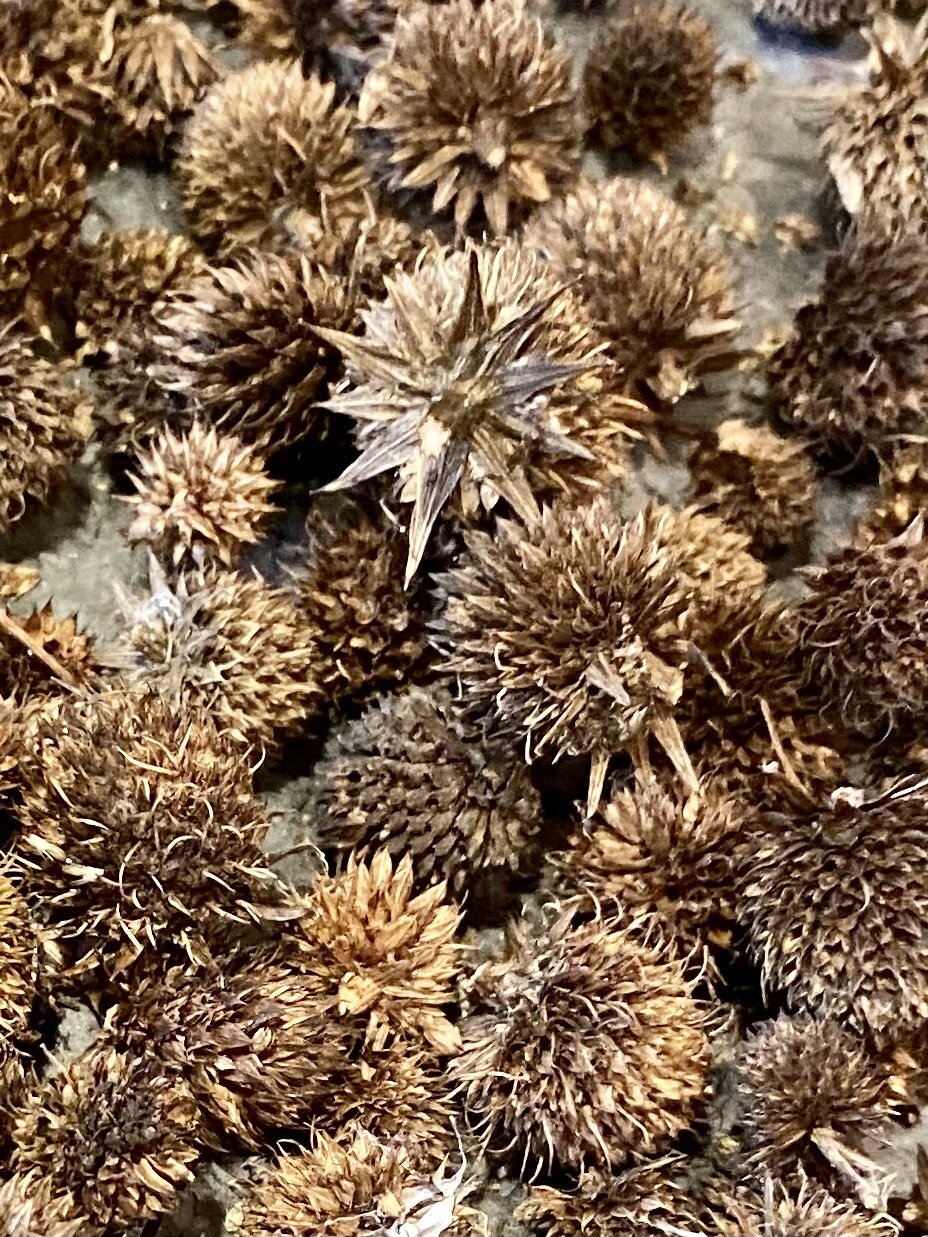
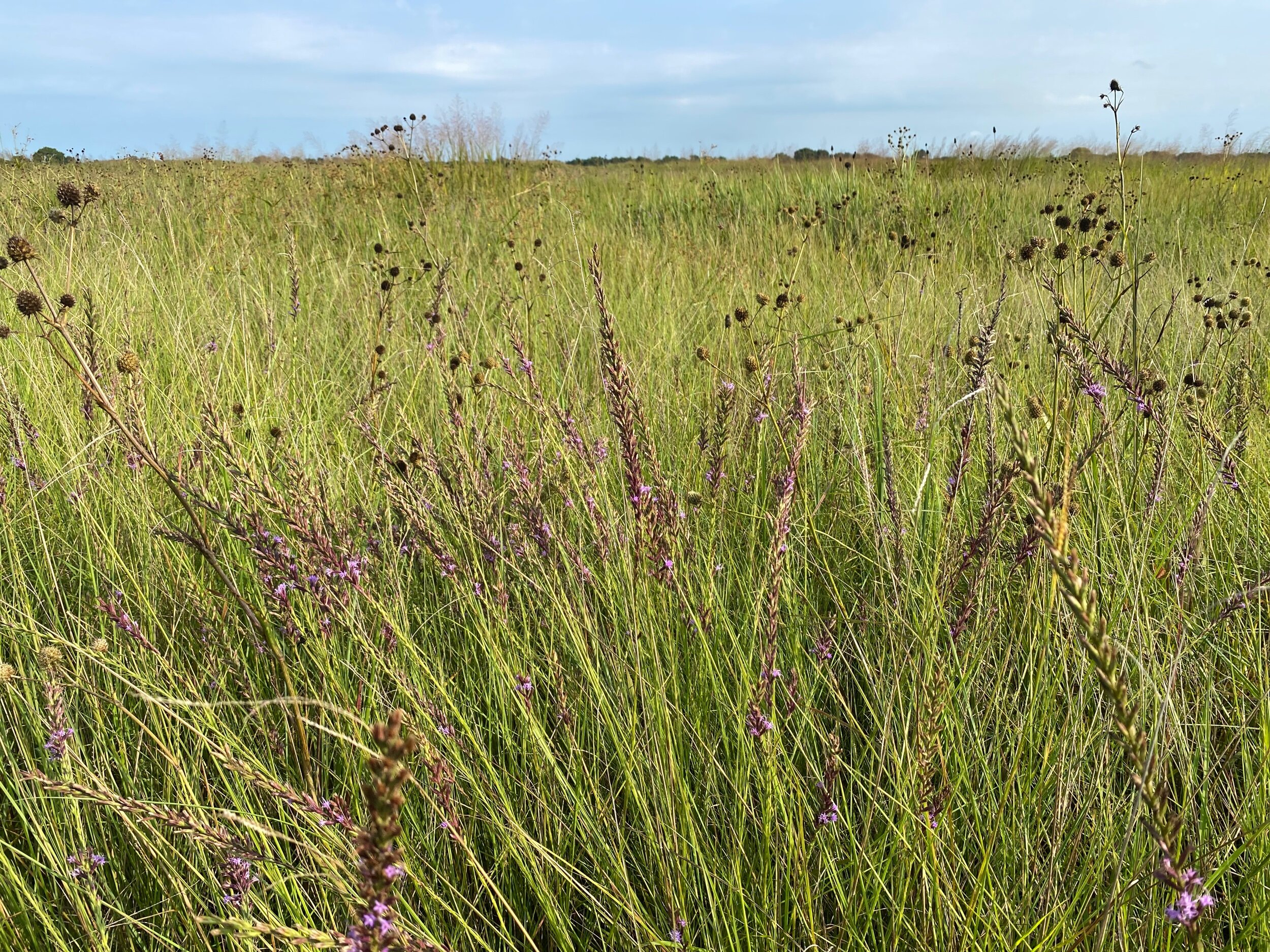
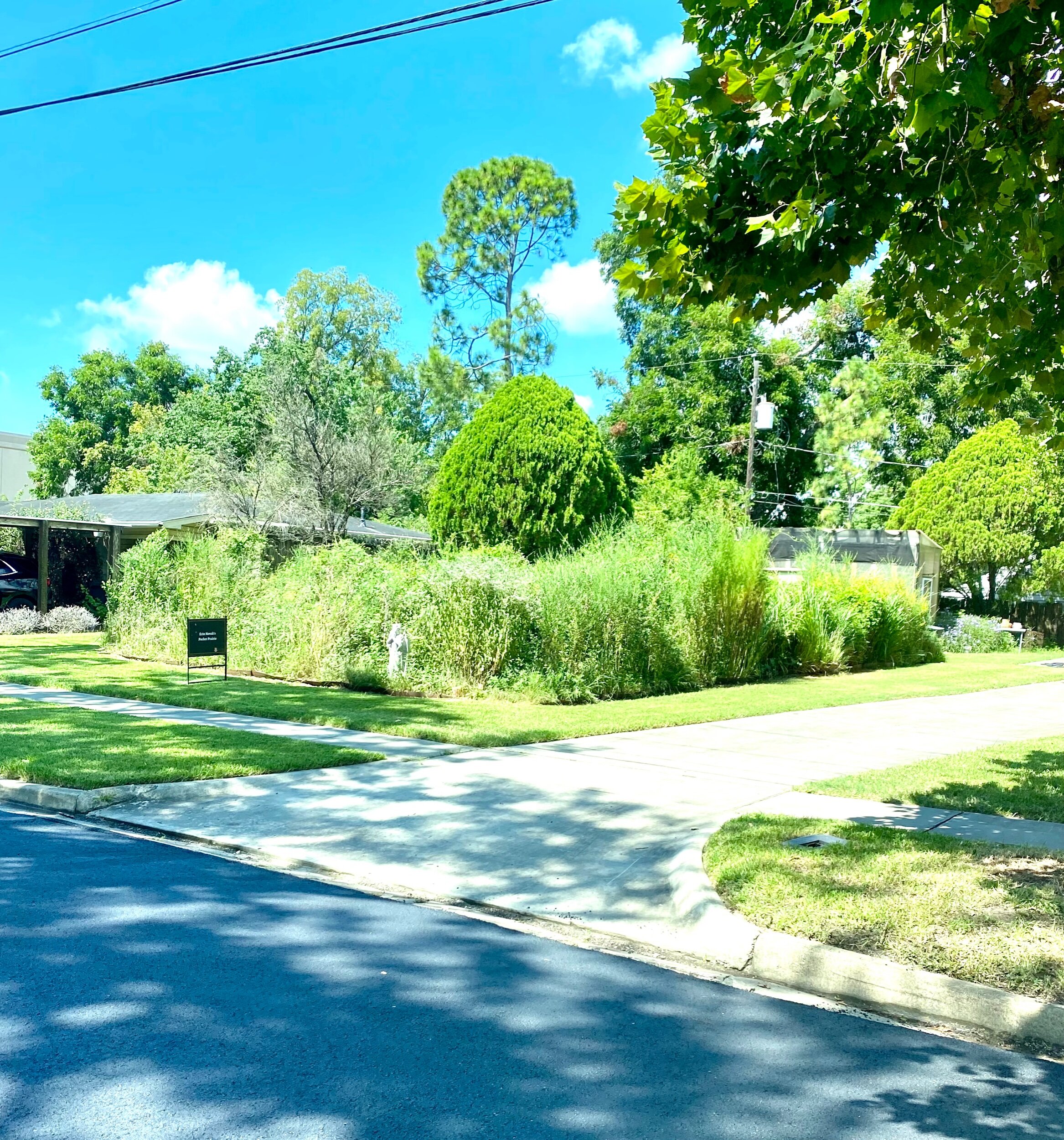
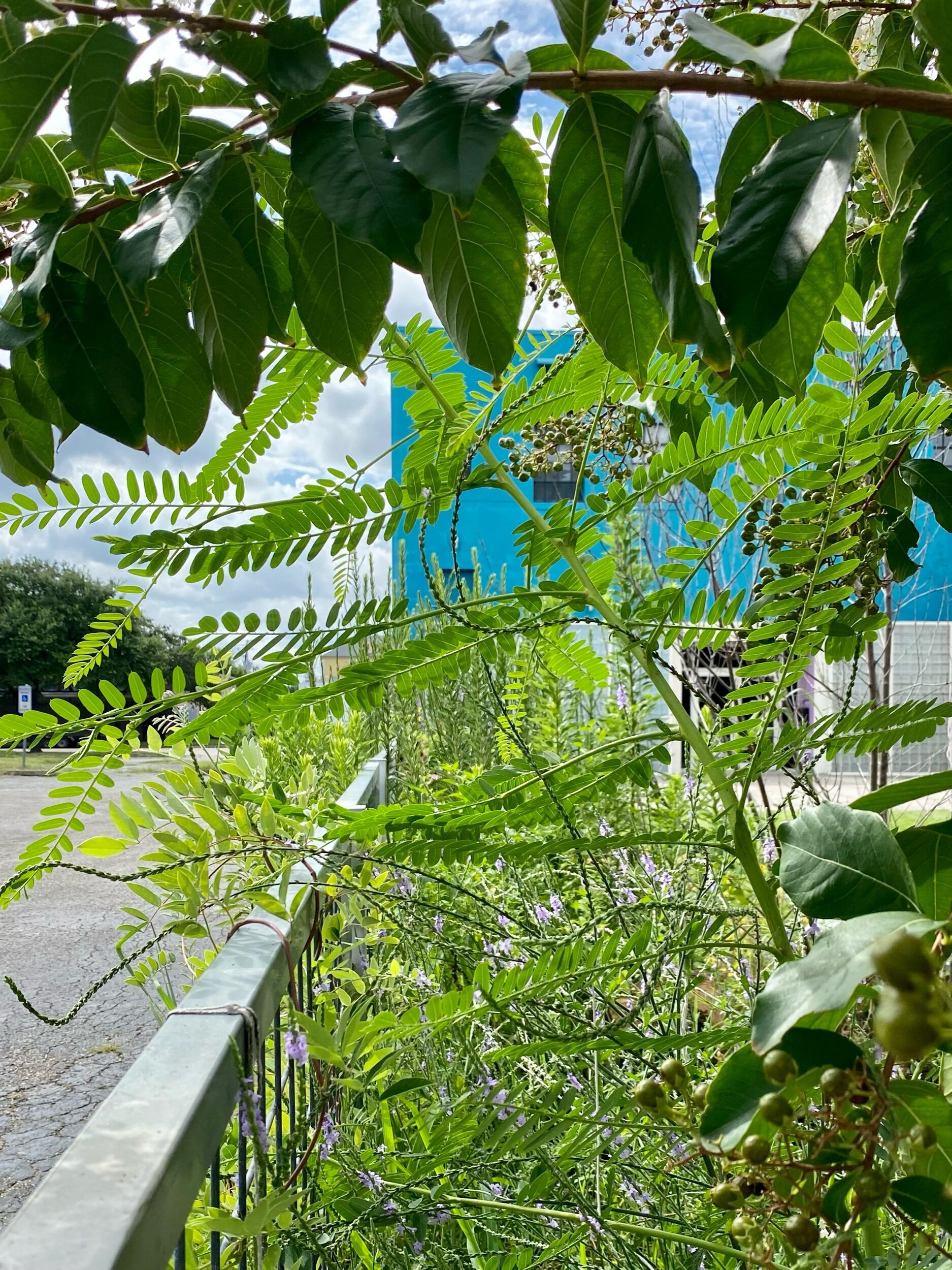
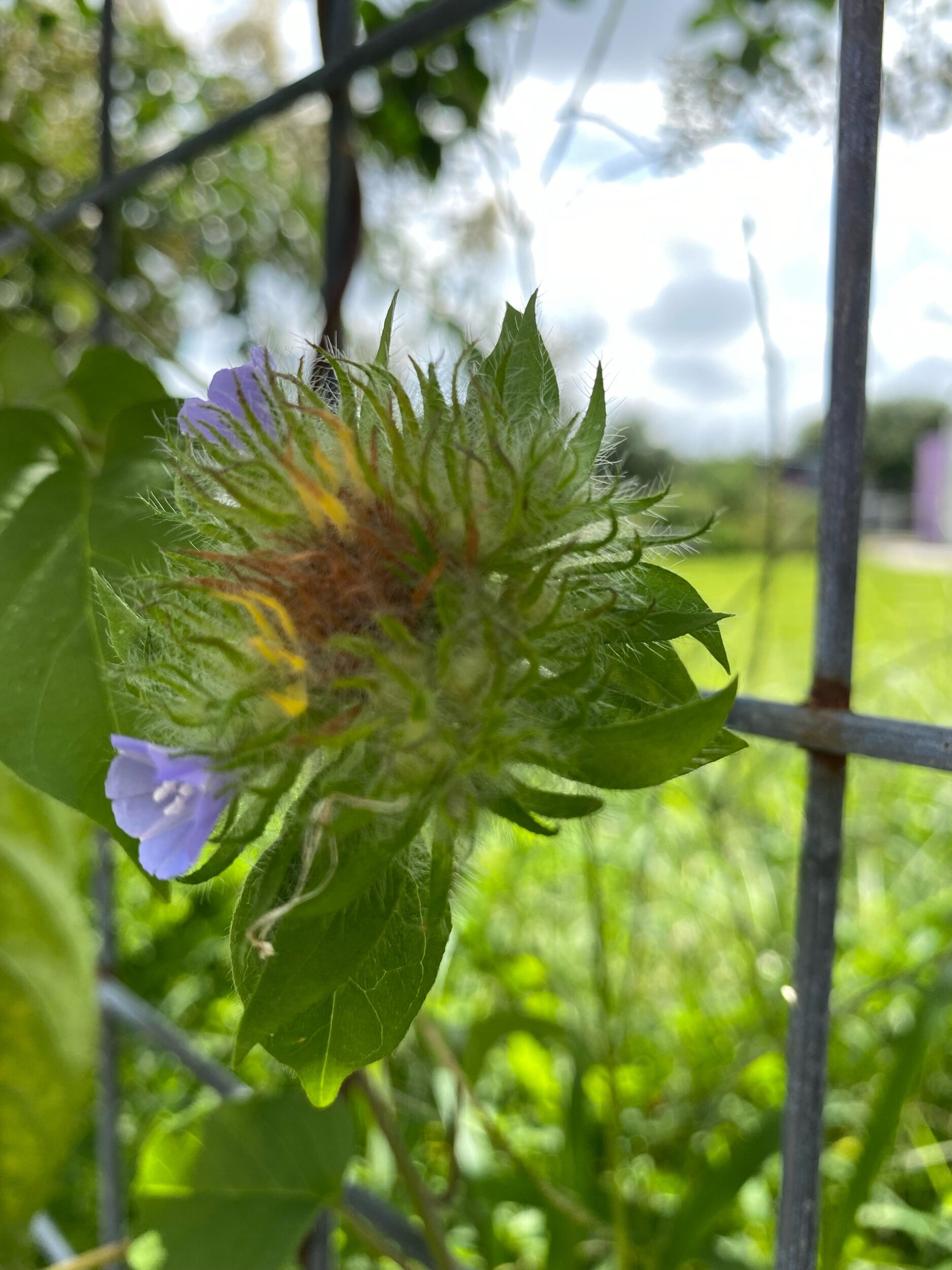
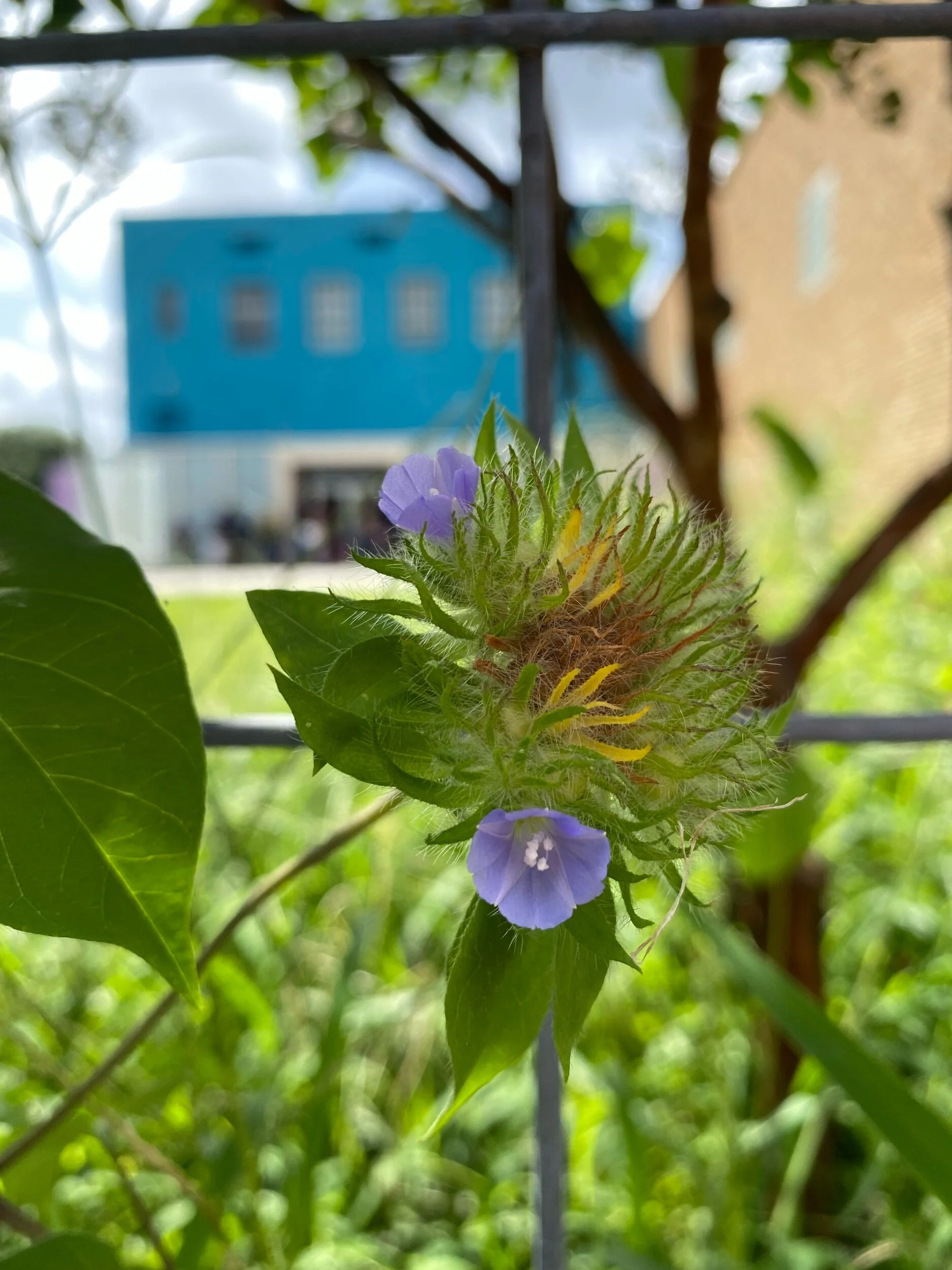
As geologists and environmentalists battle, “are we in the Holocene epoch or have we made our mark on Earth and entered a new geological period, the Anthropocene?”, I ponder weeds.
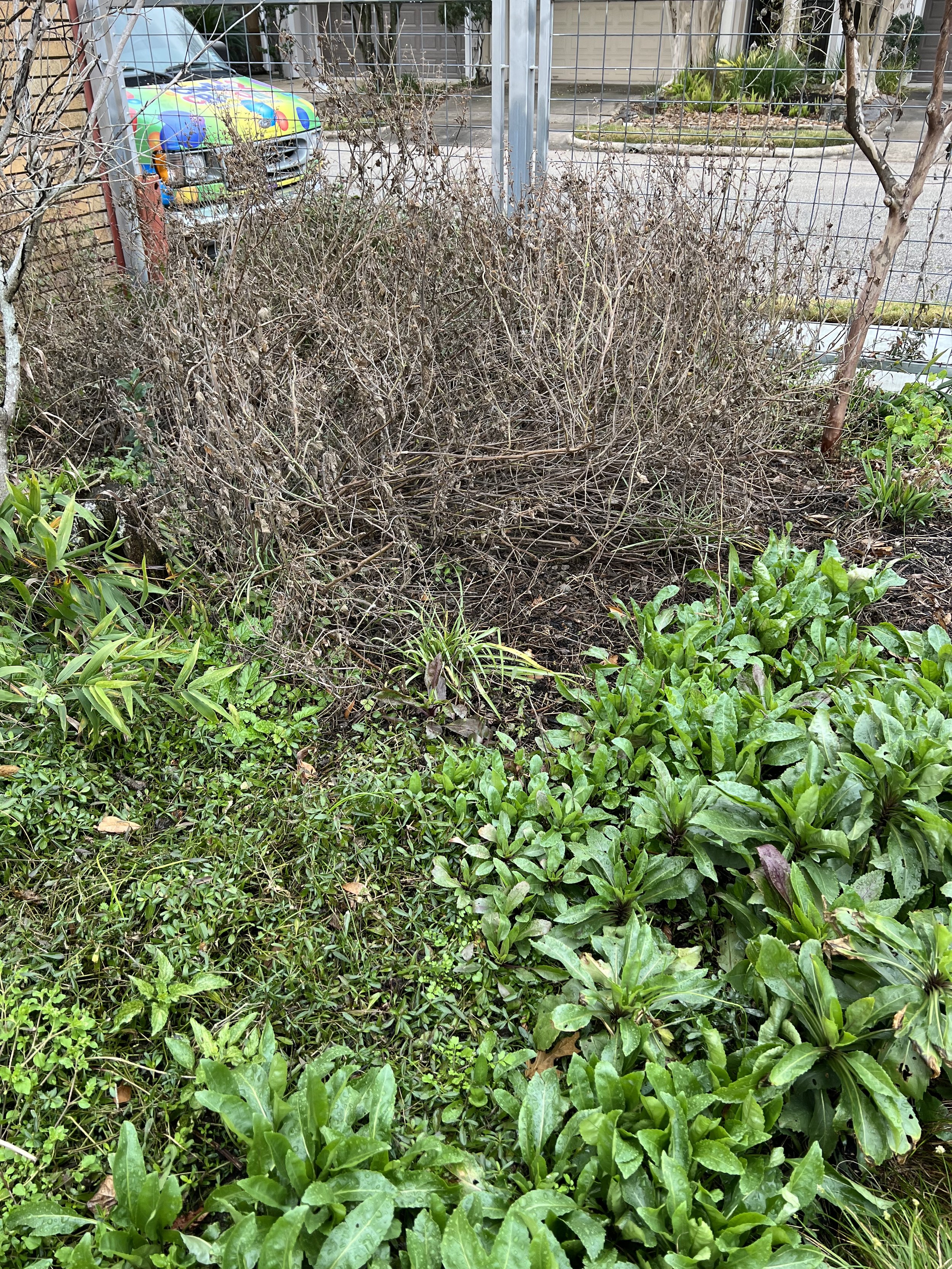
The term weed, in the Holocene, is a plant that sticks out in a monoculture. From a bipedal primate’s perspective, a weed isn’t like all the surrounding plants: we undervalue it—because it “looks” different. From a human who spells her name Cindee with two ee’s, I have to say I am attracted to weeds and not just because of the ees. Since my first installation in Symbiosis, on February 14, 2021, I have thought a lot about the word, verb, and the thing weed, asking myself so many questions and finding answers in this urban garden.
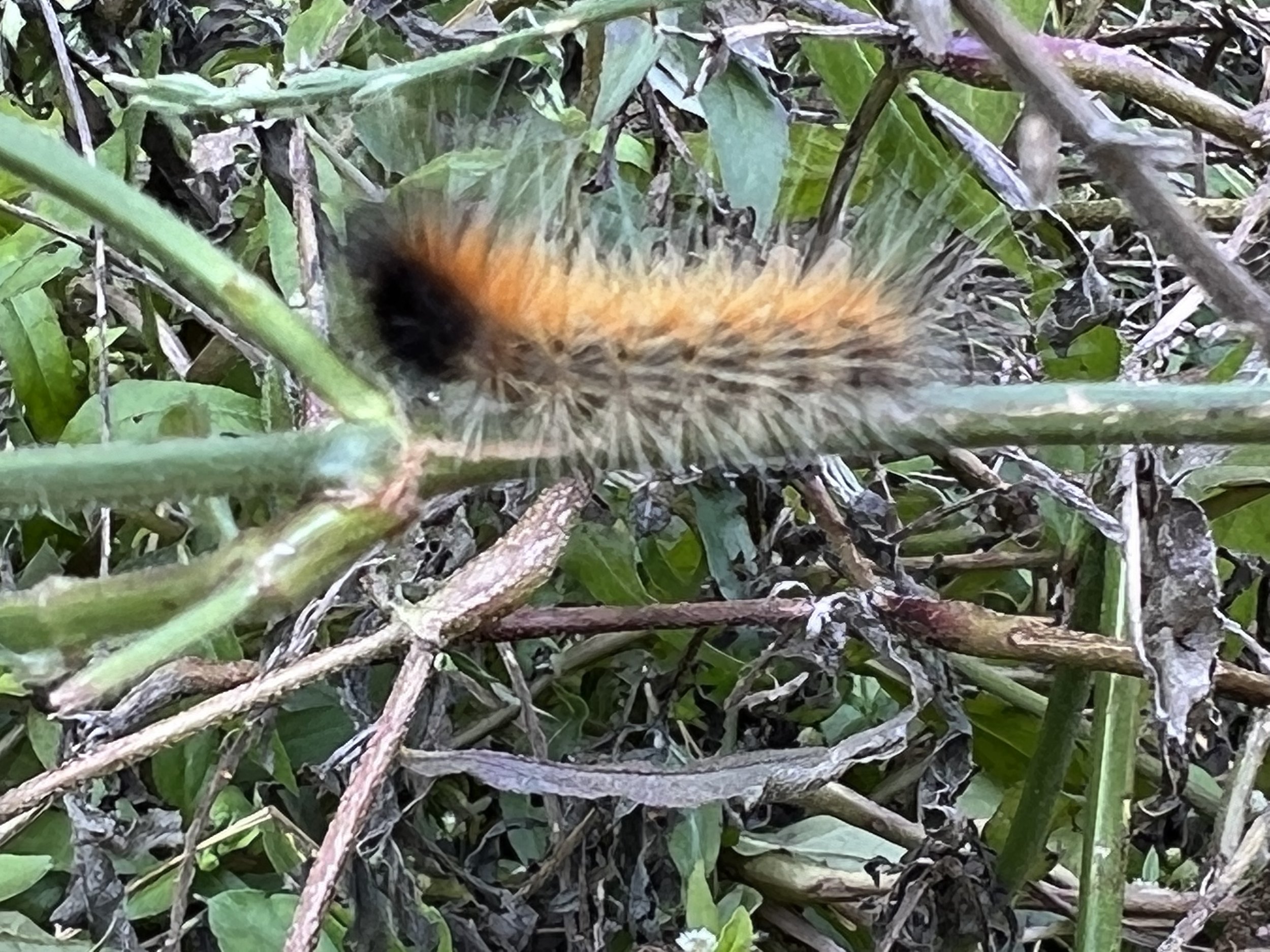
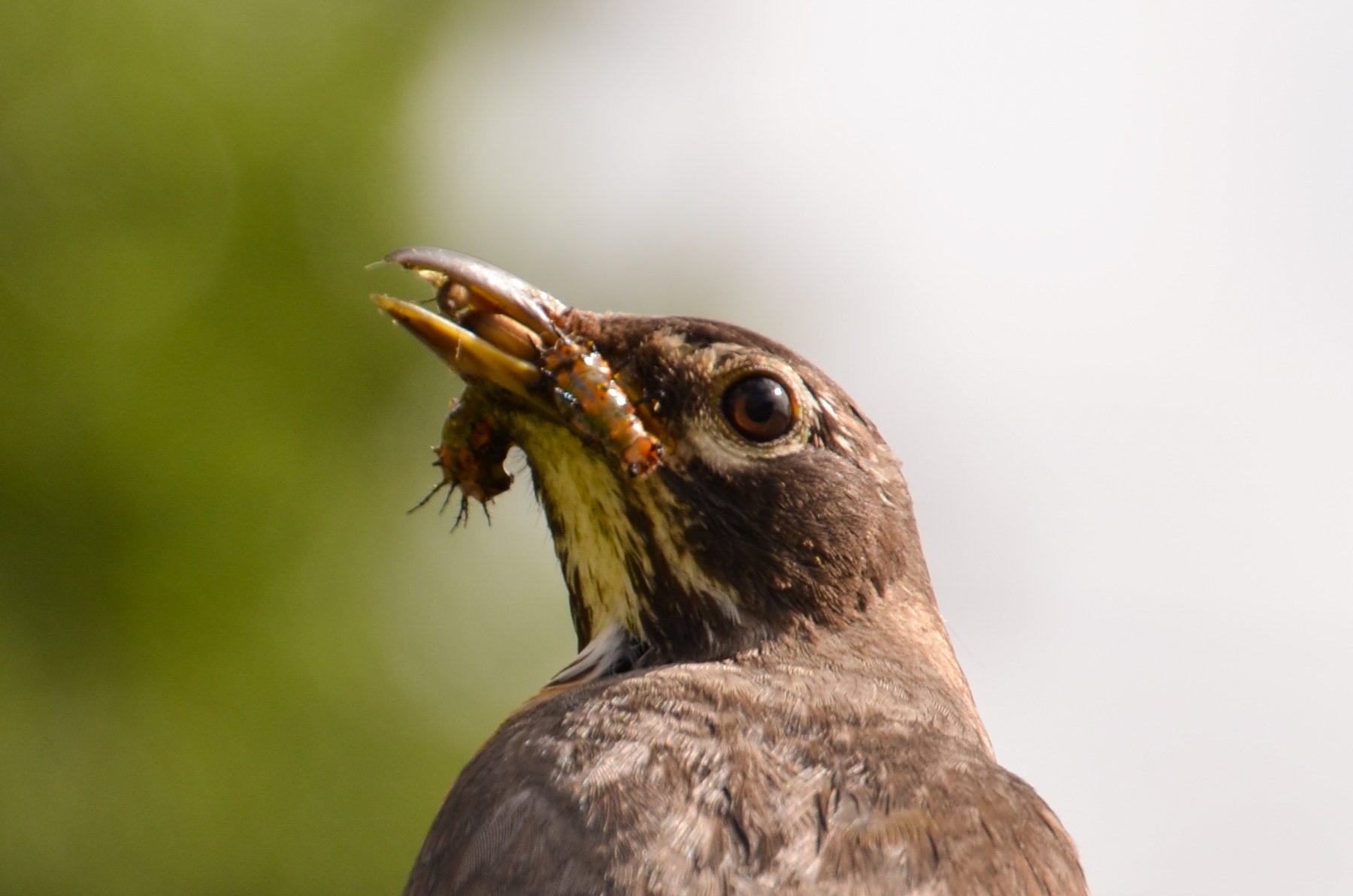
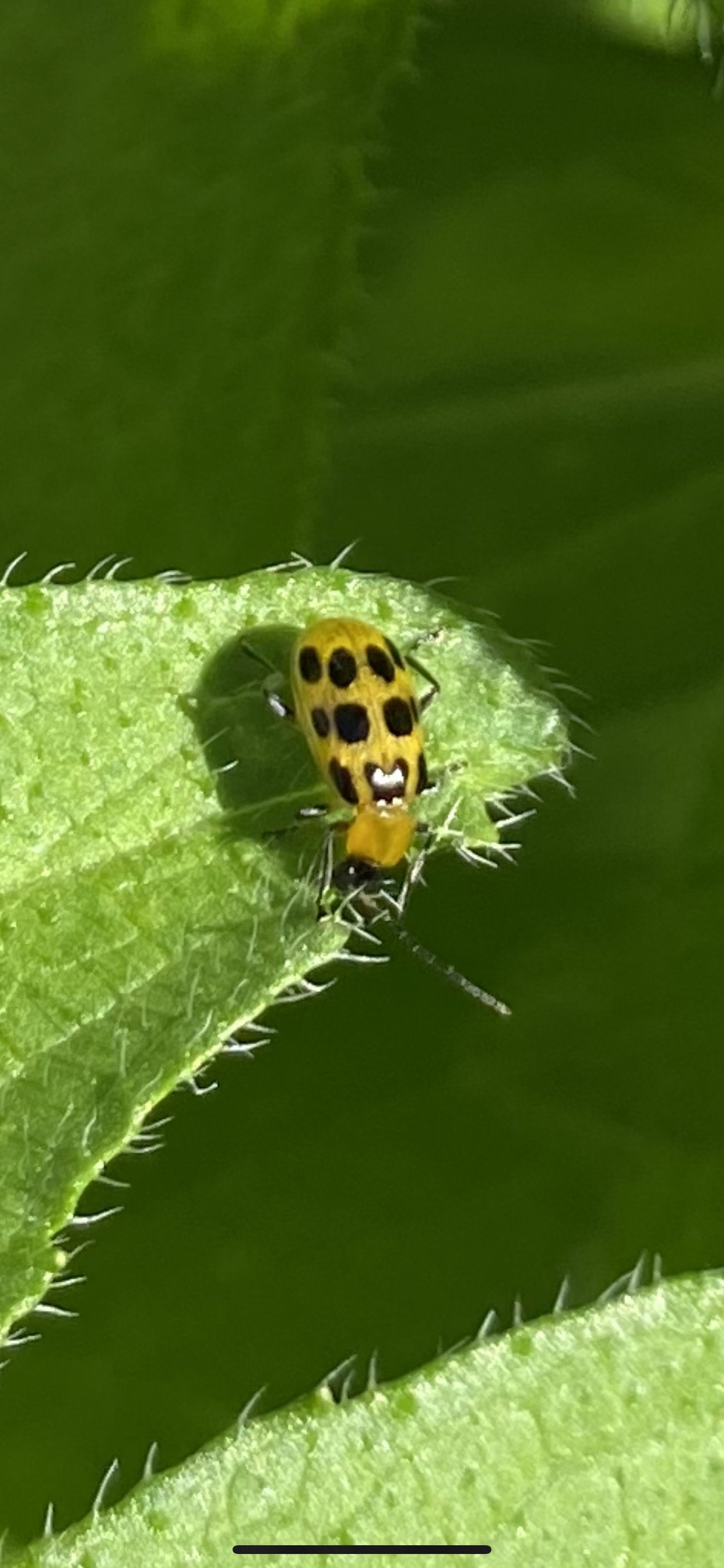
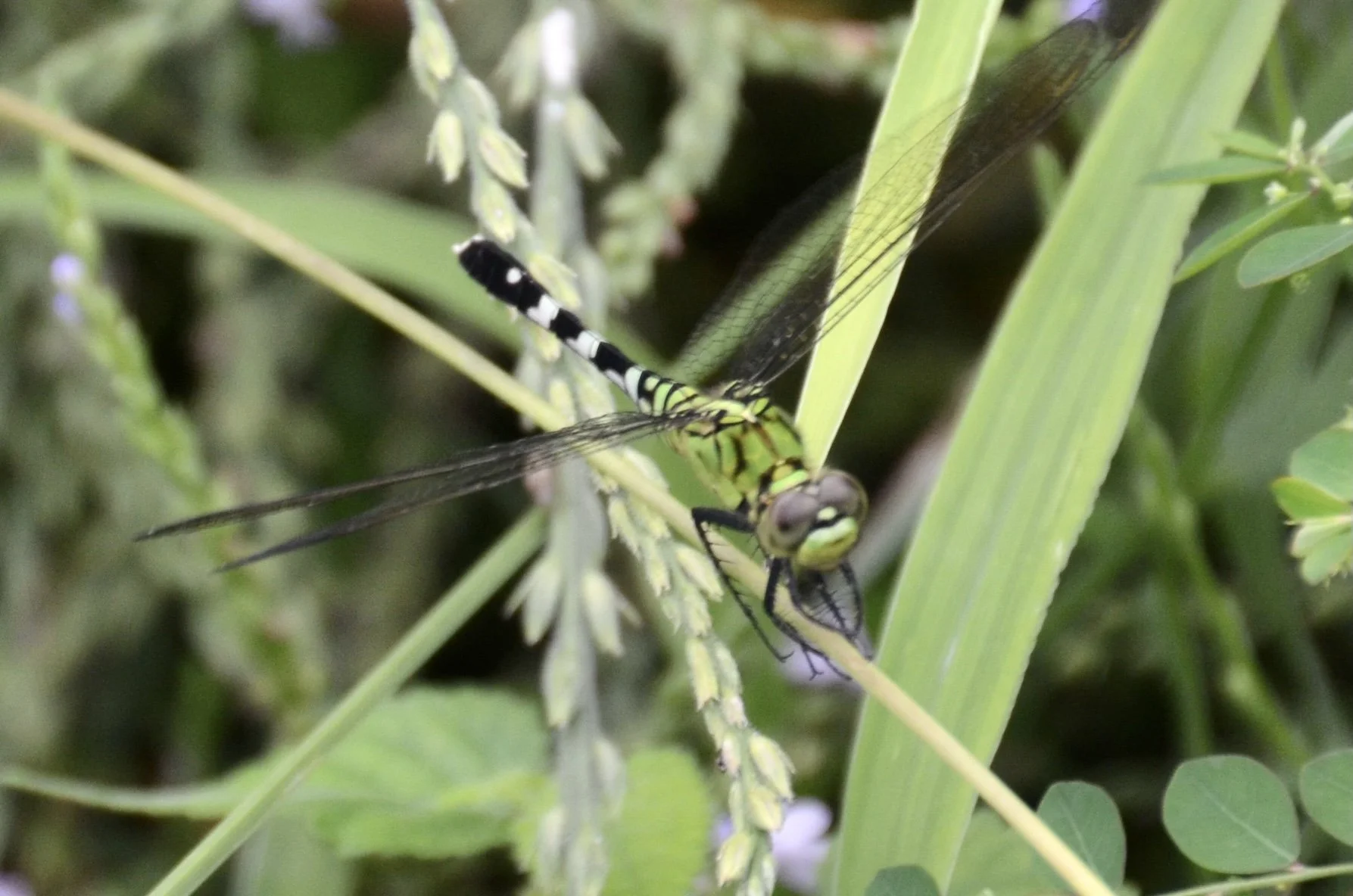
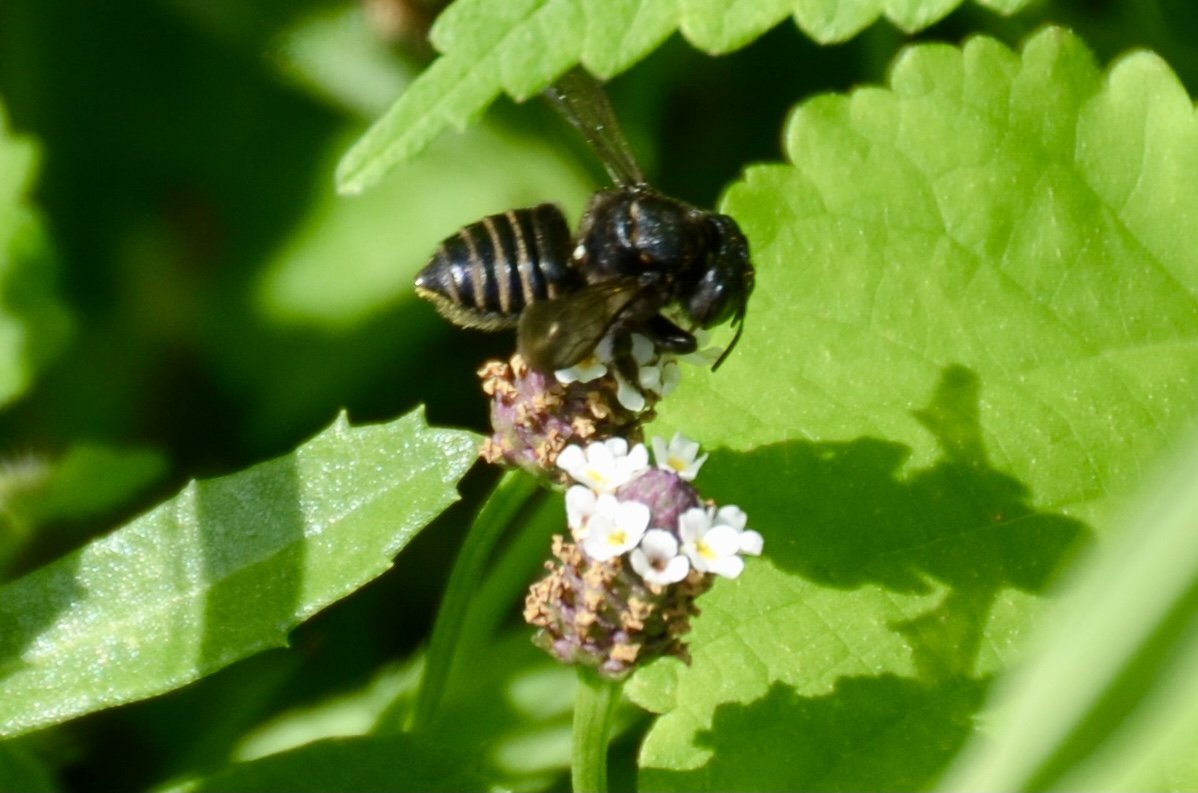
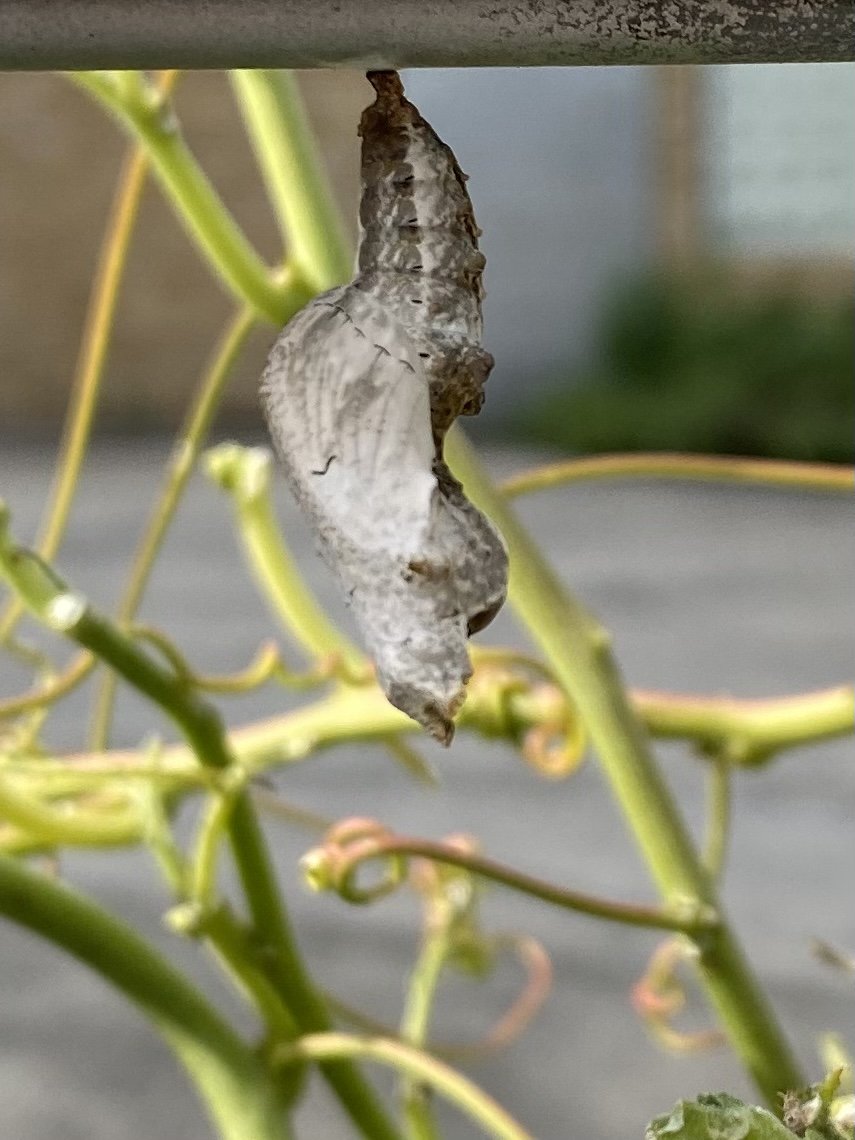
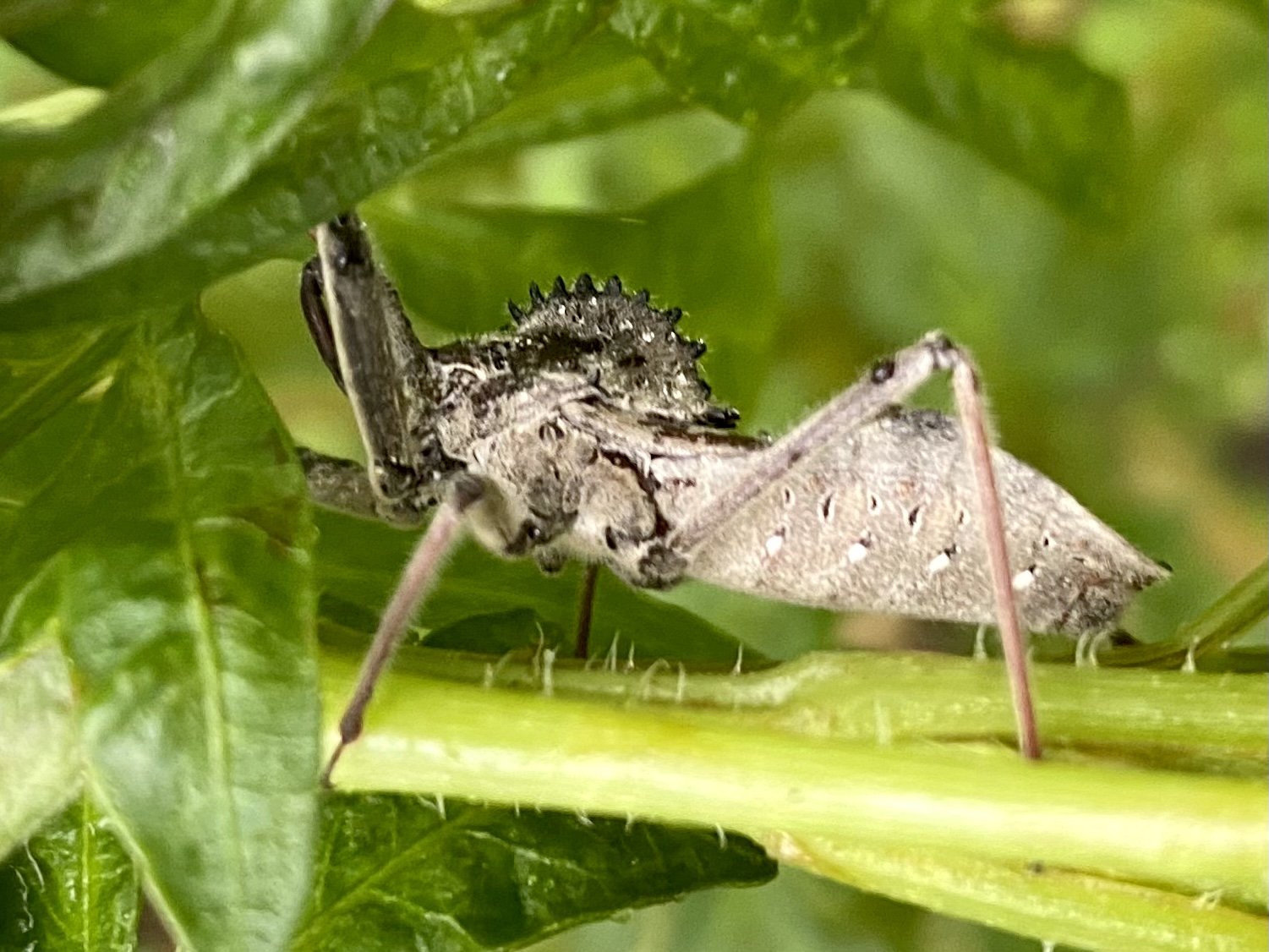
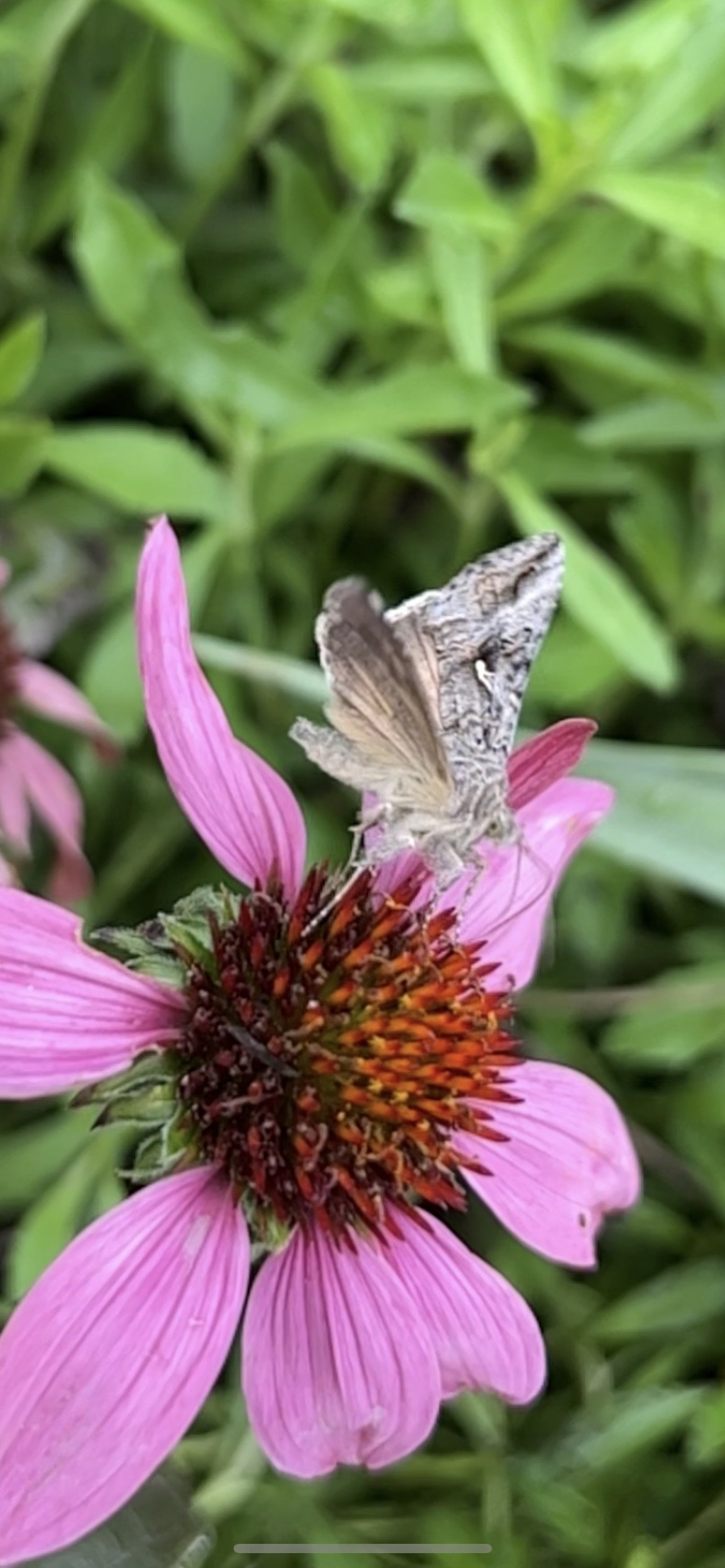
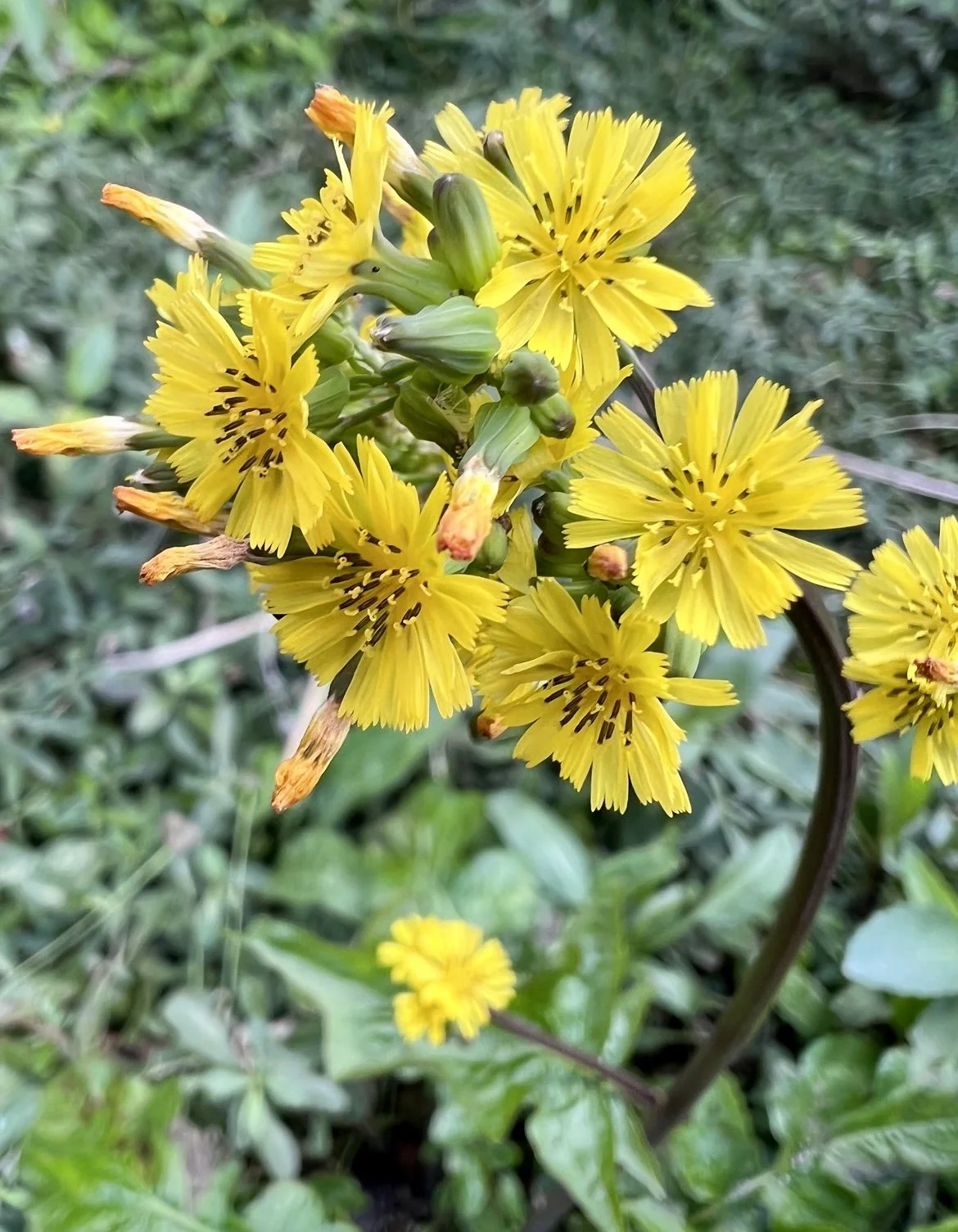
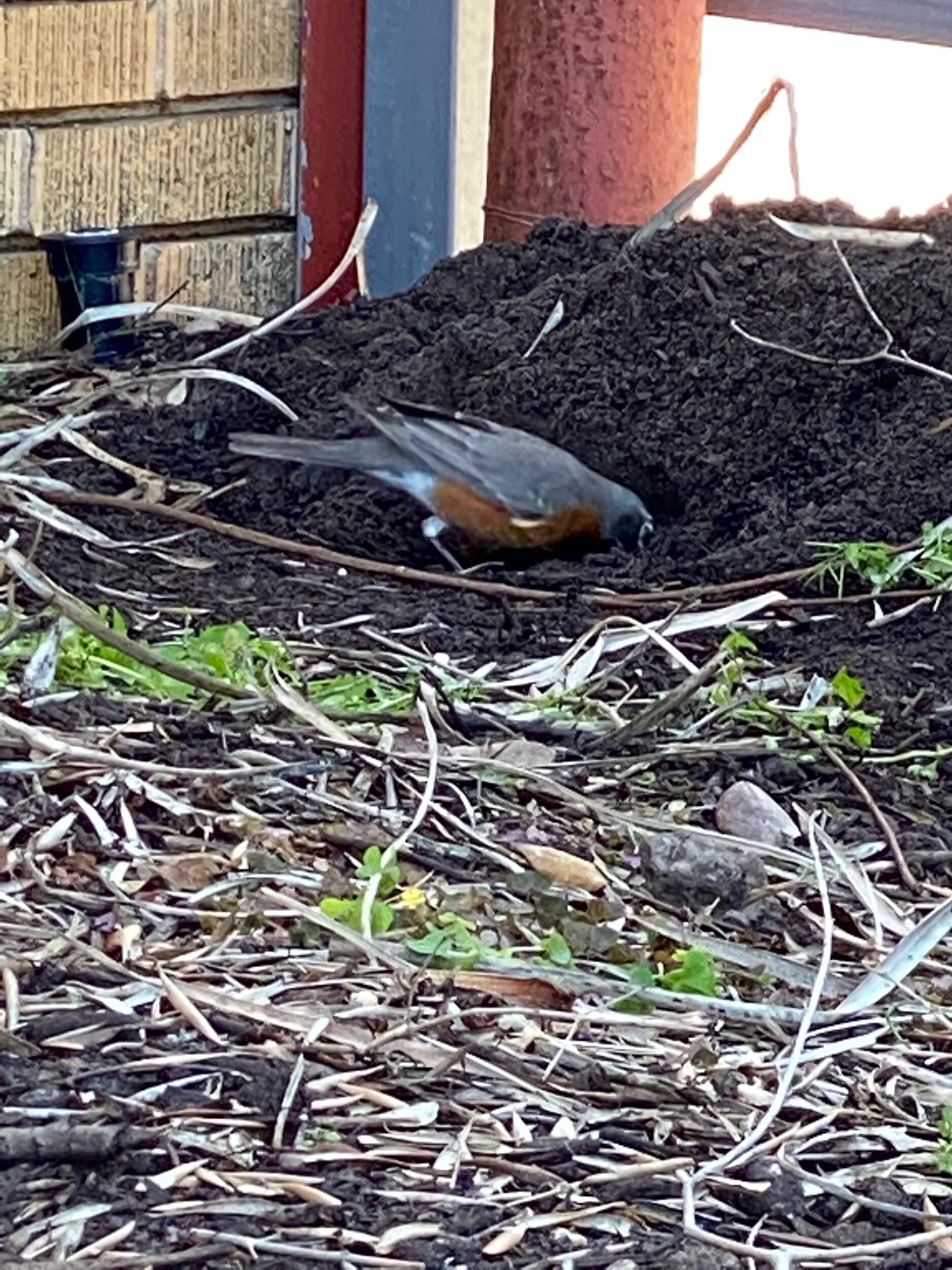
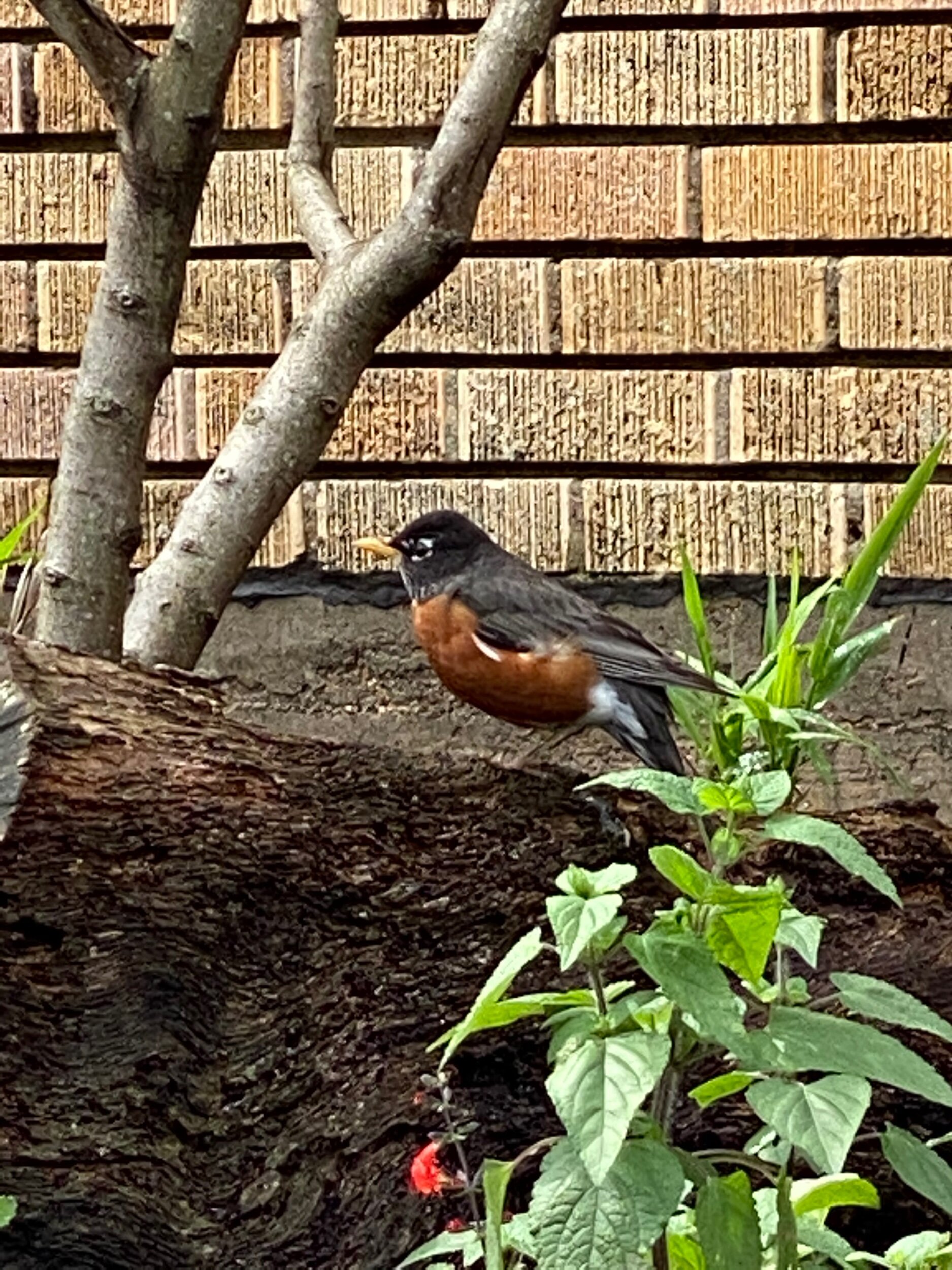
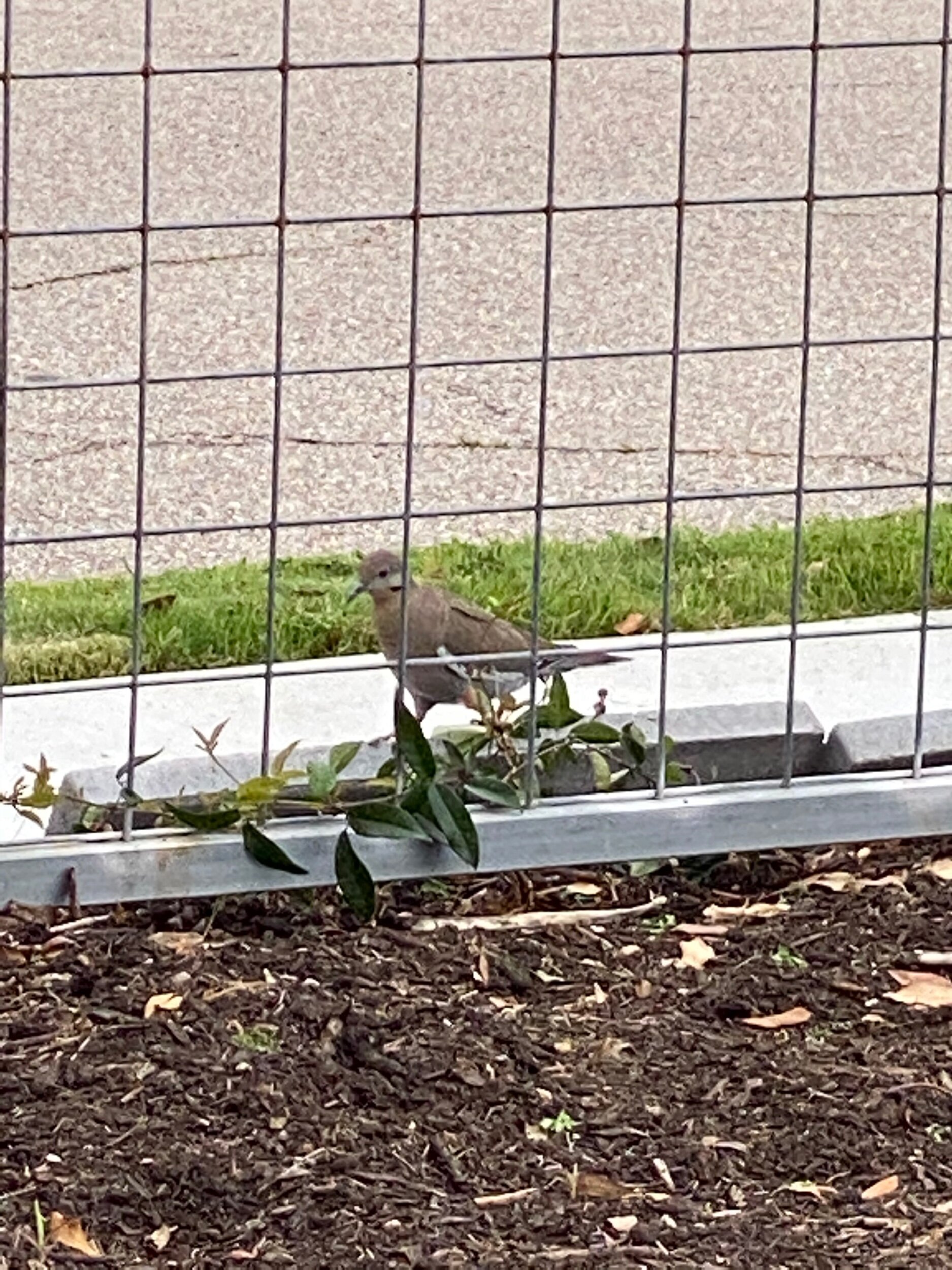
In nature and in Symbiosis, I observe weeds and now see them as Earth’s first responders to large or small ecological disasters. Weeds are seeds, roots, stems, leaves, berries, and blooms—organic matter. Weeds are vegetative volunteers in the ecological services division of Earth; they provide emergency services for its living organisms above and below ground. Hear me out — when the Earth’s green skin is left bare, tilled, stripped, eroded, poisoned, burned, flooded, neglected, or disturbed by natural or human occurrences, Mother Earth cherry-picks from embryos sleeping in the soil her first responders—our weeds-seeds. Like our own“compounded prescriptions,” seeds are biologically programmed for the site’s specific ecological condition—temperature, moisture, and daylight—to grow fast and spread quickly; they are speed healers. As they mature, I see emergency room physicians administering oxygen masks for underground organisms, protective bandages for the Earth’s epidermis, and poison antidotes. Their organic matter lowers the Earth’stemperatures, thereby keeping soil and its living microorganisms alive. And they provide shelter, food, and nectar for the site’s microorganisms, wildlife, and humans. These ecological first responders are full-service providers, slowing rainwater, reducing soil erosion, replenishing the aquifer, cooling the planet, sequestering carbon, and stabilizing it in the ground for those debating geological periods to come.
From a sculptural perspective, if the shape, texture, or color of a volunteer first responder “weed” does not satisfy my artistic vision, I no longer yank it out of the ground in a knee-jerk response. I stop—look—think, why was it sent in? I take a holistic approach. I weigh the service it is providing our above and below ground micro-ecosystem, the armature that supports the life of the sculpture. I then consider what human adjustments I might implement to holistically balance these roles nature’s first responders are providing to achieve my artistic vision, supporting my sculpture. I consider the needs of other species from the bacteria, fungi, nematodes, and insects to the small mammals, birds, and humans whose life work supports my work. I know that the small systems have to be right for the global systems to run smoothly and I see that too much is at risk to resort to pesticides. I create ways that weeds’ delicately shaped blooms can work in my living land art.
From a practical standpoint, weeds are convenient, cost-effective tools in my human-made nature scape, a catalyst for environmental change, Symbiosis. So, while intellectuals debate the ages, I get out of weeds way, pull over to the right and let the weeds do their job.
In Wikipedia, weed is “of unknown origin.” Ironically, weeds are of unknown origins in most landscapes. So I break down the word weed into three parts.
We – all of us, me, you and I.
ee – In the English language, double e’s are a tool to
denote one connected.
ed – denotes verb, performs an action.
Holocene or Anthropocene? In this age of uncertainty, if humans “weed out” weeding, can all species win the battle? — I wonder…
Additional Weed Readings
WEEDS Control Without Poisons, by Charles Walters.
WHEN WEEDS TALK, by Jay, L. McCaman — includes charts with the functions of each species.
I purchased my copies on Acres USA.